RespiratoryCare Practice Exam
Gary Persing, TMC Q&A + Rationale
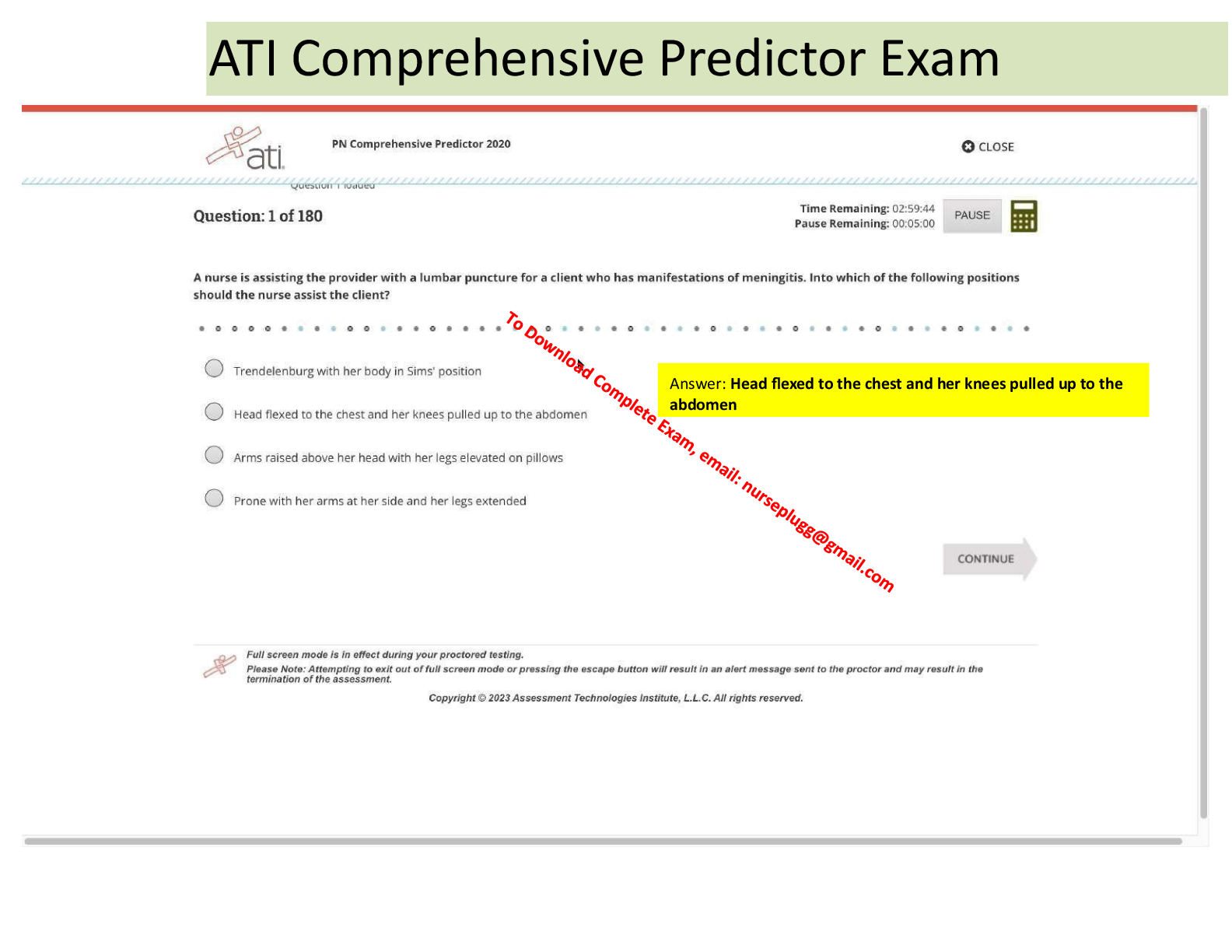
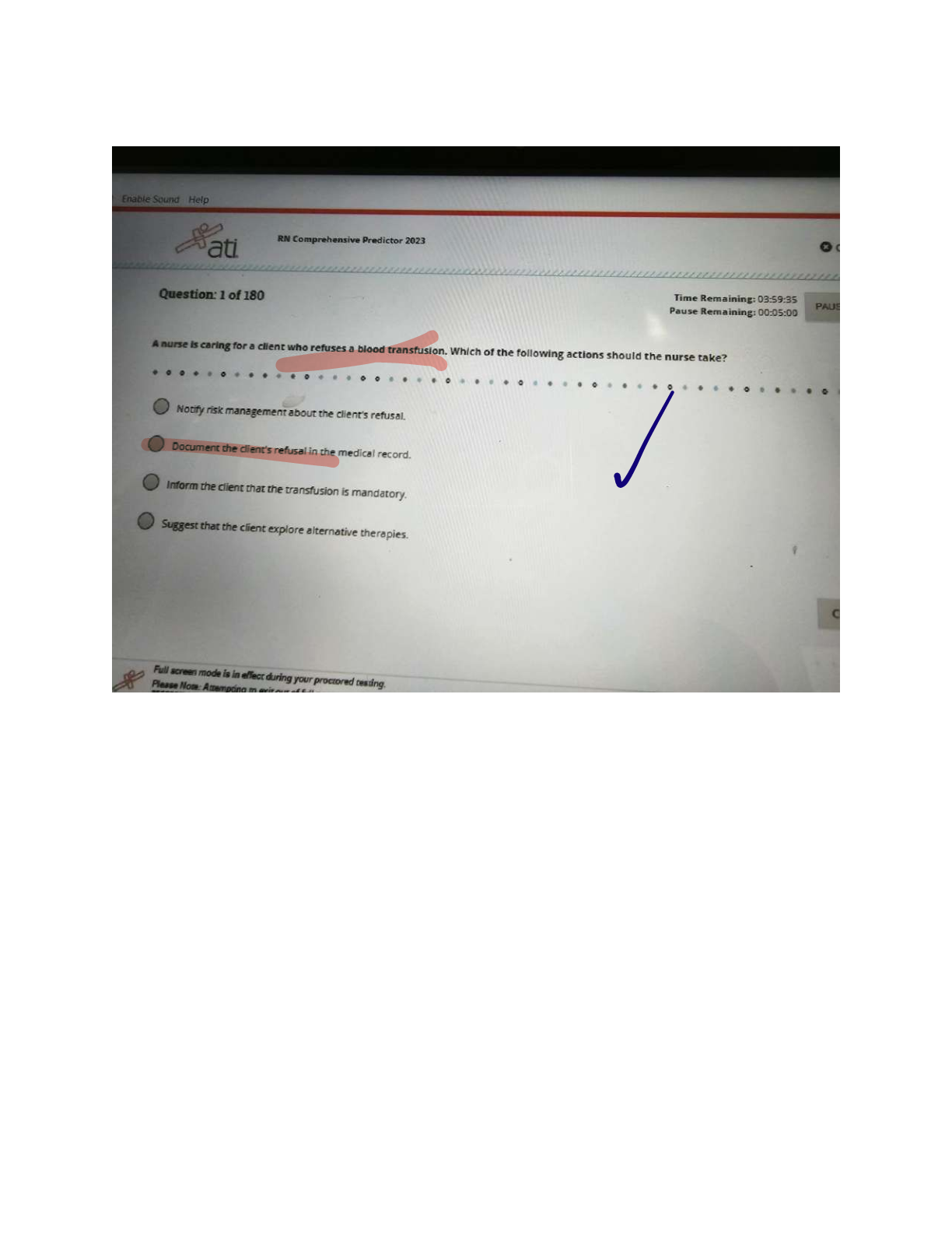
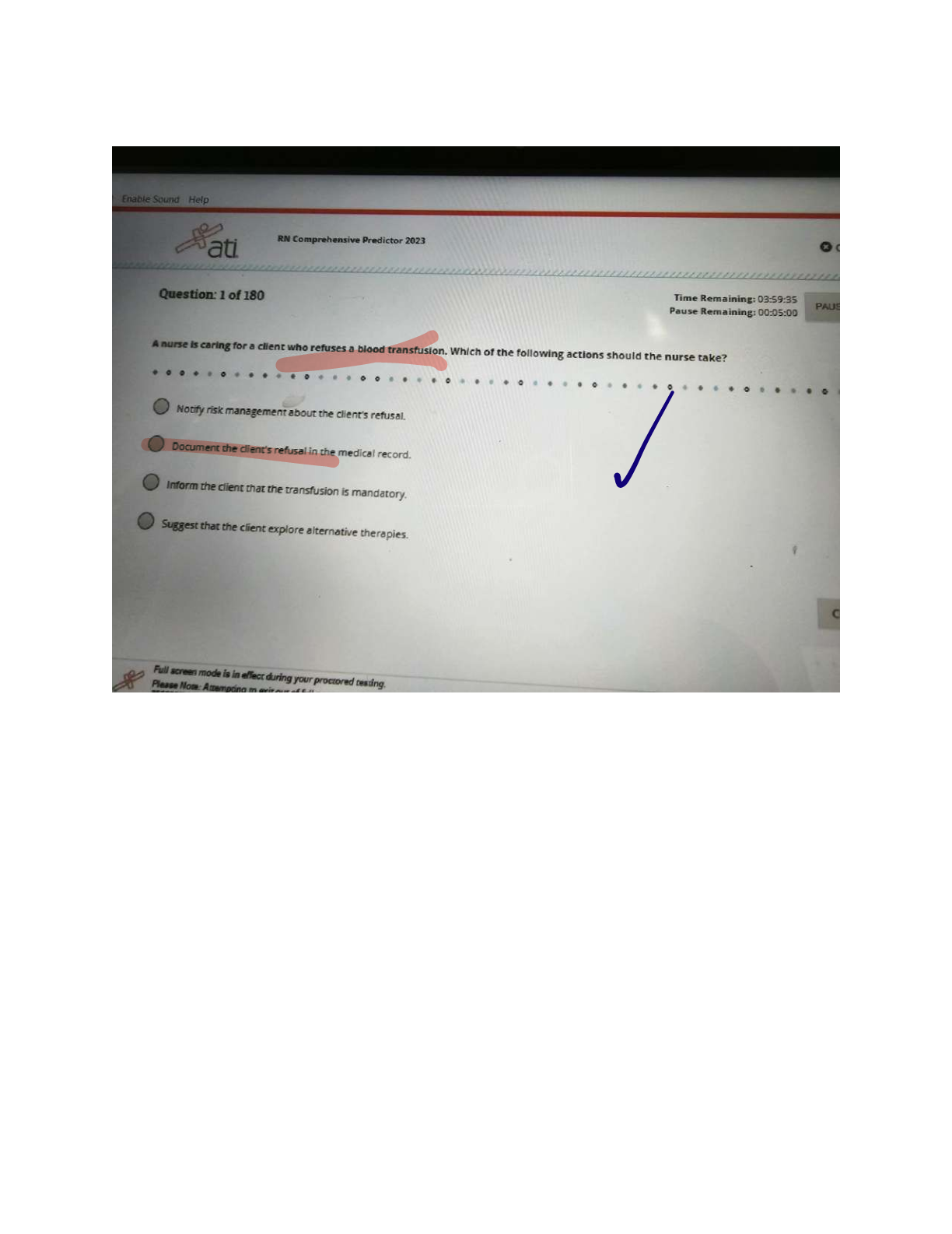
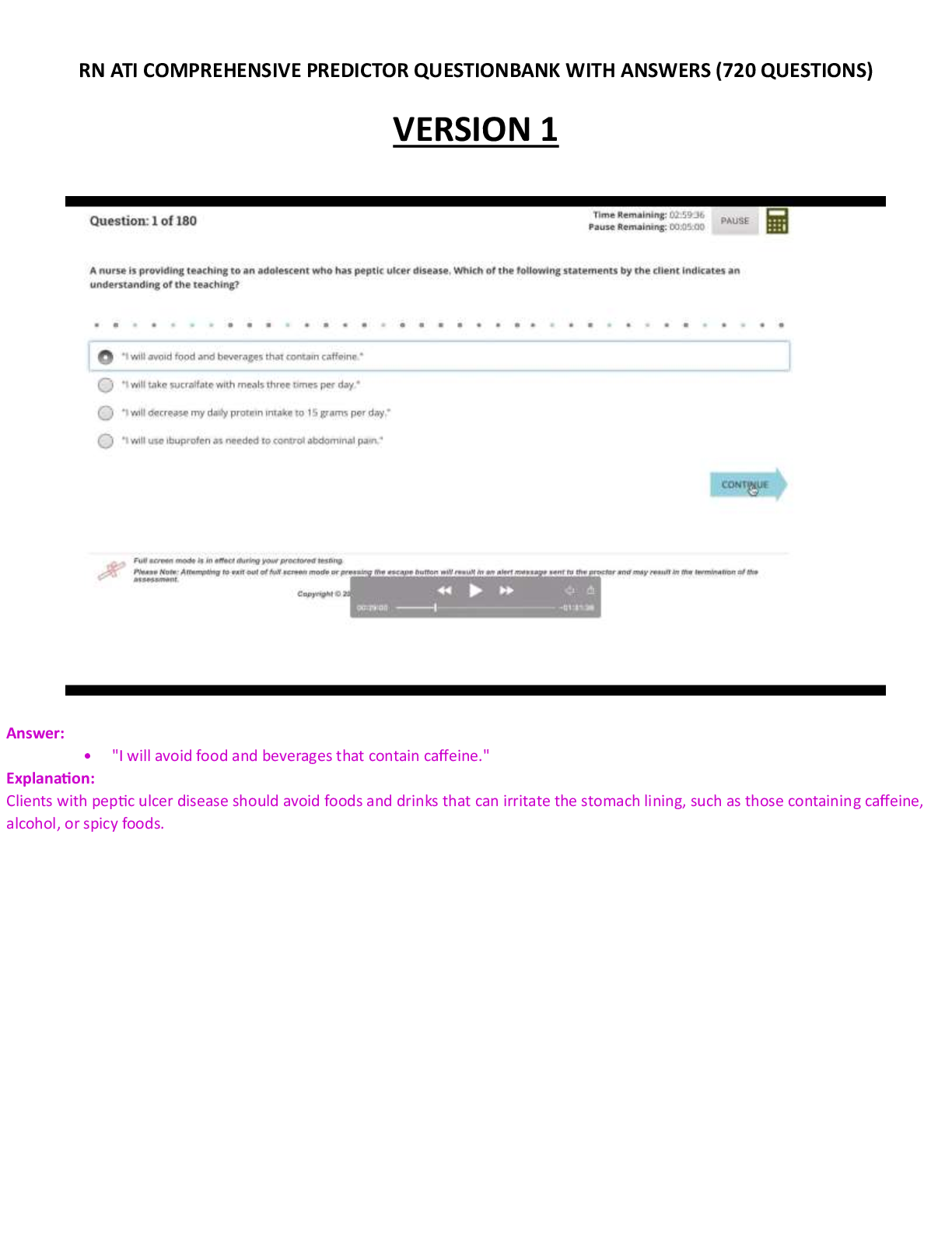
1) A patient receiving positive expiratory pressure (PEP) therapy through a mouthpiece at 10 cm H2O
has minimal secretion production. Course crackles are
...
RespiratoryCare Practice Exam
Gary Persing, TMC Q&A + Rationale
1) A patient receiving positive expiratory pressure (PEP) therapy through a mouthpiece at 10 cm H2O
has minimal secretion production. Course crackles are heard during auscultation. The respiratory
therapist should recommend which of the following?
A. Decrease the PEP to 5 cm H2O.
B. Discontinue the treatment and begin percussion and postural drainage.
C. Increase the PEP to 15 cm H2O.
D. Administer the treatment with a mask instead of the mouthpiece.
Correct Answer is C
