Portage Learning: Microbiology Module
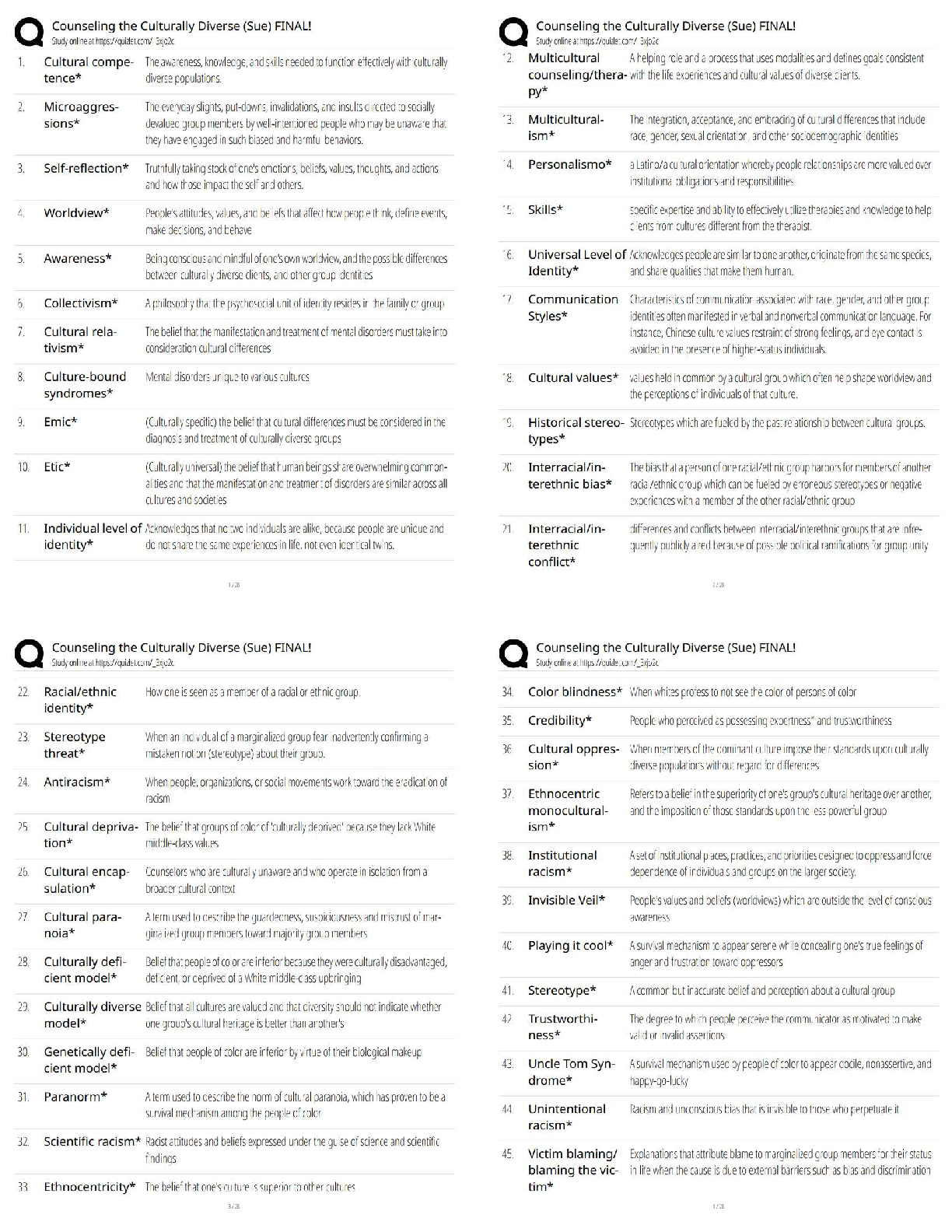
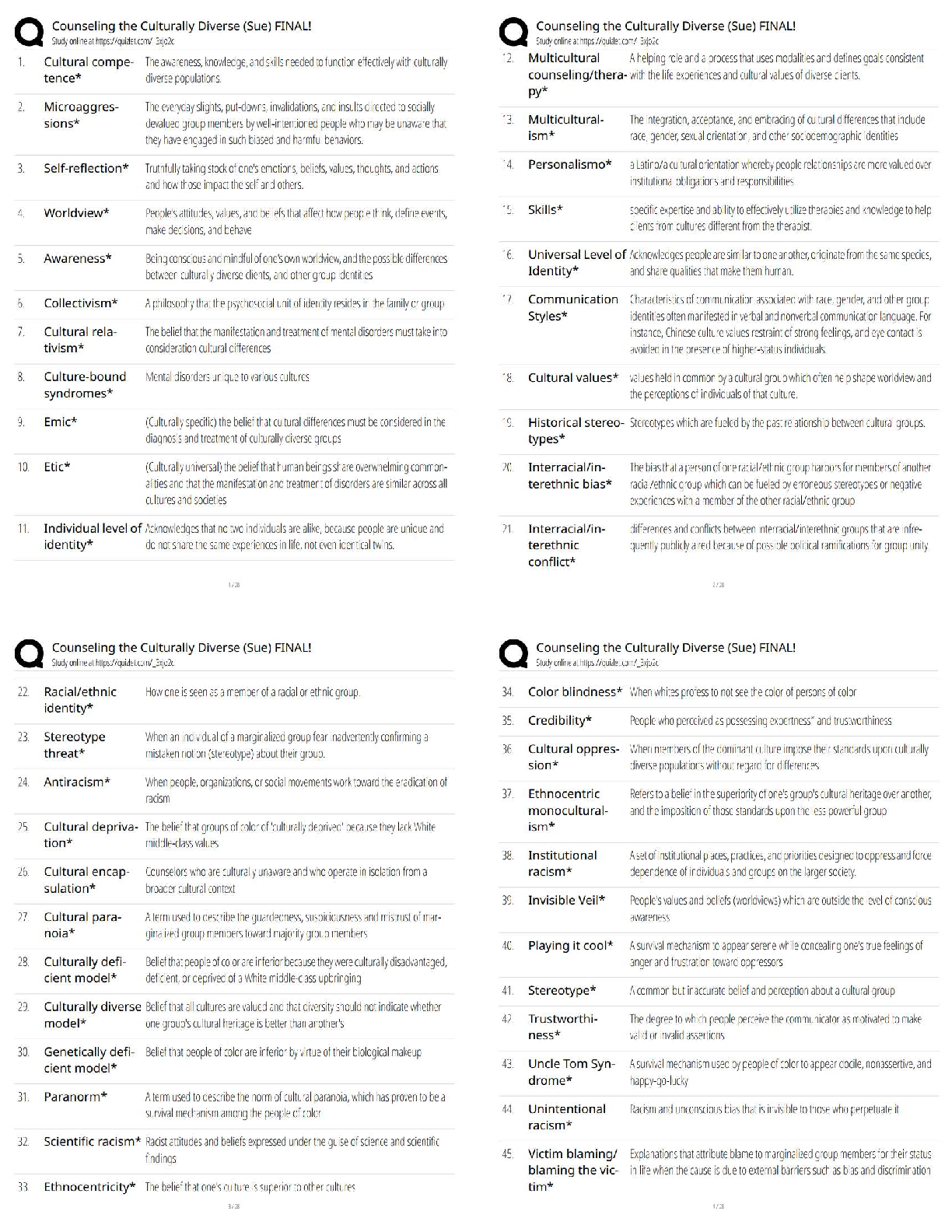
3 Latest 2022
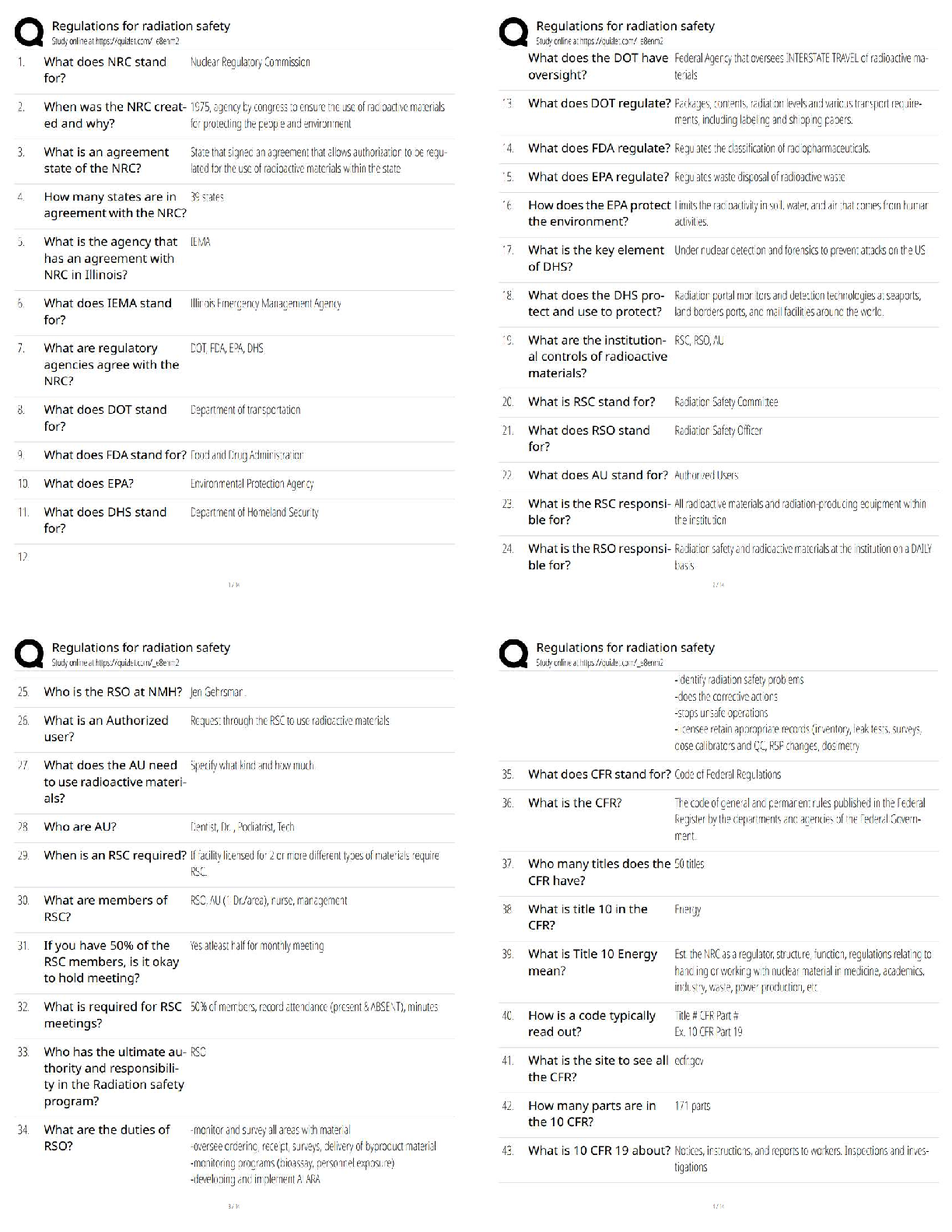
Define the measurements micrometer and nanometer. ✔✔A micrometer (µm) is defined as being
one-millionth of a meter and is commonly designated at 10-6 meters. A nanom
...
Portage Learning: Microbiology Module
3 Latest 2022
Define the measurements micrometer and nanometer. ✔✔A micrometer (µm) is defined as being
one-millionth of a meter and is commonly designated at 10-6 meters. A nanometer (nm) equals
10-9 m or one-billionth of a meter.
