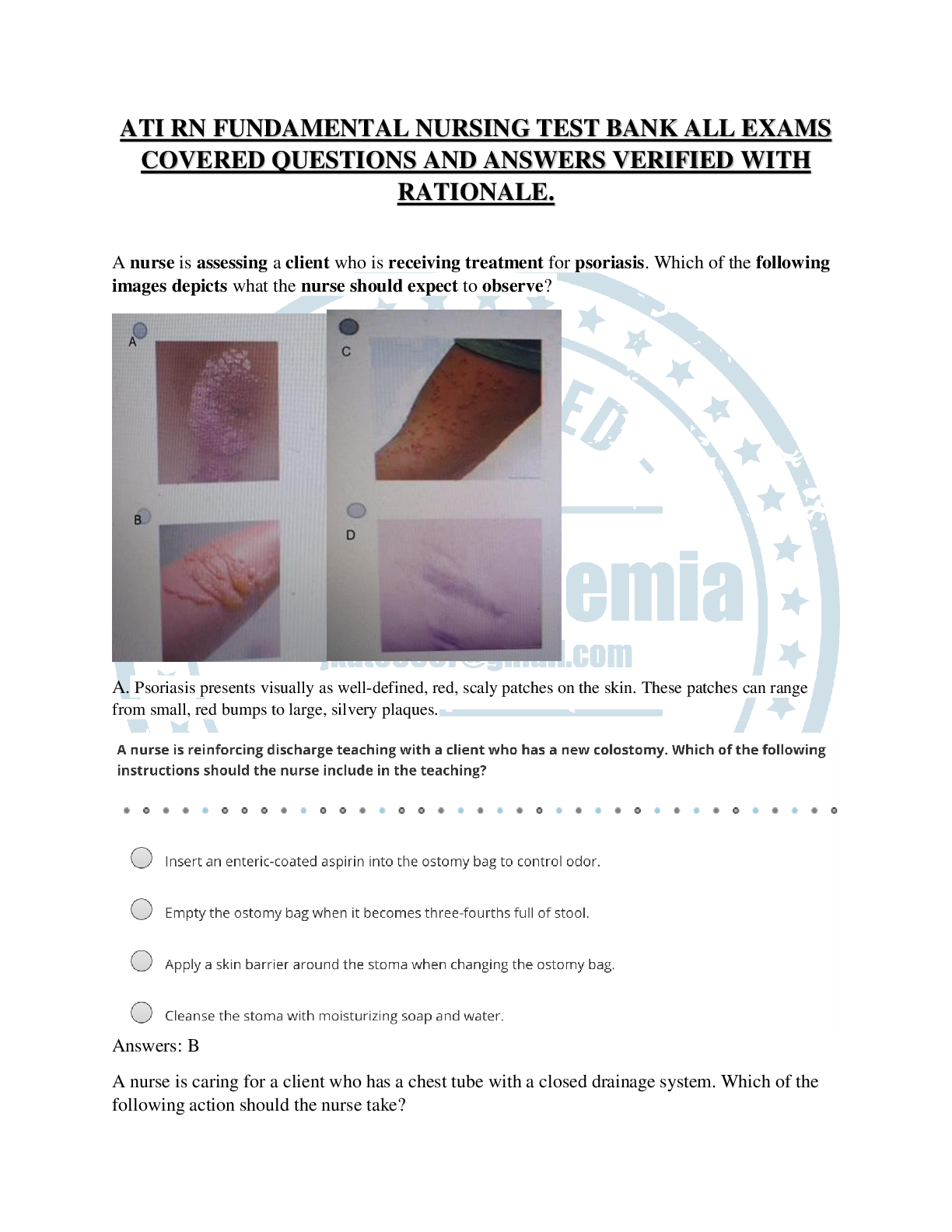
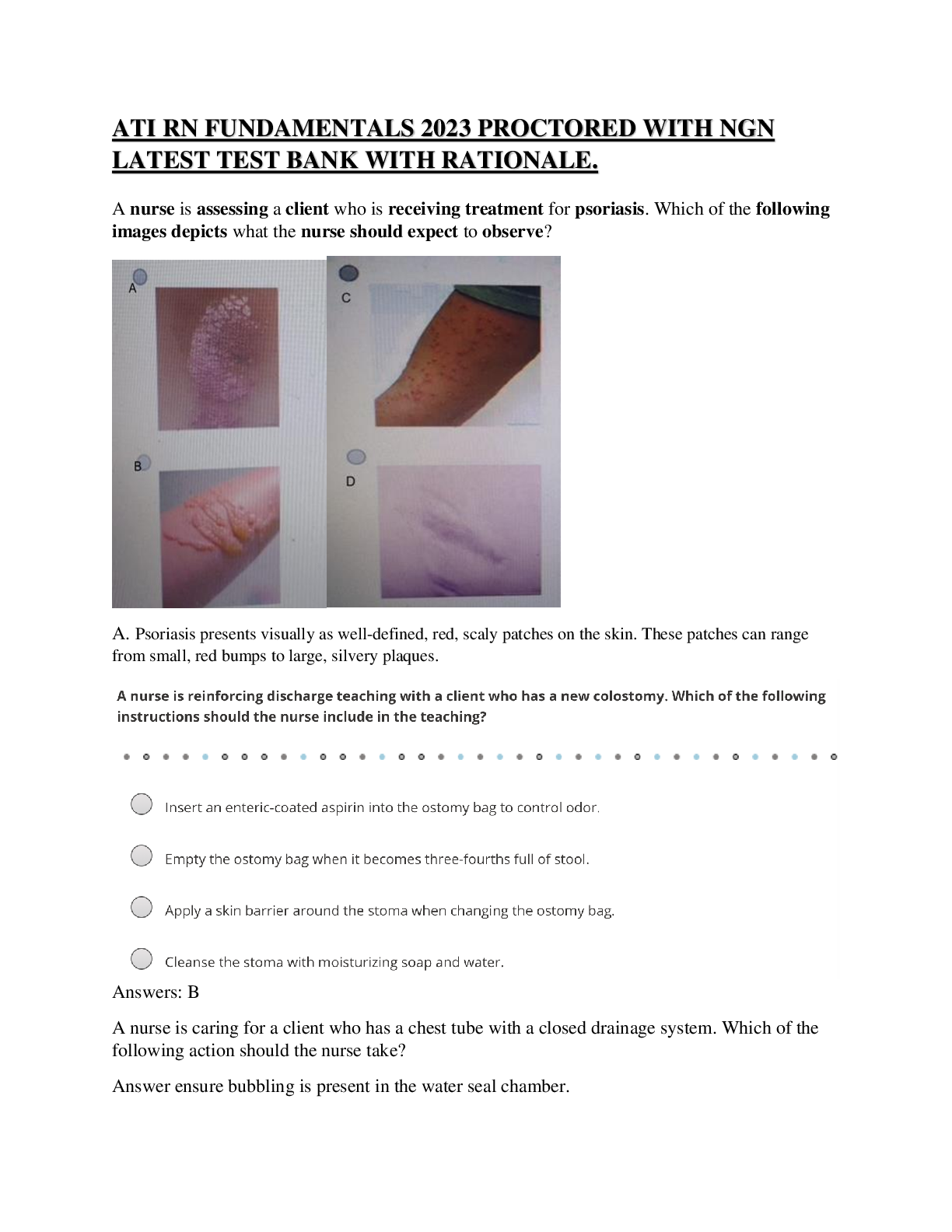
