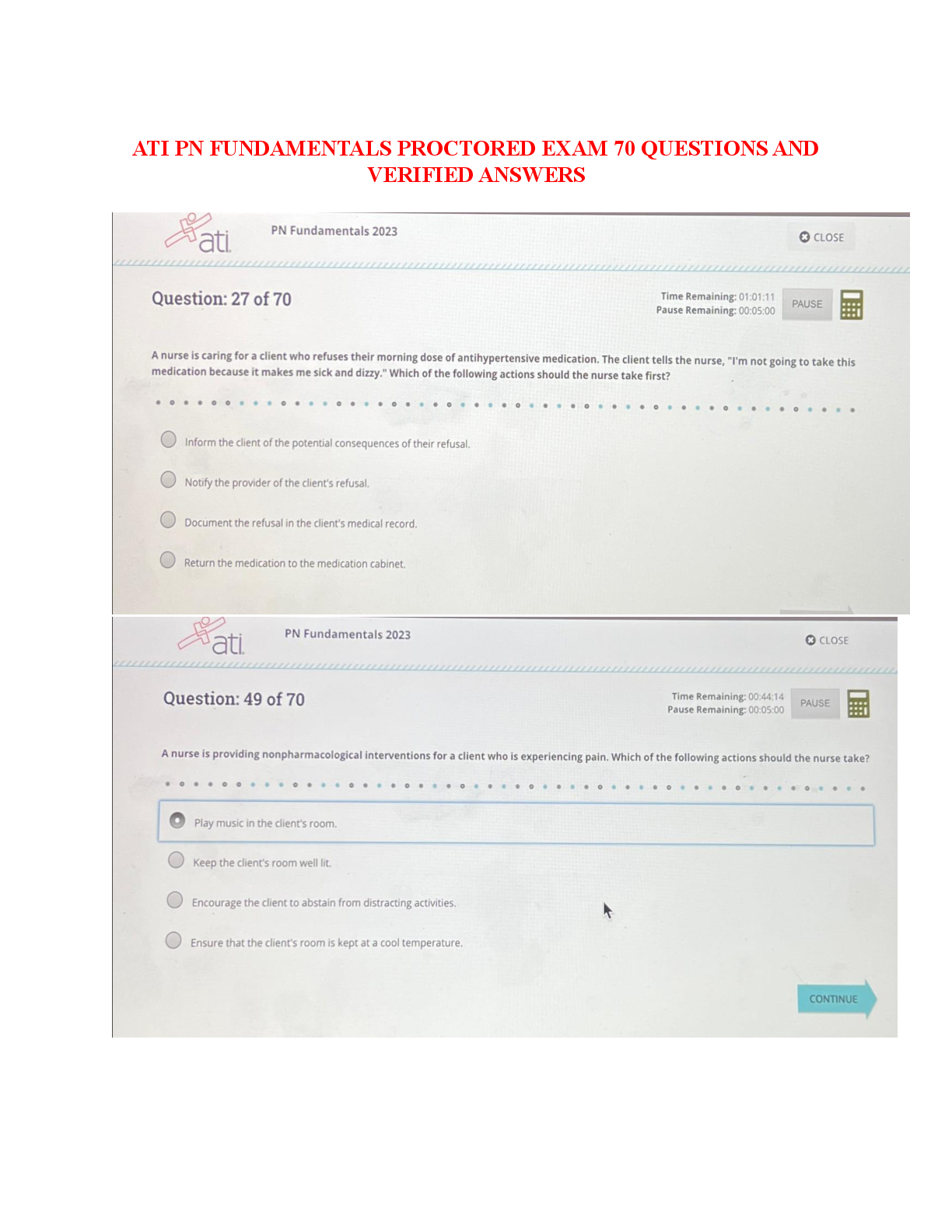
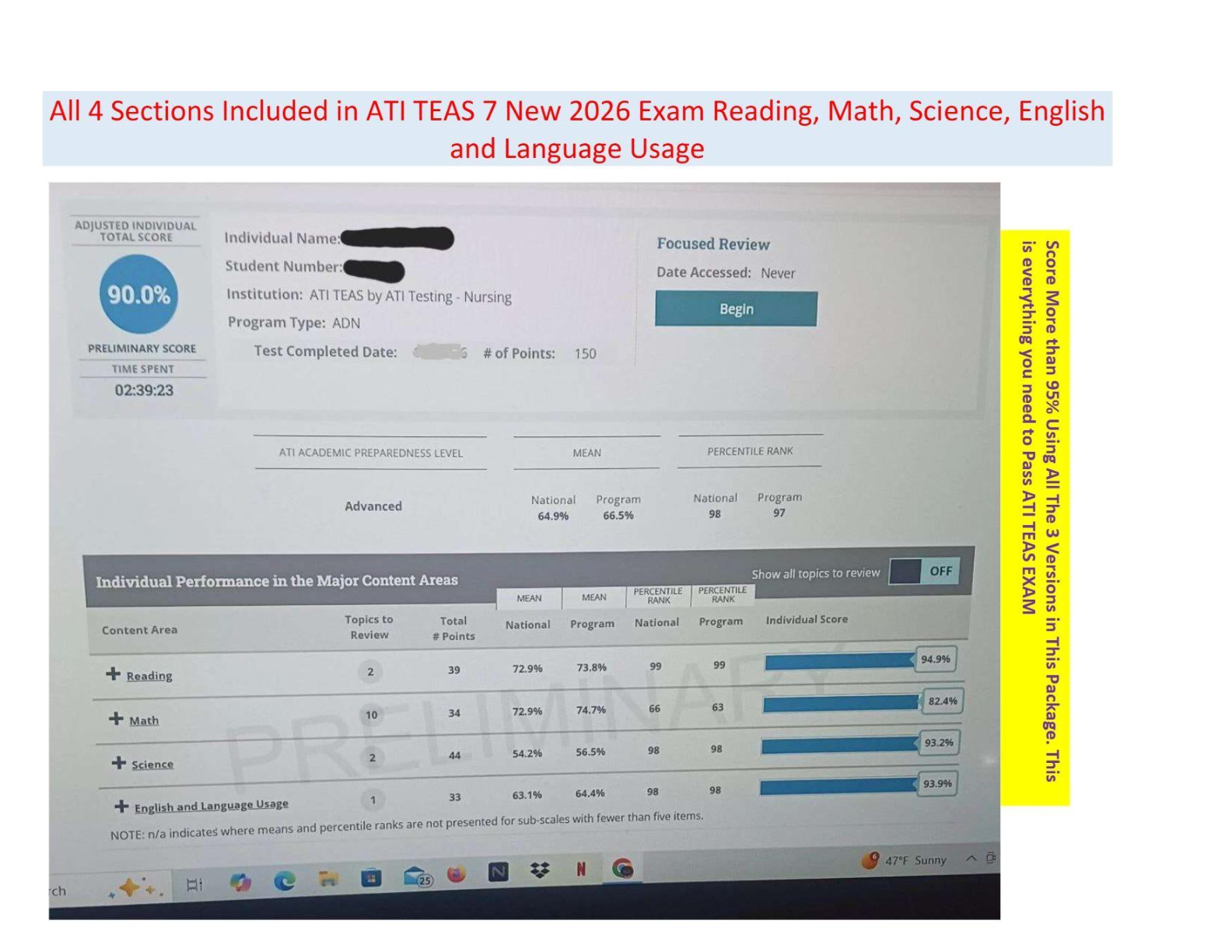
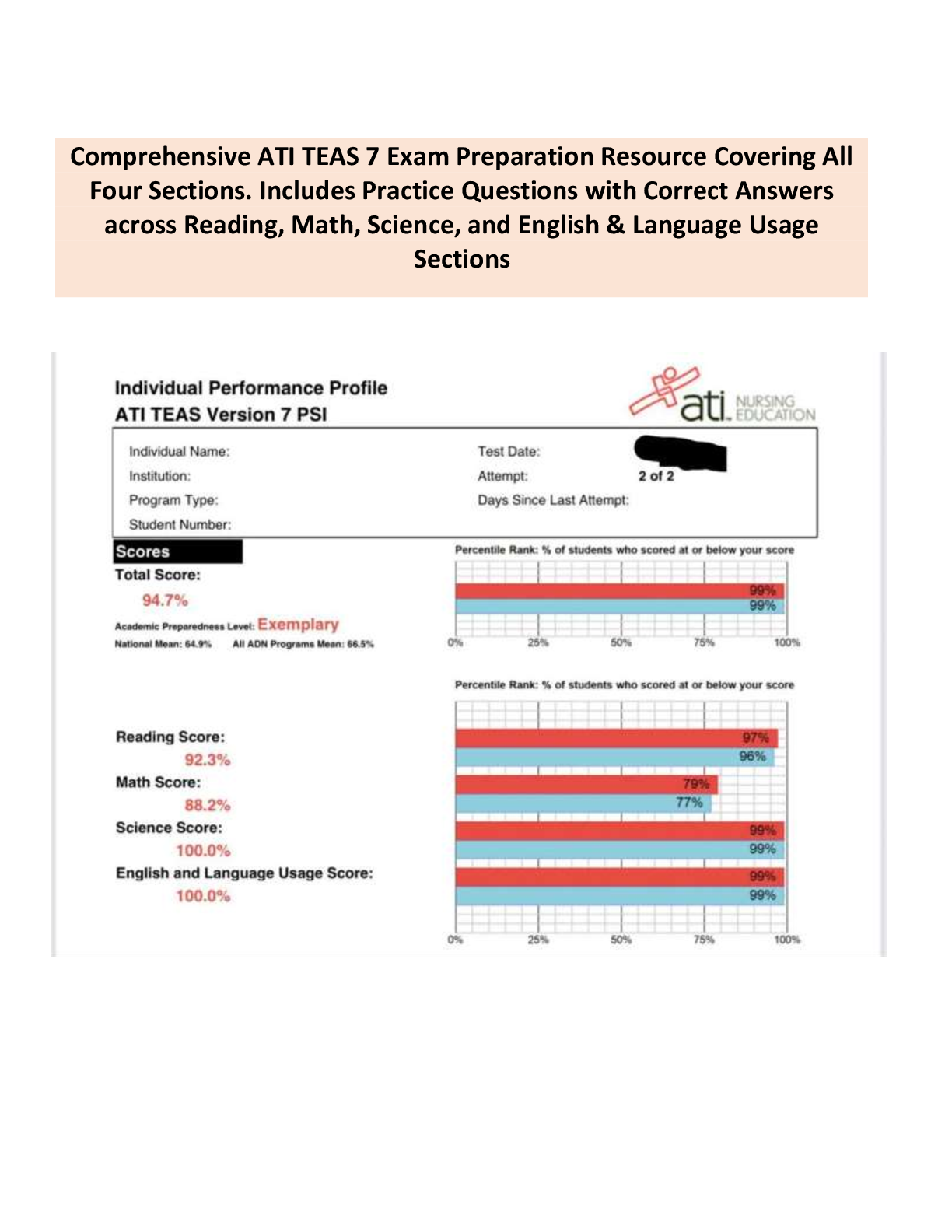
