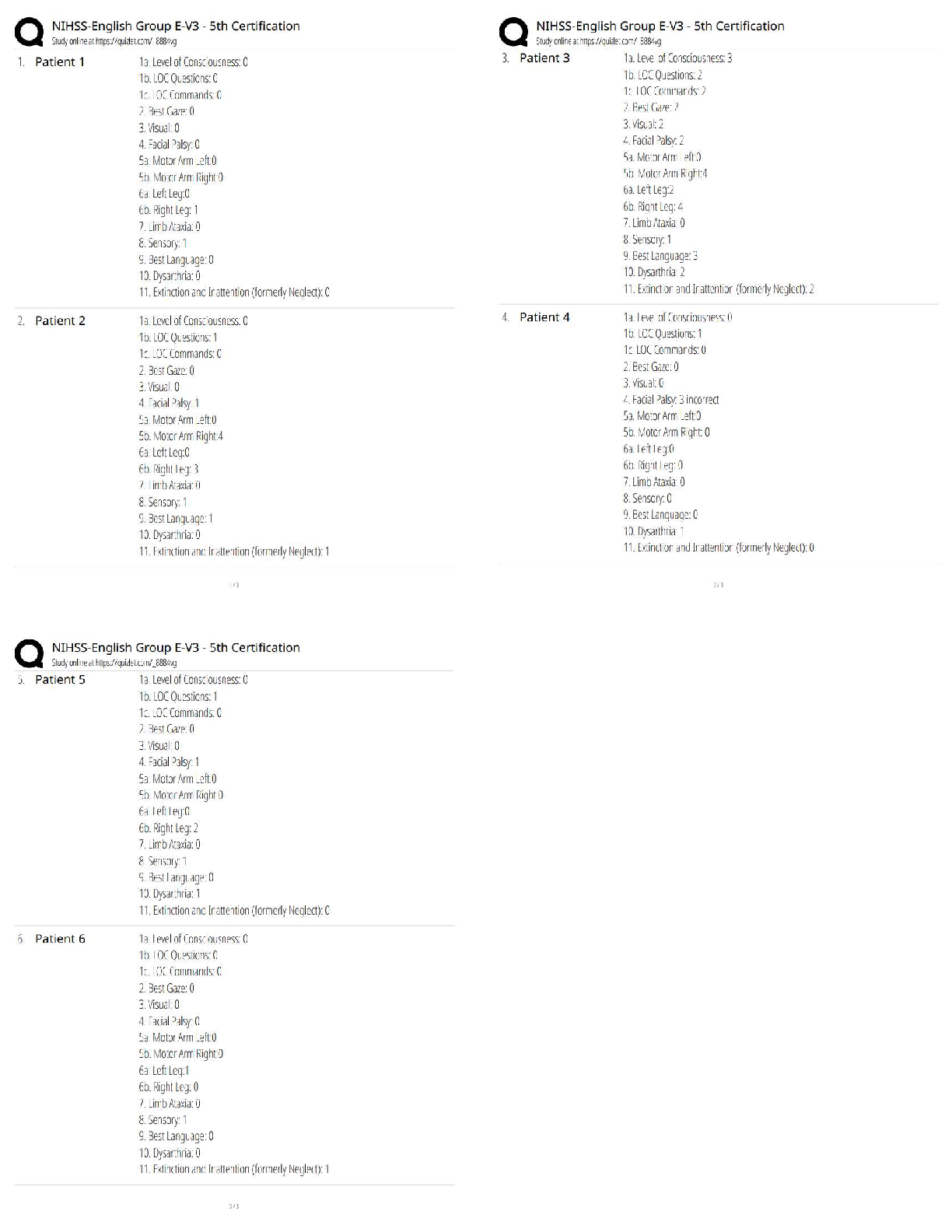
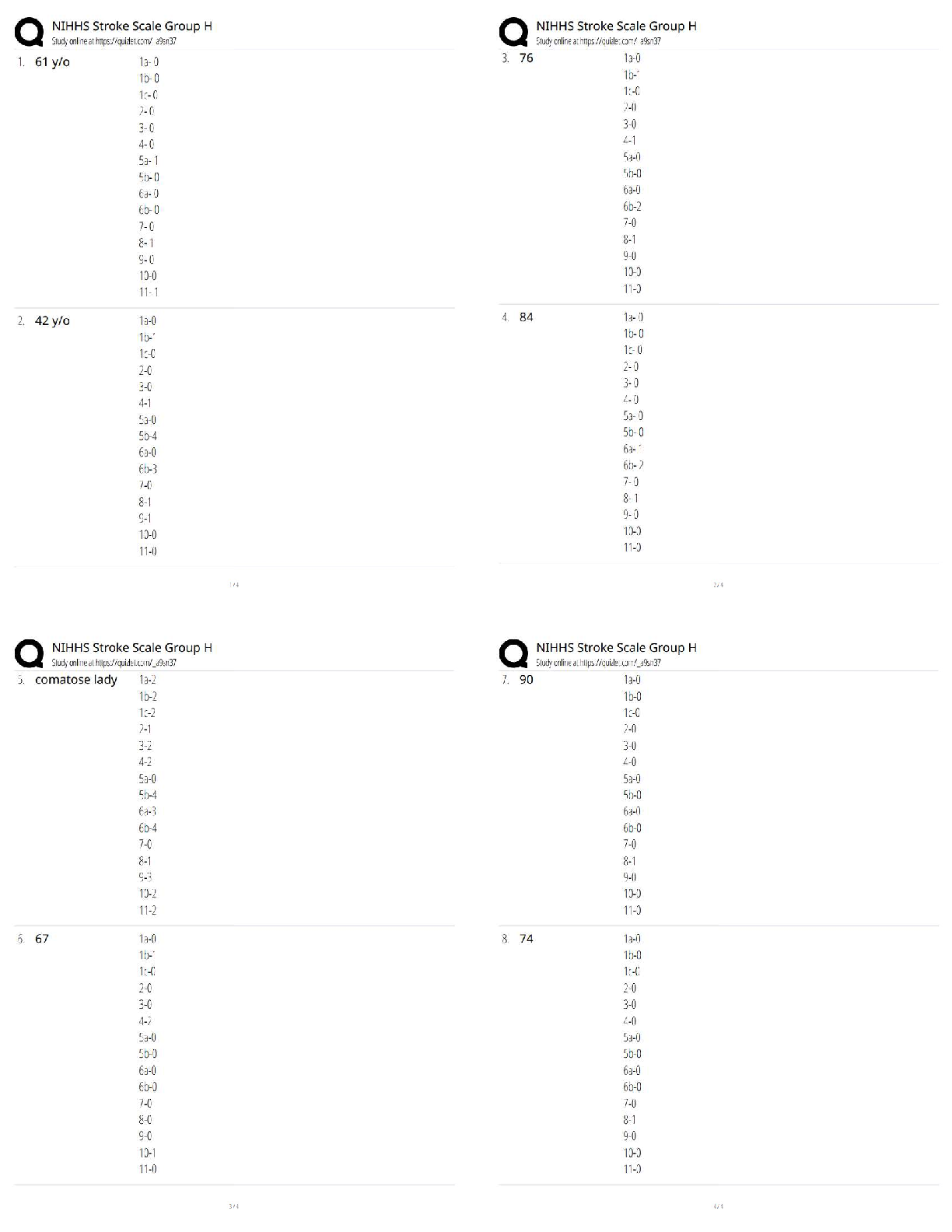
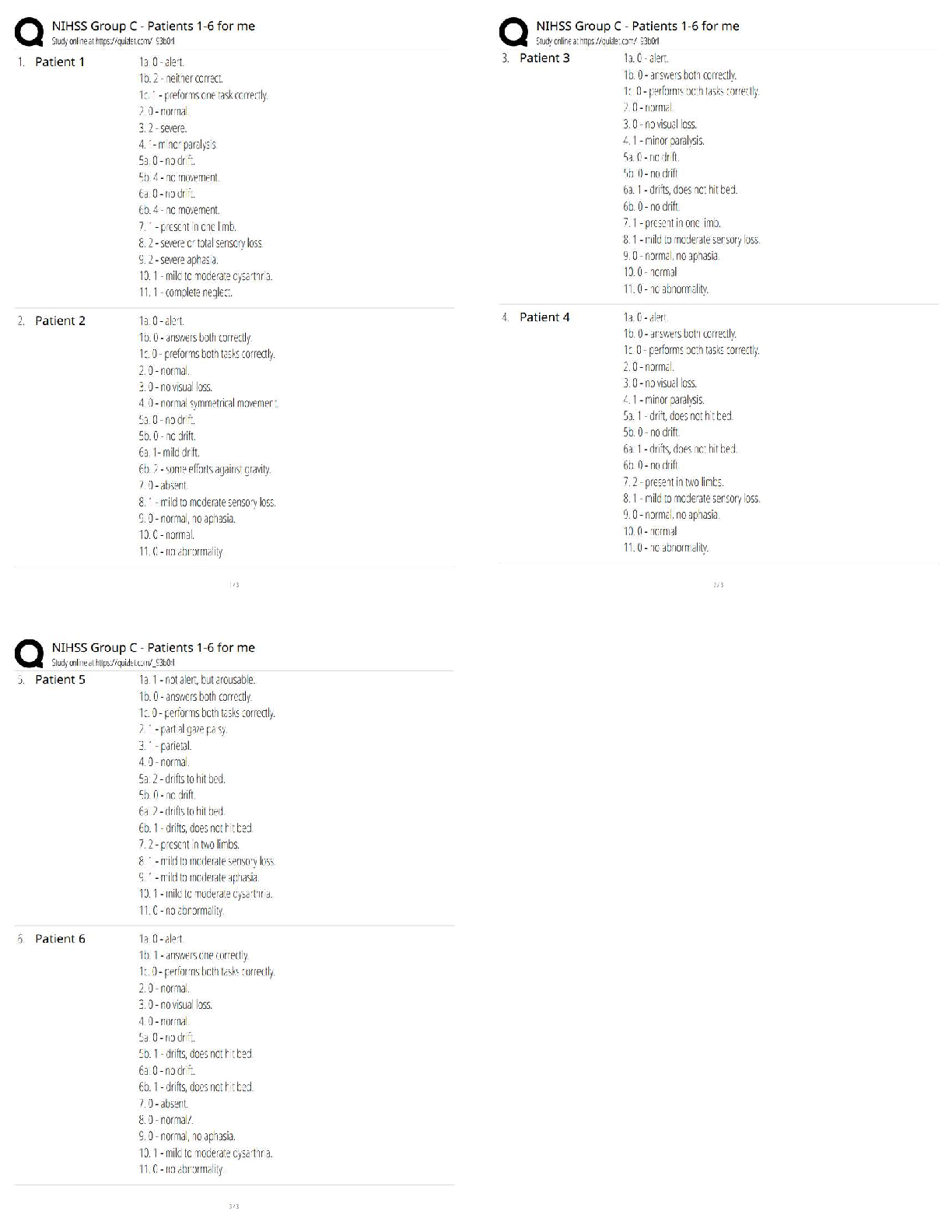
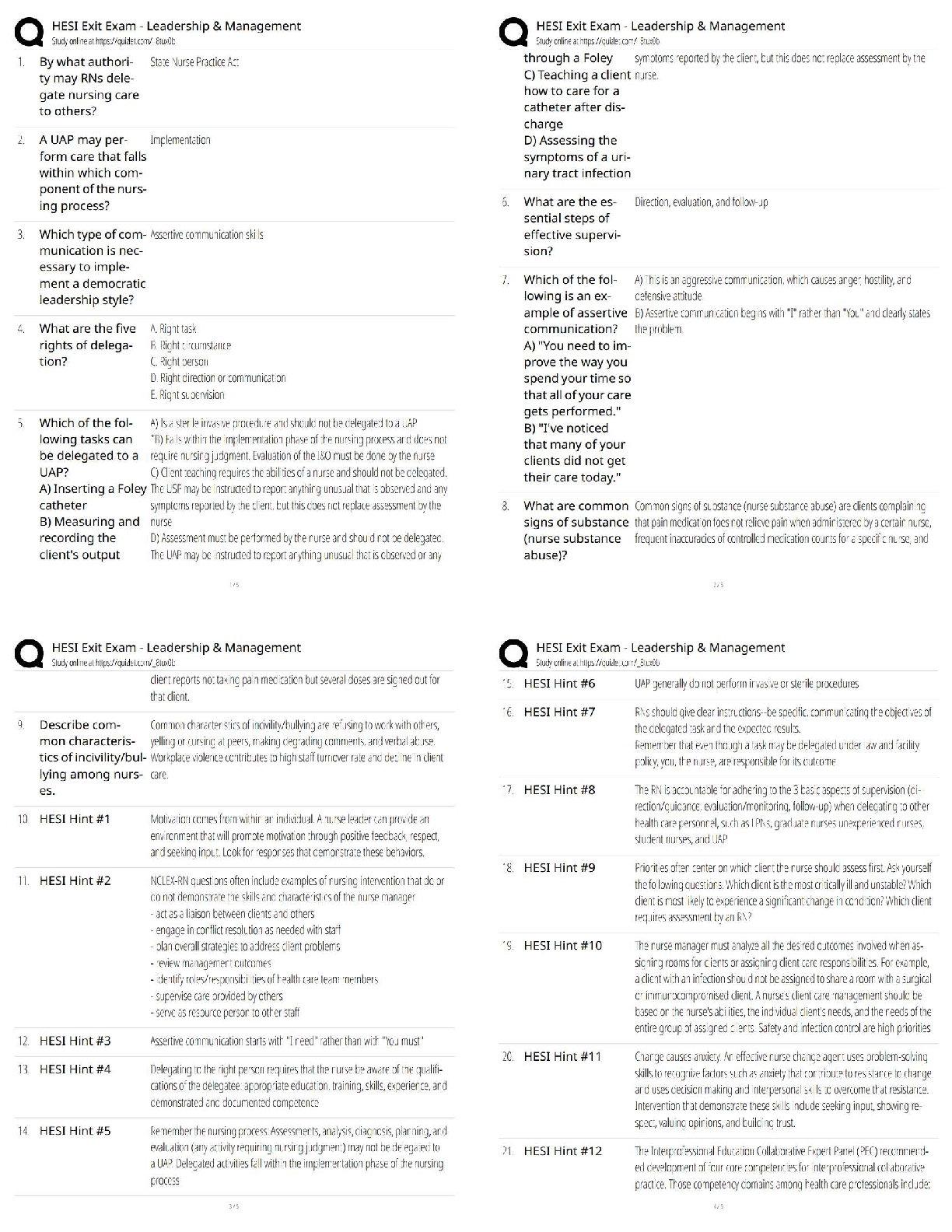
Finance > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Multiple Choice Questions on Analysis of Financial Statements. This document contains over 700 quest (All)
Multiple Choice Questions on Analysis of Financial Statements. This document contains over 700 questions and aswers. These are the most tested questions on Finance/Financial Statements.
