Causes include ingestion of alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs; can also be caused by a virus, bacteria, an autoimmune disorder
Treatment: Remove the offending agent!
Chronic Gastritis - ANSWER *H.Pylori is almost always a fac
...
Causes include ingestion of alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs; can also be caused by a virus, bacteria, an autoimmune disorder
Treatment: Remove the offending agent!
Chronic Gastritis - ANSWER *H.Pylori is almost always a factor
Causes: Person-to-Person, Fecal/Oral, Reservoir in water sources
Complications: PUD, Atrophic Gastritis, Gastric Adenocarcinoma, Mucosal Lymphoma, Decreased Acid, and Intrinsic Factor
PUD - Peptic Ulcer Disease - ANSWER Disorders of the upper GI Tract caused by the action of Acid and Pepsin.
Injury to the mucosa of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
Causes: *H.Pylori (HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS), NSAIDs, Stress, Smoking, and Genetics
Clinical Manifestations: Epigastric burning pain (relieved by food intake or antacids)
Complications: GI Bleeding and Perforation
Tx: Sulcralfate, PPIs, Avoid caffeine and alcohol
PUD - Ulcer Types: MOST COMMON - ANSWER Gastric Ulcer: Pain occurs on an empty stomach; may present soon after a meal
Duodenal Ulcer: Pain 2-3 hours after meal; relieved by food intake
Ulcerative Colitis (IBD - Inflammatory Bowel Disease) - ANSWER Chronic inflammation of the mucosa - rectal and colon - leading to large ulcers
Complications: *Bloody Diarrhea, Lower abdominal pain; *Exacerbations and Remissions
Treatment: Corticosteroids, Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Chron's Disease - ANSWER An immune-mediated disease that can affect any part of the digestive tract. There is NO CURE.
Complications: Granulomas, Fistulas, Ulcerations, Strictures, and Fibrosis
Bowel Obstruction Manifestations - Types - ANSWER Mechanical: Increased bowel sounds, abdominal pain, and N/V
Functional: Absent bowel sounds
Upper Jejunal: Vomiting, dehydration, and electrolyte depletion
Distal Small Bowel/Ilium: Constipation
What percentage of the pancreas is Endocrine function? - ANSWER 5% - Pancreas secretes hormones into the blood
*Exocrine function: Pancreas secretes digestive juice into the duodenum
Pancreatic Cancer - ANSWER About 2% of all CA; Ranks 4th among malignant deaths.
Risks: Smoking, Obesity
Manifestations: Jaundice, Malabsorption, weight loss, abdominal pain, nausea
Tx: Surgery, Chemo
Gastroesophageal Varices Management - ANSWER Varicies are a result of Portal Hypertension d/t Cirrhosis of the liver; Alcoholism and Viral Hepatitis
Dx: Endoscopy, Abdominal CT Scan, Upper GI Barrium
Tx: Fluids (NaCl), Administer Blood Products, Vasopressin IV, H2 Blockers, PPIs; Surgical Banding and Balloon Therapy
Diverticulosis - ANSWER Syndrome of "Outpouchings"/Herniations through the muscular layer of the colon.
*HIGH FIBER DIET
Diverticulitis - ANSWER Inflammation of the "Outpouchings"
*LOW FIBER DIET
Assessment of Kidney Disease - ANSWER Palpation of the CVA for pain/tenderness
*CVA = Costalvertebral Angle
Kidney Cancer S/S - ANSWER Is typically asymptomatic until advanced. Most common is CVA tenderness, hematuria, palpable abdominal mass, dyspnea, cough, bone pain secondary to metastasis
Dialysis Benefits and Risks - ANSWER Used for pts with ATN/CKD in stage 5 in order to remove metabolic waste and correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
Pts are at risk for Hypotension after treatment because they Hypertensive prior to treatment.
TYPES of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) - ANSWER PRERENAL: Conditions that diminish perfusion of the kidney - Hypovolemia, Hypotension, Heart Failure, Renal Artery Obstruction, Fever, Burns, Edema, Ascites, ACE Inhibitors, NSAIDs
POSTRENAL: Obstruction of the normal outflow of urine from kidneys - Renal Pelvis, Ureters, Bladder Outlet, Urethra
Causes: BPH, Kinked Catheter, Intra-abdominal Tumors, Strictures, Calculi
INTRINSIC/INTRARENAL: Primary dysfunction of the nephrons and the kidney itself! The most common problem within the renal tubules results in *ATN(Acute Tubular Necrosis). Causes of ATN: Nephrotoxic insults: Contrast Media, Sepsis, Vancomycin, Chemo; Lack of O2, Alcohol, Drugs
PHASES of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) - ANSWER PRODROMAL: *Insult to the kidney has already occurred. Serum BUN and Creatinine is ELEVATED.
