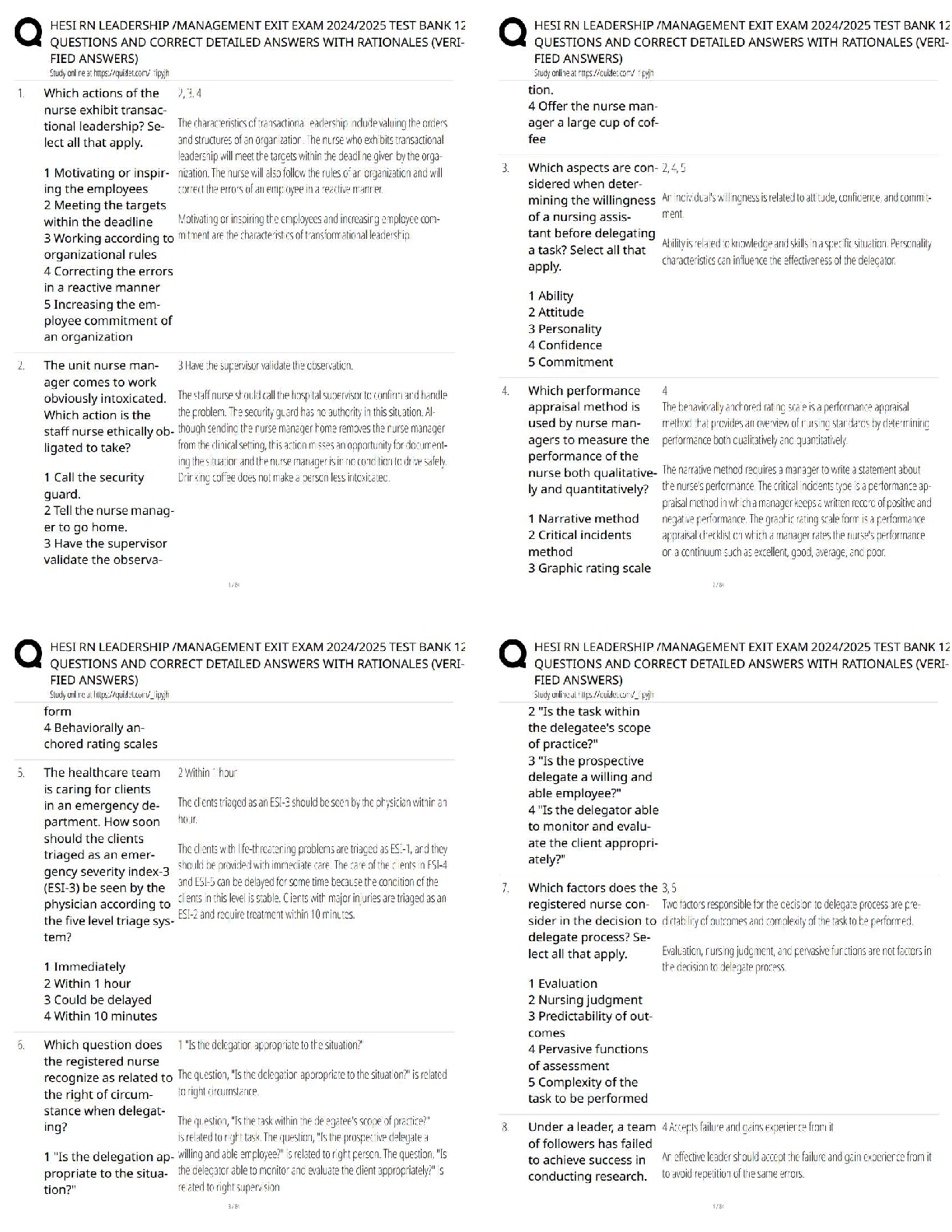
Education > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU C952: Computer Architecture Questions and Answers Already Passed (All)
WGU C952: Computer Architecture Questions and Answers Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
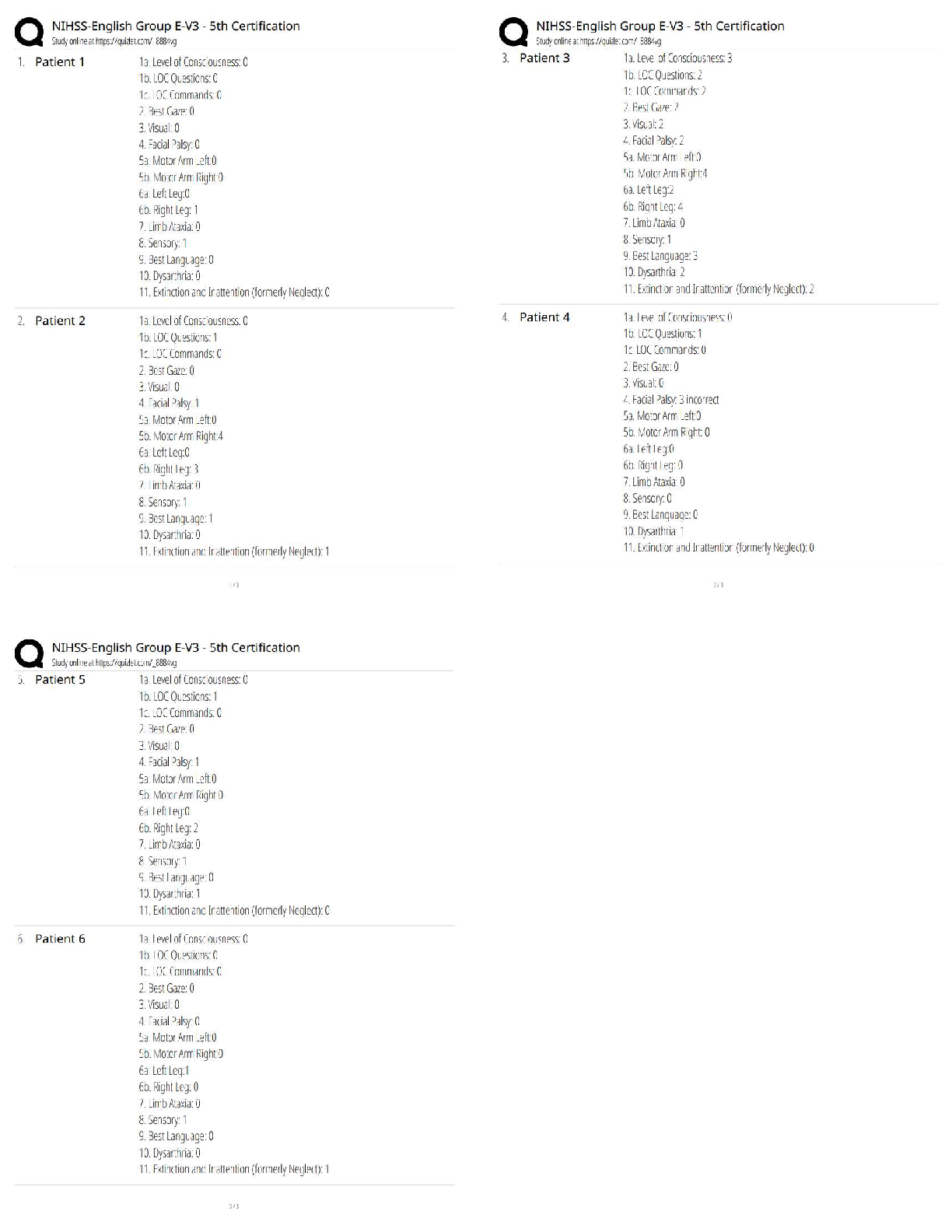
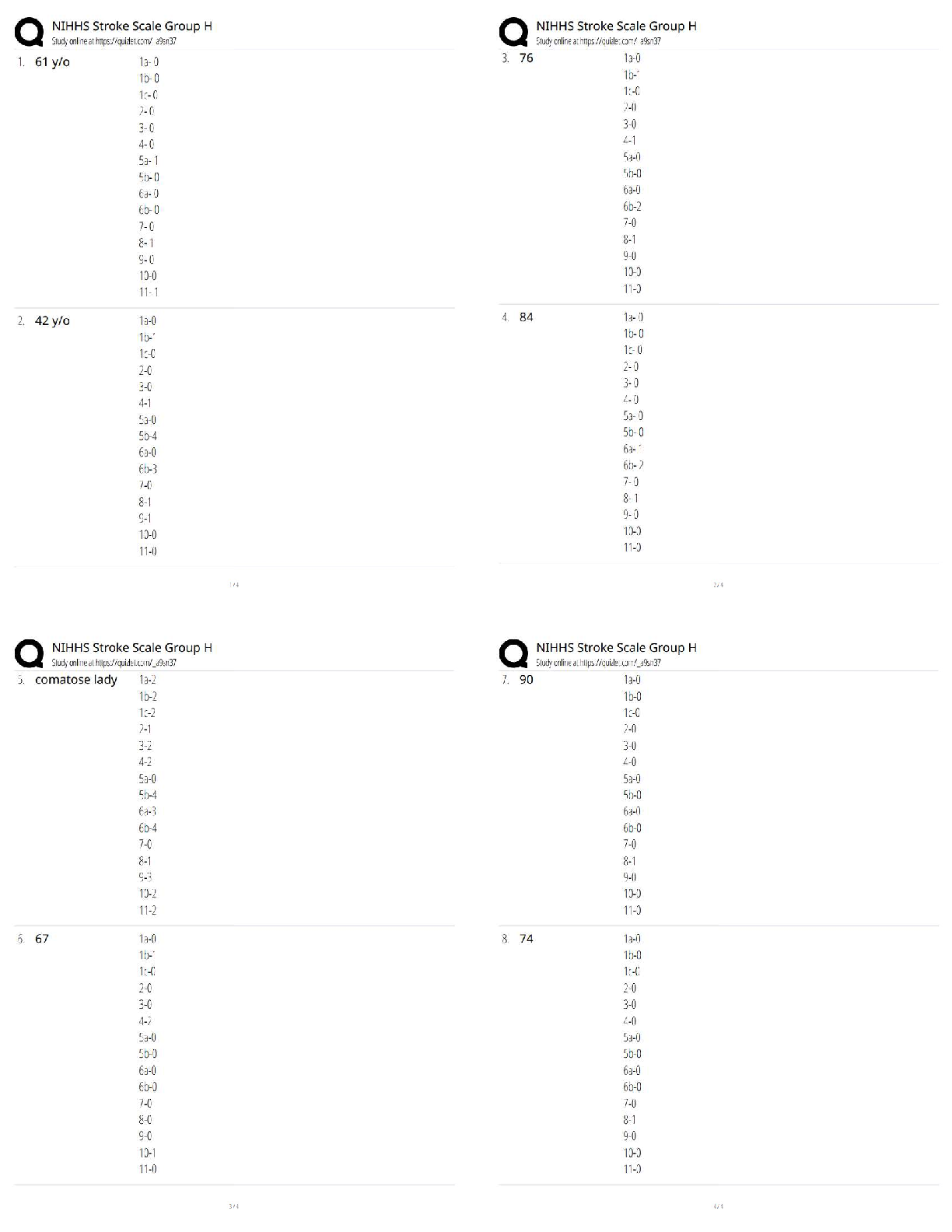
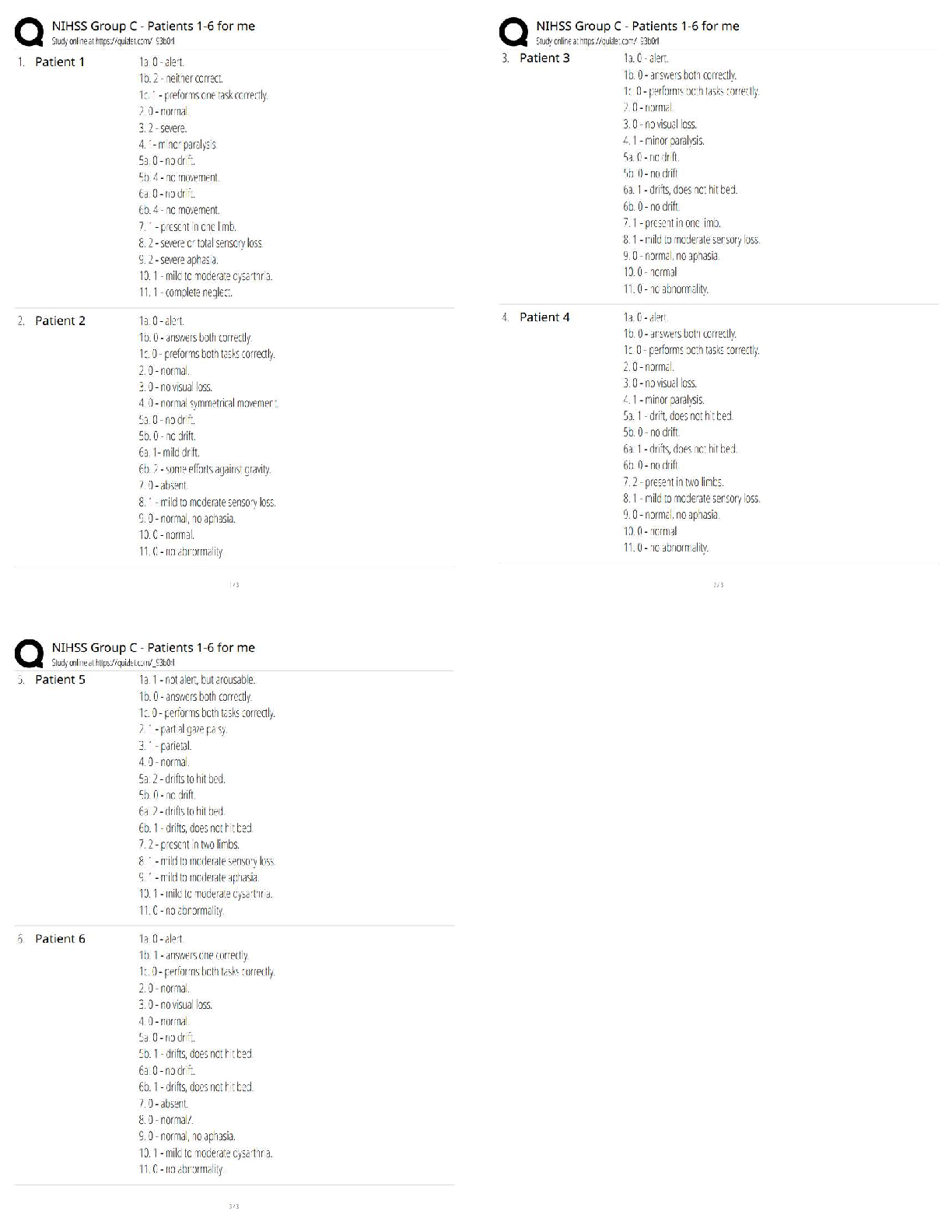
WGU C952: Computer Architecture Questions and Answers Already Passed Main memory ✔✔also known as "primary memory" typically consists of DRAM Secondary memory ✔✔ex: hard disk drive Branch p ... rediction ✔✔A way to resolve a branch hazard by seeing if the branch was taken last time it was encountered. The result is stored in the branch prediction buffer (aka branch history table) reservation station ✔✔one primary unit within dynamic scheduling that holds the operands and the operation within a functional unit (see pic) commit unit ✔✔The unit in a dynamic or out-of-order execution pipeline that decides when it is safe to release the result of an operation to programmer-visible registers and memory. (see