During an emergent crisis, DO NOT - ANSWER alarm the patient
3 essentials when performing blood draws - ANSWER 1. test requisition review
2. proper patient identification
3. site choice
2 essentials when performi
...
During an emergent crisis, DO NOT - ANSWER alarm the patient
3 essentials when performing blood draws - ANSWER 1. test requisition review
2. proper patient identification
3. site choice
2 essentials when performing EKG or other cardiac monitoring - ANSWER 1. inform pt. of what is expected
2. observe for complications
CLIA-waived tests - ANSWER simple, performed with low risk of error
When performing a CLIA-waived test, always... - ANSWER 1. identify the patient
2. wear PPE
3. read all manufacturer directions and instructions
BIG OSHA (needle) protocol - ANSWER do NOT recap needles
Sharps container - ANSWER Puncture and leak proof and labeled with biohazard symbol for disposal of scalpels, needles and any other sharp object
Biohazard bag - ANSWER Leak proof bag for disposal of gloves, gauze and bandages
Standard Precautions - ANSWER ALL bodily fluids except sweat are to be considered infectious for all patients.
Change gloves... - ANSWER When handling contaminated surfaces and in-between patients
Before putting gloves on you should always - ANSWER wash hands with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer
Blood pressure measures the - ANSWER pressure of blood against the walls of the artery and ventricles
The artery and ventricles contract so that the ... - ANSWER blood is pushed to the aorta and pulmonary artery
Systole - ANSWER heart contracts
Diastole - ANSWER heart relaxes
FIRST thing you do when taking any pt. vitals - ANSWER Tell patient what you're going to do
If you have to manually obtain a BP, what should you palpate? - ANSWER Brachial artery in antecubital region of arm
When taking BP, which arm should you use? - ANSWER Generally the right unless the left has stronger pulse
Heart rate gives physician information about the heart's... - ANSWER rhythm, volume and vessel elasticity
How long should you count to get a pt.'s HR? - ANSWER 30 sec. (multiply by 2) or 1 minute
*IF there are irregularities, count for 1 minute
T/F: You should tell the pt. when you are measuring their respirations. - ANSWER False, do NOT tell the pt. as this may cause them to change their breathing patterns.
How long should you observe a pt.'s respirations for? - ANSWER 30 sec. (multiply by 2) or 1 minute
Most common site for a temperature reading - ANSWER oral
Question to ask pts. before taking their oral temp: - ANSWER "Have you eaten anything, had anything to drink, smoked, or exercised within 30 minutes of coming to the doctor today?"
What position do you put patients in to obtain a rectal temperature? - ANSWER Sims or lateral recumbent position: pt. lies on left side, left hip and leg straight, right hip and knee bent
For an aural/tympanic temperature, how should you manipulate the ear in a pt. over the age of 3? - ANSWER Pull up and back
For an aural/tympanic temperature, how should you manipulate the ear in a pt. under the age of 3? - ANSWER Pull down and back
Where is the temporal artery temperature readings taken? - ANSWER On the forehead
Where is the axillary temperature reading taken? - ANSWER Armpit
Anthropometric measurements include... - ANSWER height and weight
For an infant or child up to 3 years old, growth is measured via... - ANSWER head circumference, length and weight
Conversion C -> F - ANSWER (C x 9/5) + 32
Conversion F -> C - ANSWER (F - 32) x 5/9
lbs -> kg - ANSWER lbs x 0.45
kg -> lbs - ANSWER kg x 2.2
ft -> in - ANSWER (ft x 12) + in
in -> cm - ANSWER in x 2.54
cm -> in - ANSWER cm x 0.39
Supine - ANSWER pt. flat on back, face up
Dorsal recumbent - ANSWER supine, with knees bent
Fowler's position - ANSWER lay on table, table elevated 90 deg
Prone - ANSWER pt. lies face down
Sim's position - ANSWER pt. lay on left side, left leg extended, right bent with knee on table
Knee-Chest - ANSWER pt. rests knees and chest on table with head turned to side
Trendelenburg - ANSWER pt. supine, bottom of table elevated 30 deg
After every patient, the exam room must - ANSWER Be inspected for cleanliness, waste and spills must be cleaned, restocked, paper must be changed
5 steps to prep patient for an exam - ANSWER 1. check medical record for completion
2. pt. needs to sign all consent forms
3. ask pt. reason for visit
