SIMUText Ch. 4 Exam Prep Questions
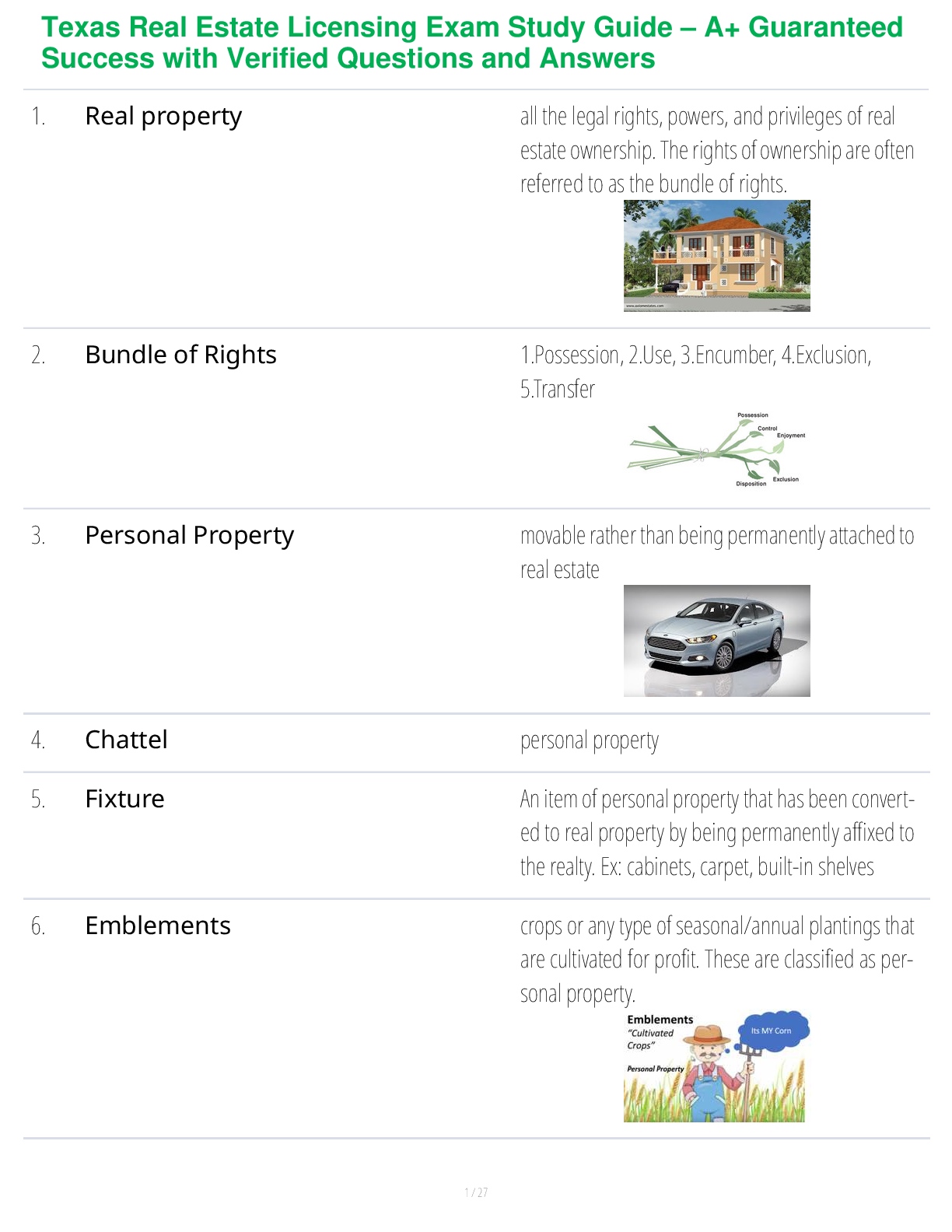
What is a population? - ANS - a group of individuals of a single species living in the same general area
Why is measuring population growth important? - ANS - 1) some populations coul
...
