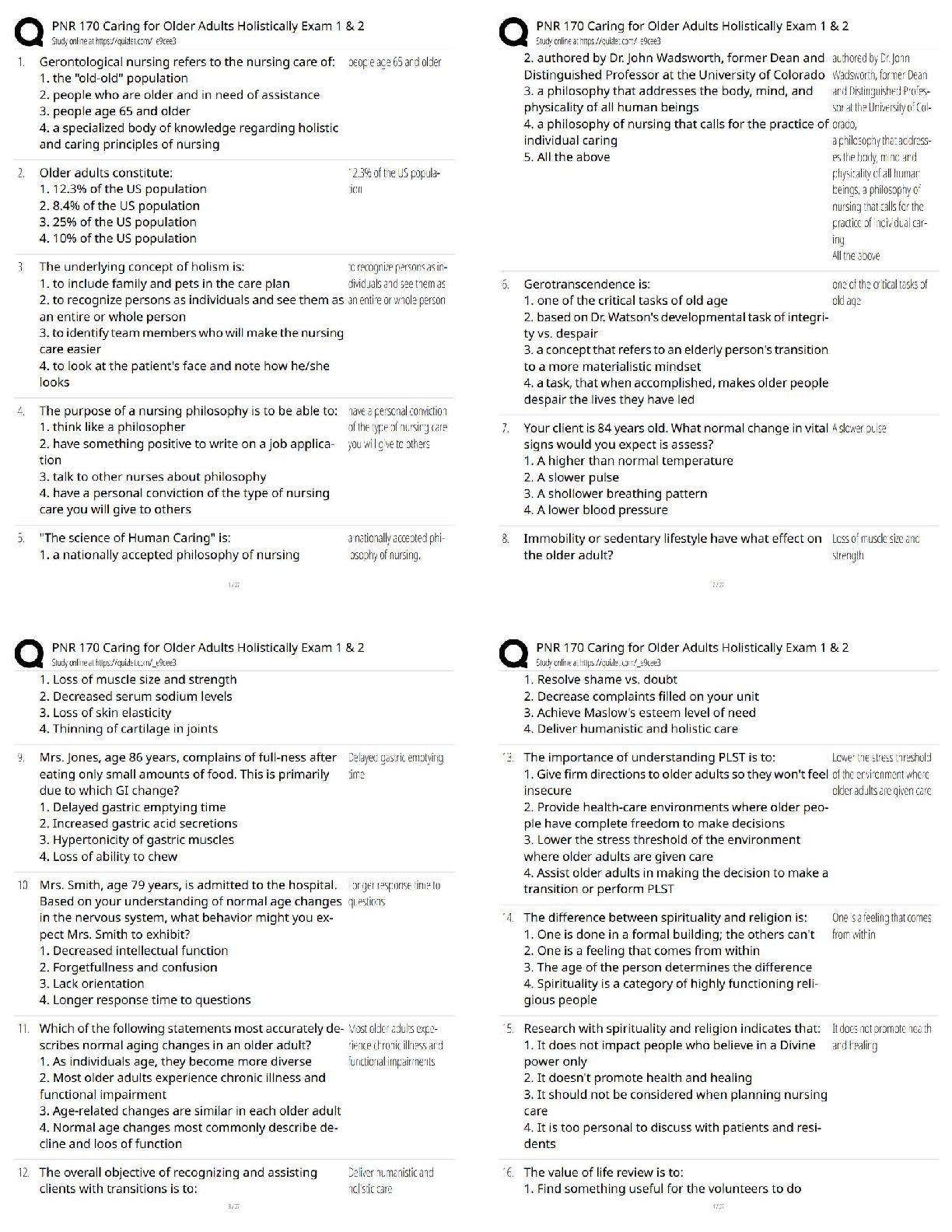
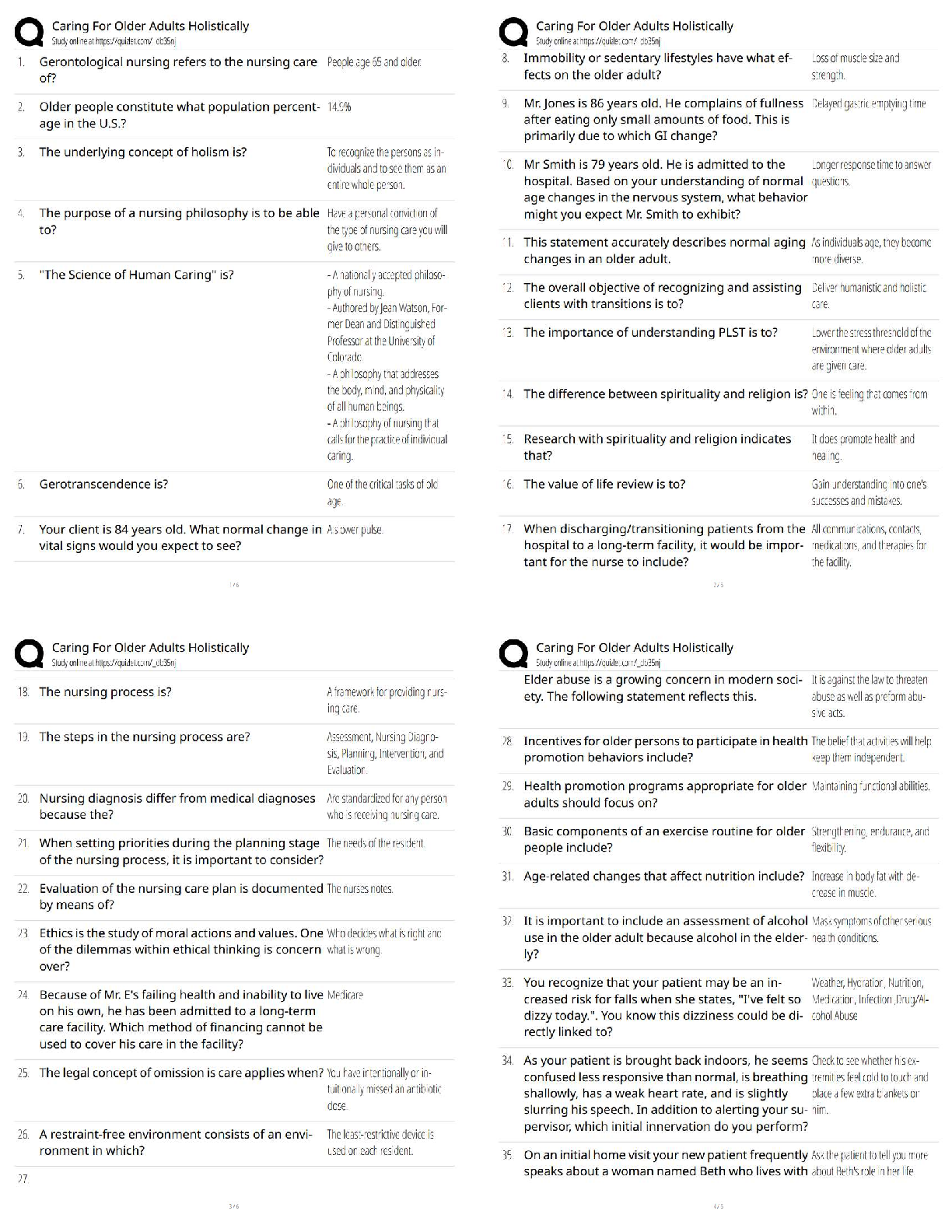
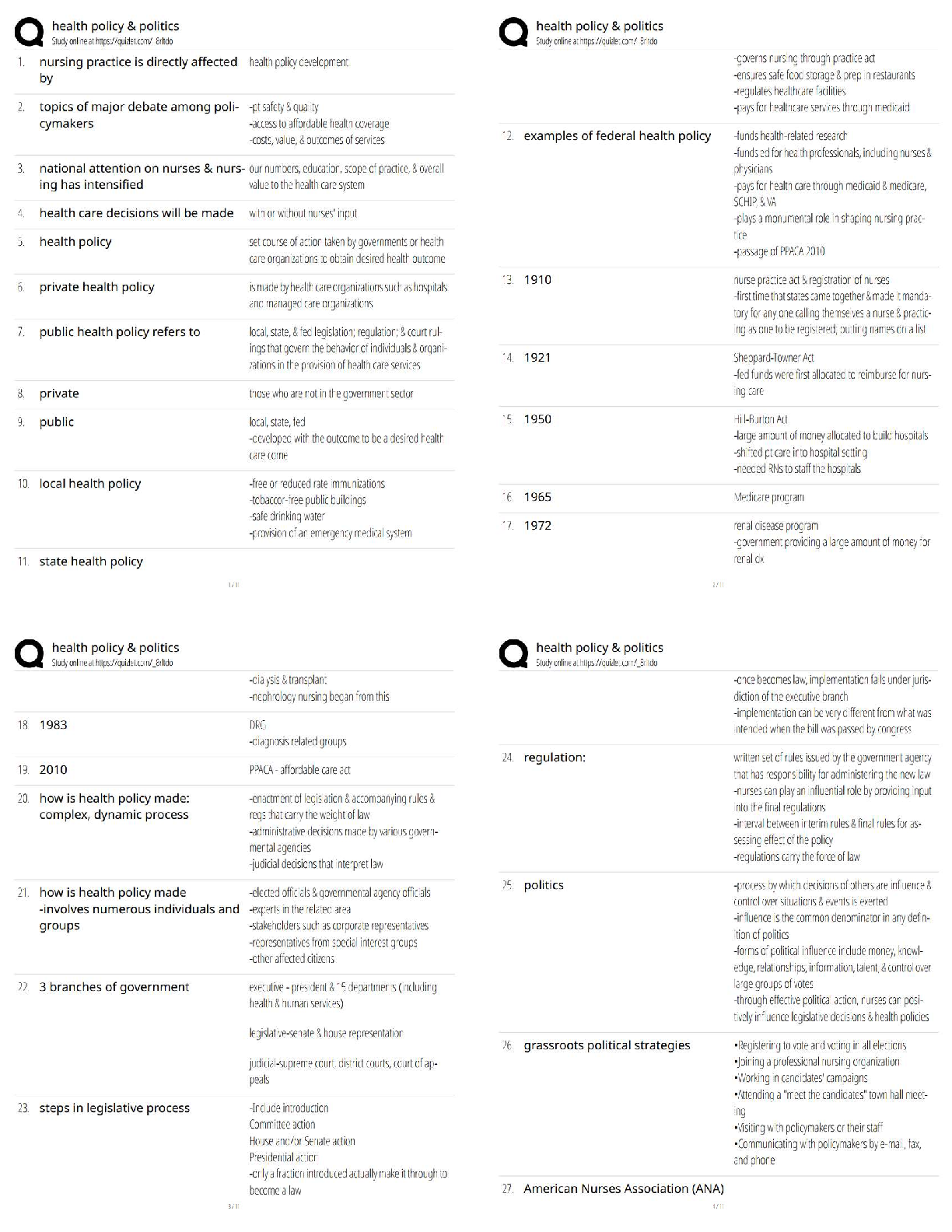
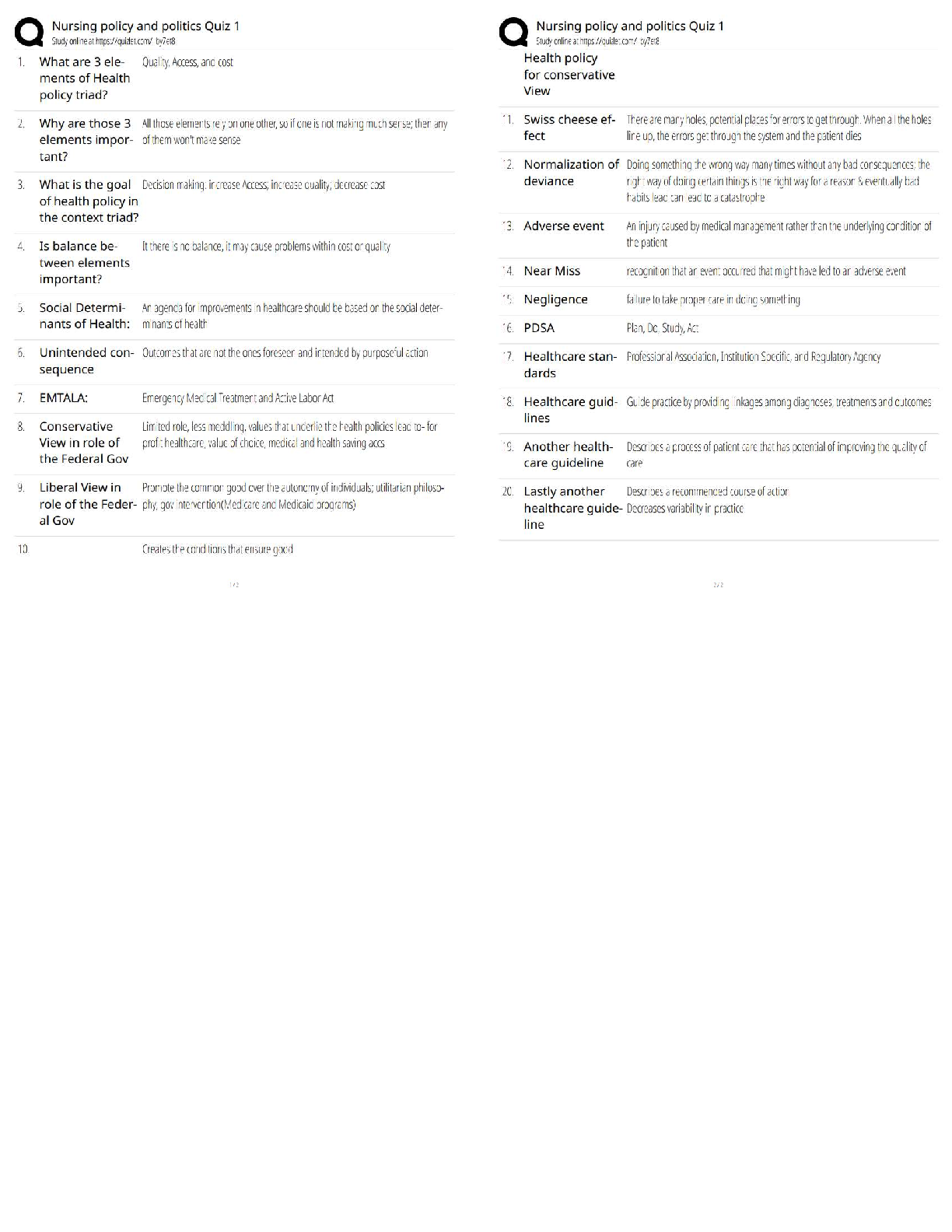
VATI Comp Predictor Overall Review 2
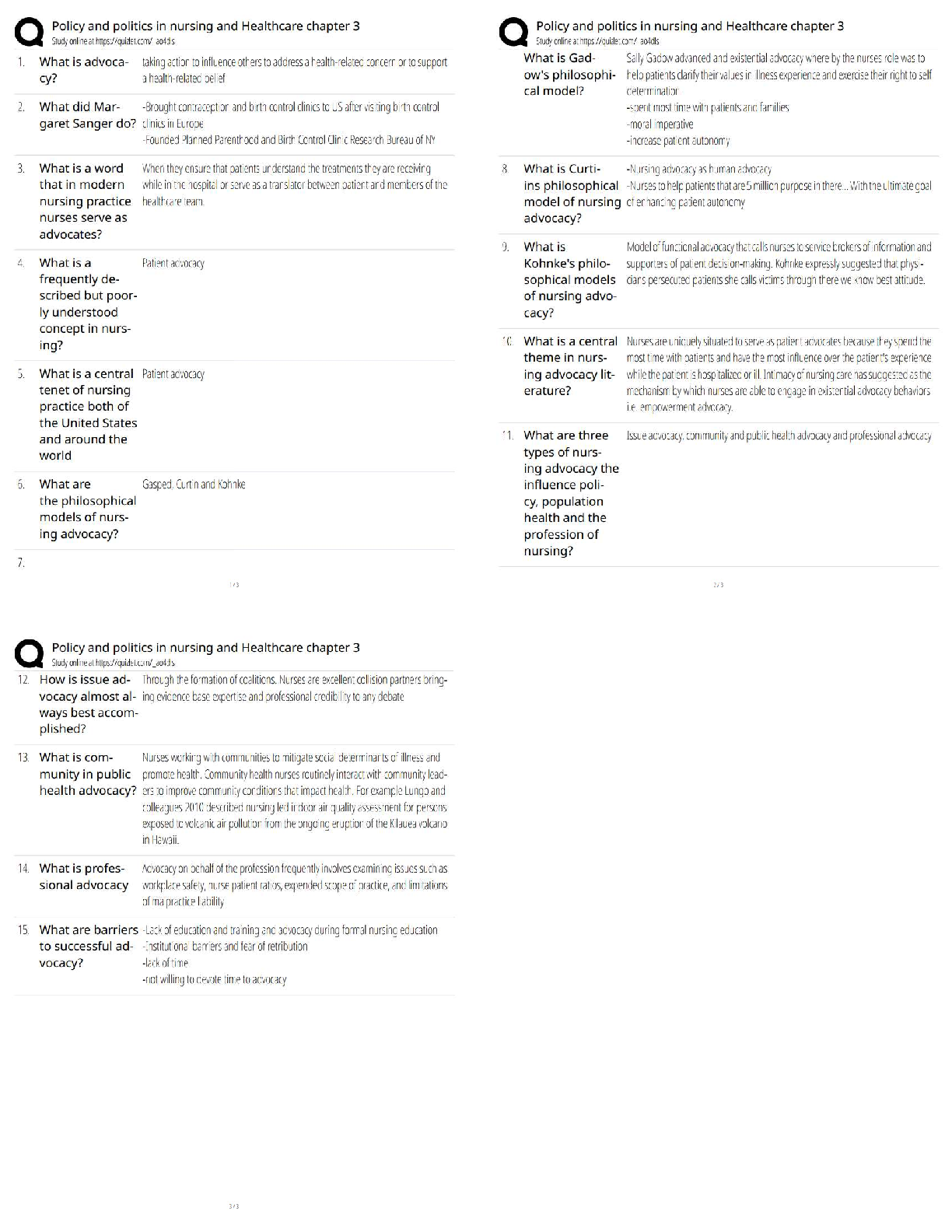
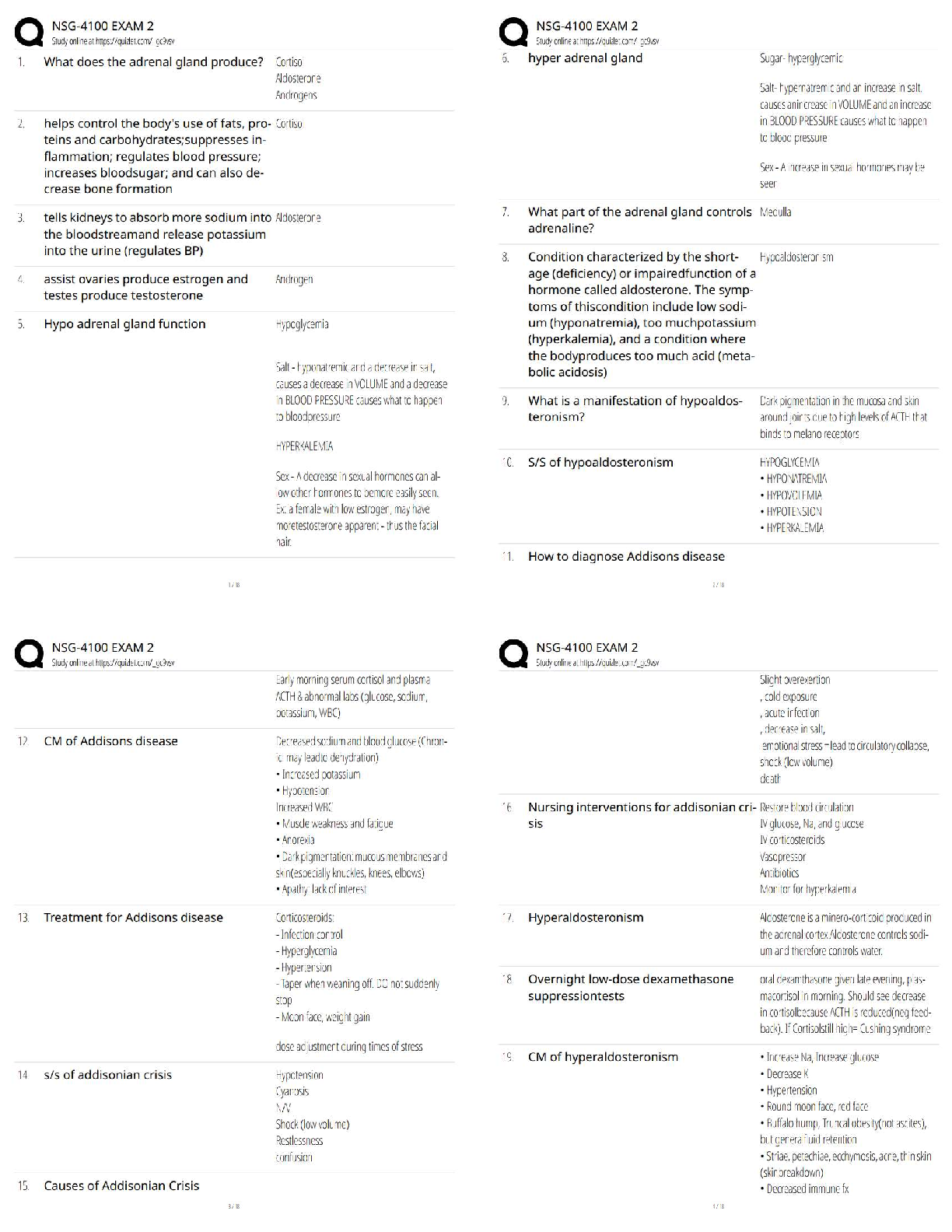
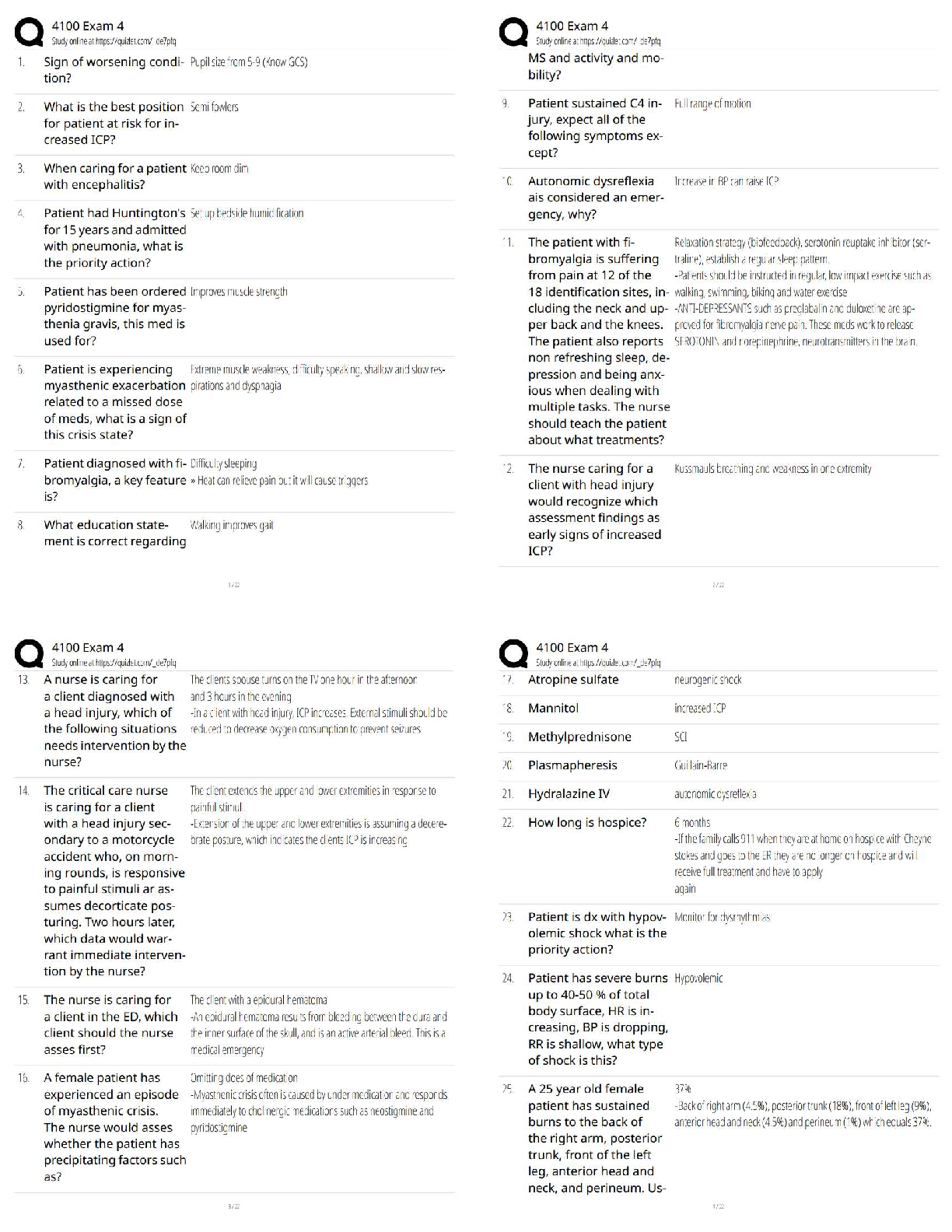
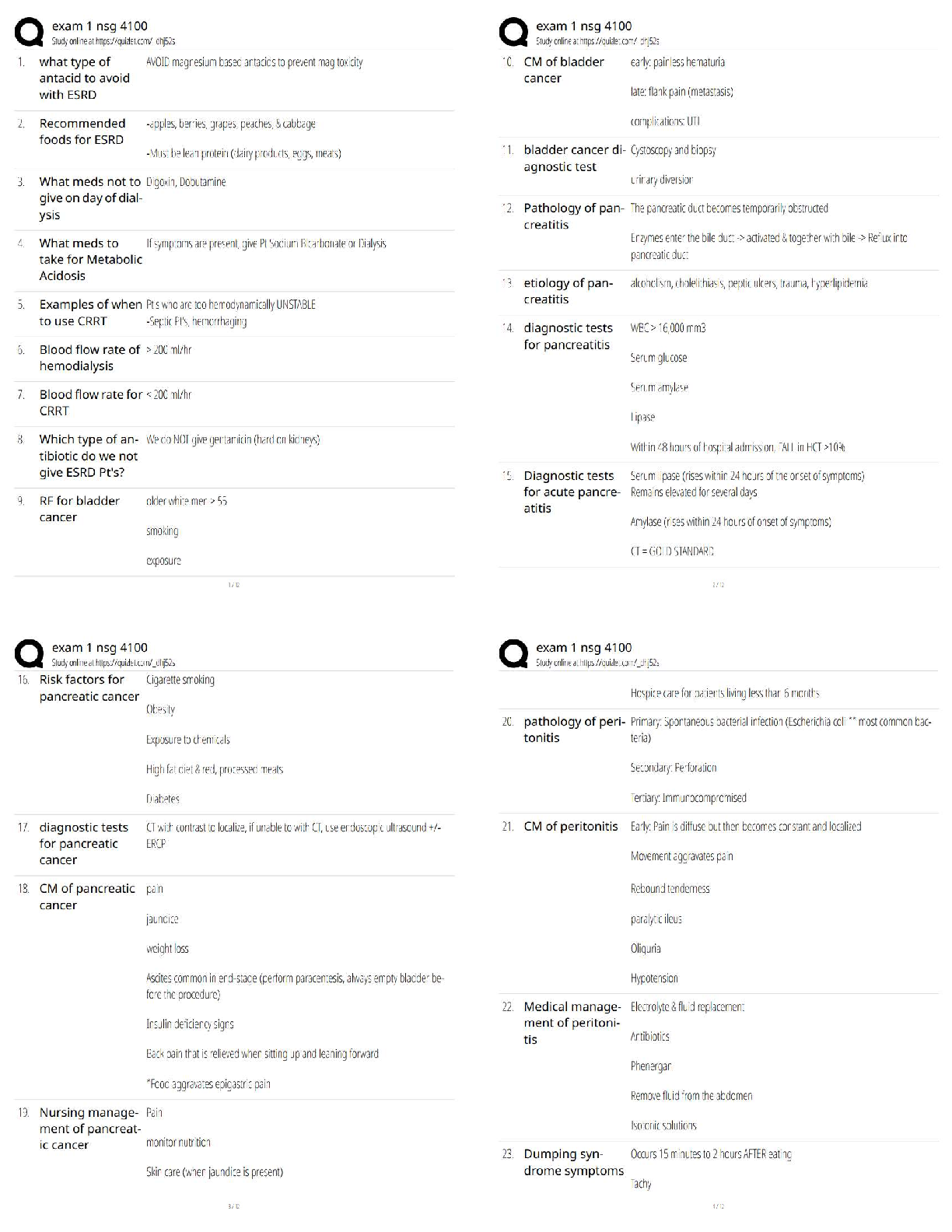
Already Passed
Lab Value - Calcium (Ca )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔8.6 - 10.2 mg/dL