4. answer any questions pt. has
5. review medical record and have any lab results out for Doc
T/F: Honestly discuss any discomfort a pt. may have during an exam up front. - ANSWER True
Most important concepts when administering medications - ANSWER 1. always check pt. allergies
2 double check expiration dates
3. review meds and clarify with Dr. before administering
4. check 3 times to ensure dose matches order and that it is measured properly
How many times should the dose and measurement be checked against the physician's order? - ANSWER 3 times
It's always important to observe a patient for __ & __ __ when administering oral medications - ANSWER choking & adverse reactions
Before administering parenteral/topical medications, the patient should be notified of - ANSWER any tingling or burning they may experience
Before administering ___/___ medications, check the skin for any complications - ANSWER parenteral / topical
Transdermal medication - ANSWER typically patch of some form
DO NOT place transdermal medication on... - ANSWER broken skin
What should you write directly on the transdermal patch for a patient? - ANSWER Removal date
T/F: Pt. cannot shower with transdermal patch. - ANSWER False
What 4 things should you ALWAYS tell the patient before administering any type of injection? - ANSWER 1. what the medication is
2. how it is applied
3. any side effects
4.the fact that it may pinch
What 2 things should you always check and re-check before administering a medication? - ANSWER the medication itself and its expiration date
Items to assemble before administering an injection are:
*hint: there are 7! - ANSWER 1. the meds, 2. gloves, 3. alcohol wipes, 4. syring, 5. sterile needle, 6. gauze, 7. sharps container
Steps to take BEFORE administering ANY type of injection: - ANSWER 1. wash hands and glove up
2. assemble items
3. wipe vial with alcohol swab
4. draw up medication- no air!
Steps to take AFTER administering ANY type of injection: - ANSWER 1. place gauze next to needle and remove at the same angle as it was inserted
2. place needle in sharps container
3. if pressure is needed, apply now
4. remove gloves and wash hands
5. document the dosage, method, location and any complications in the pt.'s chart
Area to insert needle into for INTRAMUSCULAR injections - ANSWER deltoid muscle
Area to insert needle into for INTRADERMAL injections - ANSWER volar forearm
Area to insert needle into for SUBCUTANEOUS injections - ANSWER abdomen, back of upper arm, outer thighs, upper buttocks
Angle to insert needle for INTRAMUSCULAR injections - ANSWER 90 deg
Angle to insert needle for INTRADERMAL injections - ANSWER 15 deg
Angle to insert needle for SUBCUTANEOUS injections - ANSWER 45 deg
During INTRAMUSCULAR injections, do you aspirate? - ANSWER Aspirate before injecting, then inject slow and steady
During INTRADERMAL injections, do you aspirate? - ANSWER NO! Be swift with injection.
During SUBCUTANEOUS injections, do you aspirate? - ANSWER Aspirate before injecting, then inject slow and steady
After INTRAMUSCULAR injection, what do you do? - ANSWER Apply pressure and wiggle muscle
After INTRAERMAL injection, what do you do? - ANSWER DO NOT apply pressure or wiggle
After SUBCUTANEOUS injection, what do you do? - ANSWER Apply pressure at the Doc's request
PFT - ANSWER pulmonary function test
For a PFT to be accurate, pt. must not have done what 3 things? - ANSWER Smoke, use nebulizer, or use bronchodilator within 6 hours of taking test
How many times must you repeat a PFT ? - ANSWER 3
Long distance visual test - ANSWER Snellen chart
Basic outline of long-distance Snellen chart test - ANSWER start on line 27, stop when pt. gets 2 incorrect
First step in suture removal (after washing hands & explaining procedure, etc.) - ANSWER 1. place gauze sponge next to first suture
During suture removal, you use forceps to do what? - ANSWER Grab the knot of the suture, beginning with the first suture, gently pull it away from the skin so that you can cut the suture close to the skin with siccors
After the suture is cut, what do you do next? - ANSWER Gently pull the suture through the skin and place it on the gauze sponge
What are the final steps of suture removal after the suture has physically been removed? - ANSWER Inspect the area then continue until all sutures have been removed. Dispose of trash in biohazard container and cover wound with SteriStrip or a bandage.
