Biochemistry - Exam 1 Practice
Questions
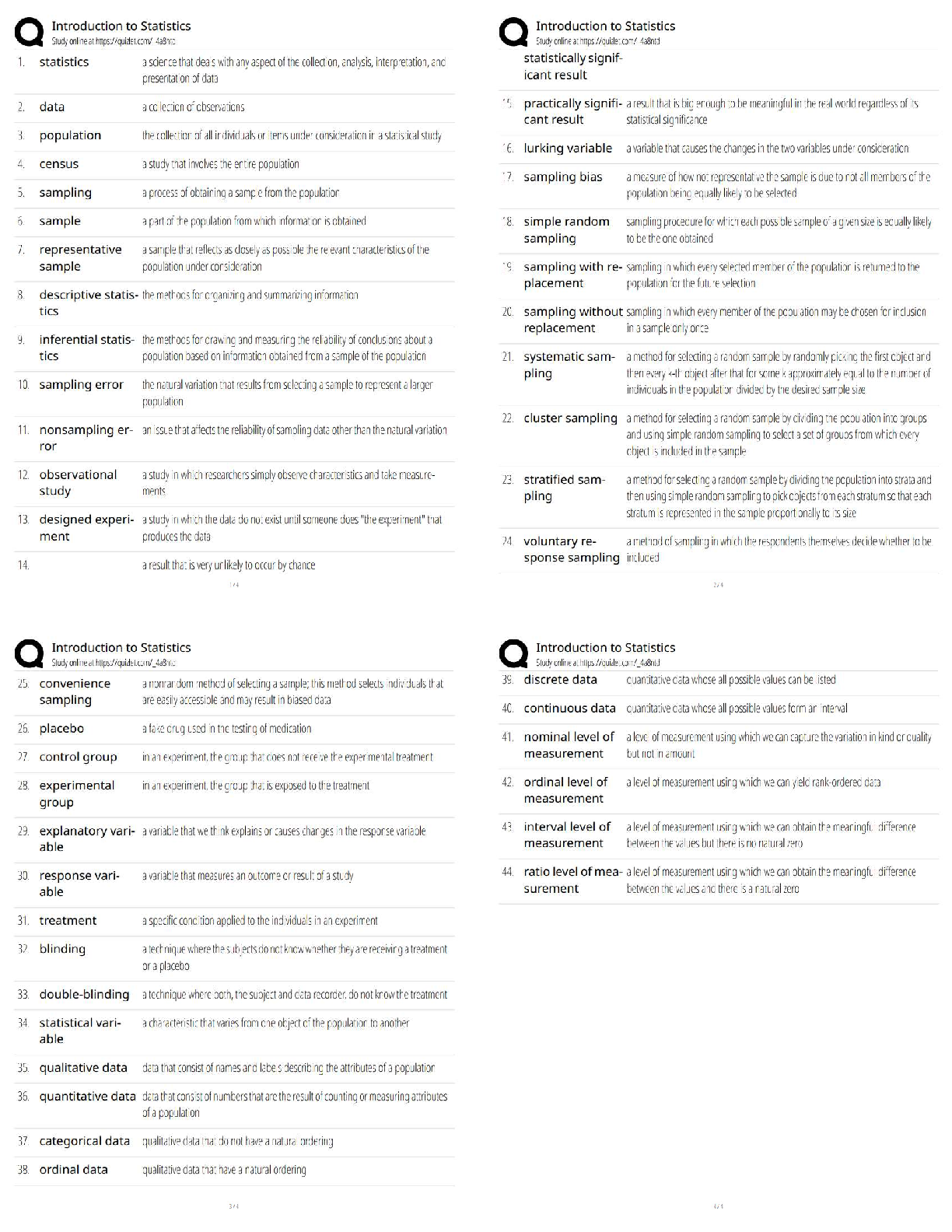
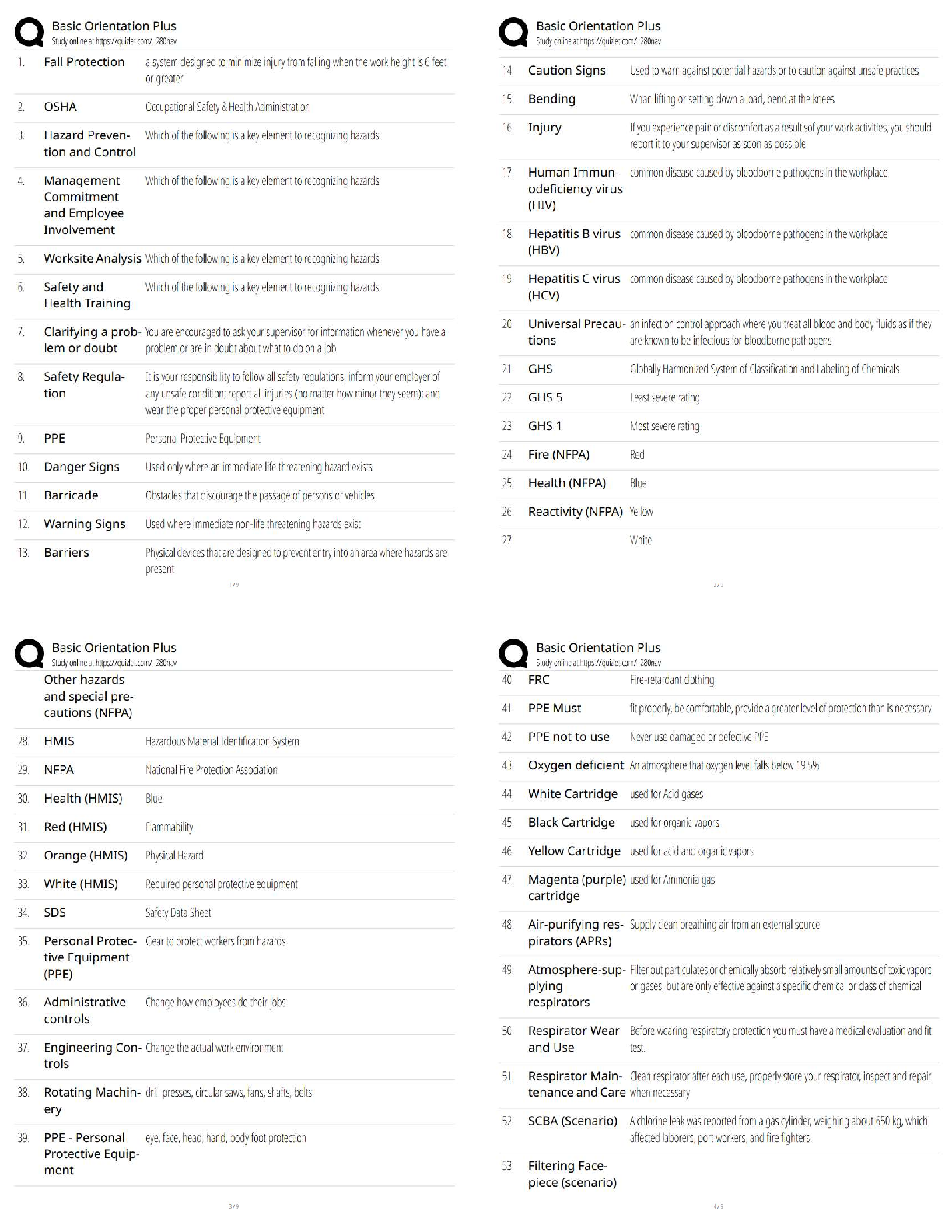
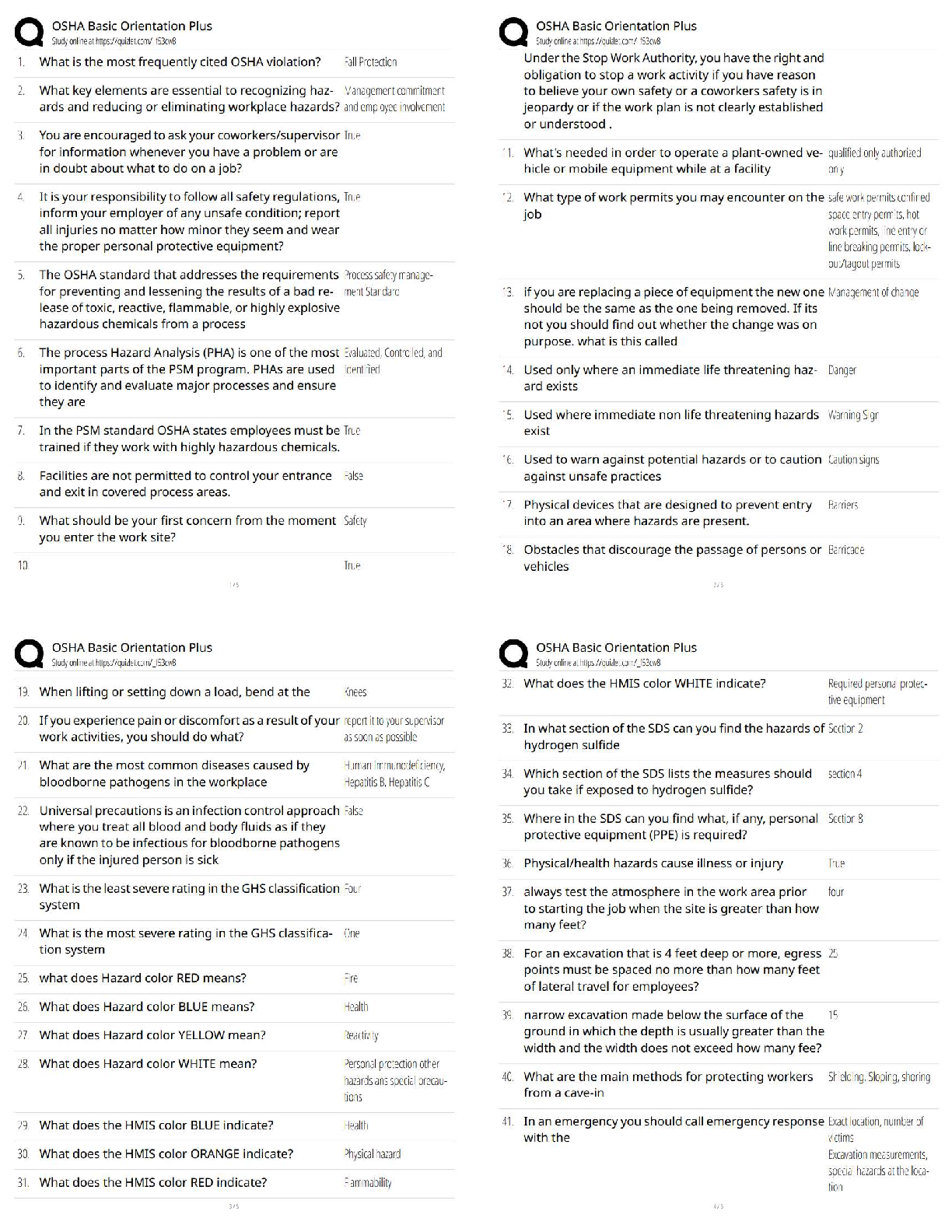
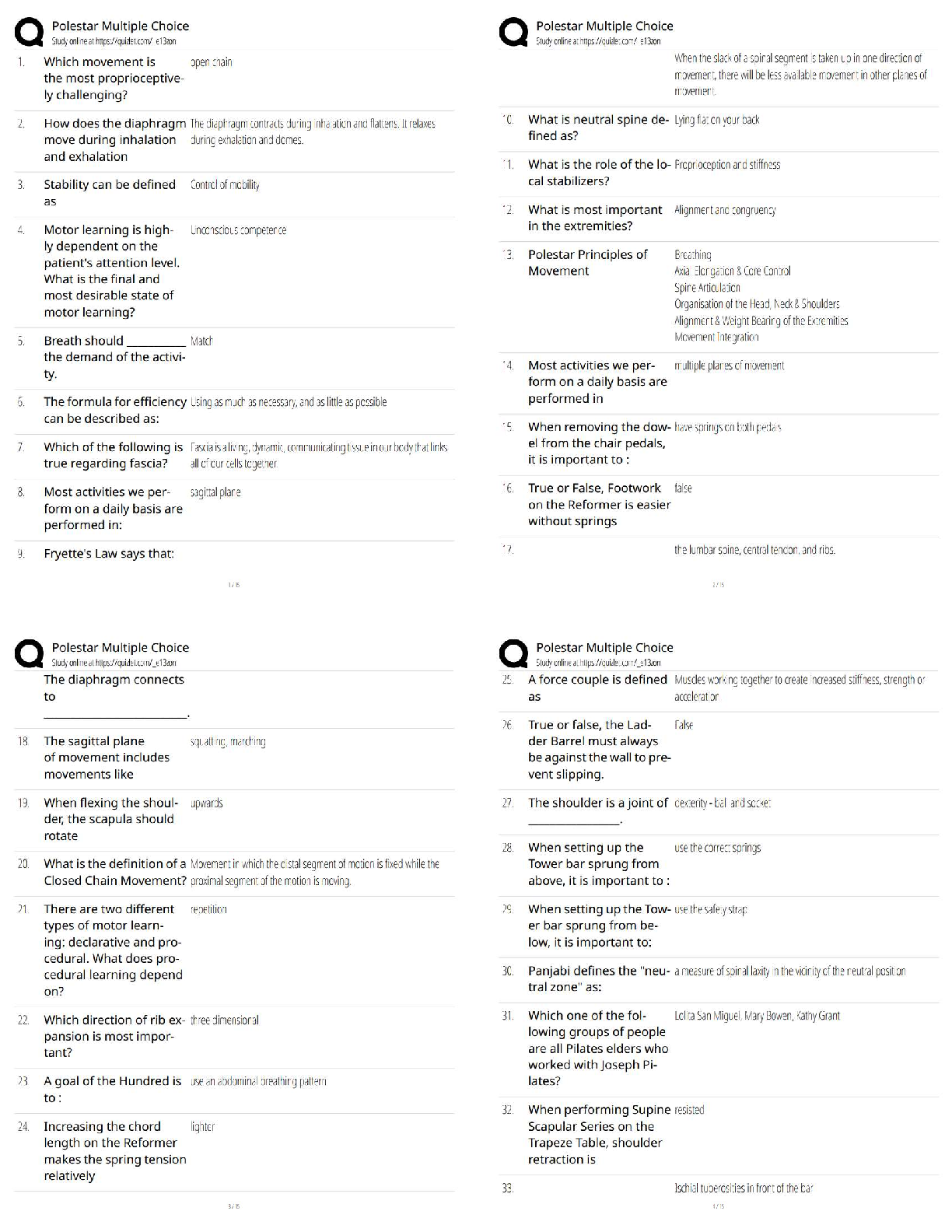
In a bacterial cell, the DNA is in the:
A) cell envelope.
B) cell membrane.
C) nucleoid.
D) nucleus.
E) ribosomes. - ✔✔nucleoid
A major change occurring in the evolution o
...
Biochemistry - Exam 1 Practice
Questions
In a bacterial cell, the DNA is in the:
A) cell envelope.
B) cell membrane.
C) nucleoid.
D) nucleus.
E) ribosomes. - ✔✔nucleoid
A major change occurring in the evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes was the
development of:
A) DNA.
B) photosynthetic capability.
C) plasma membranes.
D) ribosomes.
E) the nucleus - ✔✔the nucleus
In eukaryotes, the nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the:
A) cell membrane.
B) nuclear envelope.
C) nucleolus.
D) nucleoplasm.
E) nucleosome. - ✔✔nuclear envelope
The dimensions of living cells are limited, on the lower end by the minimum number of
biomolecules necessary for function, and on the upper end by the rate of diffusion of
solutes such as oxygen. Except for highly elongated cells, they usually have lengths
and diameters in the range of:
A) 0.1 µm to 10 µm.
B) 0.3 µm to 30 µm.
C) 0.3 µm to 100 µm.
D) 1 µm to 100 µm.
E) 1 µm to 300 µm - ✔✔0.3 µm to 100 µm
The bacterium E. coli requires simple organic molecules for growth and energy—it is
therefore a:
A) chemoautotroph.