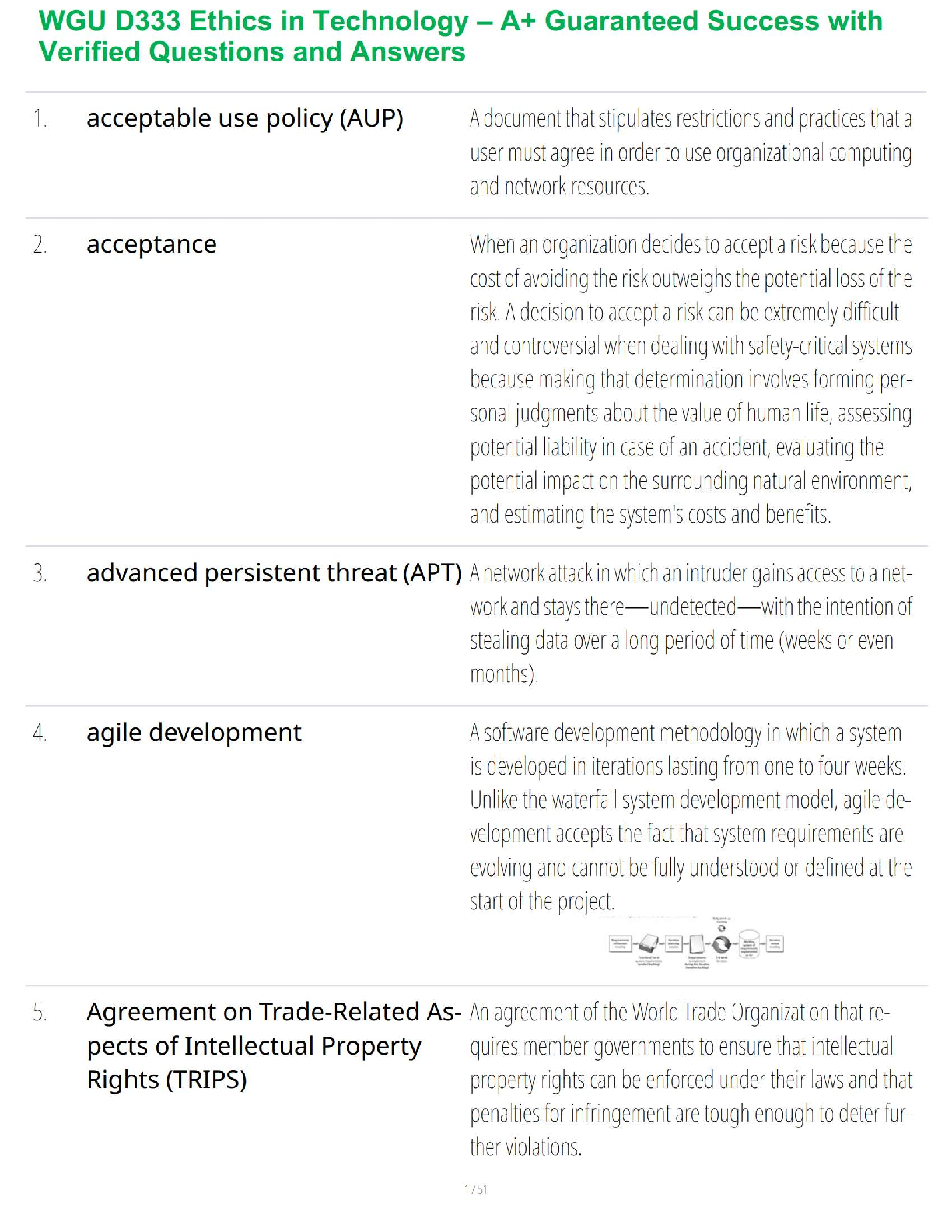
-If a patient has severe hypocalcemia, take seizure precautions and assess the airway. Also, monito
...
VATI Comp Predictor Overall Review 2
Already Passed
Lab Value - Calcium (Ca )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔8.6 - 10.2 mg/dL
-If a patient has severe hypocalcemia, take seizure precautions and assess the airway. Also, monitor
