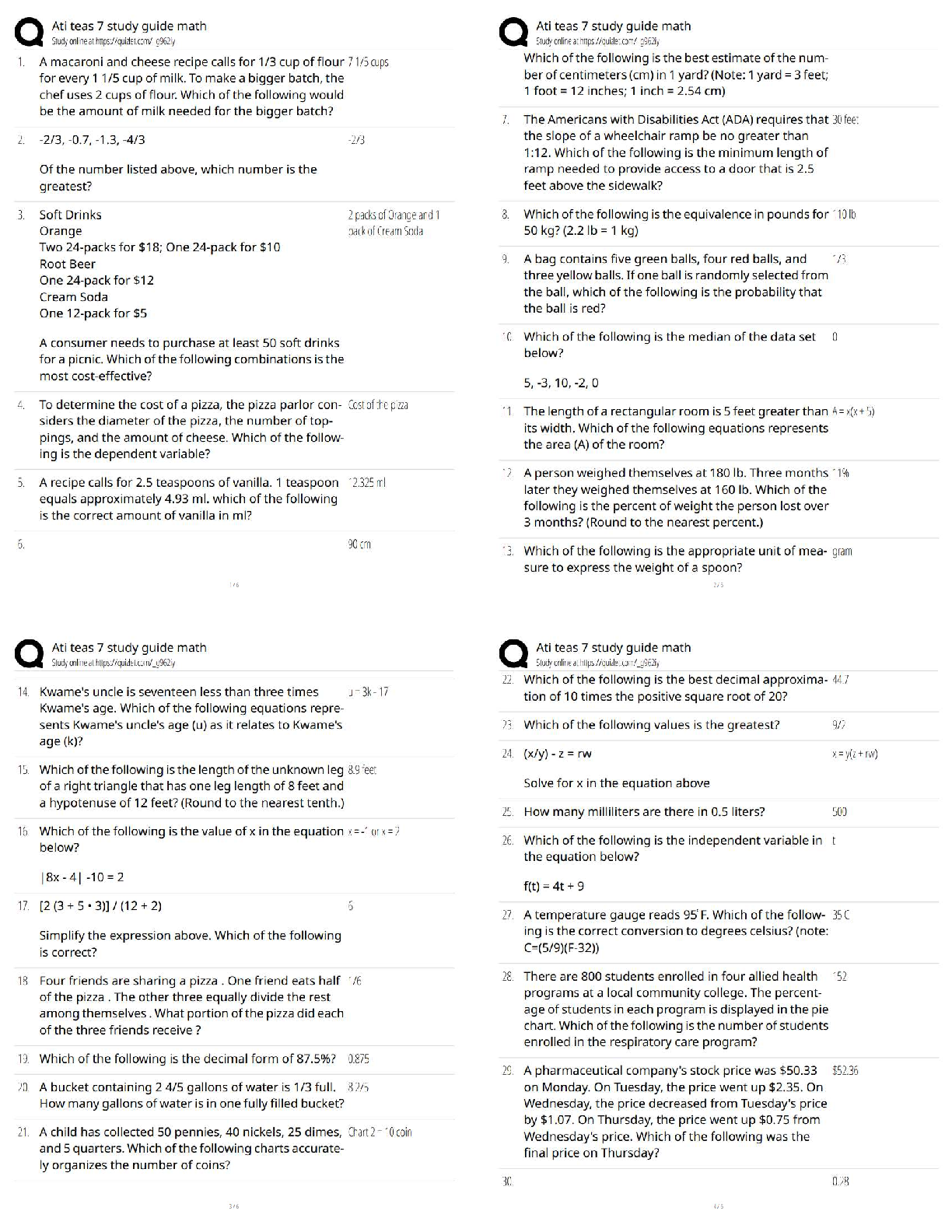
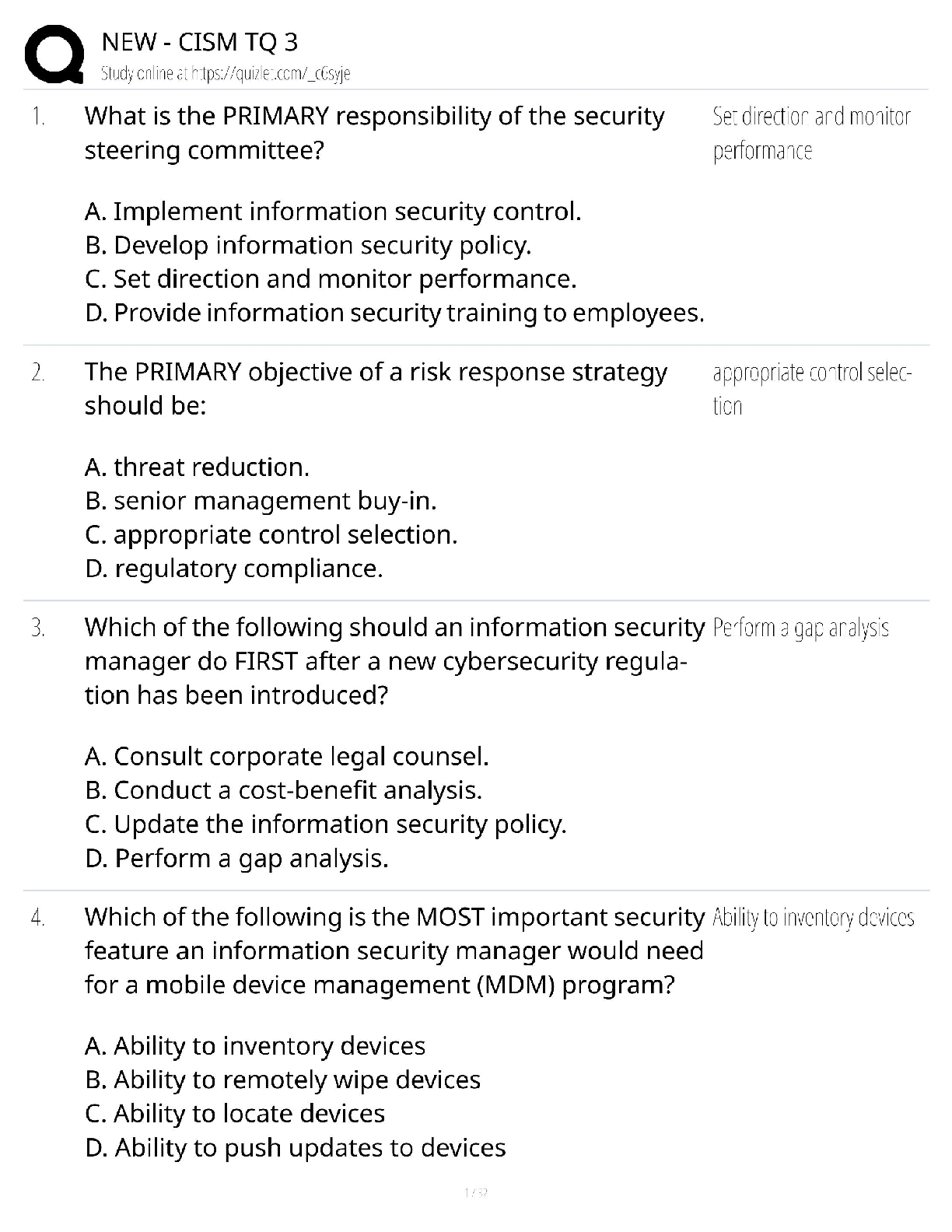
Microbiology - Portage Module 2
