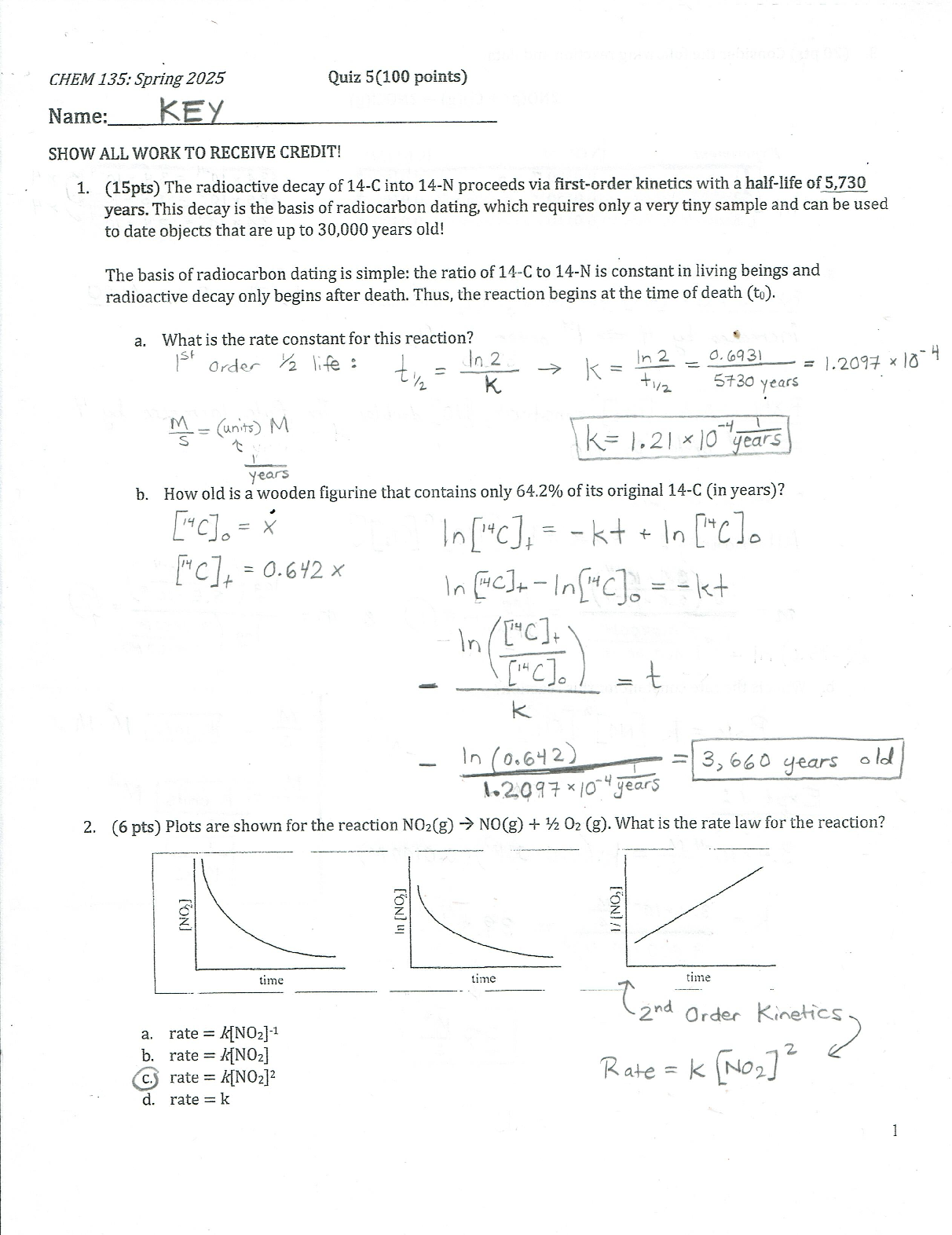
what is an EKG? - ANSWER - presents a graphical representation of the heart's electrical activity
- the printed record is known as a rhythm strip/12 lead (best way to see electrical activity in all areas)
how many
...
