Chapter 51-- Hepatic, Biliary Tract, and Pancreatic Dysfunction: Nursing Management
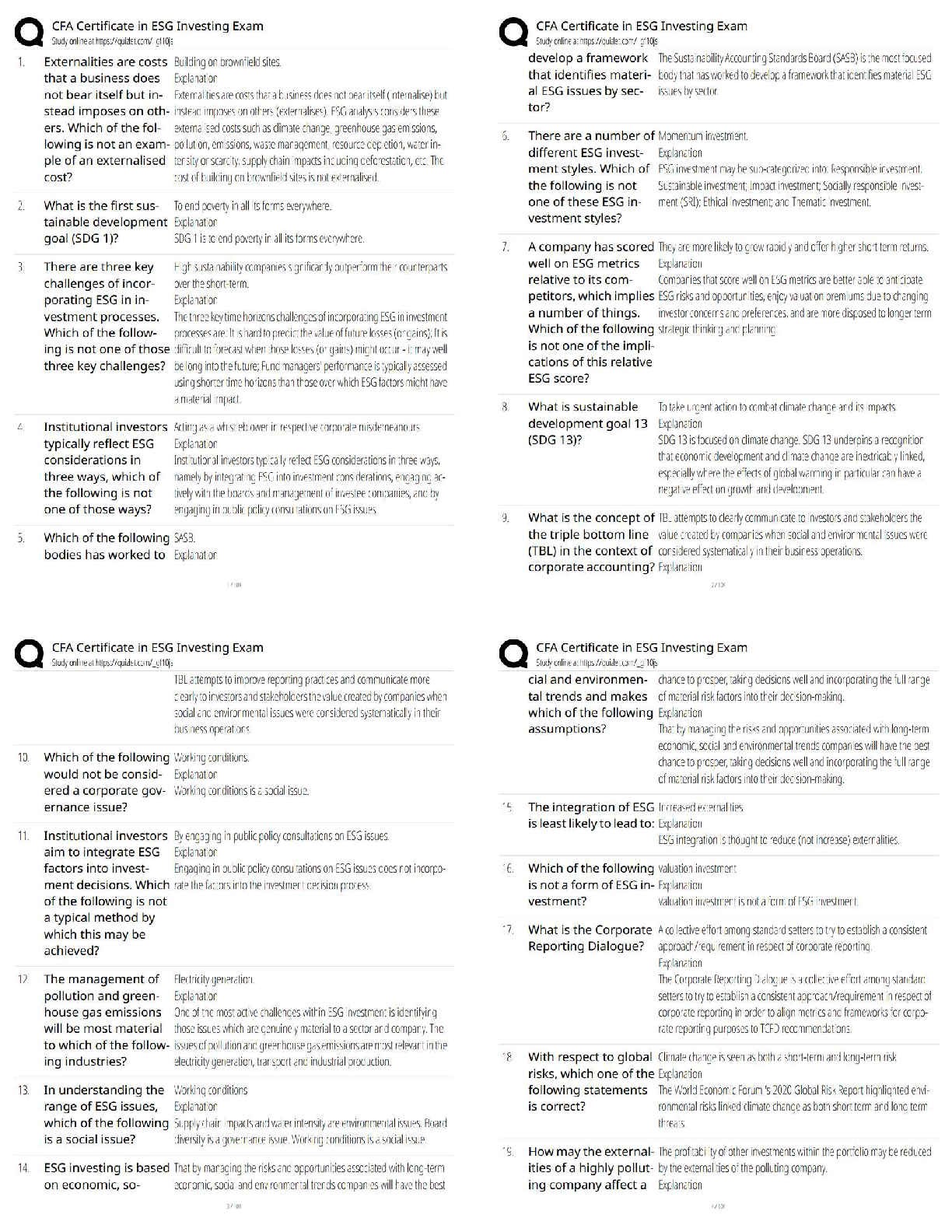
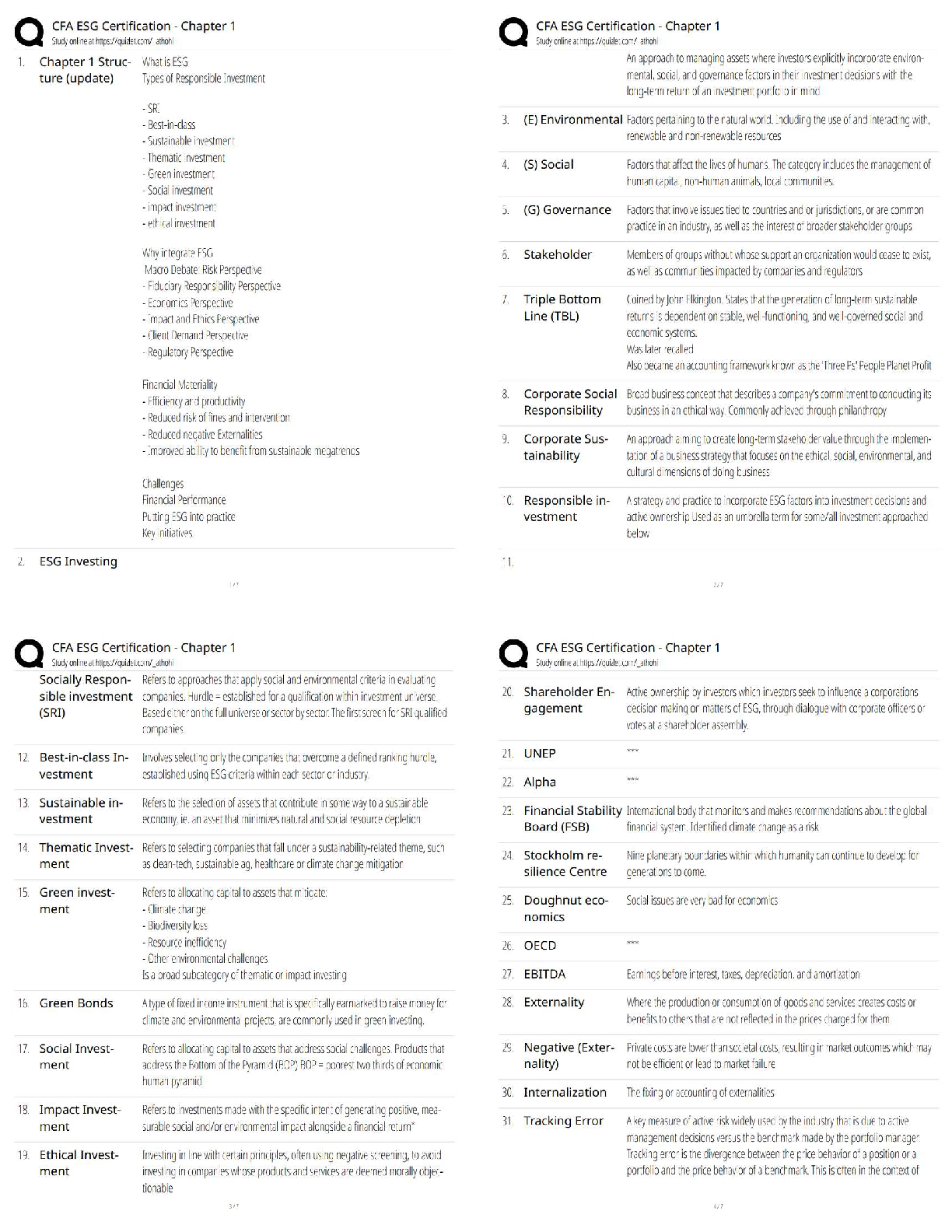
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A child care worker complains of flu-like symptoms. On further assessment, hepatitis is suspected. The
nurse reali
...
Chapter 51-- Hepatic, Biliary Tract, and Pancreatic Dysfunction: Nursing Management
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A child care worker complains of flu-like symptoms. On further assessment, hepatitis is suspected. The
nurse realizes that this individual is at risk for which type of hepatitis?
1. Hepatitis A
2. Hepatitis B
3. Hepatitis C
4. Hepatitis D
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Table 51-1 Comparison of the Types of Hepatitis
2. An older male is diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver. The nurse knows that the most likely cause of
this problem is:
1. being in the military.
2. traveling to a foreign country.
3. drinking excessive alcohol.
4. eating bad food.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Cirrhosis
3. When the liver is seriously damaged, ammonia levels can rise in the body. One of the treatments for
this is:
1. administering intravenous (IV) neomycin.
2. giving vitamin K.
3. giving lactulose.
4. starting the patient on insulin.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Hepatic Encephalopathy: Planning and Implementation
4. A client is scheduled for a liver biopsy. The nurse realizes that the most important sign to assess for is:
1. infection.
2. bleeding.
3. pain.