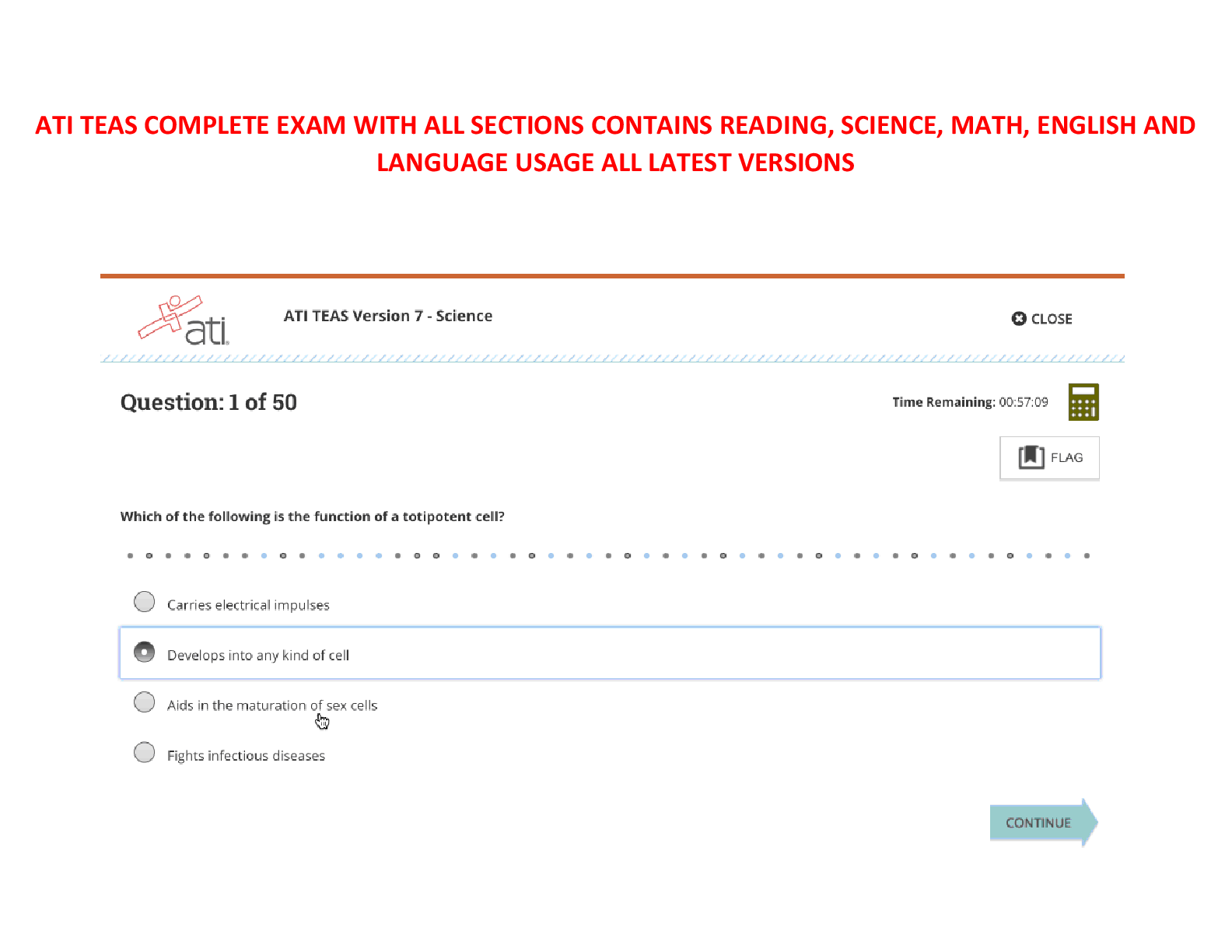
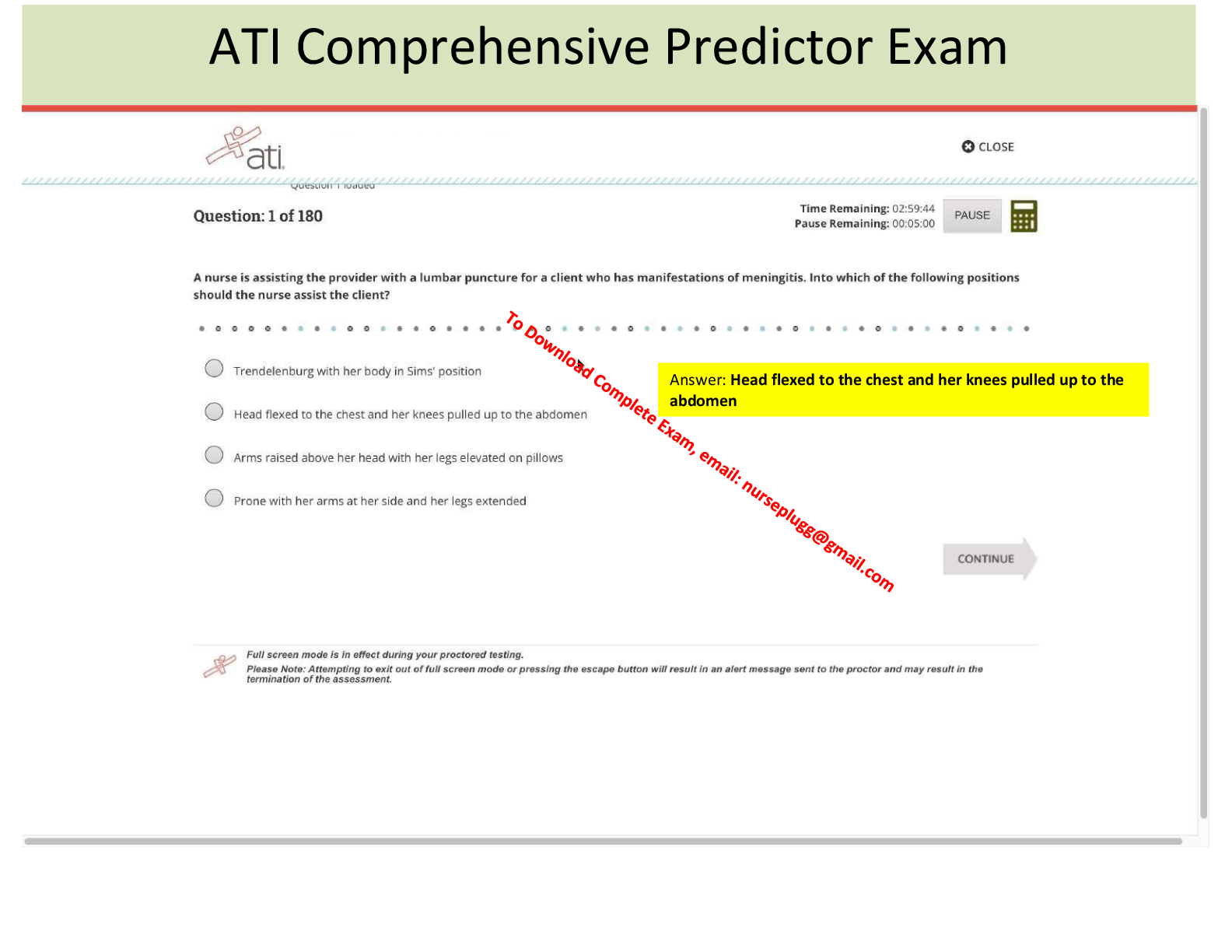
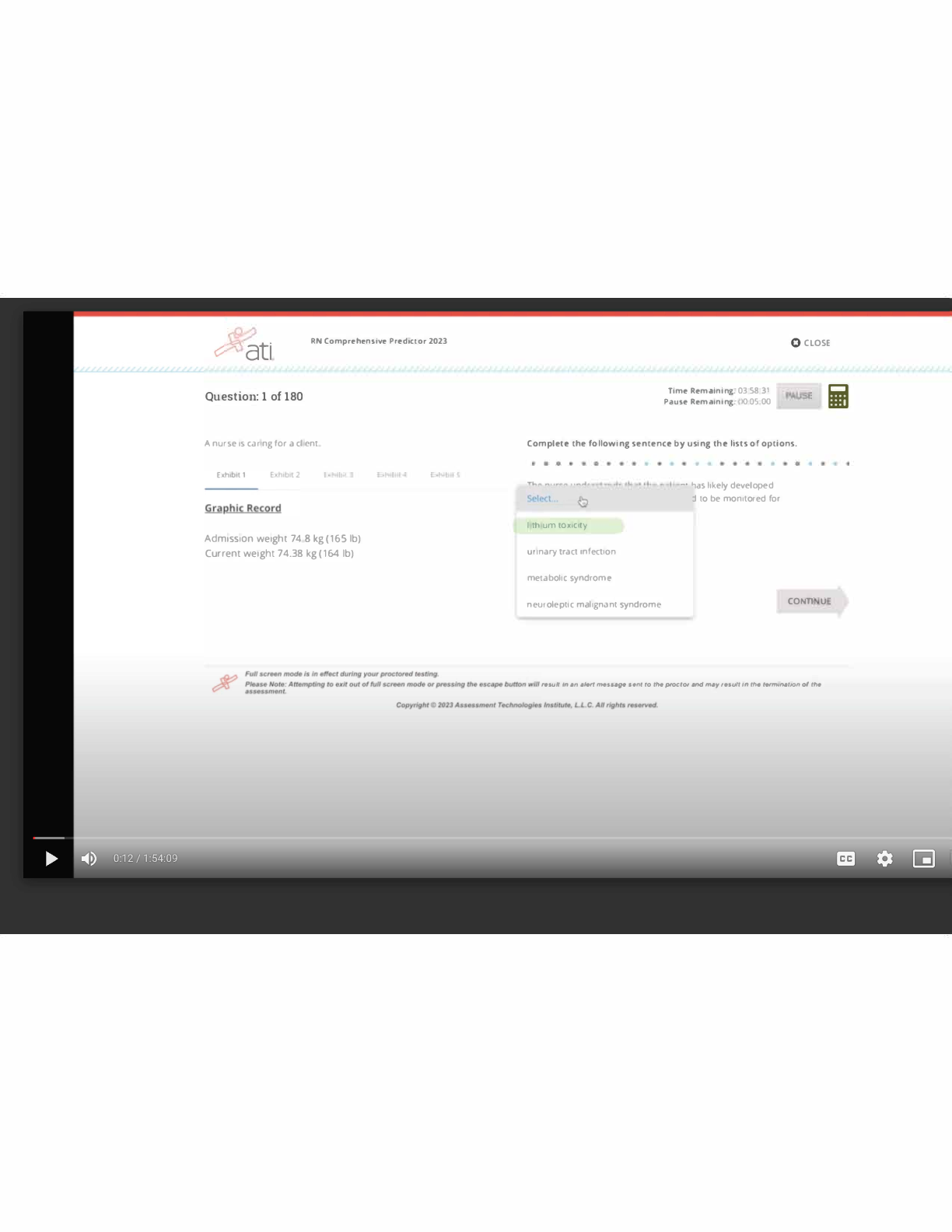