Document Content and Description Below
MCQ on Analysis of Financial Statements A technique uses in comparative analysis of financial statement is A. graphical analysis B. preference analysis C. common size analysis D. returning analy ... sis Net income available to stockholders is $125 and total assets are $1,096 then return on common equity would be A. 0.11% B. 11.40% C. 0.12 times D. 12% Price per share is $30 and an earning per share is $3.5 then price for earning ratio would be A. 8.57 times B. 8.57% C. 0.11 times D. 11% Price per share is $25 and cash flow per share is $6 then price to cash flow ratio would be A. 0.24 times B. 4.16 times C. 4.16% D. 24% Low price for earning ratio is result of A. low riskier firms B. high riskier firms C. low dividends paid D. high marginal rate Profit margin = 4.5%, assets turnover = 2.2 times, equity multiplier = 2.7 times then return on assets will be A. 26.73% B. 26.73 times C. 9.40% D. 0.4 times Formula such as net income available for common stockholders divided by total assets is used to calculate A. return on total assets B. return on total equity C. return on debt D. return on sales Price per ratio is divided by cash flow per share ratio which is used for calculating A. dividend to stock ratio B. sales to growth ratio C. cash flow to price ratio D. price to cash flow ratio A techniques uses to identify financial statements trends are included A. common size analysis B. percent change analysis C. returning ratios analysis D. Both A and B Net income available to stockholders is $150 and total assets are $2,100 then return on total assets would be A. 0.07% B. 7.14% C. 0.05 times D. 7.15 times A formula such as net income available to common stockholders divided by common equity is used to calculate A. return on earning power B. return on investment C. return on common equity D. return on interest Companies that help to set benchmarks are classified as A. competitive companies B. benchmark companies C. analytical companies D. return companies Total assets divided common equity is a formula uses for calculating A. equity multiplier B. graphical multiplier C. turnover multiplier D. stock multiplier Price per share divided by earnings per share is formula for calculating A. price earning ratio B. earning price ratio C. pricing ratio D. earning ratio Profit margin multiply assets turnover multiply equity multiplier is used to calculate A. return on turnover B. return on stock C. return on assets D. return on equity Company low earning power and high interest cost cause financial changes which have A. high return on equity B. high return on assets C. low return on assets D. low return on equity Ratios which relate firm's stock to its book value per share, cash flow and earnings are classified as A. return ratios B. market value ratios C. marginal ratios D. equity ratios An equation in which total assets are multiplied to profit margin is classified as A. du DuPont equation B. turnover equation C. preference equation D. common equation Price earning ratio and price by cashflow ratio are classified as A. marginal ratios B. equity ratios C. return ratios D. market value ratios Return on assets = 5.5%, Total assets $3,000 and common equity $1,050 then return on equity would be A. $22,275 B. 15.71% C. 1.93% D. 1.925 times If profit margin = 4.5% and total assets turnover = 1.8% then return on assets DuPont equation would be A. 2.50% B. 8.10% C. 0.40% D. 4 times High price to earning ratio shows company's A. low dividends paid B. high risk prospect C. high growth prospect D. high marginal rate Return on assets = 6.7% and equity multiplier = 2.5% then return on equity will be A. 16.75% B. 2.68% C. 0.37% D. 9.20% Process of comparing company results with other leading firms is considered as A. comparison B. analysis C. benchmarking D. return analysis An equity multiplier is multiplied to return on assets to calculate A. return on assets B. return on multiplier C. return on turnover D. return on stock MCQ on Bonds and Bond Valuation Second mortgages pledged against bond's security are referred as A. loan mortgages B. medium mortgages C. senior mortgages D. junior mortgages Long period of bond maturity leads to A. more price change B. stable prices C. standing prices D. mature prices If coupon rate is equal to going rate of interest then bond will be sold A. at par value B. below its par value C. more than its par value D. seasoned par value Falling interest rate leads change to bondholder income which is A. reduction in income B. increment in income C. matured income D. frequent income Bonds issued by corporations and exposed to default risk are classified as A. corporation bonds B. default bonds C. risk bonds D. zero risk bonds Treasury bonds are exposed to additional risks that are included A. reinvestment risk B. interest rate risk C. investment risk D. Both A and B If bond's call provision is practiced in first year of issuance then an additional payment is classified as A. issuance provision B. bond provision C. call provision D. first provision Reinvestment risk of bond's is higher on A. short maturity bonds B. high maturity bonds C. high premium bonds D. high inflated bonds Bonds that have high liquidity premium are usually have A. inflated trading B. default free trading C. less frequently traded D. frequently traded Bond which is offered below its face value is classified as A. present value bond B. original issue discount bond C. coupon issued bond D. discounted bond Risk of fall in income due to fall in interest rates in future is classified as A. income risk B. investment risk C. reinvestment risk D. mature risk Redemption option which protects investors against rise in interest rate is considered as A. redeemable at deferred B. redeemable at par C. redeemable at refund D. redeemable at finding Payment divided by par value is classified as A. divisible payment B. coupon payment C. par payment D. per period payment An official entity that represents bondholders and ensures stated rules in indenture is classified as A. trustee B. trust C. stated entity D. owner entity An annual interest payment divided by current price of bond is considered as A. current yield B. maturity yield C. return yield D. earning yield If coupon rate is more than going rate of interest then bond will be sold A. more than its par value B. seasoned par value C. at par value D. below its par value Call provision practiced by company which states that call price will be paid is classified as A. super refund provision B. super put redemption C. make-whole call provision D. super call provision Difference between bond's yield and any other security yield having same maturities is considered as A. maturity spread B. bond spread C. yield spread D. interest spread Protective covenant devised in market to reduce event risk and to control debt cost is classified as A. super poison covenant B. super poison put C. super poison call D. super poison redemption Coupon rate of convertible bond is A. higher B. lower C. variable D. stable Rate denoted as r* is best classified as A. real risk-free interest rate B. real-risk free nominal rate C. real-risk free quoted rate D. real-risk free nominal premium An outstanding bonds are also classified as A. standing bonds B. outdated bonds C. dated bonds D. seasoned bonds An inflation rate includes in bond's interest rates is one which is inflation rate A. at bond issuance B. expected in future C. expected at time of maturity D. expected at deferred call A premium charged by lenders for securities that cannot be converted into cash is classified as A. required premium B. liquidity premium C. marketability premium D. Both B and C An unsecured bond that provides no lien against property as security for bond obligation is classified as A. secured bond B. debenture C. obligation bond D. specific bond Unsecured bonds which is designated for only notes payable or all other debts are classified as A. designated bonds B. payable bonds C. ordinate bonds D. subordinated bonds A market interest rate for specific type of bond is classified as bond's A. required rate of return B. required option C. required rate of redemption D. required rate of earning Bond which is issued in market and few days are passed of its issuance is classified as A. instable bond B. outstanding bond C. standing bond D. stable bond Real risk-free rate is applicable when it is expected that there will be A. high inflation B. low inflation C. no inflation D. none of above Bonds that do not pay original coupon payment but payment is made from additional bonds are classified as A. payment in-kind bonds B. payment off-kind bonds C. kind payment D. additional bond According to top rating agencies S&P double-B and other lower grade bonds are classified as A. development bonds B. junk bonds C. compounded bonds D. discounted bonds Bond call provision that is not practiced even after several years of issuance is classified as A. original provision B. deferred call C. deferred provision D. permanent provision Price of an outstanding bond increases when market rate A. never changes B. increases C. decreases D. earned An average inflation rate which is expected over life of security is classified as A. inflation premium B. off season premium C. nominal premium D. required premium Type of bond which pays interest payment only when it earns is classified as A. income bond B. interest bond C. payment bond D. earning bond Type of bonds that pays no coupon payment but provides little appreciation are classified as A. depreciated bond B. interest bond C. zero coupon bond D. appreciation bond In call provision, it is stated that company will pay to issue an amount A. higher than par value B. lower than par value C. equal to par value D. zero to par value If coupon rate is less than going rate of interest then bond will be sold A. seasoned par value B. more than its par value C. seasoned par value D. at par value Type of provision which allows an orderly retirement of an issued bond which is classified as A. whole call provision B. super fund provision C. floating fund provision D. sinking fund provision Bonds issued by small companies tend to have A. high liquidity premium B. high inflation premium C. high default premium D. high yield premium An interest yield = 7.9% and capital gains yield = 2.5% then total rate of return is A. 10% B. 3.16% C. 0.31% D. 5.40% Stated value of bonds or face value is considered as A. state value B. par value C. bond value D. per value Type of bond in which payments are made on basis of inflation index is classified as A. borrowed bond B. purchasing power bond C. surplus bond D. deficit bond An bond whose price will rise above its face value is classified as A. premium face value B. premium bond C. premium stock D. premium warrants Coupon rate of bond is also called A. nominal rate B. premium rate C. quoted rate D. both a and c Bond's promised rate of return is also considered as A. yield to earning B. yield to investors C. yield to maturity D. yield to return A premium which reflects possibility of issuer who does not pay principal amount of bonds is called A. seasoned risk premium B. nominal risk premium C. default risk premium D. quoted risk premium Real risk-free interest rate in addition with an inflation premium is equal to A. required interest rate B. quoted risk-free interest rate C. liquidity risk-free interest rate D. premium risk-free interest rate An increasing in interest rate leads to decline in value of A. junk bonds B. outstanding bonds C. standing bonds D. premium bonds Bonds issued by government and backed by U.S government are classified as A. issued security B. treasury bonds C. U.S bonds D. return security Legal document in which rights of issuing corporation and bondholders state is classified as A. legal rights classification B. indenture C. ownership statement D. guarantee statement Price of an outstanding bond decreases when market rate is A. increased B. decreased C. earned D. never changed Rate of interest which is usually discussed by investors whenever rate of return is discussed is classified as A. yield to maturity B. yield to return C. yield to earning D. yield to investors Tax free bonds issue for welfare by industrial agencies or pollution control agencies are classified as A. agent bonds B. development bonds C. pollution control bonds D. Both B and C Value generally promises to pay at maturity date and a firm borrows is considered as bond's A. bond value B. per value C. state value D. par value Maturity date decides at time of issuance of bond and legally permissible is classified as A. original maturity B. permanent maturity C. artificial maturity D. valued maturity Bonds with deferred call have protection which is classified as A. provision protection B. provision protection C. deferred protection D. call protection Bonds issued by local and state governments with default risk are A. municipal bonds B. corporation bonds C. default bonds D. zero bonds Indexed bonds that are issued by linking payments to inflation are classified as A. treasury inflation protected securities B. premium protected securities C. risk protected securities D. liquidity protected securities Bonds having zero default risk are classified as A. U.S bonds B. return security C. issued security D. treasury bonds Right held with corporations to call issued bonds for redemption is considered as A. artificial provision B. call provision C. redeem provision D. original provision Bond that has been issued in very recent timing is classified as A. mature issue B. earning issue C. new issue D. recent issue Type of options that permit bond holder to buy stocks at stated price are classified as A. provision B. guarantee C. warrants D. convertibles When price of bond is calculated below its par value, it is classified as A. classified bond B. discount bond C. compound bond D. consideration earning Required rate of return in calculating bond's cashflow is also classified as A. going rate of return B. yield C. earning rate D. Both A and B An interest rate which is used in calculation of cash flows of bonds is called A. required rate of redemption B. required rate of earning C. required rate of return D. required option According to top rating agencies S&P triple-A and double-A rating bonds are classified as an A. extremely discounted B. extremely safe C. extremely risky D. extremely inflated Rate on debt that increases as soon market rises is classified as A. rising bet rate B. floating rate debt C. market rate debt D. stable debt rate If market interest rate rises above coupon rate then bond will be sold A. equal to return rate B. seasoned price C. below its par value D. above its par value Bonds that can be converted into shares of common stock are classified as A. convertible bonds B. stock bonds C. shared bonds D. common bonds Type of bonds that are issued by foreign governments or foreign corporations are classified as A. zero risk bonds B. zero bonds C. foreign bonds D. government bonds Specific day at which bond value is repaid can be considered as A. valued date B. repayment date C. payment date D. maturity date An usage of proceeds of new issue to retire issue with high-rate is classified as A. refunding operation B. funding operation C. proceeds operation D. deferred operation If default probability is zero and bond is not called then yield to maturity is A. mature expected return rate B. lower than expected return rate C. higher than expected return rate D. equal to expected return rate Rate of return (in percentages) consists of A. capital gain yield interest yield B. return yield + stable yield C. return