OLIGURIC: Normal urine output of 50-400mL daily. Oliguria, Uremia, decreased GFR, Hypervolemia.
S/S: Fluid excess, Hyperkalemia, Uremic Syndrome, Metabolic Acidosis
POSTOLIGURIC: Termination of the Oliguric phase represents recovery. Urine volume increases, tubular function improves fluid volume deficit until kidneys recover.
Cystitis - ANSWER Acute onset of frequency, Urgency and Dysuria, Suprapubic Pain, Hematuria, Cloudy Urine. LOC in elderly could present as Dementia, as well as new-onset incontinence.
Toxic Causes of Intrarenal Kidney Injury - ANSWER Prolonged postrenal failure, blood transfusion reaction, antibiotics/antifungal, antiviral, *CONTRAST MEDIA, chemo drugs, recreational drugs, snake venom, environmental factors
Renin Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) and the relationship between the autoregulation and the kidneys - ANSWER Kidneys attempt to: Regulate Perfusion and Maintain GFR
Glomerulus - ANSWER Is located in the Nephron inside the kidney. It is also the site of fluid filtration
Gomerulonephritis - ANSWER Inflammation of the glomeruli within the kidney. Immune-mediated conditions that produce IgA Nephropathy, Berger's Disease: These are the most commonly diagnosed
What will be spilling into the urine? PROTEIN!
Characterized by abrupt onset of hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria, edema, and hypertension
Staph infection associated with glomerulonephritis
Type I Diabetes - ANSWER *Makes NO insulin. It is characterized by the destruction of B cells of the pancreas. It affects children and adolescents.
HYPERGLYCEMIA
Type II Diabetes - ANSWER *Insulin Resistant and is the most common type of diabetes. What is resistant to the insulin? CELLS and PERIPHERAL TISSUE.
Risks include: Obesity, Aging, Sedentary Lifestyle
Polys of Diabetes - ANSWER *Hyperglycemia: Polydipsia, Polyphasia, Polyuria
Cushing's Syndrome - ANSWER *Hypercortisolism: Characterized by mood swings, insomnia, Moon Face, Fine hair, Hirsutism, Truncal Obesity, Thin skin
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) - ANSWER A traumatic insult to the brain capable of producing physical, intellectual, emotional, social, and vocational changes. *Leading cause of death and disability in the U.S.
TBI - Primary Injury - ANSWER Result of the initial trauma or injury on brain cells.
Focal:Localized Injury
Polar: Caused by acceleration/deceleration movement of brain within the the skull: Double injury
Diffuse: Caused by movement of brain within the skull: Axonal injury
TBI - Secondary Injury - ANSWER Increases ICP and pt usually dies
Reperfusion Injury - ANSWER Secondary injury that occurs after reestablishing blood flow.
Tx/Therapy: Medication, Surgery to restore blood flow to blocked arteries
Increased Cranial Pressure (ICP) - ANSWER The pressure exerted by the contents of the cranium.
0-15 mm Hg
The volume of the cranium consists of CSF, Blood and Brain Tissue
The patient might be sedated. May need to raise the HOB and ensure there is no stimulation in the environment
What is the most sensitive indicator of altered brain function? - ANSWER Change in the patient's LOC!
Cerebrovascular Disease (CVA): Types of Stroke - ANSWER ISCHEMIC: Sudden occlusion of a cerebral artery secondary to thrombus formation or embolization. Insufficient blood flow to the brain tissue results in oxygen deprivation and rapid cerebral deterioration.
Thrombotic is r/t atherosclerosis and hypercoaguability
Embolic is r/t cardiac source
HEMORRHAGIC: Intracerebral brain bleed
Diagnosed by CT Scan!