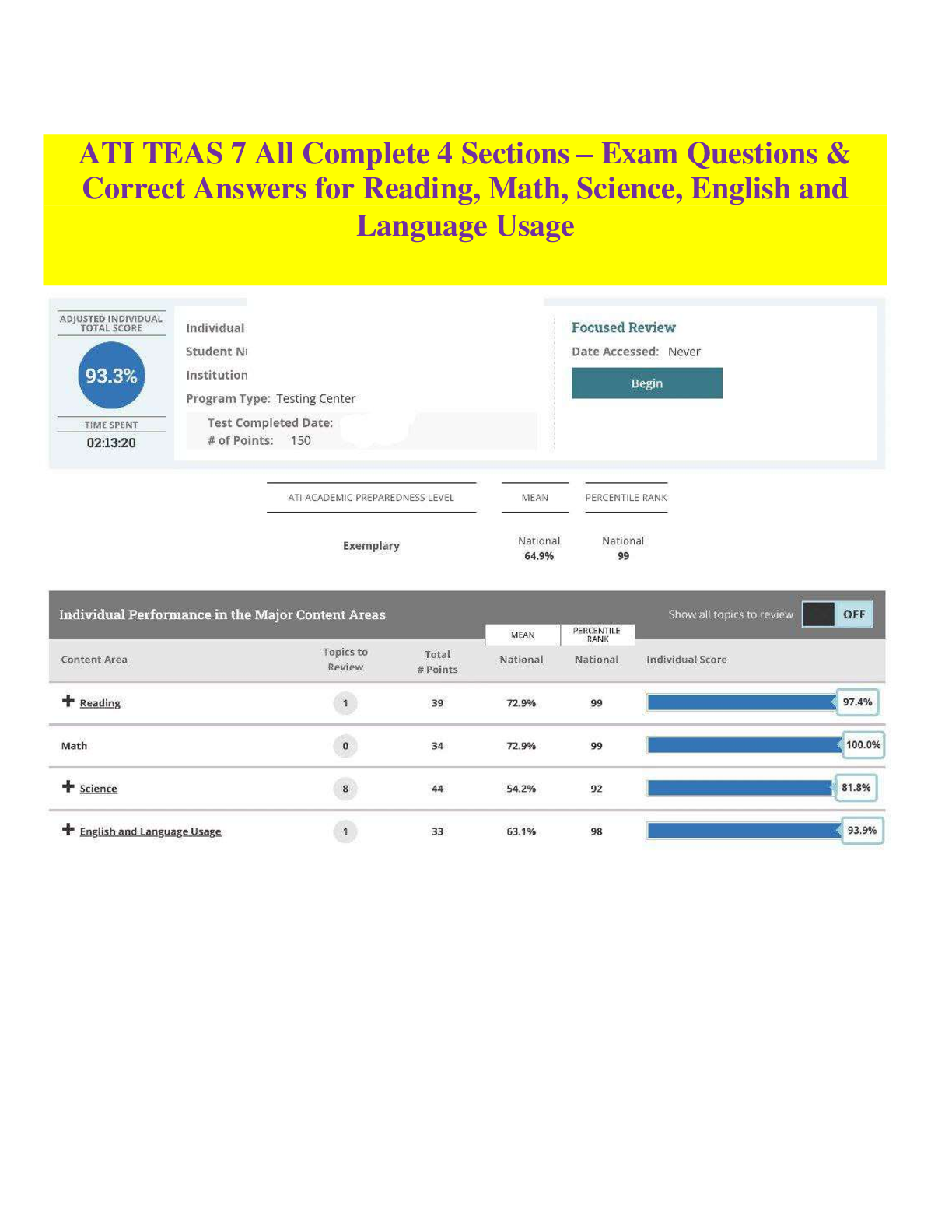
MATH 2720 MIDTERM 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Most of you did well on the course questions. These are “easy” questions that furthermore are important.