yield + instable yield D. par value + market value Reinvestment risk of bond's is usually higher on A. income bonds B. callable bonds C. premium bonds D. default free bonds If market interest rate fells below coupon rate then bond will be sold A. below its par value B. above its par value C. equal to return rate D. seasoned price Yield of interest rate which is below than coupon rate, this yield is classified as A. yield to maturity B. yield to call C. yield to earning D. yield to investors An inflation rate including in quoted interest rate on security, is inflation rate A. expected over security life B. expected at deferred call C. at bond issuance D. expected at time of maturity Market in which bonds are traded over-the-counter than in an organized exchange is classified as A. organized markets B. trade markets C. counter markets D. bond markets Coupon payment is calculated with help of interest rate, then this rate considers as A. payment interest B. par interest C. coupon interest D. yearly interest rate An effect of interest rate risk and investment risk on a bond's yield is classified as A. reinvestment premium B. investment risk premium C. maturity risk premium D. defaulter's premium Coupon payment of bond which is fixed at time of issuance A. remains same B. becomes stable C. becomes change D. becomes low MCQ on Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis Required increasing in current assets and an increasing in current liabilities is subtracted to calculate A. change in net working capital B. change in current assets C. change in current liabilities D. change in depreciation Cash flows that could be generated from an owned asset by company but not use in project are classified as A. occurred cost B. mean cost C. opportunity costs D. weighted cost In capital budgeting, cost of capital is used as discount rate and is based on pre-determines A. cost of inflation B. cost of debt and equity C. cost of opportunity D. cost of transaction Economists consider effects of started project on other parts of company or on environment of company is called A. externalities B. foreign effects C. weighted effects D. opportunity effects Situation in which company replaces existing assets with new assets is classified as A. replacement projects B. new projects C. existing projects D. internal projects Relevant cash flow which company expects when its will implement project is classified as A. irrelevant cash flow B. relevant cash flow C. incremental cash flow D. decrease cash flow Free cash flow is $12000, an operating cash flow is $4000, an investment outlay cash flow is $5000 then salvage cash flow would be A. −$21000 B. $21,000 C. −$3000 D. $3,000 Cash flows that should be considered for decision in hand are classified as A. relevant cash flows B. irrelevant cash flows C. marginal cash flows D. transaction cash flows Nominal interest rates and nominal cash flows are usually reflected the A. inflation effects B. opportunity effects C. equity effects D. debt effects Net investment in operating capital is $5000 and net operating profit after taxes is $8000 then free cash flow would be A. $13,000 B. −$3000 C. $3,000 D. −$13000 Situation in which new business reduces an existing business of firm is classified as A. non-cannibalization effect B. cannibalization effect C. external effect D. internal effect In cash flow estimation and risk analysis, real rate will be equal to nominal rate if there is A. no inflation B. high inflation C. no transactions D. no acceleration In cash flow estimation, depreciation shelters company's income from A. expansion B. salvages C. taxation D. discounts Weighted average cost of debt, preferred stock and common equity is classified as A. cost of salvage B. cost of interest C. cost of taxation D. cost of capital An investment outlay cash flow is $4000, operating cash flow is $1000 and salvage cash flow is $5000 then free cash flow would be A. $10,000 B. $8,000 C. zero D. none of above Rate of return which is required to satisfy stockholders and debt holders is classified as A. weighted average cost of interest B. weighted average cost of capital C. weighted average salvage value D. mean cost of capital Net investment in operating capital is $7000 and net operating profit after taxes is $11,000 then free cash flow will be A. −$18000 B. $18,000 C. −$4000 D. $4,000 Free cash flow is $17000 and net investment in operating capital is $10000 then net operating profit after taxes would be A. $7,000 B. $27,000 C. −$27000 D. −$7000 An investment outlay cash flow is $2000, an operating cash flow is $1500 and salvage cash flow is $3000 then free cash flow would be A. $500 B. $2,500 C. 6.50% D. $6,500 Free cash flow is $15000 and net investment in operating capital is $9000 then net operating profit after taxes will be A. $24,000 B. $6,000 C. −$6000 D. −$24000 In cash flow estimation, depreciation is considered as A. cash charge B. noncash charge C. cashflow discounts D. net salvage discount Net operating profit after taxes is $4500, net investment in operating capital is $8500 and then free cash flow would be A. −$4000 B. $4,000 C. −$18000 D. $18,000 Net investment in operating capital is subtracted from net operating profit after taxes to calculate A. relevant inflows B. free cash flow C. relevant outflows D. cash outlay Project which is started by firm for increasing sales is classified as A. new expansion project B. old expanded project C. firm borrowing project D. product line selection Real interest rate and real cash flows do not include A. equity effects B. debt effects C. inflation effects D. opportunity effects Gross fixed asset expenditures is $6000 and free cash flow is $8000 then operating cash flows will be A. −$14000 B. $2,000 C. $14,000 D. −$2000 Real rate expected cash flows and nominal rate expected cash flows must be A. accelerated B. equal C. different D. inflated Double declining balance method and sum of years digits are included in A. yearly method B. single methods C. double methods D. accelerated methods Free cash flow is $15000, operating cash flow is $3000, investment outlay cash flow is $5000 then salvage cash flow will be A. $17,000 B. −$17000 C. $7,000 D. −$7000 An operating cash flows is $12000 and gross fixed asset expenditure is $5000 then free cash flow will be A. −$7000 B. $7,000 C. $17,000 D. −$17000 Cost which has occurred already and not affected by decisions is classified as A. sunk cost B. occurred cost C. weighted cost D. mean cost An analysis and estimation of cash flows include A. input data and key output B. depreciation schedule C. net salvage values D. all of above MCQ on Cost of Capital During planning period, a marginal cost for raising a new debt is classified as A. debt cost B. relevant cost C. borrowing cost D. embedded cost Cost of common stock is 14% and bond risk premium is 9% then bond yield will be A. 1.56% B. 5% C. 23% D. 64.28% In weighted average cost of capital, a company can affect its capital cost through A. policy of capital structure B. policy of dividends C. policy of investment D. all of above A risk associated with project and way considered by well diversified stockholder is classified as A. expected risk B. beta risk C. industry risk D. returning risk Cost of common stock is 13% and bond risk premium is 5% then bond yield would be A. $18 B. 2.60% C. 8% D. 18% Variability for expected returns for projects is classified as A. expected risk B. stand-alone risk C. variable risk D. returning risk Cost of common stock is 16% and bond yield is 9% then bond risk premium would be A. 7% B. $7 C. 1.78% D. 25% If future return on common stock is 14% and rate on T-bonds is 5% then current market risk premium will be A. 19% B. 9% C. $9 D. $19 Cost of capital is equal to required return rate on equity in case if investors are only A. valuation manager B. common stockholders C. asset seller D. equity dealer Interest rate is 12% and tax savings (1-0.40) then after-tax component cost of debt will be A. 7.20% B. 7.2 times C. 17.14 times D. $17.14 Retention ratio is 0.60 and return on equity is 15.5% then growth retention model would be A. 14.90% B. 25.84% C. 16.10% D. 9.30% Method uses for an estimation of cost of equity is classified as A. market cash flow B. future cash flow method C. discounted cash flow method D. present cash flow method An attempt to make correction by adjusting historical beta to make it closer to an average beta is classified as A. adjusted stock B. adjusted beta C. adjusted coefficient D. adjusted risk Method in which company finds other companies considered in same line of business to evaluate divisions is classified as A. pure play method B. same play method C. division line method D. single product method Bond risk premium is added in to bond yield to calculate A. cost of American option B. cost of European option C. cost of common stock D. cost of preferred stock Stock selling price is $45, an expected dividend is $10 and an expected growth rate is 8% then cost of common stock would be A. $55 B. $58 C. $53 D. 30.22% A type of beta which incorporates about company such as changes in capital structure is classified as A. industry beta B. market beta C. subtracted beta D. fundamental beta Dividend per share is $18 and sell it for $122 and floatation cost is $4 then component cost of preferred stock will be A. 15.25% B. 0.1525 times C. $15.25 D. 0.15% In weighted average capital, capital structure weights estimation does not rely on value of A. investors equity B. market value of equity C. book value of equity D. stock equity Interest rates, tax rates and market risk premium are factors which an/a A. industry cannot control B. industry cannot control C. firm must control D. firm cannot control For each component of capital, a required rate of return is considered as A. component cost B. evaluating cost C. asset cost D. asset depreciation value If payout ratio is 0.45 then retention ratio will be A. 0.55 B. 1.45 C. 1.82 D. 0.45 Stock selling price is $35, expected dividend is $5 and expected growth rate is 8% then cost of common stock would be A. $40 B. 22.29% C. 0.1428 D. $80 Retention ratio is 0.55 and return on equity is 12.5% then growth retention model would be A. 11.95% B. 6.88% C. 13.05% D. 22.72% Preferred dividend is divided by preferred stock price multiply by (1-floatation cost) is used to calculate A. transaction cost of preferred stock B. financing of preferred stock C. weighted cost of capital D. component cost of preferred stock Stock selling price is $65, expected dividend is $20 and cost of common stock is 42% then expected growth rate will be A. 0.1123 times B. 11.23% C. 11.23 times D. $11.23 In retention growth model, percent of net income firms usually pay out as shareholders dividends is classified as A. payout ratio B. payback ratio C. growth retention ratio D. present value of ratio In weighted average cost of capital, rising in interest rate leads to A. increase in cost of debt B. increase capital structure C. decrease in cost of debt D. decrease capital structure Bond risk premium is 3% and bond yield is 10.2% then cost of common stock will be A. 3.40% B. 13.20% C. 7.20% D. 30.60% Cost of new debt or marginal debt is also classified as A. historical rate B. embedded rate C. marginal rate D. Both A and B Bond yield is 12% and bond risk premium is 4.5% then cost of common stock would be A. 37.50% B. 7.50% C. 15.50% D. 2.67 times Forecast by analysts, retention growth model and historical growth rates are methods used for an A. estimate future growth B. estimate option future value C. estimate option present value D. estimate growth ratio Premium which is considered as difference of expected return on common stock and current yield on Treasury bonds is called A. current risk premium B. past risk premium C. beta premium D. expected premium An interest rate which is paid by firm as soon as it issues debt is classified as pre-tax A. term structure B. market premium C. risk premium D. cost of debt Beta which is estimated as regression slope coefficient is classified as A. historical beta B. market beta C. coefficient beta D. riskier beta In weighted average cost of capital, capital components are funds that usually offer by A. stock market B. investors C. capitalist D. exchange index Cost which is used to calculate weighted average cost of capital is classified as A. weighted cost of capital B. component cost of preferred stock C. transaction cost of preferred stock D. financing of preferred stock Special situation in which large projects are financed by with and securities claims on project's cashflow is classified as A. claimed securities B. project financing C. stock financing D. interest cost Type of cost which is used to raise common equity by reinvesting internal earnings is classified as A. cost of mortgage B. cost of common equity C. cost of stocks D. cost of reserve assets If future return on common stock is 19% and rate on T-bonds is 11% then current market risk premium will be A. $30 B. 30% C. 8% D. $8 Historical growth rates, analysis forecasts and retention growth model are approaches to estimate A. present value of gain B. growth rate C. growth gain D. discounted gain In weighted average cost of capital, cost of capital which is risk adjusted and developed for each category of A. long-term projects B. industry [industrial] projects C. divisional projects D. short-term projects In retention growth model, payout ratio is subtracted from one to calculate A. present value ratio B. future value ratio C. retention ratio D. growth ratio If retention rate is 0.68 then payout rate will be A. 1.47% B. 1.68 C. 0.32 D. 0.68 Cost of common stock is 15% and bond yield is 10.5% then bond risk premium will be A. 1.43% B. $70 C. 25.50% D. 4.50% Cost of equity which is raised by reinvesting earnings internally must be higher than the A. cost of initial offering B. cost of new common equity C. cost of preferred equity D. cost of floatation Dividend per share is $15 and sell it for $120 and floatation cost is $3.0 then component cost of preferred stock will be A. 12.82 times B. 0.1282 times C. 12.82% D. $12.82 In pure play method, a company can calculate its own cost of capital with help of averaging an A. other company capital policy B. other company beta C. other company cost D. other division cost Capital budgeting decisions are analyzed with help of weighted average and for this purpose A. component cost is used B. common stock value is used C. cost of capital is used D. asset valuation is used A formula of after-tax component cost of debt is A. interest rate-tax savings B. marginal tax-required return C. interest rate + tax savings D. borrowing cost + embedded cost Risk free rate is subtracted from expected market return is considered as A. country risk B. diversifiable risk C. equity risk premium D. market risk premium Type of variability in which a project contributes in return of company is considered as A. variable risk B. within firm risk C. corporate risk D. Both B and C Rate of required return by debt holders is used for estimation the A. cost of debt B. cost of equity C. cost of internal capital D. cost of reserve assets MCQ on Financial Options and Applications in corporate Finance According to Black Scholes model, stocks with call option pays the A. dividends B. no dividends C. current price D. past price An exercise of option in future and part of option call value depends specifically on A. PV of exercising cost B. FV of exercising cost C. PV of cost volatility D. FV of cost volatility Yield on Treasury bill with a maturity is classified as a risk free rate but must be equal to an A. option closing