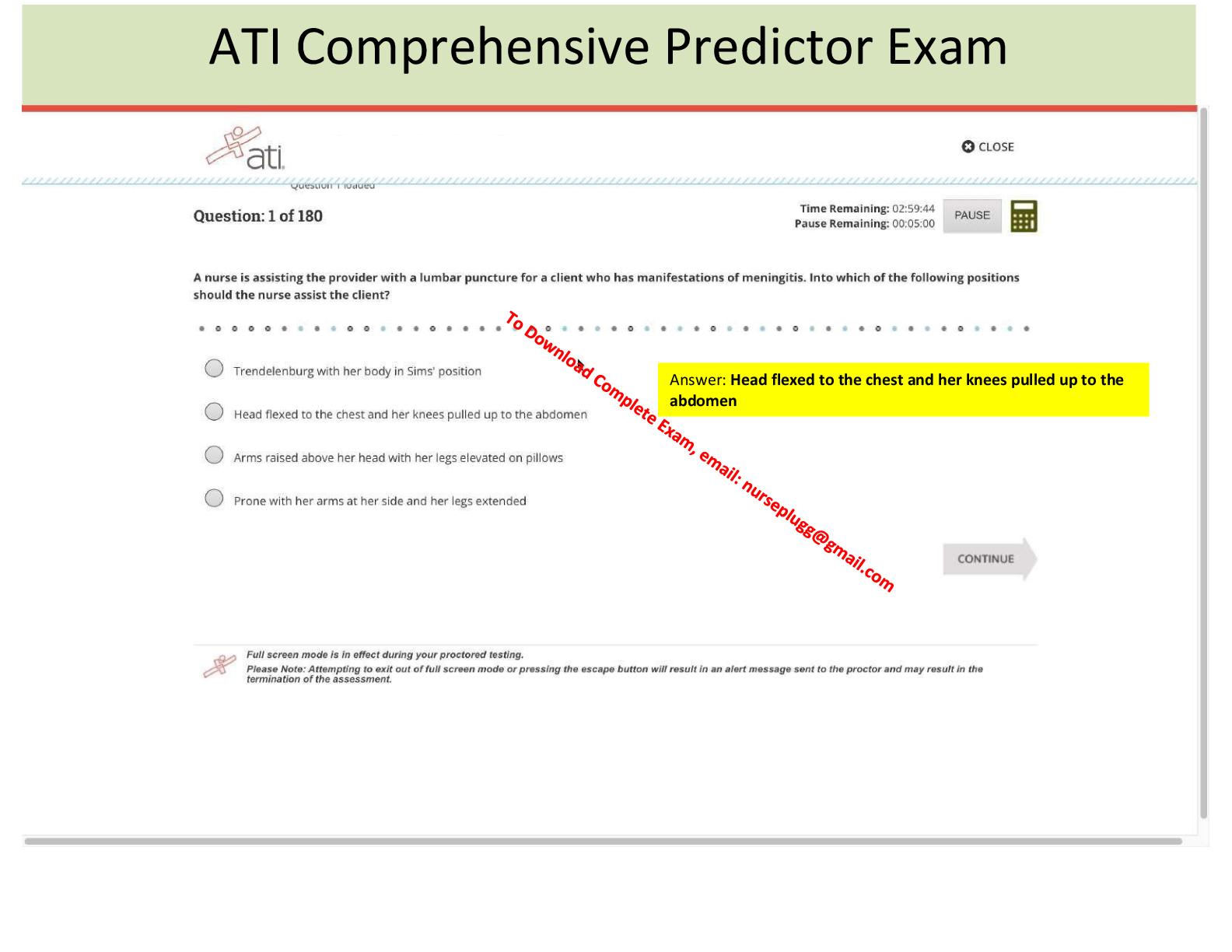
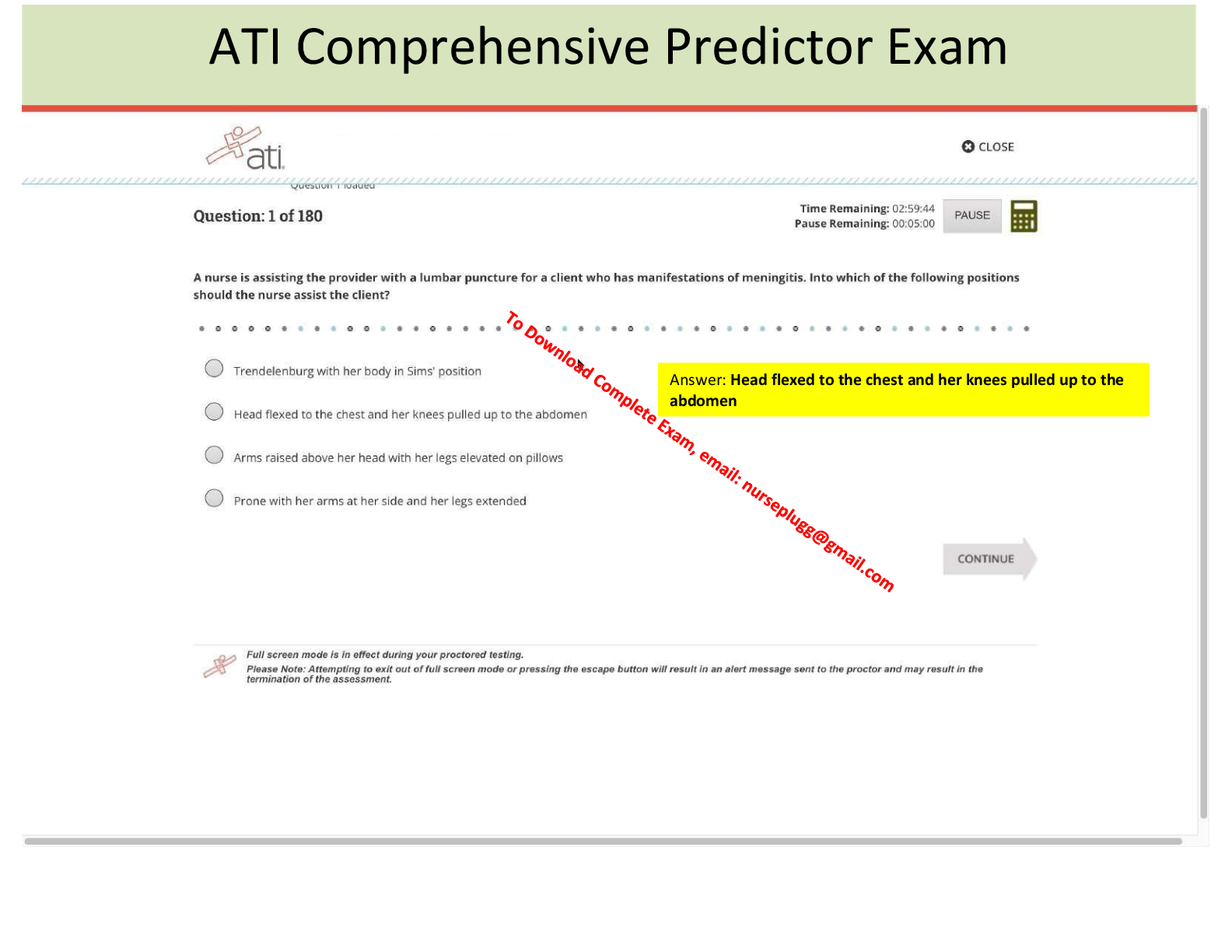
Meningitis - ANSWER Inflammation of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord.
Microbial invasion of the CNS.
Streptococcus Pneumoniae is the most common bacterium.
Bacteria reaches the CNS via the bloodstream, para-nasal sinuses or ears
Encephalitis - ANSWER Inflammation of the brain usually caused by a virus.
Herpes Virus is the most common viral cause.
Glascow Coma Scale (GCS) - ANSWER A neurological scaled used to determine the level of consciousness of a patient.
Mild 13-15
Moderate 9-12
Severe 8 or below
Seizure Disorders: Classifications - ANSWER Generalized: Whole-brain surface is affected
Absence (Petit-Mal): Kids, Staring spells
Atypical Absence: Myoclonic Jerks
Myoclonic: Single to Several Jerks
Atonic: DROP attack/Fall down
Tonic-Clonic (Grand-Mal): Jerking/Many Muscles
Status Epilepticus - ANSWER Back-to-Back Seizures with no recovery in between episodes
Dementia - ANSWER A slowly progressive decline in mental abilities, including memory, thinking, and judgment, that is often accompanied by personality changes