What are the two critical factors that influence your ability to see an object? ✔✔Resolution and
contrast. Resolution refers to the distance between two objects at which the objects still can be
seen as separate. Poor or low resolution means two (or more) objects may appear as one. The
contrast is the difference in light absorbance between two objects. Poor contrast gives a high
background and makes the visualization of multiple objects difficult. For instance, trying to
identify 2 dark colored objects at night (low light = low contrast) versus the same 2 objects in the
middle of a sunny afternoon (bright light against 2 dark objects = high contrast).
If you wish to increase the amount of light going into a microscope, what part would you adjust?
✔✔The iris diaphragm controls the amount of light that passes through the sample and into the
objective lens. Thus, as you open the iris more light is permitted to pass through to illuminate the
sample.
As light passes through a microscope, what is the last piece that light passes before reaching your
eyes? ✔✔Once light passes through the sample and the objective lens it is directed through the
ocular lens, or eyepiece, directly into your eye.
How is the total magnification of an object calculated? ✔✔Total magnification is calculated by
multiplying the power of the objective and the power of the eyepiece. For instance, a 40x objective
with a 10x eyepiece would make an object appear (40 x 10) 400 times larger (400x).
What is one limitation of fixing your sample? ✔✔Fixation requires you to irreversibly kill your
sample. Thus, determining the motility (cell movement) of a sample is impossible. Fixation also
runs the risk of distorting the specimen shape and arrangement.
Phase-contrast microscopy provided what benefits to imaging? ✔✔Phase contrast microscope can
provide detailed images of live cells without staining. By using specialized condensers and
objectives, a phase contrast microscope amplifies the slight differences between cells and the
surrounding medium (background) to make the cells highly distinguishable.
What is the distinguishing feature of dark field microscopy? ✔✔Unlike bright field or phase
contrast microscopy where light passes directly through the sample, dark field microscopy reflects
light off of the specimen at an angle. The resulting image is an exceptionally dark background and
a vibrant specimen.
Unlike brightfield microscope, fluorescence microscopes illuminate samples through what
spectrum? ✔✔The energy of the incoming light is in the form of the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum.
What is the primary difference between TEM and SEM? ✔✔During transmission electron
microscopy the electron passes through the sample whereas during scanning electron microscopy
the electron is reflected off the sample creating a three dimensional 'shell' model of the specimen.
Gram staining is based on what basic principle? ✔✔Gram staining, developed by Hans Christian
Gram in 1884, began with the basic observation that different types of bacteria react differently to
various dyes. Some bacteria readily take up a specific dye while others do not.
What is a key determinant in a bacteria being Gram-positive? ✔✔Gram-positive bacteria have a
thick peptidoglycan layer. The Gram stain exploits this characteristic by using the dye
combinations of Crystal violet and Iodine. Crystal violet is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell
wall and forms a stable complex with iodine (upon its addition) effectively trapping the dyes in
the cell. The resulting mixture is a purple coloration of the cell.
What is the purpose of heat fixing a sample? ✔✔Heat fixing ensures the samples tightly adhere to
the glass slide prior to staining (and washing) procedures.
What is the primary purpose of a wet mount? ✔✔Wet mounts are most often performed to
visualize live cells as well as the motility and behavior of an organism.
The acid-fast stain is most often used to identify what specific microorganism? ✔✔Acid-fast stains
are used to identify bacterial stains showing a high degree of resistance to decolorization.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the most common use for an acid-fast stain.
