Vocabulary:center of mass, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, elasticity,
kinetic energy, momentum, speed, vector, velocity
Prior Knowledge Questions(Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
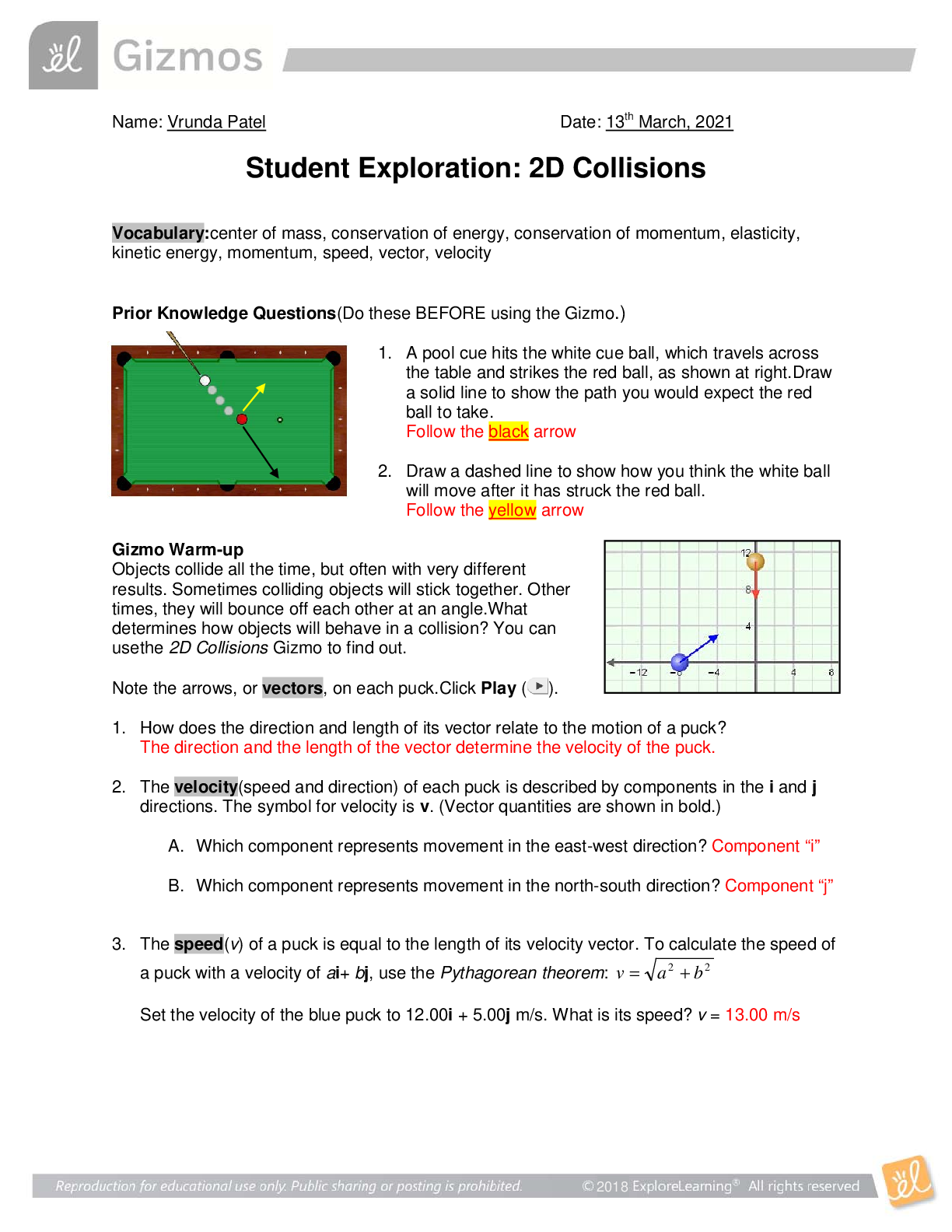
1. A pool cue hits
...
Vocabulary:center of mass, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, elasticity,
kinetic energy, momentum, speed, vector, velocity
Prior Knowledge Questions(Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
1. A pool cue hits the white cue ball, which travels across
the table and strikes the red ball, as shown at right.Draw
a solid line to show the path you would expect the red
ball to take.
Follow the black arrow
2. Draw a dashed line to show how you think the white ball
will move after it has struck the red ball.
Follow the yellow arrow
Gizmo Warm-up
Objects collide all the time, but often with very different
results. Sometimes colliding objects will stick together. Other
times, they will bounce off each other at an angle.What
determines how objects will behave in a collision? You can
usethe 2D Collisions Gizmo to find out.