pic) dynamic pipeline scheduling ✔✔Hardware support for reordering the order of instruction execution so as to avoid stalls. frame buffering ✔✔The process of storing the image to be represented onscreen before it is read out to the graphics display (see pic) SIMD ✔✔single instruction stream, multiple data streams: The same instruction is applied to many data streams, as in a vector processor. MIMD ✔✔multiple instruction streams, multiple data streams: A multiprocessor. SPMD ✔✔single program, multiple data streams: The conventional MIMD programming model, where a single program runs across all processors. SISD ✔✔single instruction stream, single data stream: A uniprocessor. data stream ✔✔bi-directional flow between memory and the CPU benefits of vector-based code ✔✔1) reduces the dynamic instruction bandwidth 2) Lowers frequency of pipeline hazards pipeline hazards ✔✔There are situations in pipelining when the next instruction cannot execute in the following clock cycle. These events are called hazards, and there are three different types. MMX ✔✔x86's multimedia extension instructions; instructions for multimedia? ALU ✔✔An arithmetic unit, or ALU, enables computers to perform mathematical operations on binary numbers. They can be found at the heart of every digital computer and are one of the most important parts of a CPU (Central Processing Unit). datapath ✔✔A datapath is a collection of functional units such as arithmetic logic units or multipliers that perform data processing operations, registers, and buses. overflow ✔✔the need for more bits in order to accurate represent an arithmetic result approximate range of a 64-bit unsigned interger ✔✔0 to 2^64 − 1 (18,446,744,073,709,551,615ten) locality principles ✔✔programs access a relatively small portion of their address space at any instant of time spatial ✔✔(locality in space): if an item is referenced, items whose addresses are close by will tend to be referenced soon. For example, when you brought out the book on early English computers to learn about the EDSAC, you also noticed that there was another book shelved next to it about early mechanical computers, so you likewise brought back that book and, later on, found something useful in that book. Libraries