price B. option beginning price C. option expiration D. option model Long-term equity anticipation security is usually classified as A. short-term options B. long-term options C. short money options D. yearly call Types of option markets do not include A. European option B. American option C. expiry option D. covered options In binomial approach of option pricing model, value of stock is subtracted from call option obligation value to calculate A. current value of portfolio B. future value of portfolio C. put option value D. call option value According to exercise value and option price, market value of option will be zero when A. stock price is maximum B. option price is zero C. stock price is zero D. stock price is minimum An excess of actual price of option over an exercise value of option is classified as A. time value options B. actual options C. estimated options D. optional pricing At last day when European and American option can be exercised is classified as A. European date B. American date C. expiration date D. money date Current value of stock in portfolio with current option price $20 is $50, then present value of portfolio would be A. $30 B. $70 C. 1.67% D. 30% Situation in financial options in which strike price is less than current price of stock is classified as A. in-the-money B. out-of-the-money C. out-of-the-portfolio D. in-the-portfolio In put call parity relationship, present value of exercise price is added to call option which is equal to A. put option stock B. call option + stock C. call option + market price D. put option + market price An option that gives investors right to sell a stock at predefined price is classified as A. put option B. call option C. money back options D. out of money options Value of stock is $250 and call option obligation is $100 then current value of portfolio would be A. 0.35 times B. $150 C. $350 D. $2.50 In binomial approach of option pricing model, fourth step is to create A. equalize domain of payoff B. equalize ending price C. riskless investment D. high risky investment Current value of portfolio is $550 and to cover an obligation of call option is $200 then value of stock would be A. $350 B. 2.75% C. $750 D. 2.75 times According to Black Scholes model, purchaser can borrow fraction of security at risk free interest rate which is A. short term B. long term C. transaction cost D. no transaction cost Type of option which cannot be exercised before an expiry date which is classified as A. European option B. American option C. Australian option D. money option * In put call parity relationship, put option minus call option in addition with stock is equal to A. exercise price present value B. exercise price future value C. time line value D. time value of bond Current option is $800 and current value of stock in portfolio is $1900 then present value of portfolio would be A. −$1100 B. $2,700 C. $1,100 D. −$2700 Second step in binomial approach of option pricing is to define range of values A. at expiration B. at buying date C. at exchange closing time D. at exchange opening time An increase in value of option leads to low present value of exercise cost only if it has A. low volatility B. interest rates are high C. interest rates are low D. high volatility Third step in binomial approach of option pricing is to A. equalize beginning price B. equalize range of payoffs C. equalize domain of payoff D. equalize ending price A type of contract in which contract holder has right to sell an asset at specific period for predetermining price is classified as A. option B. written contract C. determined contract D. featured contract According to Black Scholes model, short term seller receives today price which A. short term cash proceeds B. proceeds in cheques C. full cash proceeds D. zero proceeds An investor who writes stock call options in his own portfolio is classified as A. due option B. covered option C. undue option D. uncovered option According to put call parity relationship, an call option minus put option in addition with present value of exercise is equal to A. binomial property B. constant property C. constant and variable property D. stock Current value of stock included in portfolio is subtracted from current option price to calculate A. future value of stock B. present value of portfolio C. future value of portfolio D. present value of stock In financial planning, most high option price will lead to A. longer option period B. smaller option period C. lesser price D. higher price Current option is $700 and current value of stock in portfolio is $1400 then present value of portfolio will be A. −$700 B. $2,100 C. $700 D. 2% Present value of portfolio is $500 and current option price is $1200 then value of stock included in portfolio will be A. $1,700 B. −$1700 C. $700 D. −$700 Present value of portfolio is $1300 and current value of stock in portfolio is $2300 then current option price will be A. $3,600 B. $1,000 C. 1.76% D. 1.76 times An investor who buys shares and writes a call option on stock is classified as A. put investor B. call investor C. hedger D. volatile hedge Value of stock is $1000 and current value of portfolio is $1500 then obligation to cover call option will be A. 66.60% B. $2,500 C. 1.50% D. $500 In an option pricing, a rises in risk free rate results in option's value A. slight time decreases B. slight increases C. slight decreases D. slight time increases If current price increases from lower to higher then an A. option value equal to one B. option value will increase C. option value will decrease D. option value equal to zero In financial planning, formula MAX[current price of stock-strike price‚0] is used to calculate A. option return rate B. exercise value C. option value D. stock value According to put call parity relationship, call option plus present value of exercise price minus stock is to calculate A. present value of option B. call option C. put option D. future value of option When two portfolios have identical values and payoffs then it is classified as A. binomial parity relationship B. put parity relationship C. put option parity relationship D. put call parity relationship Greater value of option, larger span of time value is usually results in A. shorter call option B. longer call option C. longer put option D. shorter put option Price at which European and American options can be exercised is classified as A. exercise price B. strike price C. horizon price D. Both A and B Current option price is added to present value of portfolio for calculating A. future value of portfolio B. current value of stock C. future value of stock D. present value of portfolio In options pricing, an exercise price rises from lower to higher which leads to A. volatile options B. option value increases C. option value decreases D. option value stable In stock option, a little chance exists for large gain on stock when price of stock A. have volatile movement B. moves freely C. rarely moves D. stays same According to Black Scholes model, rate which is constant and known is classified as A. short term return rate B. long term return rate C. risk free interest rate D. risky rate of return According to Black Scholes model, trading of securities and stock prices moves respectively A. constant and randomly B. randomly and constant C. randomly and continuously D. continuously and randomly In binomial approach of option pricing model, last step for finding an option is A. price hike B. price value C. put price D. call price Type of options that do not have stock in portfolio to back up options is classified as A. undue options B. due options C. naked options D. total options Market value of option which is out-of-money is A. greater than zero B. equal to zero C. lesser than zero D. equal to one Present value of portfolio is $900 and current value of stock in portfolio is $1500 then current option price would be A. $2,400 B. −$600 C. −$2400 D. $600 Stock option is considered more valuable in situation when stock have A. price hike in market B. market stability C. not volatile D. highly volatile Pricing model approach in which it is assumed that stock price can have one of two values of stock is classified as A. valued approach B. marketability approach C. stock approach D. binomial approach An option which can be exercised any desired time before an expiry date is classified as A. Australian option B. money option C. European option D. American option In financial planning, a higher strike price leads to call option A. price is higher B. rate is lower C. price is lower D. rate is higher According to Black Scholes model, selling and buying of stock have A. discount rate B. transaction costs C. no transaction costs D. no discounts Stock option is more worthwhile if it is A. extremely volatile B. less volatile C. stable stock D. unstable price stock According to Black Scholes model, call option is well exercised on its A. mid buying date B. expiry date C. buying date D. mid selling date Sellers of options in financial markets are classified as A. expiry writer B. option writer C. contract writer D. bond writer In option pricing, an increasing in option price due to A. time of expiry increases B. time of expiry decreases C. exchange time increases D. exchange time decreases Type of options in which buyer of options has call on 200 shares in stock is classified as A. call option B. stated option C. unstated option D. contractual option Movement of price or rise or fall of prices of options is classified as A. option lattice B. pricing movement C. price change D. binomial lattice Variability of stock price, option term to maturity and risk free rate are dependents of A. price of an option B. expiry of an option C. exercise of an option D. estimation of an option Value of option which is considered as its worth as soon as it is expired is classified as A. minimum option value B. minimum value C. maximum value D. exercise value Current value of stock including in portfolio is subtracted from present value of portfolio to calculate A. last month option price B. last year option price C. current option price D. future option price Call options situation in which strike price is greater than current price of stock is classified as A. out-of-the-portfolio B. in-the-portfolio C. in-the-money D. out-of-the-money If stock market price is higher than strike price so call option A. price will be lower B. rate will be higher C. price will be higher D. rate will be lower First step in binomial approach of option pricing is to A. define ending price of stock B. define beginning price of stock C. define range of values D. define domain of values Present value of portfolio $850 and current option price $1620 then value of stock included in portfolio would be A. 1.90% B. 1.90 times C. $770 D. $2,470 MCQ on Overview of Financial Management and Environment Corporations such as Citigroup, American Express and Fidelity are classified as A. financial services corporations B. common service corporations C. preferred service corporations D. commercial service corporations Financial corporations which serve individual savers and commercial mortgage borrowers are classified as A. savings associations B. loans associations C. preferred and common associations D. savings and loans associations A regulatory body which licenses brokers and oversees traders is classified as A. international firm of auction system B. international association of network dealers C. national firm of equity dealers D. national association of securities dealers Companies take savings as premium, invest in bonds and make payments to beneficiaries are classified as A. debit unions B. life insurance companies C. credit unions D. auto purchases Federal government tax revenues if it exceeds government spending then it is classified as A. budget surplus B. budget deficit C. federal reserve D. federal budget Mutual fund allows investors to sale out their share during any normal trading hours is classified as A. exchange traded fund B. management expense C. money trade fund D. capital trade fund Step in initial public offering in which hired agents act on behalf of owners is classified as A. hiring problems B. agency problems C. corporation internal problems D. corporation external problems Financial security which is tax exempted and issues by state governments to individuals is classified as A. U.S treasury bonds B. mortgages C. municipal bonds D. corporate bonds A company sells its stock shares for raising more equity capital is classified as A. dealer communication offering B. seasoned equity offering C. electronic equity offering D. electronic order offering All partners have limited liability in A. unlimited liability partnership B. limited liability partnership C. controlled partnership D. uncontrolled partnership Markets dealing with residential loans, industry real estate loans, agricultural loans and commercial loans are called A. residential markets B. mortgage markets C. agriculture markets D. commercial markets Type of financial security in which loans are secured by borrowers property is classified as A. municipal bonds B. corporate bonds C. U.S treasury bonds D. mortgages In financial markets, period of maturity more than five years of financial instruments is classified as A. intermediate term B. capital term C. short-term D. long-term Type of financial securities that mature in less than a year are classified as A. saving intermediaries B. discounted intermediaries C. money market securities D. capital market securities Merrill Lynch, Morgan Stanley and Credit Suisse Group plan for raising capital is classified as A. investment banking houses B. exchange houses C. transfer houses D. foreign exchange houses Type of financial securities that matures in less than a year are classified as A. money market securities B. capital market securities C. saving intermediaries D. discounted intermediaries Conglomerates that combine many financial institutions within a single corporation are classified as A. preferred service corporations B. commercial service corporations C. financial services corporations D. common service corporations Corporations that buy financial instruments with money accepted from savers are classified as A. debit funds B. credit funds C. mutual funds D. insurance funds Corporate associations who have common bonds being employees of same firm are classified as A. credit unions B. debit unions C. preferred unions D. solving unions Set of rules made by corporation founders such as directors election procedure are classified as A. stock laws B. by laws C. liability laws D. corporate laws Risk of doing business in particular country and arises from foreign investments is classified as A. country risk B. foreign risk C. proffered risk D. common risk Markets which bring closer institutions needing funds and with surplus funds are classified as A. financial markets B. corporate institutions C. hedge firms D. retirement planners Process of selling company stock at large to general public and get lending from banks is classified as an A. initial public offering B. external public offering C. internal public offering D. unprofessional offering Partners who are only liable for their own part of investment are considered as A. venture partners B. corporate partners C. limited partners D. general partners Sales revenue $90,000, operating taxes $30,000 and operating capital $15,000 then value of free cash flows (in USD) will be A. 45000 B. 13500 C. 65000 D. 75000 Legal entity separation from its legal owners and managers with help of state laws is classified as A. controlled corporate business B. corporation C. limited