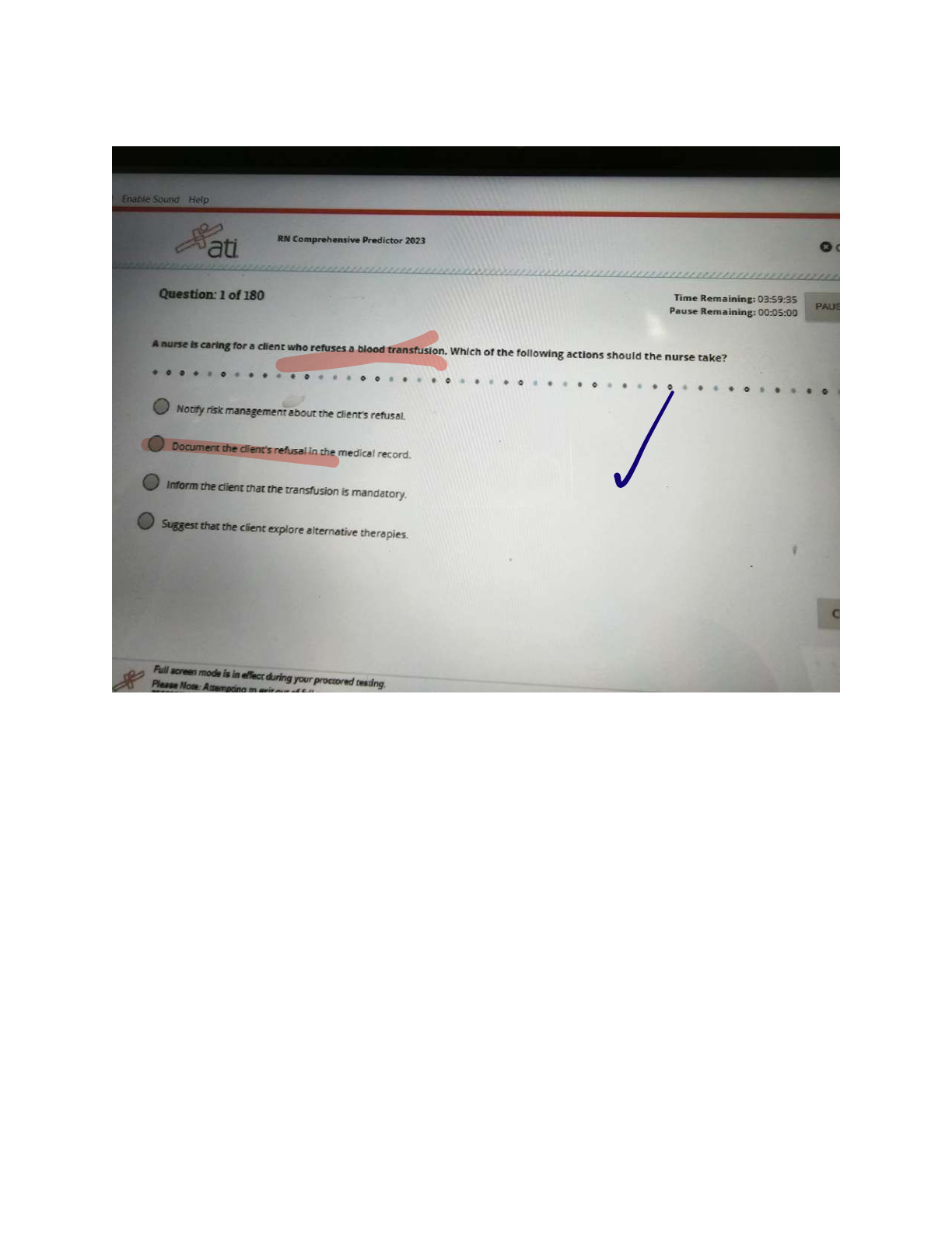
ATI Maternal Newborn Notes for the Proctored Final
1. Couvade syndrome is a pregnancy-like manifestation experienced by the expectant father. Manifestations include nausea, weight gain, and other physical manifestatio
...