Rationale: PEP therapy is indicated for patients with retained secretions. Positive pressure applied
during exhalation aids in the mobilization of secretions. Generally, PEP levels of 10 to 20 cm H2O are
used. If the PEP used does not result in the mobilization of secretions, the PEP should be increased.
2) A heated humidifier is delivering 26 mg of H2O/L of gas to an intubated patient. Which of the
following statements concerning this situation are true?
1. A humidity deficit exists.
2. The patient's secretions may become thicker.
3. The heater temperature should be decreased.
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
Correct Answer is B
Rationale: Whenever the amount of H2O being delivered to the patient is less than 44 mg/L, a
humidity deficit exists. This decreased H2O delivery can result in thickening of pulmonary secretions,
with an increased potential of mucous plugging and atelectasis distal to the plugs. Because cooler air
cannot hold as much H2O as warmer air, decreasing the heater temperature increases the humidity
deficit.
3) The respiratory therapist is administering acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) via a handheld nebulizer to a
patient who suddenly becomes short of breath. Which of the following is the most appropriate
recommendation at this time?
A. Have the patient take deeper breaths.
B. Add racemic epinephrine to the nebulizer.
C. Stop the treatment and administer albuterol.
D. Stop the treatment and administer cromolyn sodium.
Correct Answer is C
Rationale: A common complication of acetylcysteine administration is bronchospasm. When
respiratory difficulties occur during a Mucomyst treatment, suspect bronchospasm and administer a
bronchodilating agent.
4) An intubated patient's secretions tend to become thicker and harder to mobilize in which of the
following conditions?
1. Absolute humidity of 18 mg H2O/L of gas
2. 48 mg of H2O/L of gas
3. Relative humidity of 100% at 25° C
4. A H2O vapor pressure of 47 mm Hg
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 1 and 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 2 and 4 only
Correct Answer is B
Rationale: For delivery of 100% saturated gas at body temperature (100% body humidity) , the gas
must be holding 44 mg of H2O/L of gas to have an H2O vapor pressure of 47 mm Hg. Thus, choices 1
and 3 result in a humidity deficit. Although choice 3 indicates a relative humidity of 100%, it is at only
25° C, not at body temperature (37° C), so inadequate H2O is being delivered and the body has to
make up the deficit. This causes the airway to dry out and make secretions thicker.
5) Which of the following is the most appropriate ventilator VT setting for a female patient who is 5 ft,
5 in tall and weighs 85 kg (187 lb) ?
A. 450 mL
B. 600 mL
C. 800 mL
D. 900 mL
Correct Answer is A
[Show More]