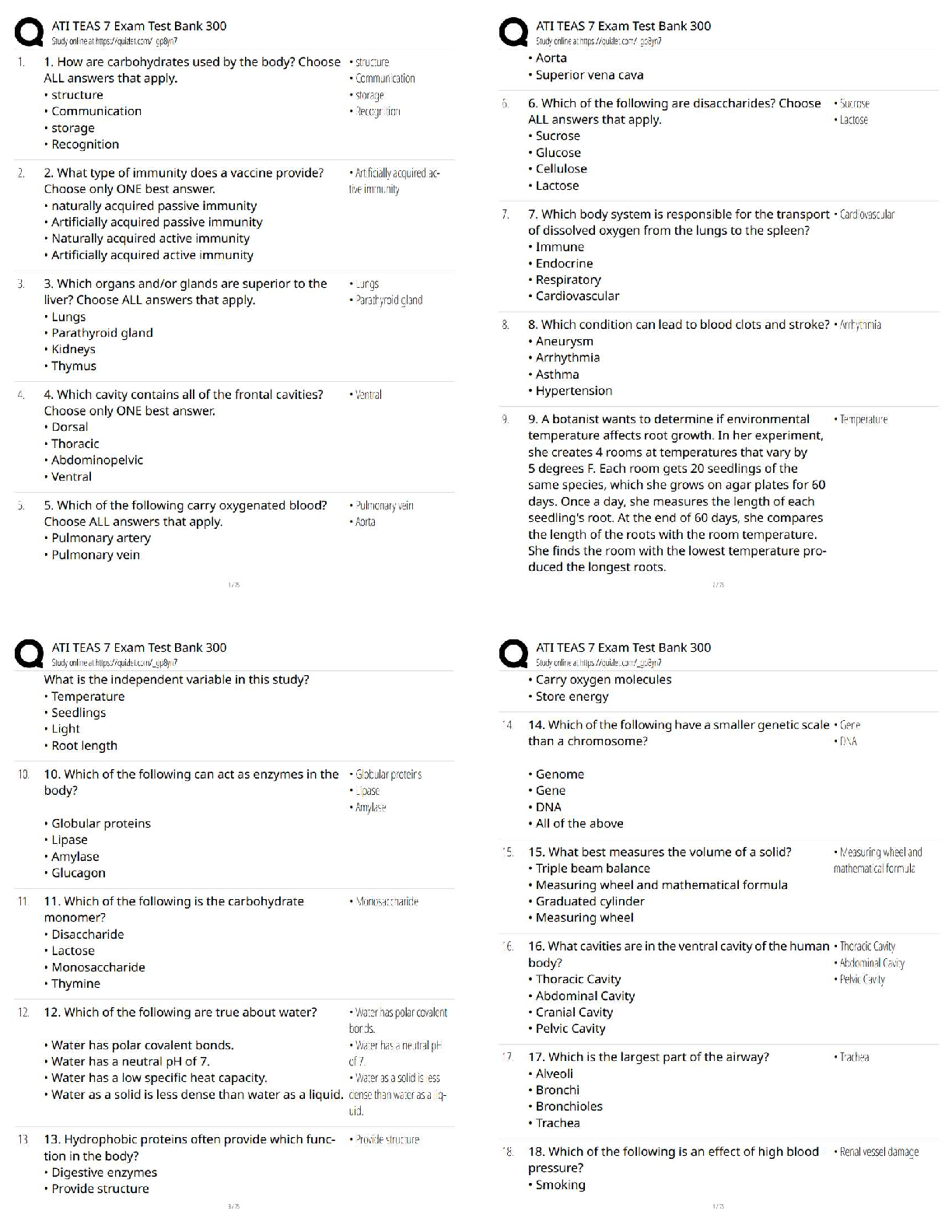
Metabolism Already Passed
What is cellular metabolism? ✔✔a controlled set of biochemical reactions that occur in living
organisms in order to maintain life
What is an enzyme? ✔✔a prote
...