corporate business D. unlimited corporate business Cost of money is affected by factors which includes A. production opportunities B. risk C. all of above D. inflation Markets in which corporations raise capital for creating market transaction which are classified as A. commercial markets B. residential markets C. primary markets D. consumer credit loans Notes, mortgages, bonds, stocks, treasury bills and consumer loans are classified as A. financial instruments B. capital assets C. primary assets D. competitive instruments Set of rules consisting of behavior towards its directors, creditors, shareholders, competitors and community is considered as A. agency governance B. hiring governance C. corporate governance D. external governance New York Stock Exchange and Nada stock market are classified as types of A. primary stock market B. equity market C. secondary stock market D. public offering market Price for debt is called A. debt rate B. investment return C. discount rate D. interest rate In corporation characteristics, an easy transferring and division of stock of shares is classified as A. ownership interest transferability B. deceased transferability C. shared division D. deceased division In financial markets, period of maturity less than one year of financial instruments is classified as A. short-term B. long-term C. intermediate term D. capital term Condition in which company's imports are more than its exports is classified as A. foreign trade B. foreign trade deficits C. foreign trade surplus D. trade surplus A markets which deals with long-term corporate stocks are classified as A. liquid markets B. short-term markets C. capital markets D. money markets Subset of primary market where firms go publicly by issuing stocks in financial markets is considered as A. initial public offering market B. stock market C. issuance market D. first stock market Corporate governance charter of rules of behaving is applicable on A. competitors B. shareholders C. directors D. all of above limited partners in partnership business have A. no control B. whole control C. corporate authority D. general authority A type of business ownership in which two or more entities join together for profit purpose is classified as A. partnership B. joint business C. joint profit D. corporate business Bonds issued to individuals by corporations are classified as A. municipal bonds B. corporate bonds C. U.S treasury bonds D. mortgages Financial security in which there is no default risk and issues by U.S governments is classified as A. U.S treasury bonds B. mortgages C. municipal bonds D. corporate bonds Financial security issues by major banks and risk depends on strength of issuer is classified as A. negotiable certificate of deposit B. mutual funds C. U.S treasury bills D. commercial paper An unlimited liability is classified as liabilities of the A. limited partners B. general partners C. venture partners D. corporate partners Financial security kept by non-financial corporations is A. deposit cheque B. distribution cost C. short term treasury bills D. short term capital cost A retirement plans funded for workers by corporations, administered and commercial banks are classified as A. retirement funds B. pension funds C. future funds D. workers funds Markets dealing loans of autos, education, vacations and appliances are considered as A. consumer credit loans B. commercial markets C. residential markets D. mortgage markets Type of partnership in which liabilities are limited for business owners is classified as A. unlimited partnership B. limited partnership C. joint corporate D. joint venture Financial security issued by banks operating outside U.S is classified as A. dollar bonds B. euro deposits C. Eurodollar market deposits D. euro bonds Value of free cash flows $55000, operating cost and taxes $30000, then value of sales revenues (in $) will be A. 25000 B. 85000 C. 35000 D. 45000 Markets which deal with buying and selling of bonds, mortgages, notes and stocks are considered as A. financial instruments B. financial asset markets C. physical asset markets D. easy markets Capital gain expected by stockholders and dividends are included in A. debt rate B. investment return C. interest rate D. cost of equity Markets where assets are bought or sold within a few days or at some future dates are classified as A. spot markets B. future markets C. Both A and B D. financial instruments Default free financial security sells by U.S treasury is classified as A. U.S treasury bills B. commercial paper C. certificate of deposit D. mutual funds Relevant information about stock market price if it is given, then this price is called A. market price B. intrinsic price C. extrinsic price D. unstable price Reduced consumer demand for loans, homes and new automobiles is result of A. less disposable income B. high disposable income C. federal disposable income D. discount disposable income Formula Sales revenue minus operating cost and taxes minus operating capital investments is used to calculate A. available income B. cash income C. free cash flows D. free distribution An attitude of investor towards dealing with risk determines the A. rate of return B. rate of exchange C. rate of intrinsic stock D. rate of extrinsic stock Firm's which helps in indirect transfer such as Merrill Lynch is classified as A. investment banking house B. investment bank C. saving house D. saving bank In corporation characteristics, losses are subject to funds invested actually is considered as A. limited liability B. unlimited liability C. general liability D. controlled ownership liability Government spending, if it exceeds federal government tax revenues then it is classified as A. federal reserve B. federal budget C. budget surplus D. budget deficit Financial security with low degree risk and investment held by businesses is classified as A. treasury bills B. commercial paper C. negotiable certificate of deposit D. money market mutual funds Type of financial security in which firms do not borrow money rather lease their assets is classified as A. leases B. preferred stocks C. common stocks D. corporate stocks 'New York Stock Exchange' is an example of A. capital markets B. money markets C. liquid markets D. short-term markets Hewlett-Packard and Microsoft are examples of A. limited corporate business B. unlimited corporate business C. controlled corporate business D. corporation Banks such as Bank of America serves a range of savers and borrowers are classified as A. transfer banks B. commercial banks C. serving banks D. nations banks An inexpensive and easy business formation and few government regulations are advantages of A. private corporation B. personal ownership C. proprietorship D. personal business Document in a corporation which consists of amount of stock, name and addresses of directors is classified as A. liability plan B. stock planning C. corporation paperwork D. charter A price for equity is called A. interest rate B. cost of equity C. debt rate D. investment return Risk in which value of investment depends on what happens to foreign exchange rates is classified as A. preferred risk B. exchange rate risk C. country risk D. foreign risk Members and employees of credit unions are loaned for A. mortgages B. home improvement loans C. auto purchases D. all of above Ability to trade at net price very quickly is classified as A. original trading B. liquidity C. offline trading D. fixed price trading Bonds which are more riskier than corporate bonds and are issued by major corporations are classified as A. common stocks B. corporate stocks C. leases D. preferred stocks In financial markets, period of maturity within one to five years of financial instruments is classified as A. short-term B. long-term C. intermediate term D. capital term Collection of money from investors and spending money in other investment activities is classified as A. future funds B. hedge funds C. retirement funds D. pension funds Markets for products such as whet, rice, cotton, real estate and autos dealing is classified as A. physical asset markets B. intangible assets C. competitive markets D. easy markets Price of stock that companies observe in financial markets is called A. market price B. intrinsic price C. extrinsic price D. fundamental price Professionals such as doctors, accountants and lawyers often make corporations are classified as A. general professionals B. professional corporation C. professional association D. Both B and C Markets which deals with high liquid and short term debt securities are classified as A. capital markets B. money markets C. liquid markets D. short-term markets Low default-risk security issued by financially secure firms is classified as A. U.S treasury bills B. commercial paper C. certificate of deposit D. mutual funds Firm's promise to pay and is backed or guaranteed by bank is classified as A. customer's acceptance B. banker's acceptance C. federal acceptance D. treasury acceptance Financial markets include A. primary markets B. capital markets C. physical asset markets D. all of above Funds which are used as an interest-bearing checking accounts are classified as A. money market funds B. capital market funds C. money mutual funds D. insurance money funds Physical location exchange or telephone networks are types of A. long-term markets B. secondary markets C. money markets D. capital markets Method of matching orders by posting orders of buying and selling is classified as A. electronic communication network B. electronic dealer network C. electronic stock network D. electronic order network An earning of business which is available for free distribution to all stockholders and creditors is classified as A. free cash flows B. free distribution C. available income D. cash income Business owned by a single person in unincorporated way is called A. proprietorship B. personal business C. private corporation D. personal ownership Loans by finance companies, banks and credit unions is classified as A. consumer credit loans B. dollar bonds C. Eurodollar market deposits D. euro bonds Bonds issue by corporations which are more riskier than preferred stocks are classified as A. leases B. preferred stocks C. common stocks D. corporate stocks Federal Reserve policy and federal surplus or deficit of budget affect the A. cost of production B. cost of money C. opportunity cost D. inflation risk Market where market makers keep record of stock of financial instruments is classified as A. stock market B. dealer market C. outcry auction system D. face to face communication An unlimited liability for business debts and less capital for growth are limitations of A. proprietorship B. personal business C. private corporation D. personal ownership Transfer through institutions such as mutual funds or banks are classified as A. non-financial intermediary B. financial intermediary C. savers intermediary D. discounted intermediary Money lends to corporations by banks is classified as A. Eurodollar market deposits B. commercial loans C. consumer credit loans D. consumer credit loans Markets in which outstanding securities are traded by investors are classified as A. primary markets B. secondary markets C. initial public offering market D. stock market MCQ on Portfolio Theory and Asset Pricing Models Beta reflects stock risk for investors which is usually A. individual B. collective C. weighted D. linear For any or lower degree of risk, highest or any expected return are concepts use in A. riskier portfolios B. behavior portfolios C. inefficient portfolios D. efficient portfolios An unsystematic risk which can be eliminated but market risk is the A. aggregate risk B. remaining risk C. effective risk D. ineffective risk An indication in a way that variance of y-variable is explained by x-variable which is shown as A. degree of dispersion is one B. degree of dispersion is two C. degree of dispersion is three D. degree of dispersion is four In regression of capital asset pricing model, an intercept of excess returns is classified as A. Sharpe's reward to variability ratio B. tenor's reward to volatility ratio C. Jensen's alpha D. tenor's variance to volatility ratio In arbitrage pricing theory, required returns are functioned of two factors which have A. dividend policy B. market risk C. historical policy D. Both A and B If book value is greater than market value comparison with investors for future stock are considered as A. pessimistic B. optimistic C. experienced D. inexperienced An average return of portfolio divided by its coefficient of beta is classified as A. Sharpe's reward to variability ratio B. treynor's reward to volatility ratio C. Jensen's alpha D. treynor's variance to volatility ratio Slope coefficient of beta is classified statistically significant if its probability is A. greater than 5% B. equal to 5% C. less than 5% D. less than 2% Second factor in Fama French three factor model is the A. size of industry B. size of market C. size of company D. size of portfolio Difference between actual return on stock and predicted return is considered as A. probability error B. actual error C. prediction error D. random error Complex statistical and mathematical theory is an approach, which is classified as A. arbitrage pricing theory B. arbitrage risk theory C. arbitrage dividend theory D. arbitrage market theory First step in determining an efficient portfolio is to consider A. set of attainable portfolios B. set of unattainable portfolios C. set of attributable portfolios D. set of attributable portfolios Tendency of people to blame failure on bad luck but given tribute of success to themselves is classified as A. self attribution bias B. self success bias C. self failure bias D. self condition bias Stock portfolio with highest book to market ratios is considered as A. H portfolio B. L portfolio C. S portfolio D. B to M portfolio High portfolio return is 6.5% and low portfolio return is 3.0% then HML portfolio will be A. 2.16% B. 9.50% C. 3.50% D. 0.4615 times Stocks which has lower book for market ratio are considered as A. optimistic B. more risky C. less risky D. pessimistic An individual stock required return is equal to risk free rate plus bearing risk premium is an explanation of A. security market line B. capital market line C. aggregate market line D. beta market line Future beta is needed to calculate in most situations is classified as A. historical betas B. adjusted betas C. standard betas D. varied betas An efficient set of portfolios represented through graph is classified as an A. attained frontier B. efficient frontier C. inefficient frontier D. unattained frontier Rational traders immediately buy stock when price is A. too low B. too high C. conditional D. inefficient portfolio All points lie on line if degree of dispersion is A. four B. one C. two D. five A high portfolio return is subtracted from low portfolio return to calculate A. HML portfolio B. R portfolio C. subtracted portfolio D. ML portfolio Second step in determining efficient portfolios is to consider efficient subset from set of A. attainable portfolios B. unattainable portfolios C. attributable portfolios D. non-attributable portfolio If market value is greater than book value then investors for future stock are considered as A. experienced B. inexperienced C. pessimistic D. optimistic According to capital asset pricing model assumptions, investors will borrow unlimited amount of capital at any given A. identical and fixed returns B. risk free rate of interest C. fixed rate of interest D. risk free expected return In calculation of betas, an adjusted betas are highly dependent on historical