ATI Maternal Newborn Notes for the Proctored Final
1. Couvade syndrome is a pregnancy-like manifestation experienced by the expectant father. Manifestations include nausea, weight gain, and other physical manifestations of pregnancy.
Cognitive restructuring is accepting the idea of pregnancy and assimilating it into the woman's life. The focusing phase is the third phase of the father's emotional response to the pregnancy. It is characterized by his active involvement in the pregnancy and his relationship with the child.
Emotional lability: rapid and unpredictable changes in mood during pregnancy. Intense hormonal changes may be responsible for mood changes that occur during pregnancy. Tears and anger alternate with feelings of joy or cheerfulness for little or no reason.
2. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is at 40 weeks of gestation and has a new prescription for misoprostol. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? The nurse should instruct the client to remain in a side-lying position for 30 to 40 min after the insertion. The nurse can administer oxytocin no sooner than 4 hr after the last dose of misoprostol. Oxytocin can be administered following misoprostol for clients who have cervical ripening and have not begun labor. The nurse should avoid administering aluminum hydroxide and magnesium-containing antacids with misoprostol.
3. The latent phase of labor is characterized by cervical dilation of 0-3cm and
contractions every 5 to 30 min, each lasting 30 to 45 seconds.
The active phase of labor is characterized by a cervical dilatation of 4-7cm
and contractions every 3 to 5 min, each lasting 40 to 70 seconds.
The transition phase of labor is characterized by a cervical dilatation of 8-10cm and contractions every 2 to 3 min, each lasting 45 to 90 seconds.
The descent phase of labor is characterized by active pushing with contractions every 1 to 2 min, each lasting for 90 seconds.
4. Expected manifestations associated with fetal exposure to SSRIs (in the first 2 days after) include irritability, agitation, tremors, diarrhea, and vomiting, tachypnea, hypoglycemia, and low birth weight are common with fetal exposure
to SSRIs.
5. The nurse should inform the client that betamethasone is a glucocorticoid that enhances fetal lung maturity by promoting the release of enzymes that release lung surfactant.
6. The nurse should identify this as an image of spina bifida occulta.
External indications of this neural tube defect include
a dimpled area over the defect and the presence of a birthmark or hairy patch above the area.
The nurse should identify this as an image of spina bifida Manifesta in the form of myelomeningocele that is open.
7. The nurse should instruct the client to stop suctioning when the newborn's cry no longer sounds like it is coming through a bubble of fluid or mucus. The client should compress the bulb before inserting the syringe tip. Compressing the bulb after it is in the newborn's nares or mouth could push secretions and mucus further inside.
8. Brownish-red discharge/lochia is expected during days 3-10 days postpartum. 4-10 days postP = lochia serosa.The client should report a large amount of lochia and large clots to the provider. Sudden onset of chills, fever, malaise, body aches, headaches, and unilateral breast pain can be indications of mastitis, an infection of the breast tissue. The nurse should instruct the client to report this manifestation to the provider. Manifestations of mastitis include fever, aches, chills, headaches, and erythema. Erythema can be detected by palpating for warmth; in some clients, the skin might appear reddened.
9. The nurse should plan to position the client upright to allow the anesthetic solution to flow downward. If additional pain management is needed for cesarean birth, the nurse can place the client supine with her head and shoulders elevated and at a lateral tilt to increase perfusion to the fetus. The nurse should plan to administer 500 to 1,000 mL of lactated Ringer's or 0.9% sodium chloride 15 to 30 min prior to the administration of the first dose of the anesthetic solution to decrease the maternal risk for hypotension. The nurse should plan to obtain a baseline blood pressure prior to the initiation of anesthetic solution. The nurse should then continue to monitor the client's blood pressure every 5 to 10 min to
[Show More]