4. nausea and vomiting.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Nursing Strategy: Complications of a Liver Biopsy
5. The nurse realizes that the organ which is a major site for metastases, harboring and growing
cancerous cells that originated in some other part of the body, is the:
1. spleen.
2. gallbladder.
3. liver.
4. stomach.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Cancer of the Liver: Secondary Liver Cancer
6. A school age child is placed on a waiting list for a liver transplant. The nurse knows that the most
common reason for children to need this type of transplant is because of:
1. cirrhosis due to hepatitis C.
2. biliary atresia.
3. diabetes.
4. Crohn’s disease.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Liver Transplantation: Etiology
7. Because health care workers are at a greater risk of hepatitis B infection, it is recommended that all
health care workers:
1. wash their hands often.
2. avoid foreign travel.
3. become vaccinated.
4. drink bottled water only.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Table 51-1 Comparison of the Types of Hepatitis
8. A client who usually smokes a pack of cigarettes a day tells the nurse that he cannot stand the smell of
smoke. The nurse realizes that this client is in which phase of hepatitis?
1. Preicteric
2. Icteric
3. Posticteric
4. Recovery
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Box 51-3 Phases of Hepatitis
9. A female client is surprised to learn that she has been diagnosed with hemochromatosis. Which of the
following should the nurse respond to this client?
1. “It doesn’t affect people until they are in their 50s.”
2. “I would ask the doctor if he’s sure about the diagnosis.”
3. “Females often do not experience the effects of the disease until menopause.”
4. “All women have the disorder but not the symptoms.”
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Hereditary Diseases of the Liver
10. A client is diagnosed with liver disease. Which of the following is one impact of this disorder on a
client’s fluid and electrolyte status?
1. Hyperkalemia
2. Hypercalcemia
3. Hypernatremia
4. Hyponatremia
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Box 51-7 Clinical Manifestations of Liver Disease
11. The nurse, caring for a client recovering from the placement of a shunt to treat portal hypertension,
should assess the client for which of the following complications associated with this surgery?
1. Myocardial infarction
2. Pulmonary emboli
3. Pulmonary edema
4. Decreased peripheral pulses.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Red Flag: Shunt Surgery
12. A client is diagnosed with macrovesicular fatty liver. Which of the following should the nurse instruct
this client?
1. Expect to develop jaundice.
2. Avoid all alcohol.
3. Increase exercise.
4. Treatment includes antibiotic therapy.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Fatty Liver: Planning and Implementation
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. A client diagnosed with cirrhosis is experiencing the complication of ascites. Which of the following
would be considered treatment for this complication? (Select all that apply.)
1. Fluid restriction
2. Low-sodium diet
3. Increased exercise
4. Diuretic therapy
5. Pain medication
6. Bed rest
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Cirrhosis: Planning and Implementation
2. A client is recovering from an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatogram (ERCP). Which of the
following should the nurse assess as possible complications from this procedure? (Select all that
apply.)
1. Perforation of the stomach
2. Perforated duodenum
3. Pancreatitis
4. Aspiration of gastric contents
5. Anaphylactic reaction to the contrast dye
6. Perforated bladder
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Diagnostic Tests
3. A client is demonstrating yellow pigmentation of the skin and sclera. Which of the following can be
used to describe this client’s symptoms? (Select all that apply.)
1. Jaundice
2. Dyspepsia
3. Icterus
4. Sclerosis
5. Kernicterus
6. Cirrhosis
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Box 51-1 Bilirubin Labels
4. The nurse is providing dietary instruction to a client diagnosed with Wilson’s disease. Which of the
following should be included in these instructions? (Select all that apply.)
1. Avoid liver.
2. Avoid shellfish.
3. Eat soy products.
4. Use avocados in salads.
5. Avoid nectarines.
6. Avoid mushrooms.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Box 51-1 Dietary Recommendations for People with Wilson's Disease
5. A client is diagnosed with a disorder of the liver. The nurse realizes this client might experience which
of the following? (Select all that apply.)
1. Low vitamin A levels
2. Increased bleeding
3. Poor digestion of fats
4. Insulin resistance
5. Elevated levels of vitamin E
6. Nerve damage
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Cirrhosis: Pathophysiology
6. A client is diagnosed with portal hypertension. The nurse should assess the client for which of the
following disorders associated with this diagnosis? (Select all that apply.)
1. Esophageal varices
2. Splenomegaly
3. Hemorrhoids
4. Caput medusae
5. Gastritis
6. Gallstone formation
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Portal Hypertension
[Show More]