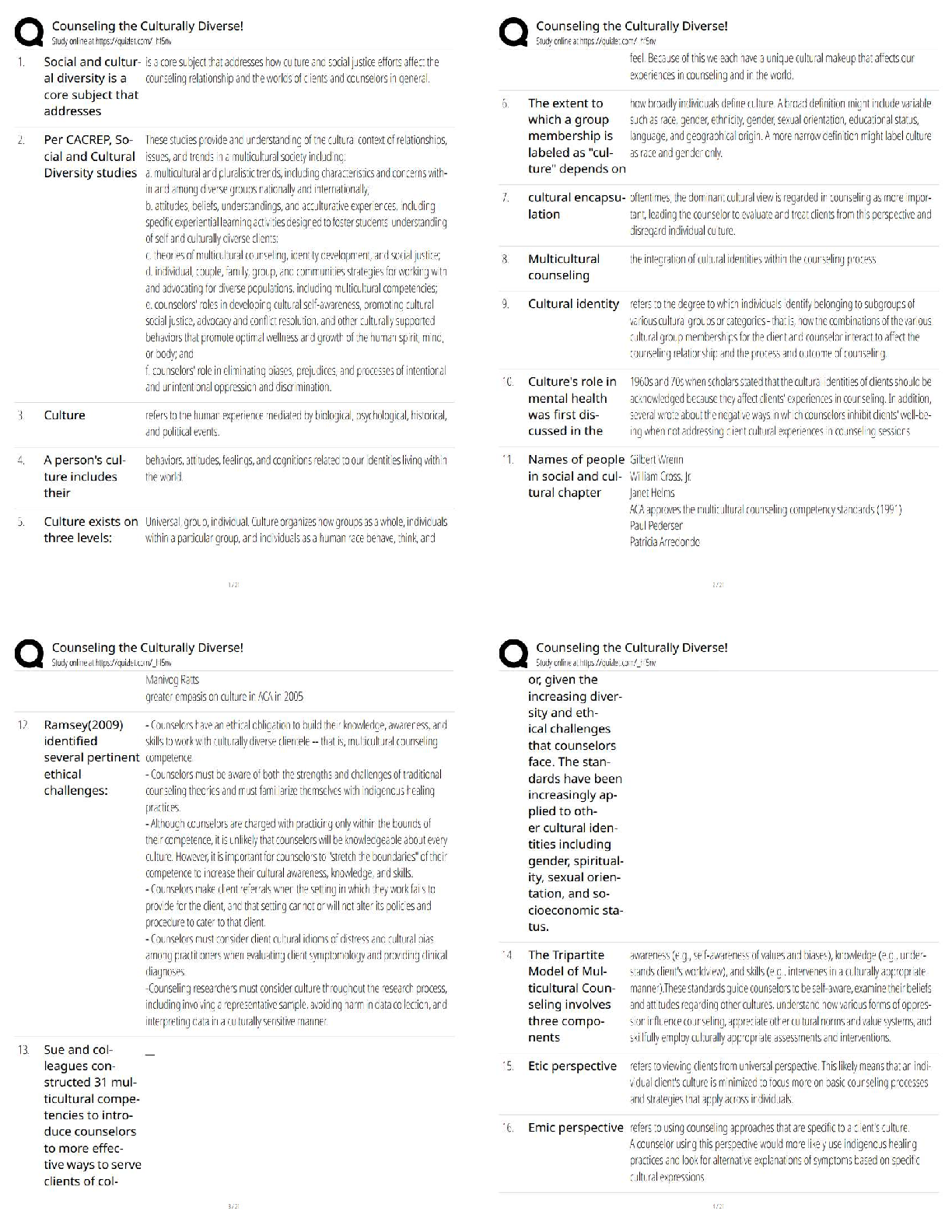
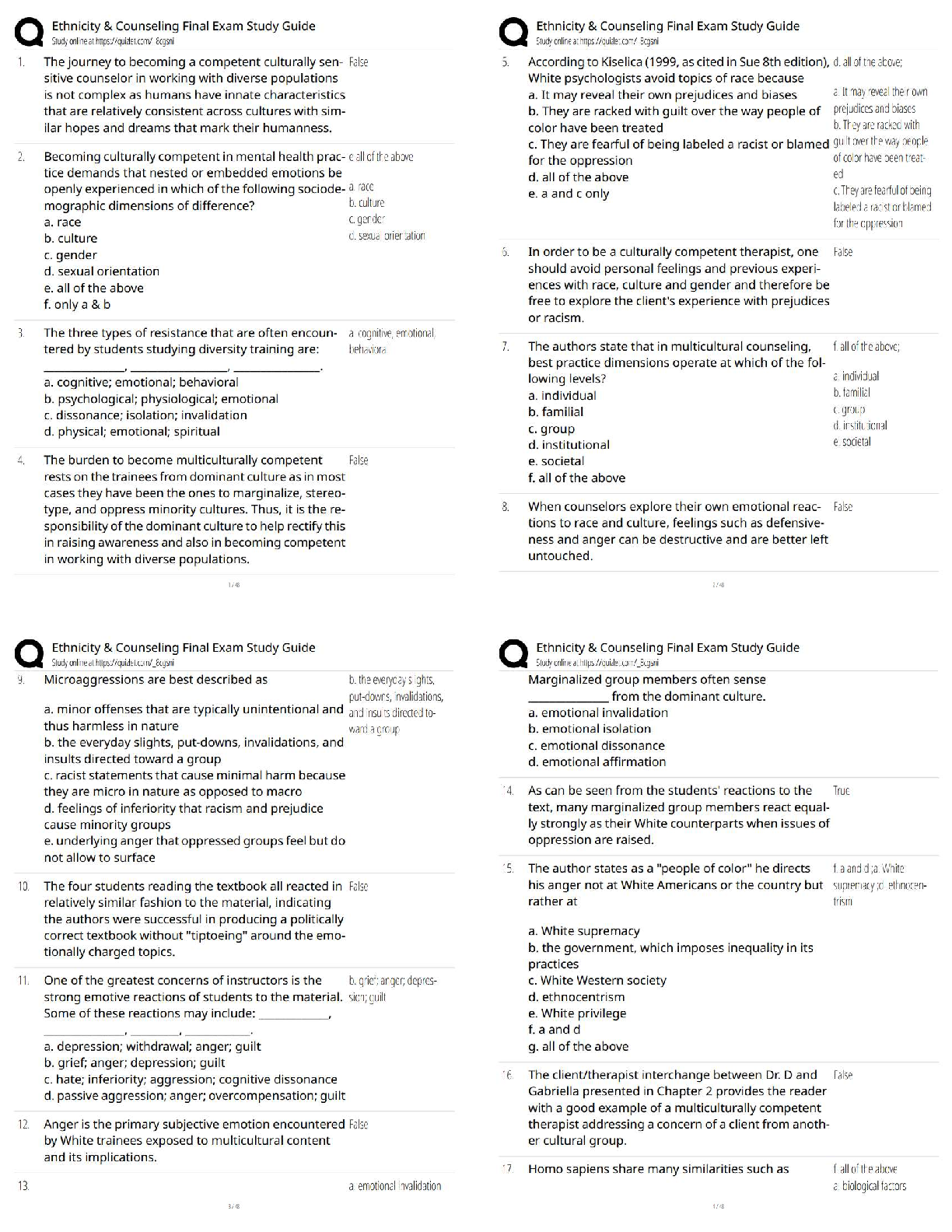
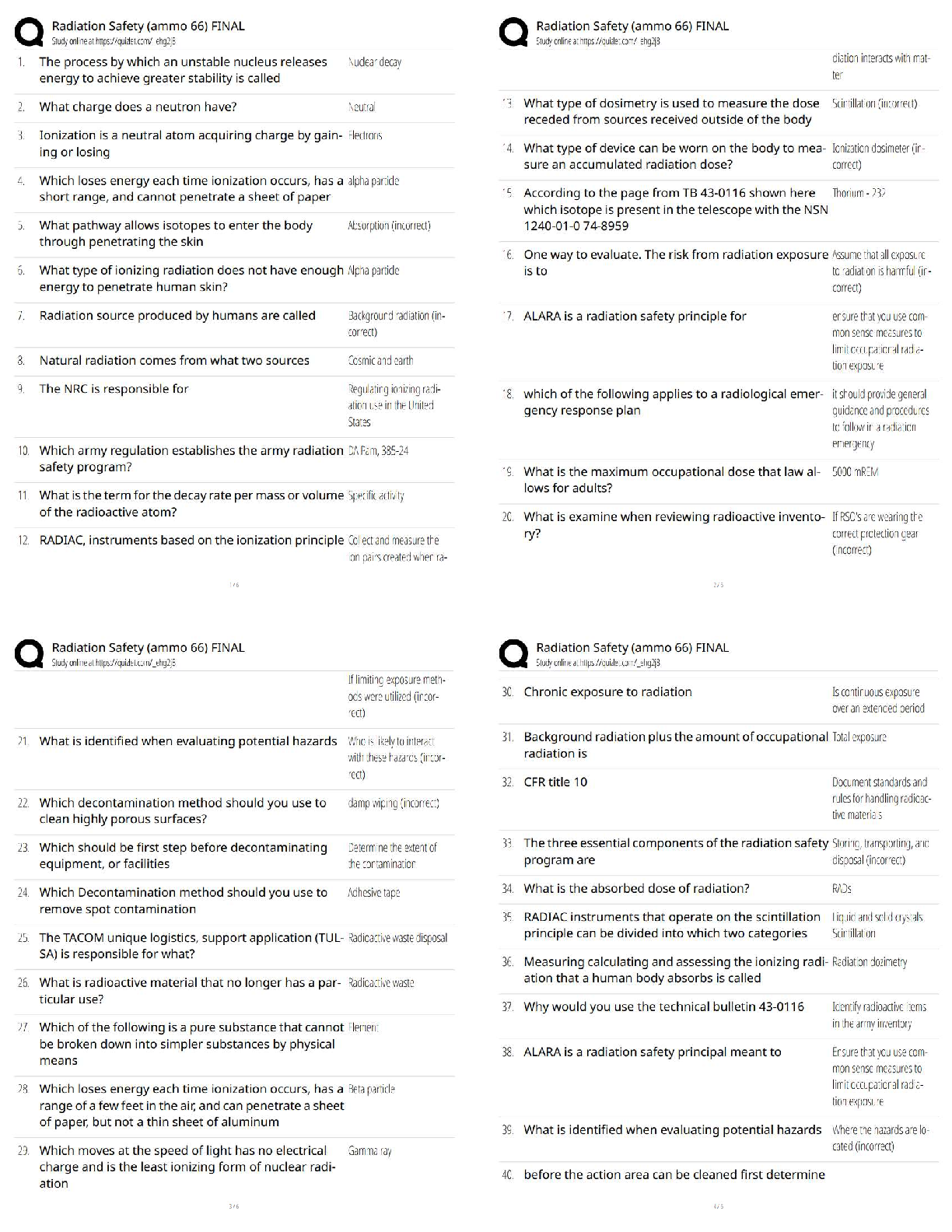
Eyepiece ✔✔
Observation tube ✔✔
Neck ✔✔
Coaxial stage controls ✔✔
Course focus ✔✔
Fine Focus ✔✔
Base ✔✔
Light source ✔✔
Iris Diaphragm ✔✔
Condenser Lens ✔✔
Stage ✔✔
Objective lense ✔✔
Nosepiece ✔✔
Brightfield Imaging ✔✔
phase contrast microscope ✔✔light microscope that enhances contrast; useful in examining living,
unstained cells
dark field microscopy ✔✔shows the specimen against a dark background and provides good
resolution
Flurescence microscope ✔✔diagnosing infection with ultraviolet radiation
laser scanning confocal microscope ✔✔a microscope that employs a beam of fluorescence and a
pin-hole aperture to produce an image with a very high resolution.
electron microscope ✔✔a microscope that focuses a beam of electrons to magnify objects
Gram staining ✔✔A method of differentiating bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
acid fast stain ✔✔a differential stain used to identify bacteria that are not decolorized by acidalcohol
[Show More]
.png)

.png)











.png)