T/F: You should make conversation with patient throughout suture removal and let them know what is going on. - ANSWER True
What should you explain to a patient after his/her sutures have been removed? - ANSWER They need to keep the area clean and dry and call the office with any issues
T/F: When documenting suture removal, it is not important to document that you gave the patient verbal instructions on how to care for their wound. - ANSWER False; this is a must
Saliva tests are different from other tests because the specimen are treated differently; how? - ANSWER Saliva specimen are frozen
Semen samples must be... (3 things) - ANSWER protected from light, kept at normal body temperature and processed within 1 hour of collection
How should a patient be positioned for eye irrigation? - ANSWER supine or sitting with head back
Difference between documenting an irrigation procedure vs. everything else: - ANSWER MUST include how much solution was used to irrigate
Basic outline of ear irrigation - ANSWER 1. inspect ear with otoscope
2. drape shoulder, place container for spills on pt shoulder, have pt. stabilize
3. pull pinna up and back for adults or down and back for kids
4. irrigate, inspect with otoscopt
5. repeat until cerumen is gone
6. dry with gauze
If a pt. goes into shock, what 3 things can a MA do? - ANSWER Make sure pt.'s airway is open, position them in supine position with feet elevated and call for help
Signs of syncope - ANSWER flushed, heavy sweating, faint (or literal fainting)
If syncope occurs when a pt. is on your watch, what do you do? - ANSWER loosen their clothes, lay them in supine position and monitor vitals for the physician
2 aseptic cleaning techniques - ANSWER sterilization & disinfection
Sterilization - ANSWER prevents contamination, usually an autoclave is involved (250-320 F)
Disinfection - ANSWER KILLS microbes; bleach is most commonly used (1:10)
Sanitization - ANSWER removes debris and reduces microbes and viruses before sterilizing or disinfecting
What two age groups should be given special patient consideration? - ANSWER pediatric patients and elderly patients
How would you introduce yourself to a patient who has arrived to have their blood drawn? - ANSWER "Hi, I'm Tess, I'm your medical assistant. I see that today we are going to have some blood drawn. I will be assisting you with that today."
Brady- - ANSWER slow
Oligo-- - ANSWER scanty
Pari- - ANSWER all
Trachy- - ANSWER fast
Eu- - ANSWER Normal
eu- - ANSWER normal
ab- - ANSWER away
de- - ANSWER down
dia- - ANSWER through/across
epi- - ANSWER above
per- - ANSWER through
hem- - ANSWER blood
vascul- - ANSWER blood vessels
-ac, -ar - ANSWER related to
-ic, -oid, -ous, -tic - ANSWER related to
-emia - ANSWER of blood
-plegia - ANSWER paralysis
-oma - ANSWER tumor
-rrhaphy - ANSWER suturing
-stomy - ANSWER surgical opening
-plasty - ANSWER repair
As a CCMA, it is NOT in your scope of practice to give a patient... - ANSWER advice
If vital signs are outside of normal ranges, what should you do with the data? - ANSWER Record it in the pt's chart and contributing factors, if any
What does the heading of a letter consist of? - ANSWER letterhead
What is the opening of a letter comprised of? - ANSWER address, salutations, attention line with title and academic degree
The body of the letter states the - ANSWER reason for correspondence
A signature is included in the _ of a letter - ANSWER closing
"Form letter" are used in... - ANSWER routine correspondence
Emails and faxes must have 2 things: - ANSWER 1) confidentiality notice, 2) instructions detailing what to do if the message is received in error
BCC (blind carbon copy) is used for an email when - ANSWER it is a bulk email message
What two things comprise the "care components" of a patient's EMR? - ANSWER nursing orders and medications
EHR & EMR help physicians eliminate - ANSWER duplicate tests and treatments from being ordered
always give patients the following basic education before an appointment: - ANSWER instructions on what to bring, how early to arrive, any lists or information they need
2 important communication modifications to make for patients using wheelchairs - ANSWER talk to the pt. at eye level and ask if assistance is needed before giving it
2 important communication modifications to make for a patient with a hearing impairment - ANSWER speak face-to-face so they can lip-read and speak naturally and clearly
1 important communication modification to make for patients with Alzheimer's or dementia - ANSWER repeat information and write it down as well
Before giving a pt. information on community resources, you should always do what first? - ANSWER Check with the resource to make sure they can still aid the pt., but without giving out too much PHI.
