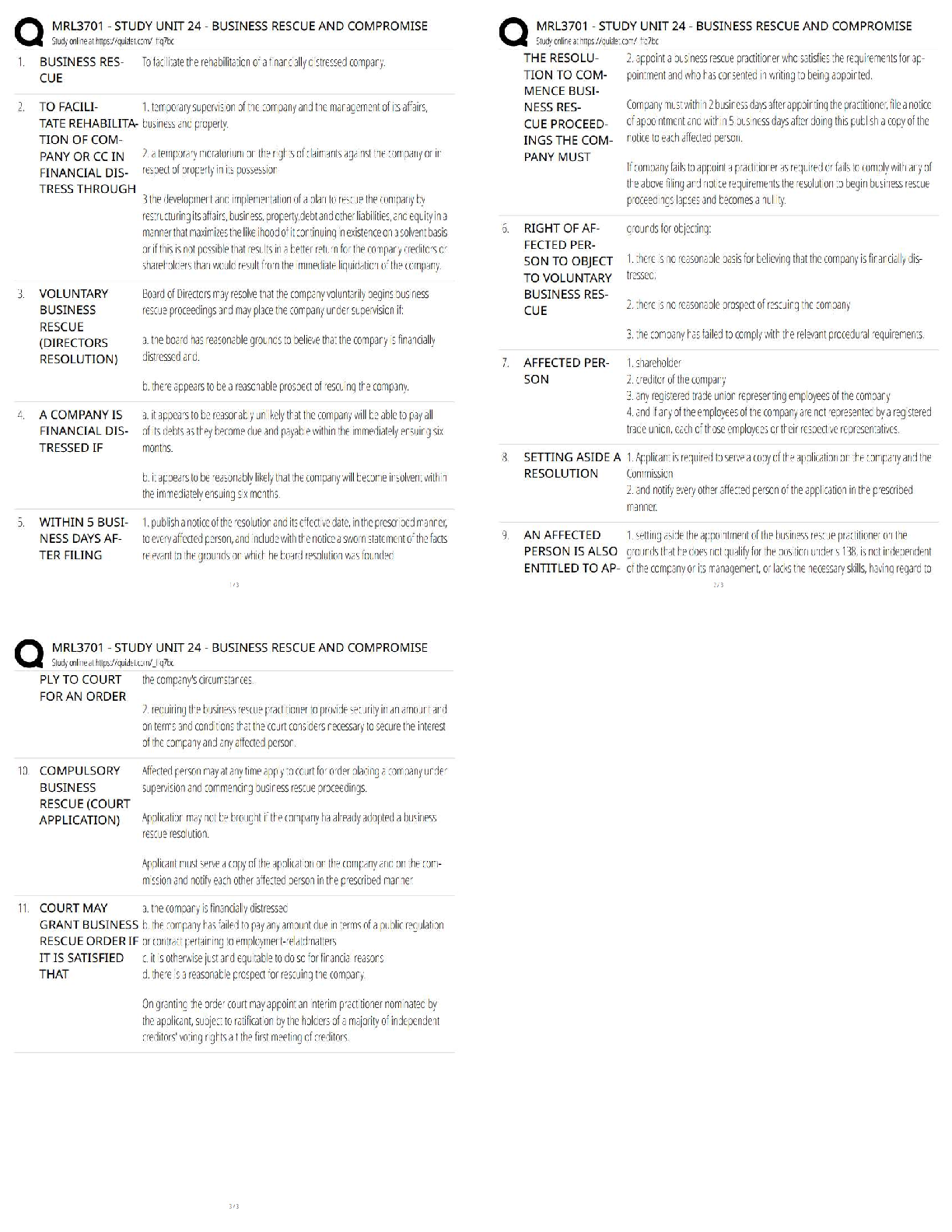
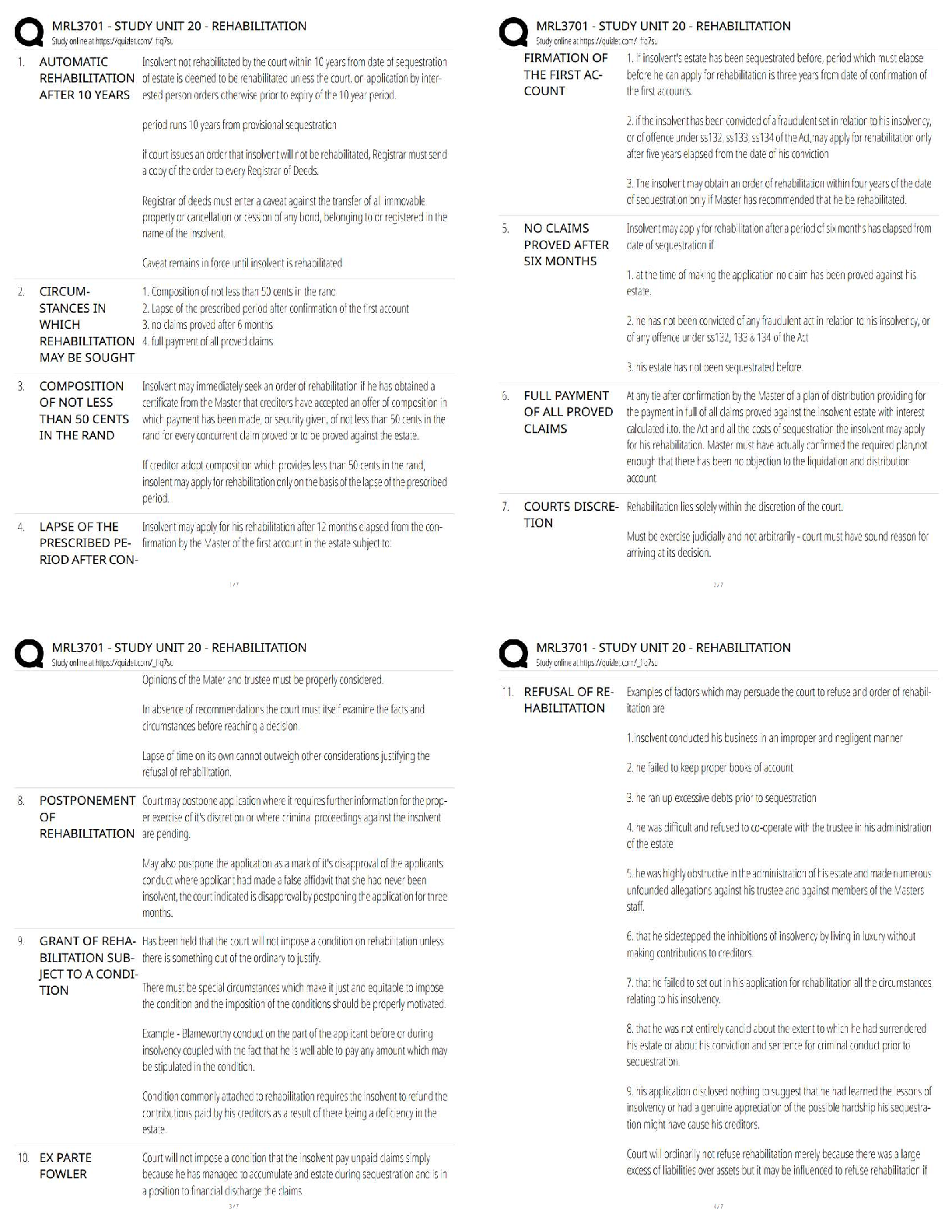
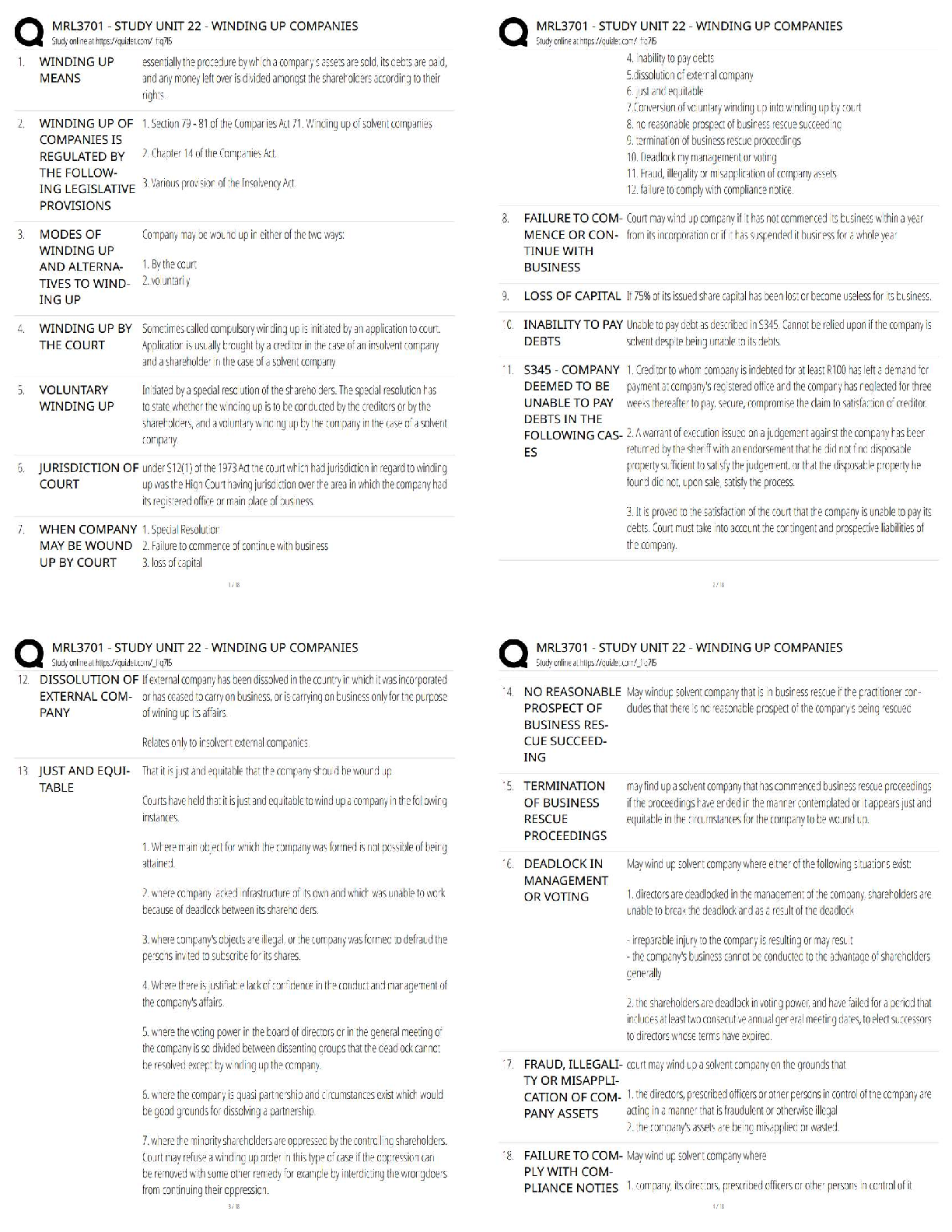
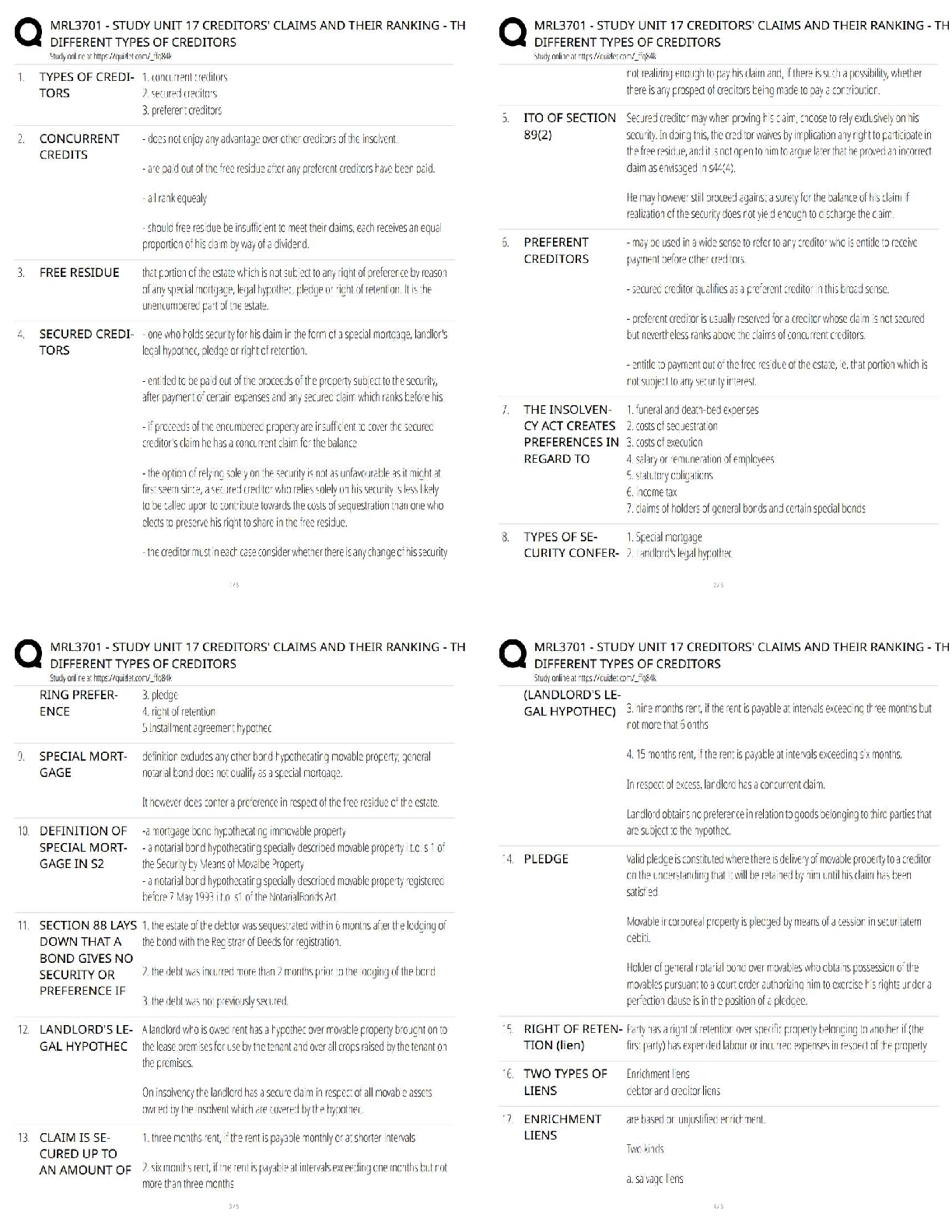
Chapter 12--Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances
MULTIPLE CHOICE
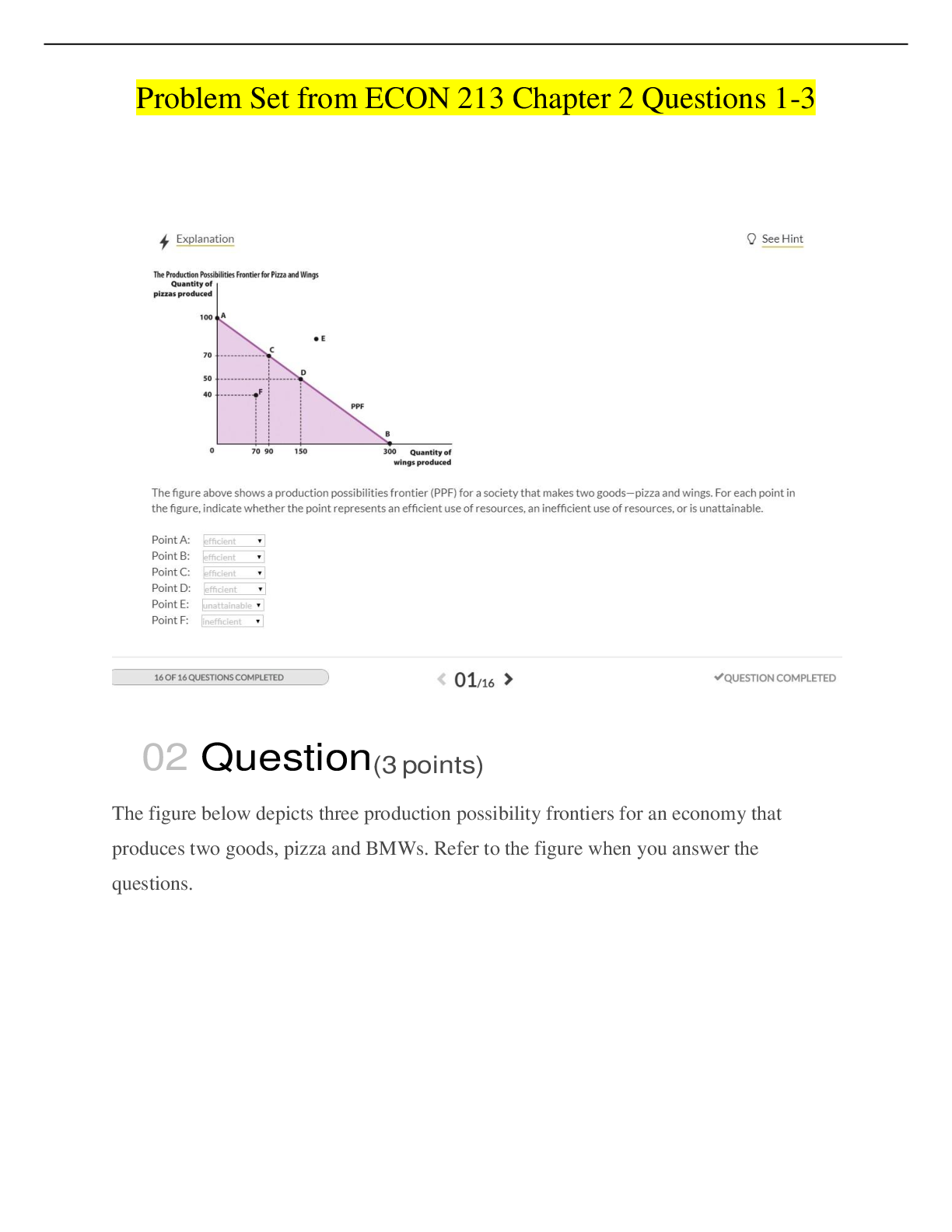
1. The nurse is concerned that a client can become dehydrated when which of the following is assessed?
1. History of arthritis
2. Appendi
...