for tetany, tingling sensations in the tips of the fingers and around the mouth, and in the feet.
Spasms of the muscles of the extremities and the face may occur. Also, be alert for ECG changes
including a prolonged QT interval.
- If a patient has hypercalcemia, increase mobilization and encourage sufficient oral intake. Take
safety precautions if confusion is present and be alert for signs of digitalis toxicity. Also, monitor
the patient's cardiac rate and rhythm.
Lab Value - Chloride (Cl )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔97 - 107 mEq/L
-Monitor the patient with hypochloremia for muscle spasms, alkalosis, and depressed respirations.
-Monitor the patient with hyperchloremia for acidosis.
Lab Value - Magnesium (Mg )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔1.3 - 2.3 mEq/L
-Hypomagnesemia can predispose a patient to digitalis toxicity or cardiac arrhthymias. Take
seizure precautions if necessary, and monitor for laryngeal stridor.
-If hypermagnesemia is present, be alert for hypotension and shallow respirations, lethargy,
drowsiness, and coma. Don't give magnesium containing medications to patient with renal failure
or compromised renal function. Check deep tendon relfexes frequently.
Lab Value - Phosphate (PO )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔2.5 - 4.5 mg/dL
-Patients with severe hypophosphatemia are at greater risk for infection. Admin IV phosphate