S in SOAP - ANSWER Subjective: the patient's complaint
O in SOAP - ANSWER Objective: evidence like lab results and the physical exam
A in SOAP - ANSWER Assessment: diagnosis
P in SOAP - ANSWER Plan: treatment and therapies for the future
Who owns a medical record? - ANSWER the facility where the record originated
POMR - ANSWER problem-oriented medical record
Four components of a POMR - ANSWER 1. database- chief complaint, lab results
2. problem- list of pt. problems
3. treatment- therapy
4. progress- #'d notes to match pt. problems
Five tasks to prepare paper records for storage - ANSWER 1. conditioning
2. releasing
3. indexing/coding
4. sorting
5. filing
Consent forms MUST contain: - ANSWER the procedure, it's risks and benefits, any alternatives and any important demographic information
Who has to witness the patient's signature? - ANSWER Someone other than the physician
T/F: The patient's questions must all be answered. - ANSWER True
The original consent form goes __ - ANSWER in the patient's chart
T/F: If an outside facility needs the consent form for any reason, they can have it. - ANSWER False, they only get a copy
A consent form for a surgical procedure must be review by the _ and the patient. - ANSWER Doctor
It (is/is not?) within the CMAA's scope of practice to answer questions and review the consent form with the patient. - ANSWER Is
When scheduling a pt. for an outpatient procedure, always ask the facility... - ANSWER if the patient needs to know any special instructions
Outpatient test results are always added to the patient's... - ANSWER medical record
Urgent care facilities utilize __ __ scheduling - ANSWER open office
HIPAA allows transfer of persona data for __ __. - ANSWER insurance payment
HIPAA Privacy Rule - ANSWER other than the basic minimum, patients must sign a release to give insurance companies any more information
HIPAA Security Rule - ANSWER any pt. information stored or transmitted must be properly protected
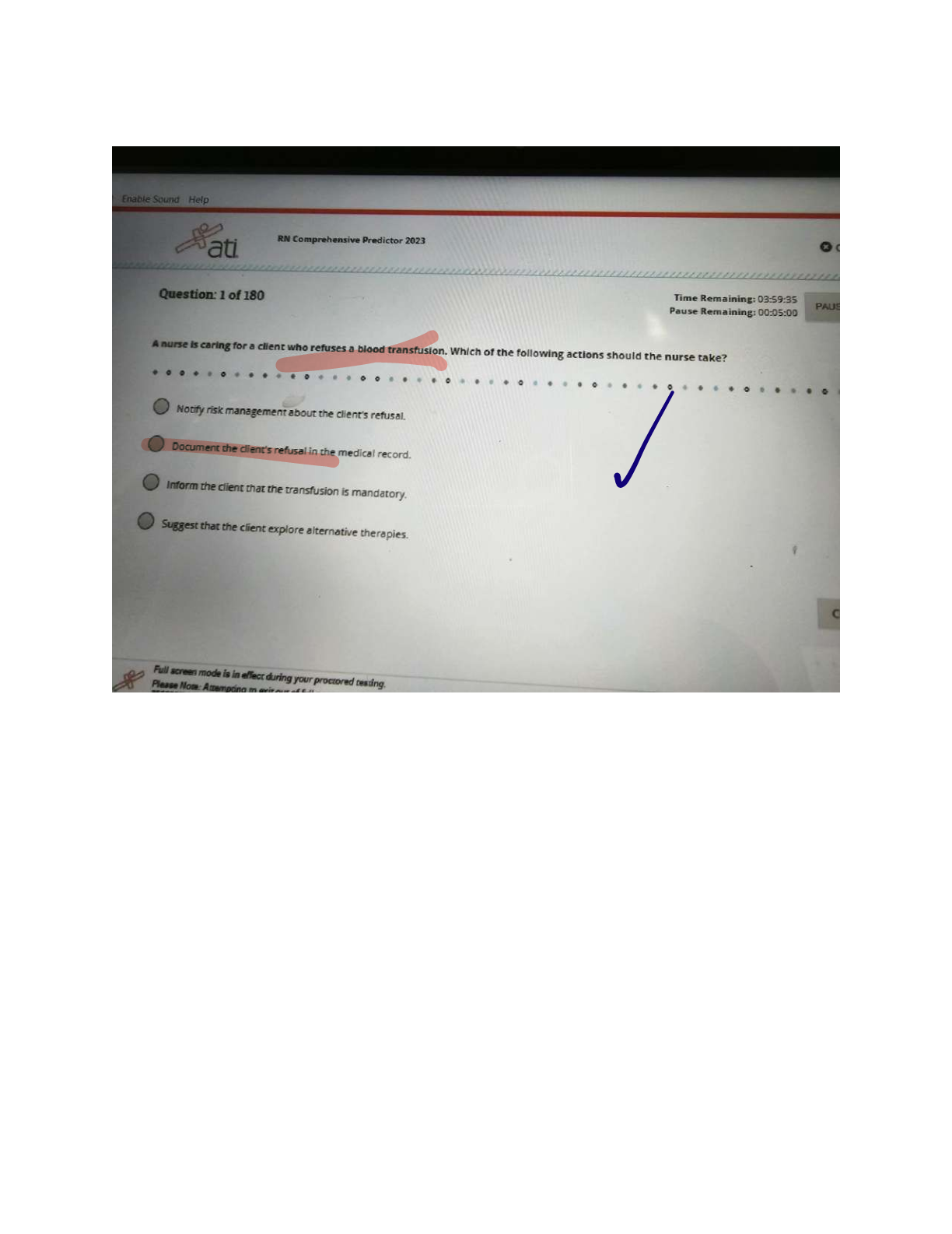
When a pt. refuses treatment, what should your initial response be? - ANSWER Ask the pt. to repeat the recommended procedure back to you to make sure you know they understand it.
"Durable" supplies - ANSWER (ex. fax and EKG machine) need serial #, maintenance and current condition and status on file
Controlled substances are to be inventoried __ - ANSWER DAILY
How many people must sign off on the daily controlled substance inventory? - ANSWER 2