1. Course questions.
[5]
(a)
State the definition of
...
MATH 2720 MIDTERM 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Most of you did well on the course questions. These are “easy” questions that furthermore are important.
1. Course questions.
[5]
(a)
State the definition of a function continuous at a ∈ Rn.
[5]
(b)
State the definition of the arc length function.
[10]
2. Consider the function
f (x, y) =
y sin 1 , x = 0
x
0, x = 0.
3. Consider the cycloid with equation c(t) = (t − sin t)i + (1 − cos t)j.
[5]
(a) What are the domain and range of c?
[5]
(b)
Is c smooth?
[5]
(c)
Show that the (orthogonal) projection of c on j is 2π-periodic, i.e., that
projjc(t + 2π) = projjc(t) for all t ∈ R.
[5]
(d)
Sketch c for t ∈ [−3π, 3π].
[5]
(e)
Compute the arc length function of c for t ≥ 0.
[5]
(f)
Compute the curvature of c. Is this curvature defined for all t?
Figure 1: The cycloid c(t) = (t sin t)i + (1 cos t)j when t [ 3π, 3π]. (Note that the coordinate system is not orthonormal (axes are not to proportion.) Plotted using the command plot([t-sin(t),1-cos(t),t=-3Pi..3Pi]) in Maple.
Figure 2: The function t − sin t.
[10]
4. Consider the system
3x + 2y + z2 + u + v2 = 0 4x + 3y + u2 + v + w + 2 = 0 x + z + w + u2 + 2 = 0.
Can this system be solved for u, v, w in terms of x, y, z near x = y = z = 0,
u = v = 0 and w = −2?
[10] 5. Sketch the region of integration and evaluate both as indicated and as dy dx the integral
∫ 2 ∫ y2
x2 + y dx dy.
Figure 3: The domain for the integral in Exercise 5. As an x-simple region, this is
D = {(x, y) ∈ R2; −3 ≤ y ≤ 2, 0 ≤ x ≤ y2}. As a y-simple reg√ion, it is the union of
two regions: the orange region, D1 = {(x, y) ∈ R2; 0 ≤ x√≤ 4, x ≤ y ≤ 2}, and the
green region, D2 = {(x, y) ∈ R2; 0 ≤ x ≤ 9, −3 ≤ y ≤ − x}.
[5]
6. (a)
Show that the change of variables formula for cylindrical coordinates is given by
∫∫∫
T (W ∗)
f (x, y, z) dV = ∫∫∫
f (r cos θ, r sin θ, z) r dr dθ dz,
where W ∗ is an elementary region in rθz-space and T : (r, θ, z) (x, y, z) = (r cos θ, r sin θ, z).
[10]
(b)
Use part (a) to integrate (x2 + y2)z2 over the part of the cylinder x2 + y2 1
inside the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 4.
7. Bonus question (5 marks). Recall that a function f : X → Y is injective (or one-to-one) if x1, x2 X, f (x1) = f (x2) x1 = x2, i.e., no two points in the domain of f have the same image. Consider the linear transformation
T : R2 → R2
u ›→ Au,
where u R2 and A a 2 2 matrix with entries aij, i, j = 1, 2. Show that T is injective if and only if det(A) = 0. [Hint: This is easy with MATH 1300-type ideas.]
8. Bonus question (5 marks). Show that if f : R3 → R is C2, then ∇ × ∇f = 0.
∂ ∂ ∂
∂x
∂f ∂y
∂f ∂z
∂f
[Show More]














.png)