B) chemoheterotroph.
C) lithotroph.
D) photoautotroph.
E) photoheterotroph - ✔✔chemoheterotroph
Which one of the following has the cellular components arranged in order of increasing
size?
A) Amino acid < protein < mitochondrion < ribosome
B) Amino acid < protein < ribosome < mitochondrion
C) Amino acid < ribosome < protein < mitochondrion
D) Protein < amino acid < mitochondrion < ribosome
E) Protein < ribosome < mitochondrion < amino acid - ✔✔Amino acid < protein <
ribosome < mitochondrion
The three-dimensional structure of macromolecules is formed and maintained primarily
through
noncovalent interactions. Which one of the following is not considered a noncovalent
interaction?
A) carbon-carbon bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) ionic interactions
E) van der Waals interactions - ✔✔carbon-carbon bonds
Which one of the following is not among the four most abundant elements in living
organisms?
A) Carbon
B) Hydrogen
C) Nitrogen
D) Oxygen
E) Phosphorus - ✔✔Phosphorus
The four covalent bonds in methane (CH4) are arranged around carbon to give which
one of the
following geometries?
A) linear
B) tetrahedral
C) trigonal bipyramidal
D) trigonal planar
E) trigonal pyramidal - ✔✔tetrahedral
The macromolecules that serve in the storage and transmission of genetic information
are:
A) carbohydrates.
B) lipids.
C) membranes.
D) nucleic acids.
E) proteins - ✔✔nucleic acids
Stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other are known as:
A) anomers.
B) cis-trans isomers.
C) diastereoisomers.
D) enantiomers.
E) geometric isomers - ✔✔enantiomers
The enzyme fumarase catalyzes the reversible hydration of fumaric acid to l-malate, but
it will not catalyze the hydration of maleic acid, the cis isomer of fumaric acid. This is an
example of:
A) biological activity.
B) chiral activity.
C) racemization.
D) stereoisomerization.
E) stereospecificity. - ✔✔stereospecificity
Humans maintain a nearly constant level of hemoglobin by continually synthesizing and
degrading it. This is an example of a(n):
A) dynamic steady state.
B) equilibrium state.
C) exergonic change.
D) free-energy change.
E) waste of energy - ✔✔dynamic steady state
If heat energy is absorbed by the system during a chemical reaction, the reaction is said
to be:
A) at equilibrium.
B) endergonic.
C) endothermic.
D) exergonic.
E) exothermic - ✔✔endothermic
If the free energy change ∆G for a reaction is -46.11 kJ/mol, the reaction is:
A) at equilibrium.
B) endergonic.
C) endothermic.
D) exergonic.
E) exothermic - ✔✔exergonic
The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is:
A) acetyl triphosphate.
B) adenosine monophosphate.
C) adenosine triphosphate.
D) cytosine tetraphosphate.
E) uridine diphosphate - ✔✔adenosine triphosphate
Enzymes are biological catalysts that enhance the rate of a reaction by:
A) decreasing the activation energy.
B) decreasing the amount of free energy released.
C) increasing the activation energy.
D) increasing the amount of free energy released.
E) increasing the energy of the transition state - ✔✔decreasing the activation energy
Energy requiring metabolic pathways that yield complex molecules from simpler
precursors are:
A) amphibolic.
B) anabolic.
C) autotrophic.
D) catabolic.
E) heterotrophic - ✔✔anabolic
Hereditary information (with the exception of some viruses) is preserved in:
A) deoxyribonucleic acid.
B) membrane structures.
C) nuclei.
D) polysaccharides.
E) ribonucleic acid. - ✔✔deoxyribonucleic acid
When a region of DNA must be repaired by removing and replacing some of the
nucleotides, what ensures that the new nucleotides are in the correct sequence?
A) DNA cannot be repaired and this explains why mutations occur.
B) Specific enzymes bind the correct nucleotides.
C) The new nucleotides base-pair accurately with those on the complementary strand.
D) The repair enzyme recognizes the removed nucleotide and brings in an identical one
to replace it.
E) The three-dimensional structure de
[Show More]



.png)