SIMUText Ch. 4 Exam Prep Questions
What is a population? - ANS - a group of individuals of a single species living in the same general area
Why is measuring population growth important? - ANS - 1) some populations could be harmful to other
species; invasive species
2) endangered species
3) organisms depend on each other
4) carrying capacity
What is unique about the species we measure in geometric growth? - ANS - they breed seasonally, and
there is a distinct time the population grows
What is the equation for calculating geometric population growth? - ANS - Nt = No * lambda ^ (t)
What do the variables represent in the geometric growth equation? - ANS - Nt = total population size
No = population size at this generation
lambda = finite rate of increase
t = number of generations
What does a lambda greater or less than 1 signify in the GGE? - ANS - if lambda is greater than 1 the
population is increasing while a lambda less than 1 means the population is decreasing
What happens if lambda gets larger and larger in GGE? - ANS - the population grows faster and faster
What is the equation to find lambda in GGE? - ANS - lambda = Nt+1 / Nt
When is the equation for exponential growth used? - ANS - it is used for organisms that are continuous
breeders, calculations may have to be repeated every year, hour, or day
What does anadromous mean? - ANS - fish breed in the rivers but live in the ocean
What is one assumption of lambda in the GGE? - ANS - it assumes that successive generations of a
population do not overlap which is not realistic for many species
What is r in the exponential growth equation? - ANS - it reflects the contribution each individual makes
to the growth of the population at each instant of time
What is the equation for exponential growth equation? - ANS - Nt = No * e ^ (rt)
How can you find r in the exponential growth equation? - ANS - r = ln (lambda)
What does r indicate for the population when it is greater or less than 0? - ANS - if greater than 0, this
means that the population is growing and less than 0 means the population is decreasing
What is rmax? - ANS - it is when conditions are optimal and is called the intrinsic rate of increase
What is the equation using rmax? - ANS - dN/ dt (instantaneous rate of change) = rmax * N
What is the sign of the rmax value? - ANS - always positive
When using the exponential growth equation, how can you find the exact population? - ANS - We can
find the exact population by finding dN/dt and adding the original population value
What determines rmax for a species? - ANS - life history characteristics and survivorship
Who has a higher rmax, large mammals or bacterium? - ANS - bacterium
What are some limitations to a population? - ANS - predators, food, water availability
When is unlimited growth possible? - ANS - introduction of an invasive species, when bacteria has
unlimited growth, reintroduction of an organism
How can you biologically control a species? - ANS - by bringing in diseases to prevent rapid growth,
but must be species species specific so it doesn't harm natural species
What are some examples of species that grow exponentially? - ANS - pests, exotics, pioneers, and
humans
What is carrying capacity (K) ? - ANS - the max number of individuals that an environment will
sustainably support
Is the value for K fixed, and what can it be changed by? - ANS - no, things like climate and drought can
influence K
What is logistic growth? - ANS - as the rate of increase slows as a population grows, it has reached its
carrying capacity
What is unique about the species that logistic growth measures? - ANS - they can be for periodic and
continuous breeders
What is the equation for logistic growth? - ANS - dN/dt = r * N ( 1-N/K )
What are density dependent factors? - ANS - factors that have an impact that change depending on
population size in an area
What are some examples of density dependent factors? - ANS - food, light, space, disease, predation,
and parasitism
What are density independent factors? - ANS - factors that have the same size effect on small and large
population
What are some examples of density independent factors? - ANS - weather events, thunderstorms,
hurricanes, pollution, and catastrophic events like fires and floods
Why might the birth rate decrease as a population increases? - ANS - because resources may become
more limited and competition for those resources increases
Why might the death rate increases as populations increase? - ANS - because as competition for
resources increases survival of adults and offspring decreases
When is there no increasing or decreasing of the population, carrying capacity is reached? - ANS - when
there is a low birth rate and a high death rate
Who is interested in maintaining populations at equilibrium? - ANS - foresters, game managers,
conversation biologists
What is meta-population theory? - ANS - a set of subpopulations connected via dispersal
What is a source-sink system? - ANS - a collection of patches in which one stable population regularly
rescues nearby smaller populations that would otherwise go extinct
What is a source? - ANS - a high quality habitat that on average allows the population to increase
What is a sink? - ANS - an unfavorable population; very low quality habitat on its own would not be
able to support a population
Why would an animal go to a sink? - ANS - get pushed out of a source; to escape competition, or find
mates
How does a meta-population work? - ANS - it contains occupied and unoccupied patches that together
sustain the meta-population for much longer than any one patch
What is environmental stochasticity? - ANS - the random variability in resources availability, ecological
community composition, predator pressure, and weather events which causes fluctuations in the
population growth rate
What is demographic stochasticity? - ANS - variation in population growth rate due to random
differences among individuals in reproduction and survival
What is the allee effect? - ANS - if the group is to small, the birth rate drops and death rates increase
What are some examples of species that experience the allee effect? - ANS - meerkats, passenger
pigeons
What is the significance of timed delays, damped oscillations, cycles, and chaos? - ANS - small changes
in initial conditions could create larger changes and unpredictable behavior over the long term
What is the benefit of emigrants? - ANS - they can rescue or recolonize a patch where deaths are greater
than births
[Show More]