put books on the same topic together on the same shelves to increase spatial locality. We'll see how memory hierarchies use spatial locality a little later in this chapter. temporal ✔✔(locality in time): if an item is referenced, it will tend to be referenced again soon. If you recently brought a book to your desk to look at, you will probably need to look at it again soon. functional unit ✔✔one of the primary units in dynamic scheduling (e.g. inter, floating point, loadstore) stalls ✔✔an event in which the next instruction is not executed on the subsequent clock cycle number of bits used in virtual memory with ARMv8 ✔✔48 bits RAID ✔✔Redundant arrays of inexpensive disks (RAID): An organization of disks that uses an array of small and inexpensive disks so as to increase both performance and reliability. page table ✔✔Page table: The table containing the virtual to physical address translations in a virtual memory system. The table, which is stored in memory, is typically indexed by the virtual page number; each entry in the table contains the physical page number for that virtual page if the page is currently in memory. reference bit ✔✔. To help the operating system estimate the Least Recently Used (LRU) pages, some computers provide a reference bit or use bit, which is set whenever a page is accessed. (ARMv8 calls it an access bit.) The operating system periodically clears the reference bits and later records them so it can determine which pages were touched during a particular time period. limit register ✔✔a way to restrict the size of the page table translation-lookaside buffer ✔✔A cache that keeps track of recently used address mappings to try to avoid an access to the page table. benefits of using virtual machines ✔✔The increasing importance of isolation and security in modern systems The failures in security and reliability of [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)
.png)
WGU C952 BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS
WGU C952 BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$20
11
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 23, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 23, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
130





.png)