Computer Science > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU C857 Software Quality Assurance - Study Guide (All)
WGU C857 Software Quality Assurance - Study Guide
Document Content and Description Below
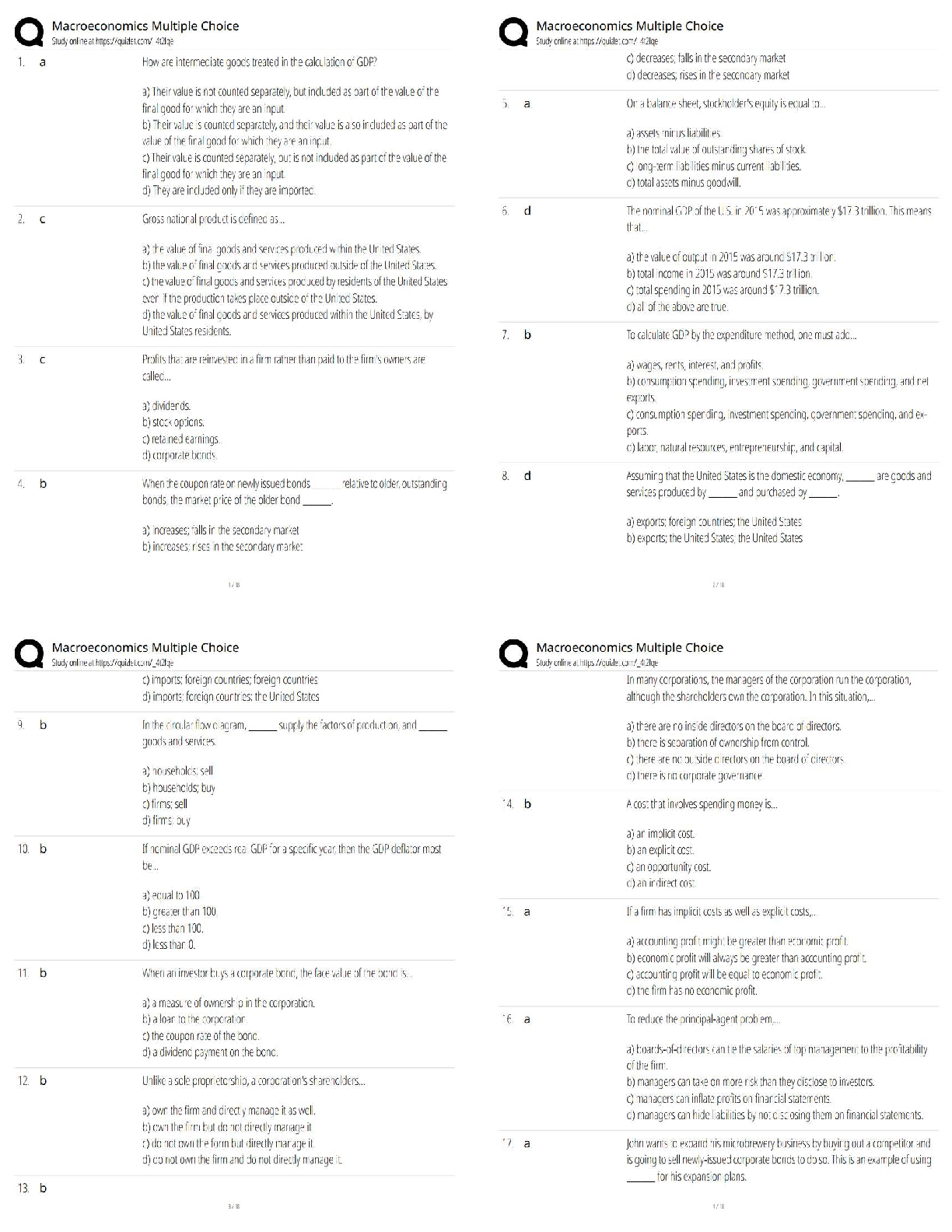
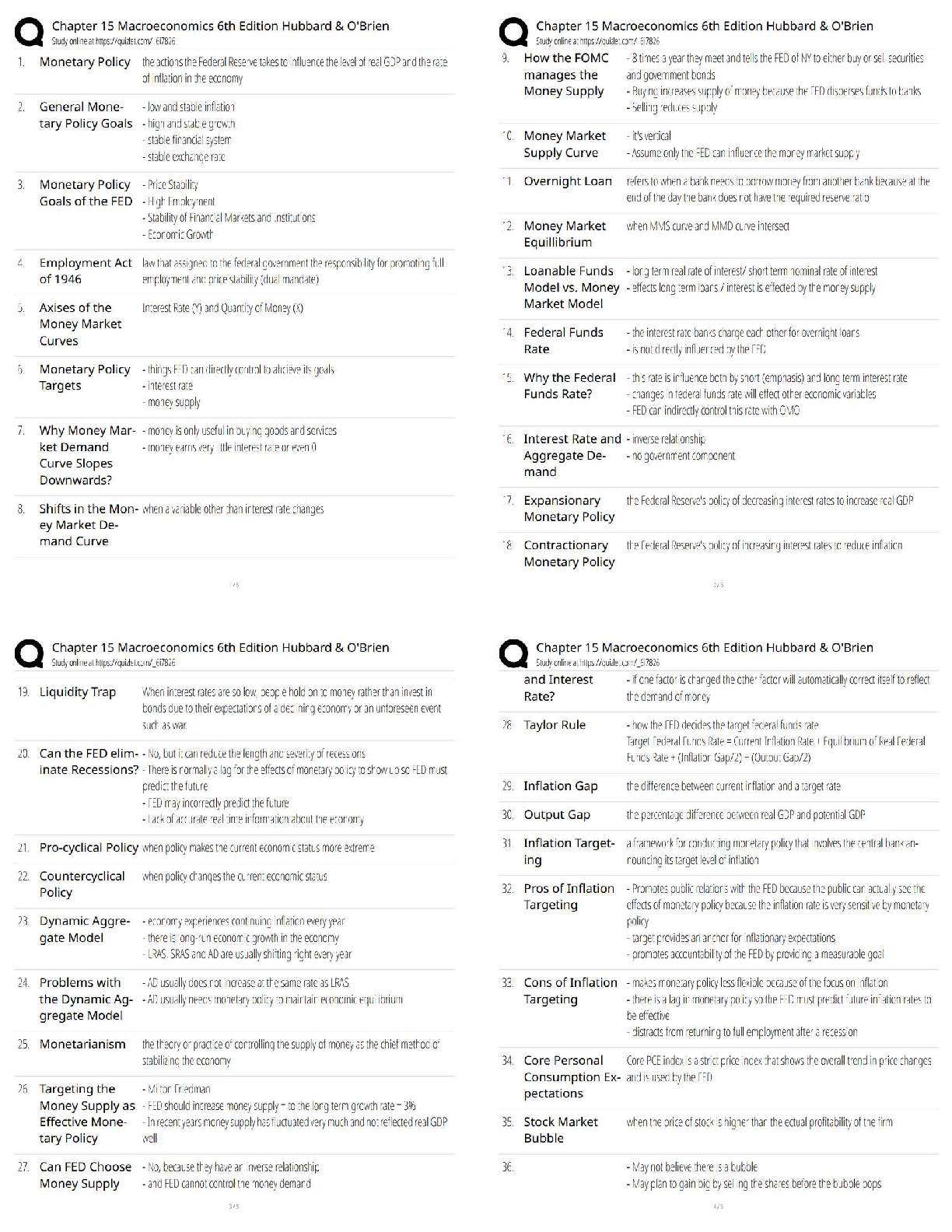
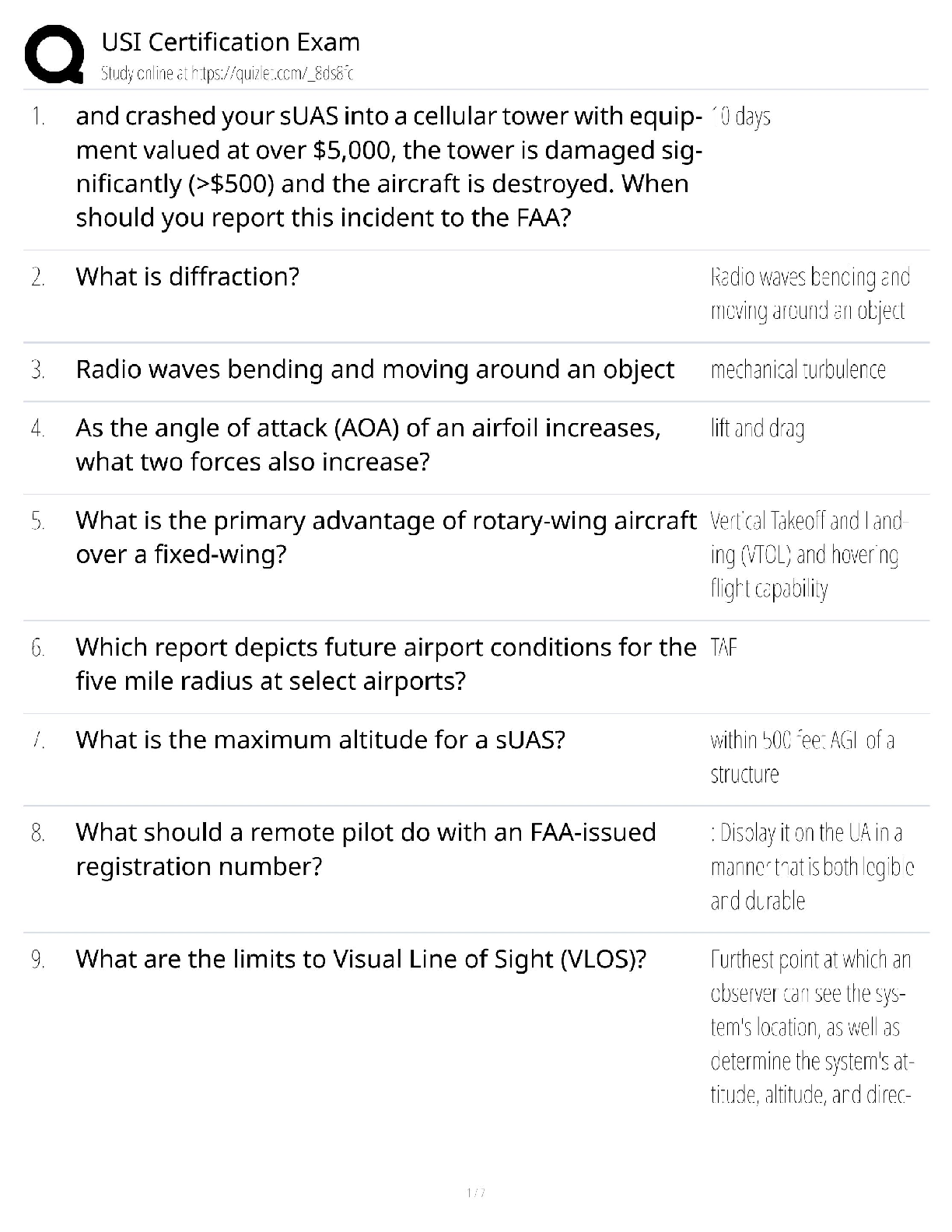
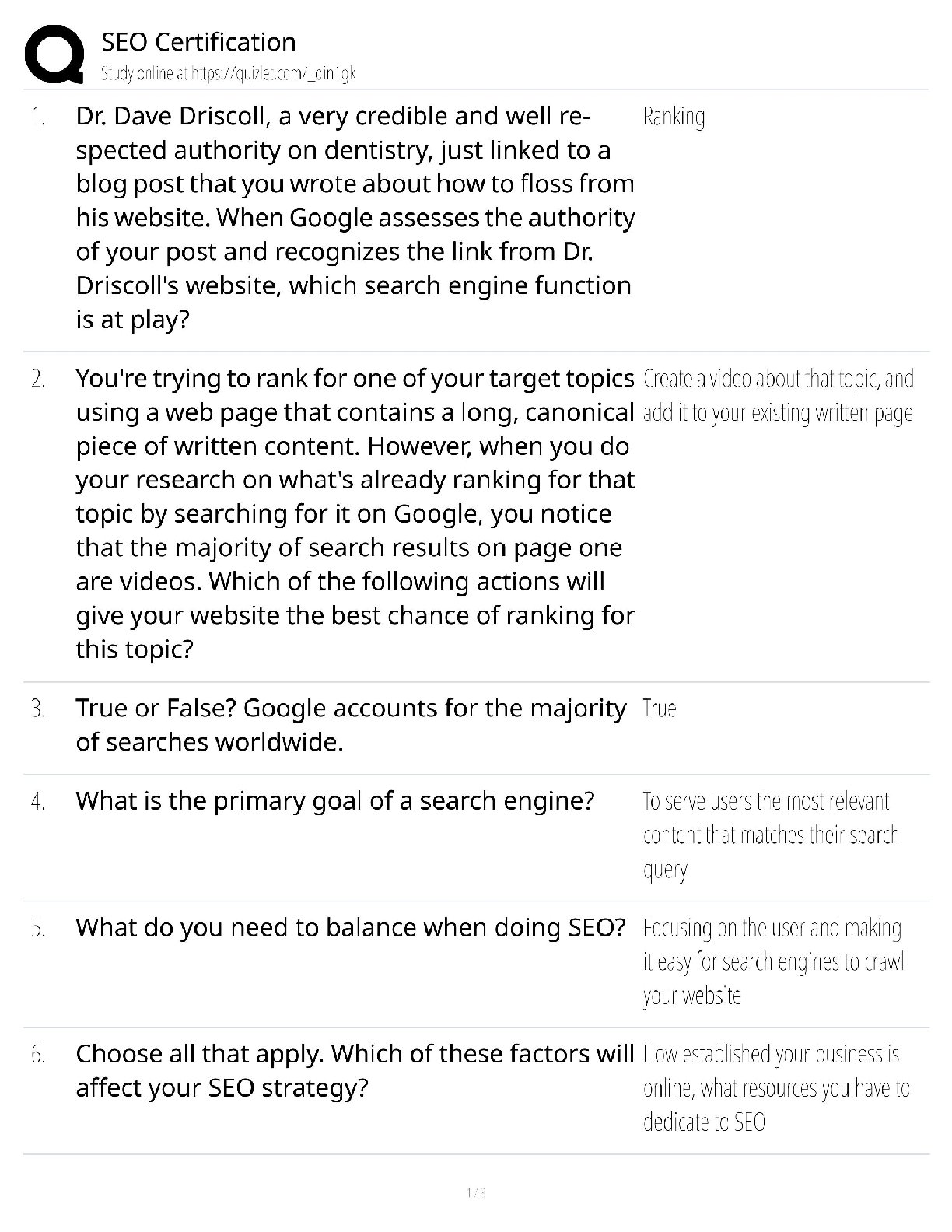
WGU C857 Software Quality Assurance - Study Guide Why should we conduct reviews? -Answer- Detect defects... Reduce costs to build and maintain better products... Reduce development time...Reduce ... testing cost and time... Reduce total system maintenance cost dramatically (as much as 10 to 1 according to recent statistics). Why should we conduct reviews? -Answer- Remove defects as close to the point of insertion as possible. Why should we conduct reviews? -Answer- Determine product progress/status. Why should we conduct reviews? -Answer- Identify potential improvements. Why should we conduct reviews? -Answer- Produce technical work of a more uniform and predictable quality. Why should we conduct reviews? -Answer- Assist employees with cross-training. The objectives of buddy checks include? -Answer- Improve the life-cycle work product... Consider alternative implementations... Exchange