Chapter 12--Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. The nurse is concerned that a client can become dehydrated when which of the following is assessed?
1. History of arthritis
2. Appendicitis diagnosis 3 years ago
3. Age 30
4. Obese female
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Fluid Balance
2. A client has lost a significant amount of blood. The nurse realizes that the fluid compartment most effected with the blood loss will be:
1. intracellular.
2. interstitial.
3. intravascular.
4. transcellular.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Fluid Balance
3. A client is diagnosed with chronic renal failure. Which of the following electrolytes should the nurse monitor for this client?
1. Hydrogen
2. Phosphorus
3. Calcium
4. Vitamin D
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF:
4. A client had a 2 kg weight loss in one day. The nurse realizes this change in weight is due to:
1. fluid loss.
2. poor appetite.
3. medications.
4. bed rest.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Fluid Imbalances: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
5. A client has a serum sodium level of 129 mEq/L. The nurse should prepare to administer which of the following intravenous solutions?
1. Dextrose 5% and Lactated Ringer
2. Dextrose 5% and 0.45% Normal Saline
3. 0.9% Normal Saline
4. Dextrose 5% and 0.9% Normal Saline
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Table 12-3 Isotonic IV Solutions; Table 12-4 Hypertonic IV Solutions
6. A client is diagnosed with fluid volume excess. Which of the following will the nurse most likely assess in this client?
1. Poor skin turgor
2. Jugular vein distention
3. Dry mouth
4. Increased heart rate
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Fluid Volume Excess: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
7. A client is demonstrating dizziness and lightheadedness upon standing. The nurse is concerned the client is experiencing postural hypotension when which of the following is assessed?