A. unadjusted betas B. adjusted historical betas C. fundamental historical betas D. fundamental varied betas A curve which shows attitude towards risk just way reflected in return trade-off function is classified as A. difference curve B. indifference curve C. efficiency curve D. affectivity curve In capital market line, risk of efficient portfolio is measured by its A. standard deviation B. variance C. aggregate risk D. ineffective risk Formula written as 0.67(Historical Beta) + 0.35(1.0) is used to calculate A. historical betas B. adjusted betas C. standard betas D. varied betas A model which regresses return of stock against return of market is classified as A. regression model B. market model C. error model D. risk free model According to capital asset pricing model assumptions, quantities of all assets are A. given and fixed B. not given and fixed C. not given and variable D. given and variable According to Fama French Three-Factor model, market value of company equity is used to calculate A. size of portfolio B. size of industry C. size of market D. size of company Negative minimum risk portfolio of any security shows that market security sold A. less than original price B. greater than original price C. equal to original price D. equal to sum of stocks In capital asset pricing model, covariance between stock and market is divided by variance of market returns is used to calculate A. sales turnover of company B. risk rate of company C. beta coefficient of company D. weighted mean of company Stocks which has high book for market ratio are considered as A. more risky B. less risky C. pessimistic D. optimistic Stock portfolio with lowest book for market ratios is considered as A. S portfolio B. B to M portfolio C. H portfolio D. L portfolio A measure which is not included in Fama French Three-Factor model is A. realized risk free rate B. rate of return on market C. random error D. risk premium An average return of portfolio divided by its standard deviation is classified as A. Jensen's alpha B. Treynor's variance to volatility ratio C. Sharpe's reward to variability ratio D. Treynor's reward to volatility ratio According to capital asset pricing model assumptions, variances, expected returns and covariance of all assets are A. identical B. not identical C. fixed D. variable Sum of market risk and diversifiable risk are classified as total risk which is equivalent to A. Sharpe's alpha B. standard alpha's C. alpha's variance D. variance Betas tend to move towards 1.0 with passage of time are classified as A. standard betas B. varied betas C. historical betas D. adjusted betas Stock issued by company have higher rate of return because of A. low market to book ratio B. high book to market ratio C. high market to book ratio D. low book to market ratio Betas that are constantly adjusted to reflect changes in capital structure and firms operations are classified as A. fundamental structure B. fundamental adjustment C. fundamental betas D. fundamental operations Type of relationship exists between an expected return and risk of portfolio is classified as A. non-linear B. linear C. fixed and aggregate D. non-fixed and non-aggregate Capital market line reflects an attitude of investors towards risk which is considered as an/a A. non-aggregate B. effective C. ineffective D. aggregate A theory which states that assets are traded at price equal to its intrinsic value is classified as A. efficient money hypothesis B. efficient market hypothesis C. inefficient market hypothesis D. inefficient money hypothesis In capital asset pricing model, characteristic line is classified as A. regression line B. probability line C. scattered points D. weighted line All assets are perfectly divisible and liquid in A. tax free pricing model B. cost free pricing model C. capital asset pricing model D. stock pricing model Relationship between risk free asset and a single risky asset are always A. linear B. non-linear C. efficient D. effective Gross domestic product, world economy strength and level of inflation are factors which is used to determine A. market realized return B. portfolio realized return C. portfolio arbitrage risk D. arbitrage theory of return Rational traders immediately sell stock when price is A. conditional B. inefficient portfolio C. too low D. too high Stock issued by company have lower rate of return because of A. high market to book ratio B. low book to market ratio C. low market to book ratio D. high book to market ratio Riskless rate in addition with risk premium is multiplied by standard deviation of portfolio for using to calculate expected return rate on A. efficient portfolio B. inefficient portfolio C. attributable portfolio D. non-attributable portfolio Realized and required return for individual stocks are classified as function of fundamental A. arbitrage factors B. economic factors C. portfolio factors D. realized theory factors First factor in Fama French three factor model is A. CAPM stock beta B. economic stock beta C. CAPM portfolio beta D. CAPM realized beta A line which shows relationship between an expected return and risk on efficient portfolio is considered as A. efficient market line B. attributable market line C. capital market line D. security market line Relationship between total risk of stock, diversifiable risk and market risk is classified as A. total risk B. standard deviation C. standard alpha D. treynor alpha In arbitrage pricing theory, higher required rate of return is usually paid on stock A. higher market risk B. higher dividend C. lower dividend D. lower market risk Formula written as market risk premium divided by standard deviations of returns on market portfolio is used to calculate A. capital market line B. security market line C. fixed market line D. variable market line In capital asset pricing model, investors assume that buying and selling activity will A. affect stock prices B. not affect stock prices C. have high taxes D. high transaction cost For investors, more steeper slope of indifference curve shows more A. risk averse investor B. risk taker investor C. in differential investor D. ineffective investment Positive minimum risk portfolio of any security shows that market security sold A. equal to original price B. equal to sum of stocks C. less than original price D. greater than original price Third factor in Fama French three factor model is ratio which is classified as A. book to market ratio B. market to book ratio C. company to industry ratio D. stock to portfolio ratio In capital asset pricing model, assumptions must be followed including A. no taxes B. no transaction costs C. fixed quantities of assets D. all of above MCQ on Risk, Return, and Capital Asset Pricing Model Two alternative expected returns are compared with help of A. coefficient of variation B. coefficient of deviation C. coefficient of standard D. coefficient of return Dollar return is divided by invested amount which is used for calculating the A. rate of return B. return amount C. investment rate D. received amount An analysis of decision making of investors and managers is classified as A. riskier finance B. behavioral finance C. premium finance D. buying finance Yield on bond is 7% and market required return is 14% then market risk premium would be A. 2% B. 21% C. 0.50% D. 7% An expected rate of return is denoted by A. e-bar B. r-bar C. r-hat D. e-hat In expected future returns, tighter probability distribution shows risk on given investment which is A. smaller B. greater C. less riskier D. highly riskier An inflation free rate of return and inflation premium are two components of A. quoted rate B. unquoted rate C. steeper rate D. portfolio rate Risk affects any firm with factors such as war, recessions, inflation and high interest rates is classified as A. diversifiable risk B. market risk C. stock risk D. portfolio risk Risk on a stock portfolio which cannot be eliminated or reduced by placing it in diversified portfolio is classified as A. diversifiable risk B. market risk C. stock risk D. portfolio risk In investment returns, a received amount is subtracted from an invested amount which is used to calculate A. dollar received B. dollar return C. dollar invested D. return percentage Past realized rate of return in period t is denoted by A. t bar r B. t hat r C. r hat t D. r bar t An amount invested is $1500 and an amount received is $2000 then dollar return would be A. $500 B. −$500 C. $3,500 D. −$3500 External factors such as expiration of basic patents and industry competition effect A. patents premium B. competition premium C. company's beta D. expiry premium Type of risk in which beta is equal to one is classified as A. multiple risk stock B. varied risk stock C. total risk stock D. average risk stock A portfolio consists of all stocks in a market is classified as A. market portfolio B. return portfolio C. correlated portfolio D. diversified portfolio Beta coefficient is used to measure market risk which is an index of A. coefficient risk volatility B. market risk volatility C. stock market volatility D. portfolio market portfolio Standard deviation of tighter probability distribution is A. long-termed B. short-termed C. riskier D. smaller An opposite of perfect positive correlation + 1.0 is called A. negative correlation B. multiple correlation C. divisor correlation D. none of above A technique of lowering risk for multinational companies and globally designed portfolios is classified as A. national diversification B. behavioral diversification C. global diversification D. behavioral finance Risk which is caused by events such as strikes, unsuccessful marketing programs and other lawsuits is classified as A. stock risk B. portfolio risk C. diversifiable risk D. market risk Required return is 11% and premium for risk is 8% then risk free return will be A. 3% B. 19% C. 0.72% D. 1.38% Range of probability distribution with 99.74% lies within A. ( + 3σ and -3σ) B. ( + 4σ and -4σ) C. ( + 1σ and -1σ) D. ( + 2σ and -2σ) Risk per unit of return or stand alone risk is represented by A. coefficient of standard B. coefficient of return C. coefficient of variation D. coefficient of deviation Risk on a stock portfolio which can be reduced by placing it in diversified portfolio is classified as A. stock risk B. portfolio risk C. diversifiable risk D. market risk An amount invested is $4000 and dollar return is $300 then rate of return will be A. $4,300 B. $3,700 C. 7.50% D. 0.08% In capital asset pricing model, stock with high standard deviation tend to have A. low variation B. low beta C. high beta D. high variation In asset portfolio, number of stocks are increased to A. reduce return B. reduce average C. reduce risk D. increase prices Standard deviation is 18% and expected return is 15.5% then coefficient of variation would be A. 0.86% B. 1.16% C. 2.50% D. −2.5% Standard deviation is divided by expected rate of return is used to calculate A. coefficient of variation B. coefficient of deviation C. coefficient of standard D. coefficient of return If stock has a great risk related to it then a required return is A. higher B. lower C. zero D. all of above An amount invested is $2000 and dollar return is $200 then rate of return would be A. 0.10% B. 10% C. $1,800 D. $2,200 A risk which is classified as its contribution to risk of portfolio is classified as A. classified risk B. contributed risk C. irrelevant risk D. relevant risk Chance of happening any unfavorable event in near future is classified as A. chance B. event happening C. probability D. risk A tighter probability distribution shows the A. higher risk B. lower risk C. expected risk D. peaked risk Stock which has higher correlation with market tend to have A. high beta, less risky B. low beta, more risky C. high beta, more risky D. low beta, less risky According to probability distribution of rates of return, a close outcome to an expected value is shown by A. value distribution B. expected distribution C. more peaked distribution D. less peaked distribution A range of probability distribution with 95.46% lies within A. ( + 1σ and -1σ) B. ( + 2σ and -2σ) C. ( + 3σ and -3σ) D. ( + 4σ and -4σ) Coefficient of variation is used to identify an effect of A. risk B. return C. deviation D. Both A and B In portfolio, beta of individual security in portfolio represented as their weighted average is classified as A. average of portfolio B. beta of portfolio C. weighted portfolio D. collective stocks Coefficient of beta is used to measure stock volatility A. coefficient of market B. relative to market C. irrelative to market D. same with market Probability distribution is classified as normal if expected return lies between A. ( + 1 and -1) B. ( + 2 and -2) C. ( + 3 and -3) D. ( + 4 and -4) Greater chance of lower actual return than expected return and greater variation is indicated by A. smaller standard deviation B. larger standard deviation C. smaller variance D. larger variance Tendency of measuring correlation of two variables is classified as A. tendency coefficient B. variable coefficient C. correlation coefficient D. double coefficient Size of firm and market or book ratio are variables which are related to A. premium returns B. unquoted returns C. quoted returns D. stock returns A model in which behavior of asset returns is measured for set of risk factors and market risk is classified as A. factorization model B. two factor model C. multifactor model D. quoted factor model Relationship between risk and required return is classified as A. security market line B. required return line C. market risk line D. riskier return line Tendency of moving together of two variables is classified as A. correlation B. move tendency C. variables tendency D. double tendency Of all stocks in a portfolio, required rate of return is classified as A. return portfolio B. in volatile portfolio C. volatile portfolio D. market portfolio Risk in average individual stock can be reduced by placing an individual stock in A. low risk portfolio B. diversified portfolio C. undiversified portfolio D. high risk portfolio Required return is 15% and premium for risk is 11% then risk free return would be A. 26% B. 4% C. $165 D. 1.36% Market required return is subtracted from risk free rate which is used to calculate A. quoted risk premium B. market risk premium C. portfolio risk premium D. unquoted risk premium An estimation by marginal investor, a higher expected return is earned on A. more riskier securities B. less riskier securities C. less premium D. high premium Term structure premium, an inflation of bond and bond default premium are included in A. risk factors B. premium factors C. bond buying factors D. multi model Mostly in financials, risk of portfolio is smaller than that of asset's A. mean B. weighted average C. mean correlation D. negative correlation If risk can be eliminated with help of diversification, then relevant risk is A. smaller than stand-alone risk B. larger than stand-alone risk C. smaller than diverse risk D. larger than diverse risk Treasury yielded by bond is 7% and market required return is 13% then market risk premium will be A. 2.16% B. 20% C. 6% D. 0.53% Chance of occurrence of any event is classified as A. probability B. risk C. chance D. event happening According to market risk premium, an amount of risk premium depends upon investor A. risk taking B. risk aversion C. market aversion D. portfolio aversion When changes in patents and industry competition occur, required rate of return A. changes B. does not change C. becomes zero D. becomes one In an individual stock, relevant risk is classified as A. alpha coefficient B. beta coefficient C. stand-alone