Note the arrows, or vectors, on each puck.Click Play ( ).
1. How does the direction and length of its vector relate to the motion of a puck?
The direction and the length of the vector determine the velocity of the puck.
2. The velocity(speed and direction) of each puck is described by components in the i and j
directions. The symbol for velocity is v. (Vector quantities are shown in bold.)
A. Which component represents movement in the east-west direction? Component “i”
B. Which component represents movement in the north-south direction? Component “j”
3. The speed(v) of a puck is equal to the length of its velocity vector. To calculate the speed of
a puck with a velocity of ai+ bj, use the Pythagorean theorem: v = a 2 + b 2
Set the velocity of the blue puck to 12.00i + 5.00j m/s. What is its speed? v = 13.00 m/s2018
Activity A:
Elastic collisions
Get the Gizmo ready
• Click Reset.Make sure Elasticity is set to 1.0.
:
• Set the blue puck’s velocity to v = 4.00i +3.00jand
the gold puck’s velocity to v = 0.00i –4.00j.
Introduction: An object’s elasticity describes how readily it returns to its original shape after it
has collided with another object. In a perfectly elastic collision (in which elasticity equals 1), the
two colliding objects return to their original shape immediately after the collision takes place.
Question: What is conserved during an elastic collision?
1. Calculate: The kinetic energy (KE) of an object is a measure of its energy of motion. The
equation for kinetic energy is: KE = mv2÷ 2, and the unit for kinetic energy is the joule (J). In
the equation,m represents an object’s mass and v represents its velocity.
A. Calculate the kinetic energy of each puck. (Note: The mass of the pucks can be
found on the CONTROLS pane, and the magnitude of the pucks’ velocities (v) can
be found at the bottom of the SIMULATION pane.)
Blue puck KE = 62.5 J Gold puck KE = 24.0 J
B. Add the kinetic energy of the blue puck to that of the gold puck to find the total kinetic
energy for the system. Total system KE = 86.5 J
2. Compare: Turn on Velocity vectors during motion. Click Play and observe the pucks.
A. Calculate the final kinetic energy of the two pucks and the total system.
Blue puck KE = 11.45 J Gold puck KE = 75.0 J Total system KE = 86.5 J
Use the CALCULATION tab to check your work.
B. How did the kinetic energies of the two pucks change, and how can you explain
these changes? The kinetic energy of blue puck decreased whereas, the kinetic
energy of golden puck increased after the collision.
C. How did the total system kinetic energy before the collision compare to that of after
the collision? The total kinetic energy before the collision equaled to the kinetic
energy after the collision. The kinetic energy was conserved during the collision.
3. Make a rule: Complete the sentence: During an elastic collision, the total kinetic energy of
the system is conserved. This rule is part of the law of conservation of energy.2018
(Activity A continued on next page)
Activity A(continued from previous page)
4. Calculate: It takes force to deflect or stop a moving object. Momentum (p)is a measure of
an object’s tendency to continue moving in a given direction. The formula for momentum is
p = mv andthe unit is newton-seconds (kg•m/s). Click Reset. Select the CONTROLS tab.
Because momentum has direction, it can be described in both the i direction and j direction.
Calculate the initial momentums (pay attention to +/- signs):
Blue puck: p in i direction = 20.0 kg•m/s p in j direction = 15.0 kg•m/s
Gold puck: p in i direction = 0.00 kg•m/s p in j direction = -12.0 kg•m/s
Total system: p in i direction = 20.0 kg•m/s p in j direction = 3.00 kg•m/s
5. Calculate: Click Play and observe the pucks collide. Calculate the final momentums:
Blue puck: p in i direction = 0.25 kg•m/s p in j direction = 10.7 kg•m/s
Gold puck: p in i direction = 19.8 kg•m/s p in j direction = -7.71 kg•m/s
Total system: p in i direction = 20.0 kg•m/sp in j direction = 3.00 kg•m/s
Use the CALCULATION tab to check your answers.
6. Compare: Look at the momentum values you calculated for before and after the collision.
A. What did you notice about the total system momentum in the i direction?
The total system momentum in the “i” direction is the same before and after collision.
B. What did you notice about the total system momentum in the jdirection?
The total system momentum in the “j” direction is the same before and after collision.
During an elastic collision, the total momentum in both the i direction and the jdirection remains
the same. This rule is part of the law of conservation of momentum
[Show More]