Billing and Coding Pretest 2022 COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 9

Army GCSS S4 Course Test 1
$ 8

Document Kenneth Bronson’s new allergy information in his patient record. | Kenneth Bronson Documentation Assignments-1.
$ 8
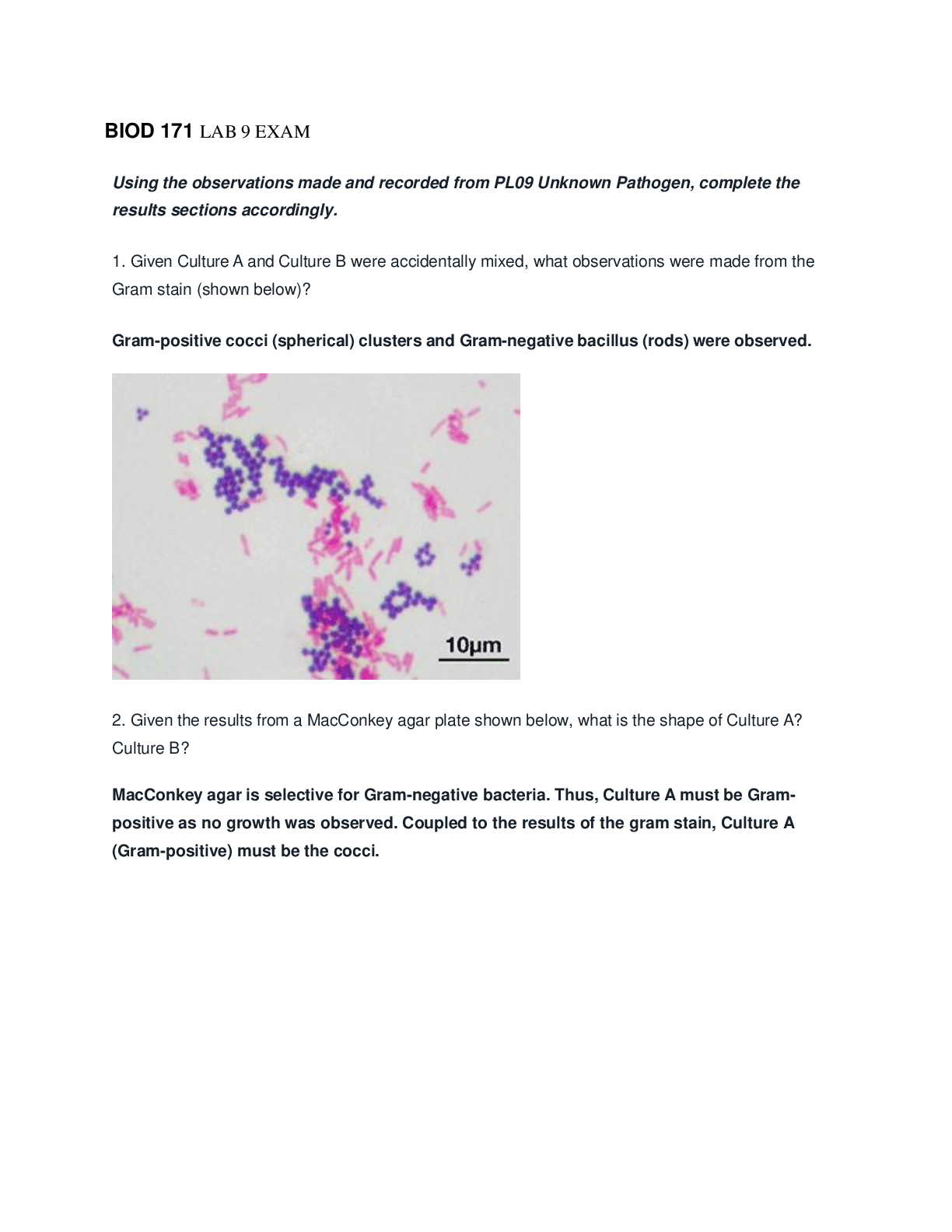
BIOD 171 LAB 9 EXAM
$ 11
.png)
WGU C702 CHFI and OA Questions and Answers with Complete Solution
$ 12

RN Comprehensive Predictor 2019 Form A
$ 10

WGU C207 Final Self-Assessment Q&A complete solution
$ 10

HA Exam #2
$ 7

CST - NBSTSA Study guide with complete solution
$ 7

D077 Module 1 Questions and Answers Rated A
$ 7

BIOD151- FINAL EXAM A&P 1.pdf
$ 13

AHA Basic Life Support (BLS) Exams A and B
$ 15

Electrical Engineering
$ 15
.png)
WGU C779 Vocabulary Latest Updated 2022 Already Graded A
$ 7

WGU C464 Introduction to Communication Questions and Answers Latest Update Graded A+
$ 5

Security question study guide for all badge holders(Complete)2022
$ 10

RN Comprehensive Online Practice 2019 B
$ 11

Unit 4 Milestone 4 Project Management
$ 19.5

HSCO 502 TEST 3- 2019 version
$ 13

(GCU) MKT 315 Introduction to Marketing - Latest Final Exam Review Q & S 2024
$ 11

Code HS 2.6-2.11Latest 2023 Rated A+
$ 7.5

Task 1 C204.docx C204 Management Comm
$ 10
.png)
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Mathematics Advanced Subsidiary PAPER 22: Mechanics 8MA0/22
$ 8

PSYC 1272 Final Exam Complete Solutions