what is an EKG? - ANSWER - presents a graphical representation of the heart's electrical activity
- the printed record is known as a rhythm strip/12 lead (best way to see electrical activity in all areas)
how many boxes make up 1 second on an EKG? - ANSWER 5 big boxes
what does the "y" axis on an EKG represent? - ANSWER amplitude
what does the "x" axis on an EKG represent? - ANSWER time
how many seconds is 1 big box? - ANSWER 0.2 seconds
what are precordial leads? - ANSWER V1-V6
- placed on a patient's chest to look at anterior and lateral wall of the heart, help identify abnormal electrical patterns
if conduction is going towards a lead, where will the wave be? - ANSWER above the isoelectric line
if conduction is going away from a lead, where will the wave be? - ANSWER below the isoelectric line (this is not normal in most leads)
what act as backups in case the SA node fails? - ANSWER AV node and bundle of HIS
**both of these conduct at 40-60 BPM
what is the primary pacemaker of the heart? - ANSWER SA node
**60 -100 BPM
if all other electrical mechanisms in the heart fail, what is the last backup mechanism? - ANSWER the ventricles and purkinje fibers
- the ventricles can depolarize on their own and produce CO, but BPM is very slow since it takes longer for depolarization
**15 to 40 BPM
- wide QRS = not normal
what does the P wave indicate? - ANSWER indicates atrial depolarization
- upright in most leads
- normal duration is not longer than 0.12 seconds (anything longer might indicate a heart block)
what does the QRS complex indicate? - ANSWER ventricular depolarization (through bundle of His, l/r bundle branches and contraction of ventricles)
- normally nor longer than 0.12 seconds
what is a pathological Q wave? - ANSWER waves that suggest a person had an old MI
what does the T wave indicate? - ANSWER ventricular repolarization
- not more than 5 mm in amplitude
- should be upright on EKG (indicates MI if upside down)
**rounded and asymmetrical
how will atrial fibrillation present on an EKG? - ANSWER no p wave
what is long QT syndrome? - ANSWER - a heart rhythm disorder that can potentially cause fast, chaotic heartbeats and ventricular fibrillation.
- These rapid heartbeats may trigger a sudden fainting spell or seizure.
- In some cases, your heart may beat erratically for so long that it can cause sudden death.
What is QTC? - ANSWER QT (interval) corrected for heart rate
above what value is QTC bad, significant, and needs to be told to the provider? - ANSWER above 500 m/s
what is Torsades de Pointes? - ANSWER - pulseless ventricular tachycardia
- need to give Mg+ BEFORE defibrillation and CPR
how do you properly evaluate an EKG strip? - ANSWER rate:
- is it regular or irregular
P wave:
- do they all look the same?
- is there a p wave before every QRS complex?
QRS complex:
- normal vs wide
- do they all look the same?
T wave:
- normal looking? (rounded, upright)
how can you use an EKG to determine heart rate? - ANSWER number of QRS complexes in 6 seconds, multiplied by 10
is a QRS > .12 seconds normal or abnormal? - ANSWER abnormal...usually has to do with a conduction abnormality
what do tall, peaked T waves indicate? - ANSWER hyperkalemia
what do low potassium and mg indicate likeliness of? - ANSWER irregular heart beats or rhythm
what are different ways to use an EXG to measure HR? - ANSWER - # or R to R in 6 seconds multiplied by 10
- # of large boxes between QRS complexes divided by 300
- # of small boxes between QRS divided by 1500
- measuring p wave to p wave
T or F: if HR is irregular, R to R in 6 seconds x 10 must be utilized - ANSWER true
what is the ST-T wave? - ANSWER ventricular repolarization
what is a RR interval? - ANSWER duration of ventricular cardiac cycle (indicator of ventricular rate)
what are the criteria for a sinus rhythm? - ANSWER - regularity: regular
- rate: 60-100 bpm
- p wave: normal and upright, one p wave in front of every qrs complex
- qrs: less than .12
what are some things that could cause sinus bradycardia? - ANSWER - athletes
- sleep
- vagal menuvers
- elevated ICP
- digoxin
- beta blockers
- ischemia of the SA node
- calcium-channel blockers
how can you manage sinus bradycardia? - ANSWER only really need to treat if patient is symptomatic
what are some things that could cause sinus tachycardia? - ANSWER - exercise
- emotions
- pain
- fever
- FVD
- shock (usually because the heart is trying to compensate)
- HF
how do you treat sinus tachycardia? - ANSWER treat underlying cause
what are some things that could cause premature heart beats (atrial contraction)? - ANSWER - emotions
- caffeine
- nicotine
- digoxin
- heart failure
how can you treat premature heart beats? - ANSWER treat underlying cause
what is a dysrhythmia? - ANSWER an arrhythmia (same thing) that is an abnormal rhythm of the heart, which can cause the heart to pump less effectively
what are some s/s of dysrhythmias? - ANSWER - weakness
- fatigue
- palpitations
- low blood pressure
- dizziness
- fainting
what are sinus dysrhythmias? - ANSWER irregularity that may be related to the phases of the respiratory cycle or to atrial dysrhythmias
[Show More]