techniques and style variations... Point out problems with clarity and understandability... What is a buddy check? -Answer- A buddy check is normally thought of as an informal verification technique in which the life-cycle work product is examined by the author and one other person. What is a buddy check? -Answer- Allow the author to look at the life-cycle work product from a different "angle" or point of view... What is a buddy check? -Answer- Mentoring of others in the concepts embedded in the life-cycle work product. What is a circulation review? -Answer- Circulation reviews take on attributes of both buddy checks and walkthroughs. Circulation reviews can be informal or follow strict rules. The life-cycle work product is circulated to each reviewer who reviews it and either attaches comments, questions, and recommendations directly on the life-cycle work product or places them into a separate document. The objectives of circulation reviews include: •Improve the life-cycle work product; •Consider alternative implementations; •Point out problems with clarity and understandability; •Point out areas of concern and offer comments and suggestions; •Gain consensus from a large population of reviewers; •Gain input from valuable contributors who cannot be present for a face-to-face review. What is a technical review? -Answer- A technical review is a formal team evaluation of a life-cycle work product to identify any discrepancies from specifications and standards, determine its suitability for use, and provide recommendations after the examination of various alternatives. The objectives of technical reviews are to ensure that: •The life-cycle work product conforms to its specifications; •The development or maintenance of the life-cycle work product is being done according to plans, standards, and guidelines applicable to the project; •Changes to the life-cycle work product are properly implemented and affect only those areas of the system identified by the change specification. What is an inspection? -Answer- An inspection is a formal verification technique in which life-cycle work products are examined in detail by a group of peers for the explicit purpose of detecting and identifying defects. The process is led by a moderator or facilitator or inspection leader who is not the author and is impartial to the life-cycle work product under review. The author is not allowed to act as the moderator. Written action on all major defects is mandatory. Rework due to corrections of major defects is formally verified. Defect data is systematically collected and stored in an inspection database. This defect data is analyzed to improve the product, the process, and the effectiveness of the inspection process. The objective of an inspection is to detect and identify life-cycle work product defects in a rigorous, formal, peer examination that does the following: •Verifies that the life-cycle work product satisfies both its specification and preceding intermediate work products. •Verifies that the life-cycle work product conforms to applicable standards. •Identifies real or potential deviations from standards and specifications. •Collects engineering data (i.e., defect and effort data). •Does not examine alternatives or stylistic issues. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

WGU C857 FULL SOLUTION PACK(ALL WGU C857 EXAMS AND STUDY QUESTIONS ARE HERE ,ALL ANSWERED CORRECTLY)
WGU C857 Software Quality Assurance – Preassessment 2022 with complete solution Software QA C857 WGU Latest 2022 Rated A+ WGU C857 Software Quality Assurance - Questions and Answers Already Pass...
By Excel 3 years ago
$15
9
Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 23, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 23, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
178