What is NOT a clinical manifestation of HYPONATREMIA? - ANSWER THIRST
T or F: Thirst is a clinical manifestation of HYPERnatremia - ANSWER True
What electrolytes are affected by the kidney's inability to regulate? - ANSWER Potassium, Phosphorous, Magnesium
Hypoventilation is a build up of what? - ANSWER PaCO2
What is the goal for a pt with ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) - ANSWER Keep the pts PaO2 value >60!
What is the tx for Tension Pneumothorax? - ANSWER Emergent needle aspiration/decompression
*Chest tube placement with H2O seal
Pneumonia - ANSWER Inflammatory reaction in the alveoli and interstitium of the lung.
*Can result from 3 sources:
1. Aspiration of Oropharyngeal secretions composed of normal bacterial flora and/or gastric contents
2. Inhalation of contaminants (virus-Mycoplasma)
3. Contamination from the systemic circulation
Classifications: Community or Hospital-Acquired, bacterial, atypical, and viral.
Risks: Elderly, pts with a diminished gag reflex, critically ill, pts hospitalized, hypoxic pts, immunocompromised pts
C.Manifestations: Chills, cough, fever, headache, malaise
Dx: Chest x-ray, Sputum C&S, WBC>15,000
Tx: Antibiotic Therapy
[Show More]