Java: Chapter 12 Quiz
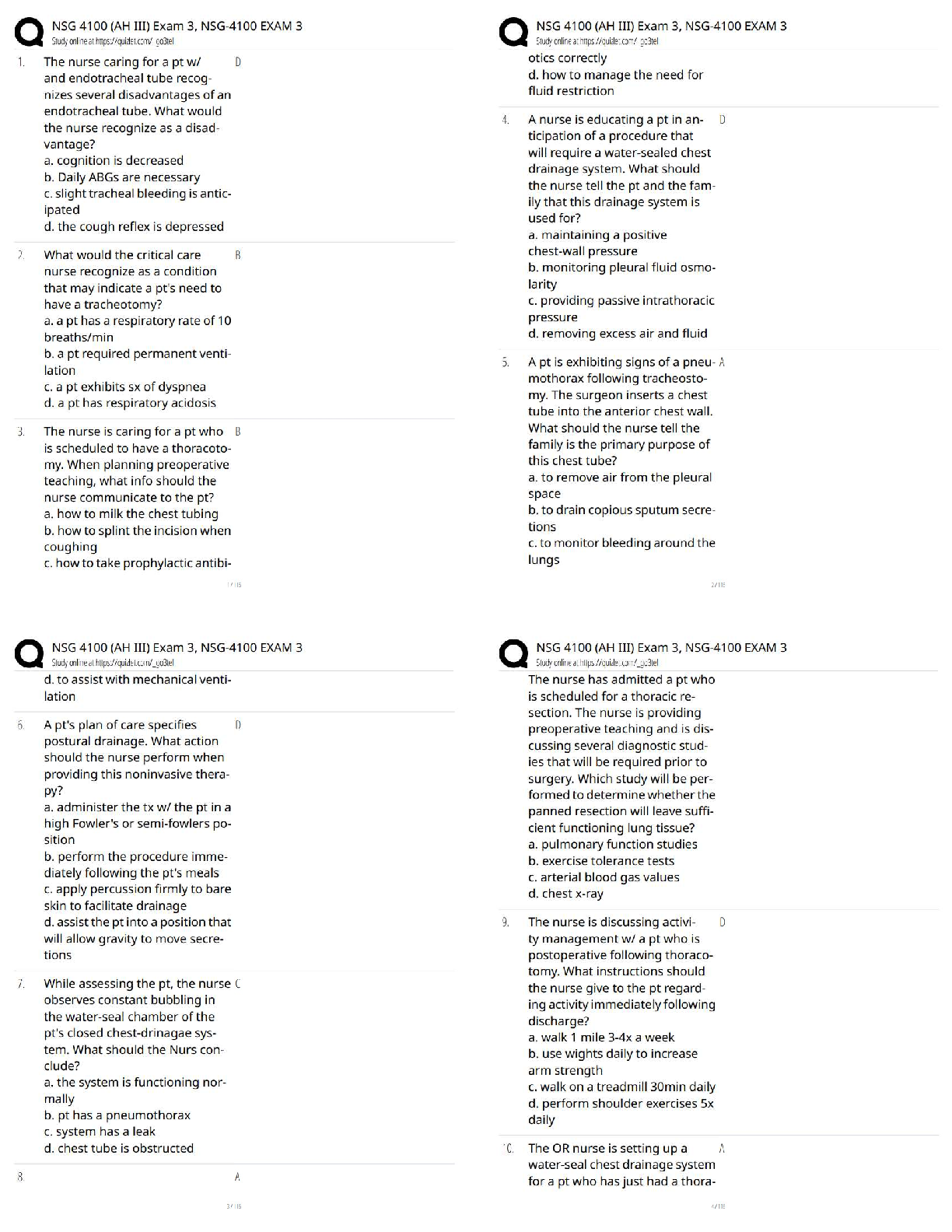
A common technique for writing an event listener class is to write it as a private inner
class inside the class that creates the GUI.
True/False - ✔✔True
A GUI program automatically stops execut
...
Java: Chapter 12 Quiz
A common technique for writing an event listener class is to write it as a private inner
class inside the class that creates the GUI.
True/False - ✔✔True
A GUI program automatically stops executing when the end of the main method is
reached.
True/False - ✔✔False
All operating systems offer the same set of GUI components.