How often is the inventory submitted to the DEA? - ANSWER every 2 years
ICD9 Vol. 1 - ANSWER V and E codes, organized by diseases and injuries
In Vol. 1 of the ICD9 manual, 3 digit codes represent... - ANSWER a specific disease
In the subcategory section of Vol. 1 in the ICD9 manual __ digit codes are used to... - ANSWER 4 digit codes are used to break diseases down further
ICD9 5-digit codes are used to symbolize - ANSWER subclassifications
ICD9 Vol. 2 contains - ANSWER an alpha ordered list of all the same diseases as volume 1
ICD9 Vol. 2 is organized into 3 sections, they are: - ANSWER 1. diseases
2. poison and chemical substance
3. alpha index of external causes of disease
ICD9 Vol. 3 is an alpha and tabular index mostly used in _ - ANSWER hospitals
ICD9 Vol. 3's codes are formatted with: - ANSWER 2 digit procedure code followed by a decimal then 1 or 2 digits
CPT codes are __ digit codes used to... - ANSWER 5-digit codes used to described procedures
CPT book that has codes for all patient and physician encounters based on place and type of service is in the __ section - ANSWER Evaluation & Management
In the __ section of the CPT book, the ASA ranks pts. by level of complexity - ANSWER Anesthesiology
In the __ section of the CPT book, there are "global periods" that describe all service that are part of patient care - ANSWER Surgery
The Radiology section of the CPT book includes information on __ and __ __ - ANSWER ultrasound and nuclear medicine
__ and __ services are grouped into panels in the CPT book. - ANSWER Lab and pathology
Services not in other sections of the CPT book may be found in this section. (ex. immunizations) - ANSWER Medicine
according to the pt. bill of rights, the pt. has a right to... - ANSWER info. about their treatment and the professionals and facility involved in their care
according to the pt. bill of rights, a pt. can choose between healthcare providers, ask for a __ __ and have access to help during an __ - ANSWER health screening, emergency
OSHA set guidelines for - ANSWER environmental protection and workplace safety
according to OSHA, when using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, use a __-sized amount - ANSWER quarter
What must be bandaged before donning gloves? - ANSWER breaks in the skin
OSHA bloodborne pathogen standard limits exposure to... - ANSWER disease-causing microorganisms
CLSI stands for - ANSWER Clinical labs and stadards institute