coefficient D. relevant coefficient Type of premium asked by investors for bearing risk on average stock is classified as A. average premium B. market risk premium C. stock premium D. buying discount Portfolio which consists of perfectly positive correlated assets having no effect of A. negativity B. positivity C. correlation D. diversification Weighted average of probabilities is classified as A. average rate of return B. expected rate of return C. past rate of return D. weighted rate of return Market risk and diversifiable risk are two components of A. stock's risk B. portfolio risk C. expected return D. stock return Market risk premium is 8% and risk free return is 7% then market required return would be A. 15% B. 1% C. $56 D. 1.14% Range of probability distribution with 68.26% lies within A. ( + 3σ and -3σ) B. ( + 4σ and -4σ) C. ( + 1σ and -1σ) D. ( + 2σ and -2σ) In capital asset pricing model, an amount of risk that stock contributes to portfolio of market is classified as A. stand-alone coefficient B. relevant coefficient C. alpha coefficient D. beta coefficient Case in which average investors risk aversion is greater then slope of line and risk premium respectively is A. steeper, greater B. steeper, smaller C. steeper, zero D. Both A and B Expected returns weighted average on assets in portfolio is considered as A. weighted portfolio B. expected return on portfolio C. coefficient of portfolio D. expected assets Correct measure of risk of stock is called A. alpha B. beta C. variance D. market relevance Standard deviation is 18% and coefficient of variation is 1.5% an expected rate of return will be A. 27% B. 12% C. 19.50% D. none of above An amount invested is $2500 and an amount received is $1500 then dollar return will be A. −$4000 B. $4,000 C. −$1000 D. $1,000 An additional desired compensation by investors for assuming an additional risk on investment is classified as A. risk premium B. investor premium C. additional premium D. assumed premium Method and model used to analyze relationship between rates of return and risk is classified as A. capital asset pricing model B. portfolio asset pricing model C. asset market pricing model D. portfolio pricing model Stocks in market portfolio are graphically represented with A. dashed line B. straight line C. market line D. risk line Stock with large amount of contribution of risk in a diversified portfolio is represented by A. high beta and standard deviation B. high beta, low standard deviation C. low beta, low standard deviation D. low beta, low variance MCQ on Stocks Valuation and Stock Market Equilibrium Shares or stocks which are protected against withdrawals of funds by an original stock owners are classified as A. protected shares B. founders shares C. withdrawal shares D. original shares Method of stock valuation which is multiple of earning per share, book value and net income is classified as A. stock multiple analysis B. dividend multiple analysis C. market multiple analysis D. stock and multiple analysis Preferred dividend is $50 and required rate of return is 2.5% then value of preferred stock would be A. 20% B. $125 C. $2,000 D. $52.50 In expected rate of return for constant growth, stock price must grow according to an expected rate and A. at same price B. at different price C. at yielded price D. at buying price Dividend present value for period of non-constant growth in addition with horizon value is used to calculate A. stock extrinsic value B. stock intrinsic value C. dividend intrinsic value D. stock intrinsic value Current price is $40 and dividend paid is $10 then dividend yield will be A. $25 B. 25% C. $4 D. 4% Capital gains yield is multiplied for beginning price to calculate A. capital gain B. growth gain C. regular yield D. variable yield Constant growth rate is 9.5% and an expected rate of return is 13.5% then expected dividend yield would be A. 23% B. 1.42% C. 4% D. $1.42 Paid dividend is $20 and current price is $50 then dividend yield will be A. 40% B. $40 C. $70 D. $30 Stock in small companies, owned by few people but not actively traded is classified as A. closely held stock B. largely held stock C. attributed stock D. successful stock Type of stock which have characteristics of bonds and common stock is classified as A. bonds equity B. common shares C. common stock D. preferred stock Process in which stockholders transfer right to vote to any other person is classified as A. proxy B. transfer process C. voting process D. assigning right process Right of common stockholders to purchase additional stock issued by company is classified as A. common right B. preemptive right C. purchase right D. selling right Type of stock in which dividends are tied to any particular part of a firm is classified as A. dividend stock B. firm part stock C. tied stock D. tracking stock Rate of return which considers riskiness and an available returns on investments is classified as A. constant dividend B. constant rate C. maximum rate of return D. minimum acceptable rate of return Stock market theory which states that stocks are in equilibrium and impossible for investors to beat market is classified as an A. inefficient market hypothesis B. efficient market hypothesis C. efficient stock hypothesis D. inefficient stock hypothesis Growth in earnings per share is primarily resultant of growth in A. dividends B. asset value C. fundamental value D. yearly value * In expected rate of return for constant growth, capital gains is divided by capital gains yield to calculate A. returning price B. ending price C. beginning price D. regular price Stock which has fixed payments and failure of payments which do not lead to bankruptcy is classified as A. common stock B. preferred stock C. bonds equity D. common shares An efficient market hypothesis states all public information which is reflected in current market prices is classified as A. weak form efficiency B. strong form efficiency C. market efficiency D. semi strong efficiency In expected rate of return for constant growth, an expected dividend yield must be A. functional decreasing B. constant C. continuously growing D. functional increasing Value of stock as concluded with help of analysis by particular investor is classified as A. particular value B. intrinsic value C. fundamental value D. Both B and C In expected rate of return for constant growth, an expected yield on capital must be A. equal to zero B. greater than expected growth rate C. less than expected growth rate D. equal to expected growth rate Capital gain is $2 and beginning price is $24 then capital gains yield will be A. $22 B. 0.1 times C. $0.12 D. 12% A formula such as an original investment plus an expected capital gain is used to calculate A. final stock B. expected stock C. expected final stock price D. final stock price Dividend expected on stock during coming year is classified as A. current dividend yield B. expected dividend yield C. yearly dividend D. past yield In expected rate of return for constant growth, capital gains is divided by beginning price to calculate A. yield of loan return B. yield of mortgage return C. yield of capital gains D. yield of fixed cost Preferred dividend is divided for required rate of return to calculate A. value of number of shares B. value of equity C. value of preferred stock D. value of common stock Value of stock is $400 and required rate of return is 20% then preferred dividend would be A. $80 B. $8,000 C. $20 D. $50 An amount of company retain earning, return on equity and inflation are factors which effect A. earning growth B. return on assets C. return on sales D. return on value Value of stock is $300 and preferred dividend is $60 then required rate of return would be A. $18,000 B. 0.2 C. $20 D. $5 Tracking stock of company is also classified as A. target stock B. dividend stock C. firm part stock D. tied stock An expected dividend yield is 5.5% and expected rate of return is 11.5% then constant growth rate would be A. 2.09% B. −$6% C. 17.50% D. 6% A right which controls and prevents transfer from current stockholders to other new stockholders is considered as A. corporate charter B. selling charter C. laws D. purchase chart In market analysis, market multiple is multiplied by firm earning before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization to calculate A. market total value B. firm total value C. industry value D. taxes value Dividend will grow at non-constant rate for N periods and periods such as N is classified as A. growth date B. terminal date C. horizon date D. Both B and C Beginning price is $25 and capital gains yield is 5% then capital gain would be A. $50 B. $1.25 C. 50 times D. $23.75 If an expected final stock price is $85 and an original investment is $70 then value of expected capital gain would be A. $15 B. −$15 C. $155 D. −$155 Third step in calculating value of stock with non-constant growth rate is to find A. p.v of expected dividends B. f.v of expected dividends C. p.v of intrinsic rate D. f.v of intrinsic rate In expected rate of return for constant growth, expected total rate of return is equal to A. buying pricing B. dividend yield C. rate of return D. selling pricing An efficient market hypothesis states in which all public or private information is reflected in current market prices is classified as A. market efficiency B. semi strong efficiency C. weak form efficiency D. strong form efficiency An expected dividend yield is added into expected growth rate to calculate A. dividend return B. expected rate of return C. expected capital D. invested capita Dividend yield is 25% and current price is $40 then dividend yield will be A. 65% B. $10 C. $65 D. $15 Paid dividend with dividend yield 25% is $5 then cost price would be A. 30% B. $30 C. 20% D. $20 An expected final stock price is $45 and an original investment is $25 then an expected capital gain will be A. $75 B. −$75 C. −$20 D. $20 Value of stock is $1200 and preferred dividend is $120 then required rate of return would be A. $144,000 B. 0.1 C. $10 D. 0.2 times Expected dividends in each year and price investor expecting to get at selling of stock are two components of A. dividend cashflow B. expected cash flows C. price cash flows D. investing cash In expected rate of return for constant growth, an expected total rate of return must be A. less than expected yield on dividend B. greater than expected yield on dividend C. equal to expected yield on dividend D. equal to one Owners of corporation having certain rights and privileges are considered as A. special stockholders B. common stockholders C. public stocks D. enactive stocks Stockholders having right to elect directors and in smaller firms have high post are classified as A. public stocks B. inactive stocks C. special stockholders D. common stockholders Constant growth rate is 7.2% and an expected rate of return is 12.5% then expected dividend yield will be A. 5.30% B. 19.70% C. −5.3% D. 1.736 An original investment is $30 and an expected capital gain is $10 then an expected final stock price will be A. $20 B. $40 C. −$40 D. −$20 Constant growth rate is 6.5% and an expected dividend yield is 3.4% then an expected rate of return would be A. 9.90% B. = 6.5*3.4 C. 3.10% D. 1.912 According to investors point of view, an expected rate of return is rate on stocks which they A. receive in future B. received in past C. yearly growth D. semi-annual growth Second step in calculating value of stock with non-constant growth rate is to find out an A. expected intrinsic stock B. extrinsic stock C. expected price of stock D. intrinsic stock Paid dividend is $20 and dividend yield is 40% then current price would be A. 60% B. $60 C. $50 D. 2% Preferred stock dividends must be paid on common stock and must have A. fixed amount of dividends B. fixed amount of shares C. variable amount of dividends D. variable amount of shares Constant growth model would not be used in condition if growth rate is A. greater than dividend paid B. equal to realized rate of return C. less than realized rate of return D. greater than realized rate of return Cash flow which is available for all investors of company is classified as A. extrinsic stock B. intrinsic stock C. investing cash D. free cash flow Present value of dividends which is expected to be provided in future is classified as an A. intrinsic value of stock B. extrinsic value of stock C. intrinsic bonds D. extrinsic bonds Stock in large companies and own by people who are not active in management is classified as A. self held stock B. privately held stock C. publicly held stock D. enactive held stock Information which is reflected in current market prices with help of past price movements is classified as A. market efficiency B. semi strong efficiency C. weak form efficiency D. strong form efficiency Capital gain is $3 and capital gains yield is 6% then beginning price will be A. $18 B. 0.18 times C. $50 D. 50% Growth rate which is predicted by marginal investors for dividends is classified as A. expected growth rate B. annual growth rate C. past growth rate D. unexpected growth rate An expected final stock price is $70 and an expected capital gain is $25 then an original investment would be A. $45 B. −$45 C. $95 D. −$95 Value of future dividends after horizon date is classified as A. hypothesis value B. horizon value C. terminal value D. Both B and C Preemptive right of common stockholders are necessarily included in company A. laws B. purchase chart C. corporate charter D. selling charter Constant growth rate is 8% and an expected dividend yield is 5.4% then expected rate of return would be A. −3.4% B. 3.40% C. 13.40% D. −13.4% Real rate of return, risk and expected inflation are primary determinants of A. minimum rate of return B. accepted return C. expected return D. real risk free rate Preferred stocks are also classified as A. intrinsic preference B. perpetuities C. extrinsic preference D. weak preference After-the-fact rate of return often consider as realized or actual can be denoted A. s hat r B. r bar s C. r hat s D. s bar r In expected rate of return for constant growth, dividends are expected to grow but with the A. constant rate B. variable rate C. yielding rate D. returning yield Expected capital gain is $20 and expected final price is $50 then original investment will be A. $30 B. −$30 C. $70 D. −$70 Preferred dividend is $60 and required rate of return is 20% then value of preferred stock will be A. $40 B. $120 C. $12 D. $300 An earning before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization average multiple for publicly traded companies is classified as A. entity multiple B. depreciation multiple C. earning multiple D. amortization multiple An expected rate of return is subtracted from capital gains yield to calculate A. expected dividend yield B. capital earning C. casual growth D. specialized growth rate An expected dividend yield is subtracted from an expected rate of return which is used to calculate A. specialized growth rate B. capital gains yield C. casual growth yield D. past growth rate First step in calculating value of stock with non-constant growth rate is to A. estimate expected dividend B. actual expected dividend C. estimate number of share D. estimate intrinsic shares Calculation of formula in common stock valuation does not include A. intrinsic value B. dividend of stockholder C. number of stock issued D. expected growth rate An expected dividend yield is 7.5% and an expected rate of return is 15.5% then constant growth rate will be A. 22% B. 8% C. 23% D. 2.06% Average rate of return which is required by all investors of company is classified as A. extrinsic cost of capital B. weighted average cost