Microbiology - Portage Module 2
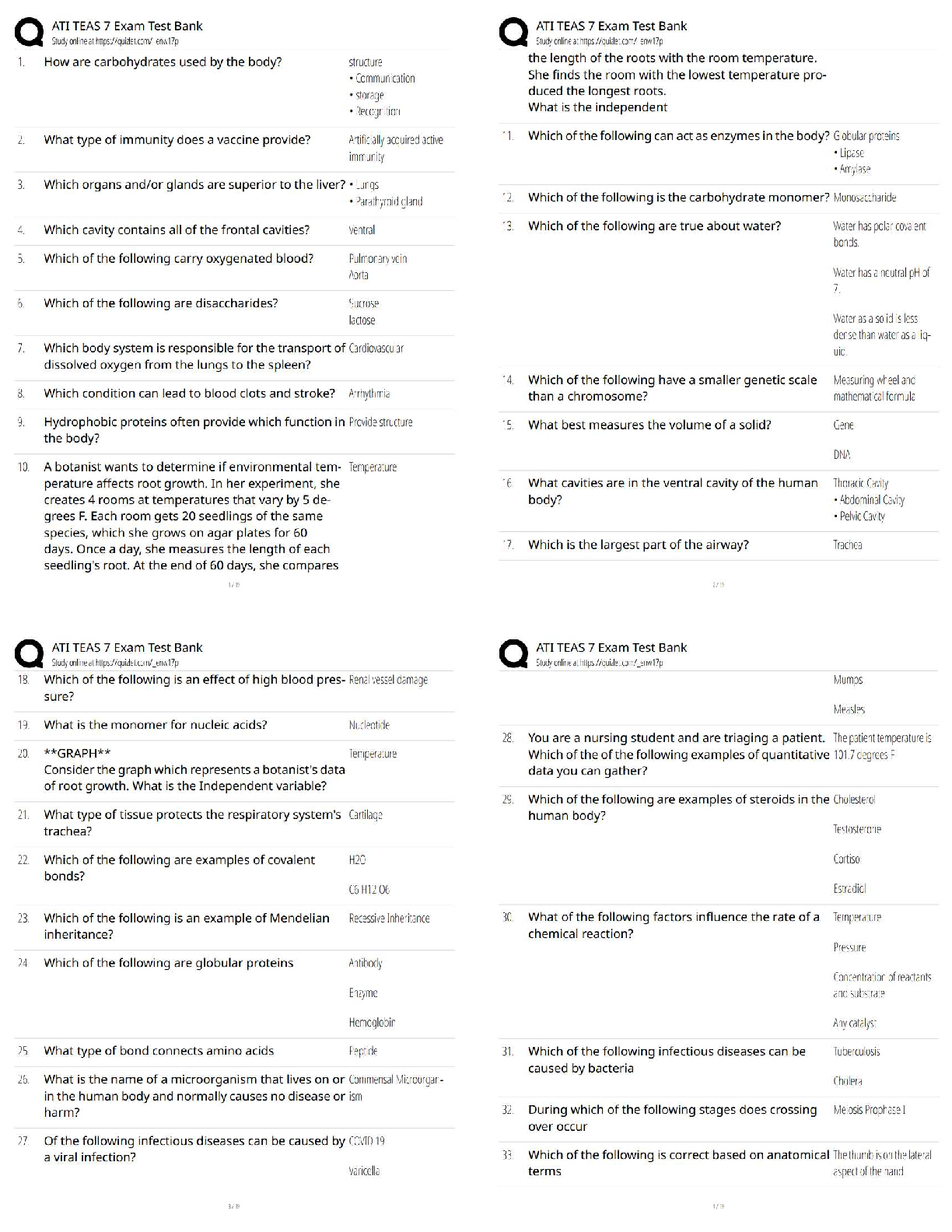
Metabolism Already Passed
What is cellular metabolism? ✔✔a controlled set of biochemical reactions that occur in living
organisms in order to maintain life
What is an enzyme? ✔✔a protein, or group of proteins, that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions
What is unique about enzymes? ✔✔the enzyme is not consumed during the reaction and can be
used repeatedly by the cell
What is a cofactor? ✔✔a small chemical component, usually metal ions, that assist enzymes during
the catalysis reactions
Do cofactors serve as regulators of chemical reactions? ✔✔Yes
In the absence of the proper cofactor what happens? ✔✔enzymes are inactive
In the presence of the proper cofactor what happens? ✔✔enzymes are active
In order to produce sufficient levels of energy what must microorganisms do? ✔✔microorganisms
must break down complex nutrients into smaller, manageable (and useful) subunits
What 3 things must enzymes break down into smaller subunits? ✔✔Enzymes must break down
proteins, lipids and polysaccharides into their smaller building-block molecules
Fats or lipids get broken down into what? ✔✔glycerol/fatty acids
Most metabolic processes can be classified as either of what 2 things? ✔✔catabolism or anabolism
What is catabolism? ✔✔the process of breaking down larger molecules into useful energy sources
What is anabolism? ✔✔the building up or biosynthesis of macromolecules from smaller molecular
units into larger complexes
The anabolic process is often used during what? ✔✔growth and repair phases of the cell.