CLSI is an organization that... - ANSWER helps laboratories develop safety programs
CDC guidelines are a set of standard precautions that... - ANSWER reduce the risk of pathogens in healthcare
As defined by the CDC standard precautions, pathogens are: - ANSWER blod, bodily fluids, mucous membranes, tissues and non-intact skin
If a chain of custody form is needed for a patient suspected of illegal drug or alcohol use, what must every person who contacts the specimen do? - ANSWER Initial and date (time) the form
Once a rape kit is opened, according to chain of custody, anyone who touches it must... - ANSWER initial and write the time on the form
If you suspect anyone of committing Medicare and/or Medicaid insurance fraud, who should you contact? - ANSWER Program Integrity contact in state office
In all and any emergent situations, what is your role as a CCMA? - ANSWER keep calm, keep patients safe and calm as well
Fire extinguishers marked with "A" are designated for what type of fire? - ANSWER Ordinary
Fire extinguishers marked with "B" are designated for what type of fires? - ANSWER Flammable liquids and vapors
Fire extinguishers marked with "C" are designated for what type of fires? - ANSWER Electrical
Fire extinguishers marked with "K" are designated for what type of fires? - ANSWER Kitchen
Wound should always be wrapped __ to proximal - ANSWER distal
Bandages should always extend __ inches beyond the dressing - ANSWER 1-2 inches
NORMAL Sodium ranges - ANSWER 135-145 mEq/L
Normal Potassium ranges - ANSWER 3.5-5.1 mEq/L
RBC males - ANSWER 4.3-5.7 x 10^6 microL
RBC females - ANSWER 3.8-5.1 x 10^6 microL
Normal Hematocrit males - ANSWER 39-49%
Normal Hematocrit females - ANSWER 35-45%
Normal Hemoglobin males - ANSWER 13.5-17.5 g/dL
Normal Hb females - ANSWER 12.0-16.0 g/dL
Normal platelet count - ANSWER 150-450 x 10^3 per microL
LDL cholesterol - ANSWER <130
HDL Cholesterol males - ANSWER >29 mg/dL
HDL cholesterol females - ANSWER >35 mg/dL
Normal glucose levels - ANSWER 70-115 mg/dL
When tending to wounds, alginates are good for - ANSWER cleaning exudating wounds; helps in debridement
When tending to wounds, foam are good for - ANSWER wounds with large drainage
When tending to wounds, hydrogels are good for - ANSWER wounds that need sloughing off (ex.necrotic tissue or burns)
When tending to wounds, gauze is good for - ANSWER minor wounds or as a second dressing
15 mL = __ tbsp. - ANSWER 1
[Show More]