of capital C. mean cost of capital D. standard cost of cash An actual rate of return is subtracted from expected growth rate then it is divided from dividend stockholders expects use for calculating A. dividend growth model B. actual growth model C. constant growth model D. variable growth model Value of stock is $900 and required rate of return is 30% then preferred dividend will be A. $270 B. $27,000 C. $90 D. $90 A situation in which an outside group solicit proxies to take control of business is classified as A. outside group B. solicit process C. proxy fight D. controlled management A stock which is issued to meet specific needs of company is considered as A. classified stock B. specific stock C. needed stock D. meeting stock MCQ on Time Value of Money An annual estimated costs of assets uses up every year are included A. depreciation and amortization B. net sales C. net profit D. net income Proceeds of company shares of sold stock is recorded in A. preferred stock account B. common stock account C. due stock account D. preceded stock account Statement of cash flows are included A. operating activities B. investing activities C. financing activities D. all of above A company purchases goods but does not pay payments to suppliers immediately and record them as A. account payable B. account receivable C. current liabilities D. accumulated liabilities In calculation of net cash flow, depreciation and amortization are treated as A. current liabilities B. income expenses C. non-cash revenues D. non-cash charges Payments if it is made at end of each period such as an end of year is classified as A. ordinary annuity B. deferred annuity C. annuity due D. Both A and B In time value of money, nominal rate is A. not shown on timeline B. shown on timeline C. multiplied on timeline D. divided on timeline Value of net income is $124,500,000 and common shares outstanding are 60,000,000 then earning per share will be A. $2.75 B. $0.48 C. $2.08 D. $2.80 Stockholders that do not get benefits even if company's earnings grow are classified as A. preferred stockholders B. common stockholders C. hybrid stockholders D. debt holders In balance sheet, sum of retained earnings and common stock are considered as A. preferred equity B. due equity C. common perpetuity D. common equity Securities with less predictable prices and have longer maturity time is considered as A. cash equivalents B. long-term investments C. inventories D. short-term investments Number of shares outstanding if it is divided by net income for using to calculate A. earning per share B. dividends per share C. book value of share D. market value of shares Purchase cost of assets over its useful life is classified as A. appreciation B. depreciation C. appreciated assets D. appreciated liabilities Process of calculating future value of money from present value is classified as A. compounding B. discounting C. money value D. stock value Type of basic financial statements consist of A. balance sheet and income statement B. statement of retained earning C. statement of cash flows D. all of above If common shares outstanding are 50,000,000 and book value per share is $19.92 then total common equity (in dollars) will be A. $996,000,000 B. $995,000,000.00 C. 992,000,000 D. 991,000,000 An income available for shareholders after deducting expenses and taxes from revenues is classified as A. net income B. net earnings C. net expenses D. net revenues Security present value is $100 and future value is $150 after 10 years and value of 'I = interest rate' will be A. 4.14% B. 0.59% C. 0.69% D. 0.79% Noncash revenues and noncash charges if it subtracted from net income is equal to A. free cash flow B. retained cash flow C. net cash flow D. financing cash flow An information uses by investors for expecting future earnings is all recorded in A. five years report B. annual report C. stock report D. exchange report In calculation of net cash flow, deferred tax payments are classified as A. non-cash revenues B. non-cash charges C. current liabilities D. income expense Land, buildings, and factory fixed equipment are classified as A. tangible asset B. non-tangible assets C. financial asset D. financial liability Rate of return that an investment provides its investor is classified as A. investment return rate B. internal rate of return C. international rate of return D. intrinsic rate of return Method of inventory recording gives lower cost of goods sold in income statement is classified as A. last in first out B. last out receivable C. first out receivable D. first in first out Type of interest rates consist of A. nominal rates B. periodic rates C. effective annual rates D. all of above Future value of interest if it is calculated once a year is classified as A. one time compounding B. annual compounding C. semi annual compounding D. monthly compounding An interest rate which is paid by money borrower and charged by lender is considered as A. annual rate B. periodic rate C. perpetuity rate of return D. annuity rate of return In calculation of time value of money, 'PMT' represents A. present money tracking B. payment C. payment money tracking D. future money payment Left side of balance sheet states the A. appreciated earnings B. liabilities C. assets D. stocks earnings Intangible assets such as copyrights, trademarks and patents are applicable for A. depreciation B. amortization C. stock amortization D. perishable assets A schedule which shows interest constitutes reduced principal and unpaid balance is considered as A. repaid schedule B. depreciated schedule C. amortization schedule D. appreciated schedule Net income is $2250 and noncash charges are $1150 then net cash flow would be A. $1,100 B. $3,400 C. $2,200 D. $3,500 Lottery payoffs and payment for rental apartments are examples of A. lump sum amount B. deferred annuity C. annuity due D. payment fixed series Finance company providing loans at 12% with 2 compounding periods per year, periodic rate is classified as A. 3% per quarter B. 6% per quarter C. 6% per year D. 0.1667 % per year Accounts payable, accruals and notes payables are listed on balance sheet as A. accrued liabilities B. current liabilities C. accumulated liabilities D. non current liabilities A loan that is repaid on monthly, quarterly and annual basis in equal payments is classified as A. amortized loan B. depreciated loan C. appreciated loan D. repaid payments An interest rate is 5%, number of period are 3, and present value is $100, then future value (in dollars) will be A. 115.76 B. 105 C. 110.25 D. 113.56 A method of inventory recording which produces high inventories in balance sheet is classified as A. first out receivable B. first in first out C. last in first out D. last out receivable Noncash revenues are $500,000 and net income is $950,000 then net cash flow would be A. $475,000 B. $485,000 C. $1,450,000 D. $450,000 Cash and equivalents, inventories and accounts receivables are classified as A. assets on balance sheet B. liabilities on balance sheet C. earnings on income statement D. payments on income statement In situation of bankruptcy, stock which is recorded above common stock and below debt account is A. debt liabilities B. preferred stock C. hybrid stock D. common liabilities If security pays $5,000 in 20 years with 7% annual interest rate, PV of security by using formula is A. 1292.10 dollars per year B. 1292.10 dollars C. 0.00077 dollars per year D. 16105.1 dollars per year An interest rate which is quoted by brokers, banks and other financial institutions is classified as A. annuity rate B. perpetuity rate C. nominal rate D. external rate of return Company who sells products to customer without demanding immediate payment but record it in balance sheet as A. account payable B. account receivable C. account equivalent D. account investment Nominal rate which is quoted to consumers on loans is considered as A. annual percentage rate B. annual rate of return C. loan rate of return D. local rate of return An inventory recording in balance sheet includes A. first in first out B. last in first out C. last in last out D. Both A and B Values recorded as determined in marketplace are considered as A. market values B. book values C. appreciated values D. depreciated values A type of security payment in which payments are made at equal intervals of time and each payment amount is same is classified as A. fixed interval investment B. fixed payment investment C. annuity D. lump sum amount Financial securities that can be converted into cash at closing to their book value price are classified as A. inventories B. short-term investments C. cash equivalents D. long-term investments Discounted cash flow analysis is also classified as A. time value of stock B. time value of money C. time value of bonds D. time value of treasury bonds Prices of bonds will be decreased if an interest rates A. rises B. declines C. equals D. none of above Right side of balance sheet states the A. appreciated earnings B. liabilities C. assets D. stocks earnings Wages and salaries of employees which company owns in this accounts are called A. accrued expenses B. accruals accounts C. Both A and B D. zero liabilities Securities future value is $1,000,000 and present value of securities is $500,000 with an interest rate of 4.5%, 'N' will be A. 16.7473 years B. 0.0304 months C. 15.7473 years D. 0.7575 years If payment of security is paid as $100 at end of year for three years, it is an example of A. fixed payment investment B. lump sum amount C. fixed interval investment D. annuity Payment of security if it is made at end of each period such as beginning of year is classified as A. annuity due B. payment fixed series C. ordinary annuity D. deferred annuity Net worth is also called A. asset net of liabilities B. liabilities net of assets C. earnings net on assets D. liabilities net of earnings An annual rate of 16% if quoted by credit card issuer usually a bank is classified as A. loan rate of return B. local rate of return C. annual percentage rate D. annual rate of return Value of payment is $25 and an interest rate is 2%, then present value will be A. 12.5 dollars B. 0.0008 dollars C. 1,250 dollars D. 0.8 dollars Collection of net income, amortization and depreciation is divided by common shares outstanding to calculate A. cash flow of financing activities B. cash flow per share C. cash flow of investment D. cash flow of operations In a statement of cash flows, a company investing in short-term financial investments and in fixed assets results in A. increased cash B. decreased cash C. increased liabilities D. increased equity Future value of annuity FVA(ordinary) is, if deposited value is $100 and earn 5% every year of total three years will be A. 315.25 dollars B. 331.0125 dollars C. 99.4875 dollars D. 318.25 dollars Total common equity divided by common shares outstanding which is used to calculate A. book value of share B. market value of shares C. earning per share D. dividends per share Prices of bonds will be increased if interest rates A. equals B. lump sum declines C. rises D. declines Earnings that are not paid as dividends to stockholders and have cumulative amount are classified as A. non-paid earnings B. common earnings C. retained earnings D. preferred earnings In time value of money, periodic rate is A. not shown on timeline B. shown on timeline C. multiplied on timeline D. divided on timeline Claim against assets are represented by A. saved earning B. retained earnings C. maintained earnings D. saving account earning Rate charged by bank 12.5% on credit loans and 3% semiannually on installment loans is considered as A. periodic rate B. perpetuity rate of return C. annual rate D. annuity rate of return Dividends paid to common shareholders and divided by common shares outstanding are equals to A. earning per share B. dividends per share C. book value of share D. market value of shares Future value of interest if it is calculated two times a year can be a classified as A. semiannual discounting B. annual discounting C. annual compounding D. semiannual compounding Payment if it is divided with interest rate will be formula of A. future value of perpetuity B. present value of perpetuity C. due perpetuity D. deferred perpetuity An earning before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization are calculated by A. subtracting operating cost from net sales B. subtracting net sales from operating costs C. adding operating cost and net sales D. adding interest and taxes Until word of preferred is used, an equity in balance sheet is treated as A. common equity B. preferred equity C. due equity D. common perpetuity Future value of annuity FVA(due) is, if deposited value is $100 and earn 5% every year of total three years will be A. 99.4875 dollars B. 318.25 dollars C. 315.25 dollars D. 331.0125 dollars Total common equity $996,000,000 and shares outstanding 50,000,000 then book value per share would be A. $0.05 B. $15 C. $19.92 D. $14 Total amount of depreciation charged on long term assets is classified as A. accumulated depreciation B. depleted depreciation C. accumulated appreciation D. accumulated appreciation schedule rate which is divided by compounding periods to calculate periodic rate must be A. annuity return B. deferred annuity return C. nominal rate D. semiannual discount rate In calculation of time, value of money, ''N ''represents A. number of payment periods B. number of investment C. number of installments D. number of premium received If deposited money $10,000 in bank pays interest 10% annually, an amount after five years will be A. 16105.1 dollars B. 0.01610 dollar per day C. 16105.1 dollars per year D. 16105.1 dollars per quarter Student loans, mortgages and car loans are examples of A. lump sum amount B. deferred annuity C. annuity due D. payment fixed series An annuity with an extended life is classified as A. extended life B. perpetuity C. deferred perpetuity D. due perpetuity Periodic rate if it is multiplied with per year number of compounding periods is called A. extrinsic rate of return B. intrinsic rate of return C. annual rate of return D. nominal annual rate Net income and depreciation is $313,650,000 and common shares outstanding are 55,000,000 then cash flow per share would be A. $5.70 B. $6.70 C. $7.70 D. $8.70 Finance company providing loans at 3% with five compounding periods per year, nominal annual rate is classified as A. 15% B. 0.60% C. 10% D. 1.67% * values of assets purchased or liabilities recorded as recorded by bookkeepers are considered as A. appreciated values B. depreciated values C. market values D. book values A stock which is hybrid and works as a cross between debt and common stock is considered as A. hybrid stock B. common liabilities C. debt liabilities D. preferred stock Paid dividends to common stockholders $67,600,000 and common shares outstanding = 55,000,000 then dividend per share will be A. $1.23 B. $0.81 C. $2.12 D. $2.78 Procedure of finding present values in time value of money is classified as A. compounding B. discounting C. money value D. stock value In uneven cashflow, 'IRR' is an abbreviation of an A. internal rate of return B. international rate of return C. intrinsic rate of return D. investment return rate A company who issues bonds or stocks in result raised funds which finally A. increases liabilities B. increases equity C. increases cash D. decreases cash [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 59 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 19, 2020
Number of pages
59
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 19, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
150