What would happen to cells without enzymes? ✔✔Without enzymes and their ability to increase
the rate of a specific chemical reaction, these reactions would take too long and exhaust too much
energy. If a cell runs out of energy before the necessary reactions conclude, it dies.
What is the most widely used form of energy in the cells? ✔✔adenosine triphosphate or ATP
Compare ATP to ADP ✔✔ATP has energy to donate while ADP can accept energy (phosphate
group) to become ATP
How does ATP work and help give the cell energy? ✔✔By donating available phosphate groups,
ATP transfers energy from catabolic (breaking down) reactions to be used for anabolism (building
up). This process of donating and/or accepting energy is what fuels a cell to carry out the necessary
biochemical reactions for survival.
The way in which microbes produce ATP, specifically the starting source of electrons, tells us
what? ✔✔It can also be used as a means to further differentiate and characterize microorganisms
How does a Phototroph acquire energy? ✔✔It acquires energy from photons of light to generate
ATP from ADP
How does a chemotroph acquire energy? ✔✔It acquires energy from preformed (already existing)
chemicals found in the environment
What are the two types of chemotrophs? ✔✔organotrophs and lithotrophs
What is an organotroph? ✔✔It removes electrons from organic molecules such as glucose
What is a lithotroph? ✔✔It removes electrons from inorganic molecules such as elemental sulfur.
In order to carry out metabolic processes must microbes also have a source of carbon? ✔✔Yes
What does the source of carbon tell us about the microbe? ✔✔Where this source of carbon comes
from may also be used to further classify microbes
What is a heterotroph? ✔✔A microorganism that derives its carbon from organic molecules such
as sugars
What is an autotroph? ✔✔organisms that derive their carbon from inorganic molecules, most often
from carbon dioxide (CO2)
Define phosphorylation ✔✔the addition of a phosphate group—that turns ADP into ATP.
Name the three types of phosphorylation ✔✔Photophosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
What is Photophosphorylation? ✔✔light energy is used to power the formation of ATP from ADP
What is Substrate-level phosphorylation? ✔✔the phosphoryl (PO3) group of a chemical
compound is transferred and donated (added) directly to ADP. The chemical compound losing the
phosphate group is referred to as the phosphorylated reactive intermediate
What is Oxidative phosphorylation? ✔✔used by chemotrophs, the energy released by the chemical
oxidation of nutrients is used to reform ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic
cells and is highly efficient.
What is the chemical formula for glucose? ✔✔C6H12O6
The complete catabolism of a single molecule of glucose yields how many ATP? ✔✔up to 38 ATP
The complete catabolism of a single molecule of glucose involves how many distinct transitions?
✔✔3
Name the 3 distinct transitions of the catabolism of glucose. ✔✔glycolysis
either fermentation or respiration
electron transport chain
How many ATP is produced from glycolysis? ✔✔2 ATP
How many ATP is produced from either fermentation or respiration? ✔✔2 ATP
How many ATP is produced from electron transport chain? ✔✔34 ATP
What are reactants? ✔✔Any molecules present and involved at the beginning of a chemical
reaction are called reactants.
What are the reactants for glycolysis? ✔✔glucose
2 NAD
2 ATP
What is NAD? ✔✔It is an electron carrier molecule. It is a coenzyme called nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide (NAD)
What is the initial input of ATP quickly used to do? ✔✔phosphorylate glucose
What is the phosphorylation of glucose called? ✔✔glucose-6-phosphate aka G6P
What is a product of a reaction? ✔✔molecules located to the right of the arrow
What are the products of glycolysis? ✔✔2 pyruvate molecules
2 NADH molecules
2 ATP
2 H+
What is the formula for glycolysis? ✔✔Glucose + 2 NAD+ + [2 ADP + 2 Pi]→ 2 Pyruvate + 2
NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H+
NAD/NADH plays a vital role in what? ✔✔generating a
[Show More]
.png)

.png)