1. Lying BP 120/70 mmHg, P 70; standing BP 116/78 mmHg, P 78
2. Lying BP 116/64 mmHg, P 62; standing BP 94/58 mmHg, P 78
3. Lying BP 130/80 mmHg, P 84; standing BP 118/72 mmHg, P 90
4. Lying BP 126/74 mmHg, P 74; standing BP 108/62 mmHg, P 84
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Fluid Imbalances: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
8. The nurse assesses a client to have mild pitting edema of the lower extremities. The nurse would document this finding as being:
1. 0+.
2. 1+.
3. 2+.
4. 3+.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Figure 12-4 Pitting Edema Grading Scale
9. An elderly client is demonstrating new signs of confusion. Which of the following should the nurse consider when caring for this client?
1. Assess for signs of elevated sodium level.
2. Restrict fluids.
3. Administer prescribed diuretic medication.
4. Monitor daily weights.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Excess Sodium Ion: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
10. A client diagnosed with hypokalemia should have which of the following electrolytes also assessed?
1. Sodium
2. Calcium
3. Bicarbonate
4. Magnesium
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Deficient Potassium Ion: Planning and Implementation
11. A client is diagnosed with hypophosphatemia. The nurse realizes that this electrolyte imbalance is most likely associated with:
1. diabetes mellitus.
2. congestive heart failure.
3. arthritis.
4. chronic alcoholism.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Deficient Phosphorus Ion: Etiology
12. A client diagnosed with chronic renal failure is experiencing muscle weakness, paresthesias, and depression. Which of the following do these assessment findings suggest to the nurse?
1. Hyperkalemia
2. Hyponatremia
3. Hypocalcemia
4. Hypermagnesemia
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Excess Magnesium Ion: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
13. A client begins rapid breathing and demonstrates anxiety after learning of a diagnosis of breast cancer. After a short while, the client complains of tingling lips and fingers. Which of the following should the nurse do to assist this client?
1. Provide oxygen.
2. Coach the client in the use of an incentive spirometer.
3. Help the client slow the respiratory rate or breathe into a paper bag.
4. Administer intravenous fluids.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Respiratory Alkalosis
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. A client is diagnosed with hyponatremia. Which of the following assessment findings would cause the nurse to become concerned? (Select all that apply.)
1. Confusion
2. Poor appetite
3. Restlessness
4. Lethargy
5. Seizures
6. Coma
.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Deficient Sodium Ion: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
2. After reviewing a client’s most recent electrocardiogram, the nurse suspects the client is experiencing hyperkalemia. Which of the following did the nurse assess on the client’s rhythm strip? (Select all that apply.)
1. Tall peaked T-waves
2. Short QRS complex
3. Dysrhythmias
4. Wide QRS complex
5. Bradycardia
6. Tachycardia
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Excess Potassium Ion: Diagnostic Tests
3. A client has a serum potassium level of 2.9 mEq/L. Which of the following should be done to assist this client? (Select all that apply.)
1. Implement continuous cardiac monitoring.
2. Check for an elevated ST segment.
3. Assess muscle strength, tone, and reflexes.
4. Monitor digoxin levels.
5. Monitor for seizure activity.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Deficient Potassium Ion: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
4. Which of the following assessment techniques can the nurse use to determine if a client is experiencing hypocalcemia? (Select all that apply.)
1. Allen test
2. Chvostek’s sign
3. Percussion of the abdomen
4. Auscultation of the lungs
5. Trousseau’s sign
6. Palpation of the neck
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Deficient Calcium Ion: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
5. A client is diagnosed with a serum calcium level of 11.2 mEq/L. Which of the following interventions would be appropriate for this client? (Select all that apply.)
1. Administer diuretics as prescribed.
2. Restrict fluids.
3. Administer intravenous fluids as prescribed.
4. Continuous cardiac monitoring.
5. Administer intravenous sodium as prescribed.
6. Change to a low fat diet.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Excess Calcium Ion: Planning and Implementation
6. Which of the following components of the arterial blood gas will the nurse focus when on determining a client’s acid-base status? (Select all that apply.)
1. pH
2. PO2
3. PCO2
4. HCO3-
5. O2 Sat
6. Hgb
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Arterial Blood Gases
[Show More]