products cautiously and give TPN cautiously in malnourished patients. Monitor for diarrhea when
taking oral supplements. A sudden increase in serum phosphate level can cause hypocalcemia.
-With hyperphosphatemia, monitor for signs of tetany. Soft tissue calcification can be a long-term
complication of chronically elevated serum phosphate levels.
Lab Value - Potassium (K )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔3.8 - 5 mEq/L
-Hypokalemia can be life-threatening. Assess for hypokalemia in patients taking digoxin. Patients
with hypokalemia are at risk for cardiac arrhythmias. Monitor for muscle cramps and weakness,
paresthesias, fatigue, anorexia, decreased bowel motility, and an irregular heartbeat. To prevent
hypokalemia, educate about abuse of laxatives and diuretics.
- Hyperkalemia can be life-threatening. Monitor pts for arrhythmias, irritability, paresthesias, and
anxiety, as well as GI symptoms such as nausea and intestinal colic. Prevent hyperkalemia by
administering potassium correctly, according to your facility policy. Also, avoid giving pts with
renal insufficiency potassium-saving diuretics, potassium supplements, or salt substitutes. Pts on
ACE inhibitors should avoid potassium supplements.
Lab Value - Sodium (Na )
(Serum Electrolyte) ✔✔135 - 145 mEq/L
[Show More]
.png)

.png)