True/False - ✔✔False
Check boxes may be grouped in a ButtonGroup, like radio buttons are.
True/False - ✔✔True
Some of the common GUI components are buttons, labels, text fields, check boxes, and
radio buttons.
True/False - ✔✔True
The ability to display splash screens was introduced in Java 6.
True/False - ✔✔True
The ActionEvent argument that is passed to an action listener's actionPerformed
method is the event object that was generated in response to an event.
True/False - ✔✔True
The FlowLayout manager does not allow the programmer to align components.
True/False - ✔✔False
The following statement adds the FlowLayout manager to the container, centers the
components, and separates the components with a gap of 10 pixels.
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
True/False - ✔✔False
The System.exit method will end the application.executing.
True/False - ✔✔True
You must use the statement import java.swing.*; in order to use the ItemListener
interface.
True/False - ✔✔False
When a splash screen is displayed, the application does not load and execute until the
user clicks the splash screen image with the mouse.
True/False - ✔✔False
________ is a library of classes that do not replace ________, but provide an improved
alternative for creating GUI applications.
A) JFC, Swing
B) AWT, Swing
C) Swing, AWT
D) JFC, AWT - ✔✔C) Swing, AWT
Assume that radio references a JRadioButton object. To click the radio button in code,
use the following statement:
A) Click(radio);
B) radio.Click();
C) radio.doClick();
D) Click(radio, true); - ✔✔C) radio.doClick();
Assume that the variable checkbox references a JCheckBox object. To determine
whether the check box has been selected, use the following code:
A) if (checkBox.doClick()) {/*code to execute,
if selected*/}
B) if (isSelected(checkBox)) {/*code to
execute, if selected*/}
C) if (checkBox) {/*code to execute, if
selected*/}
D) if (checkBox.isSelected()) {/*code to
execute, if selected*/} - ✔✔D) if (checkBox.isSelected())
{/*code to execute, if selected*/}
Because these components rely on the appearance and behavior of the underlying
operating system components, there is little that can be done by the programmer to
change their properties.
A) JFC
B) AWT
C) Swing
D) Container - ✔✔B) AWT
Event listeners must:
A) be included in private inner classes
B) exit the application once it has handled the event
C) not receive any arguments
D) implement an interface - ✔✔D) implement an interface
How many radio buttons can be selected at the same time as the result of the following
code?
hours = new JRadioButton("Hours");
minutes = new JRadioButton("Minutes");
seconds = new JRadioButton("Seconds");
days = new JRadioButton("Days");
months = new JRadioButton("Months");
years = new JRadioButton("Years");
timeOfDayButtonGroup = new ButtonGroup();
dateButtonGroup = new ButtonGroup();
timeOfDayButtonGroup.add(hours);
timeOfDayButtonGroup.add(minutes);
timeOfDayButtonGroup.add(seconds);
dateButtonGroup.add(days);
dateButtonGroup.add(months);
dateButtonGroup.add(years);
A) 4
B) 3
C) 1
D) 2 - ✔✔D) 2
If button1 is a JButton object, which of the following statements will make its
background blue?
A) button1.set.Background(BLUE);
B) button1.setBackground(Color.BLUE);
C) button1.makeBackground(BLUE);
D) button1.makeBackground(Color.BLUE); - ✔✔B)
button1.setBackground(Color.BLUE);
If panel references a JPanel object, which of the following statements adds the
GridLayout to it?
A) panel.addLayout(new (GridLayout(2,3))
B) panel.setLayout(new (GridLayout(2,3));
C) panel.GridLayout(2,3);
D) panel.attachLayout(GridLayout(2,3)); - ✔✔B) panel.setLayout(new (GridLayout(2,3));
In a Swing application, you create a frame object from the:
A) Jpanel
B) AbstractButton
C) Jlabel
D) JFrame - ✔✔D) JFrame
In Swing, labels are created with this class:
A) SwingLabel
B) JLabel
C) JFCLabel
D) AWTLabel - ✔✔B) JLabel
JFC stands for:
A) Java Fundamental Classes
B) Java Frame Class
C) Java Foundation Classes
D) Java Fundamental Core - ✔✔C) Java Foundation Classes
One of the small dots that make up a screen display is known as what?
A) pixel
B) texture
C) color
D) point - ✔✔A) pixel
Programs that operate in a GUI environment
[Show More]