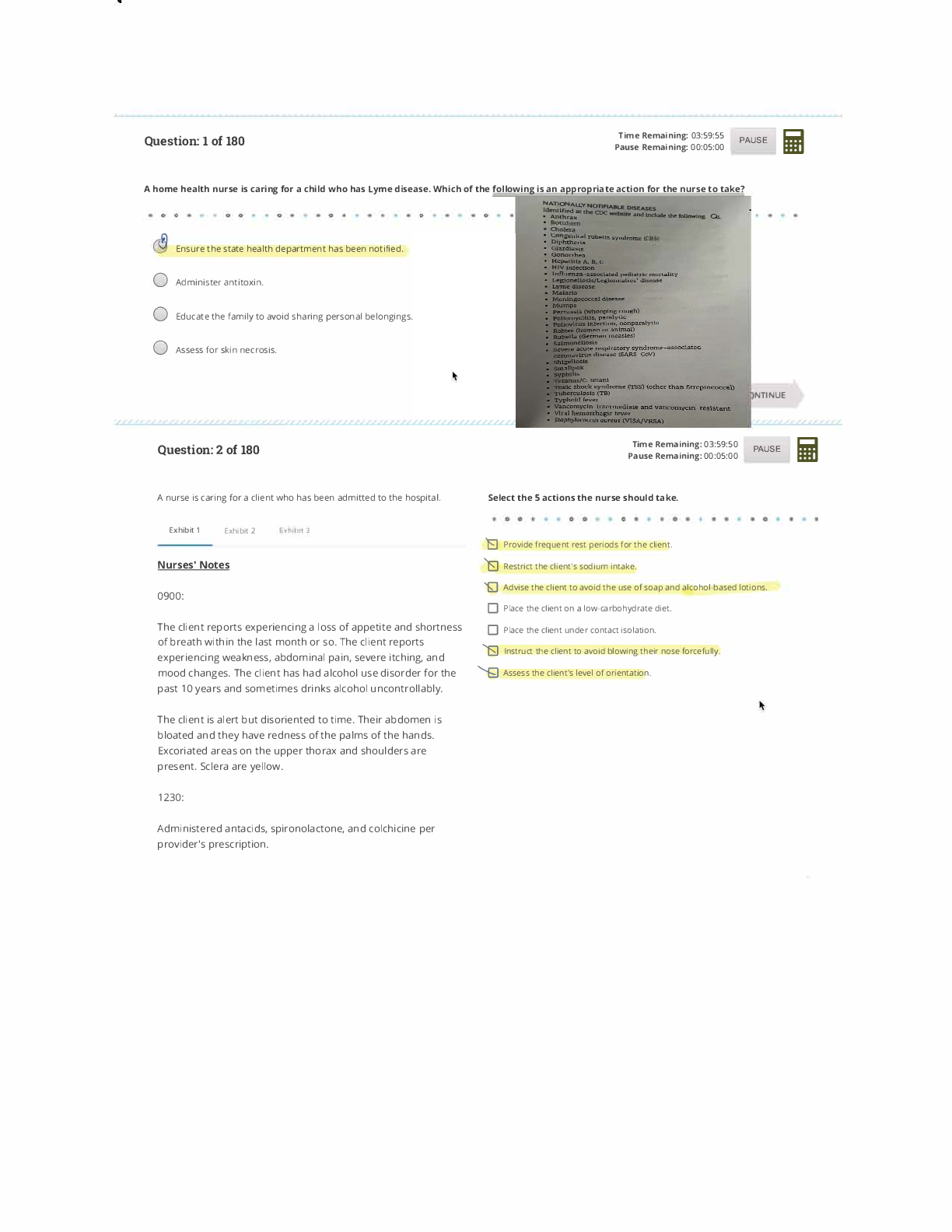
Which of the following is NOT an indication for continuous mechanical ventilation?
A. MIP -20 cmH2O
B. acute ventilatory failure
C. Vt < 5 mL/kg
D. VC < 10 mL/kg - ANSWER MIP -20 cmH2O
Optium PEEP therapy can be i
...
Which of the following is NOT an indication for continuous mechanical ventilation?
A. MIP -20 cmH2O
B. acute ventilatory failure
C. Vt < 5 mL/kg
D. VC < 10 mL/kg - ANSWER MIP -20 cmH2O
Optium PEEP therapy can be identified by all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Inflection point of a volume-pressure loop graphic
B. Acceptable oxygenation with no cardiovascular side effects
C. Increasing oxygenation with increasing plateau pressures
D. Increasing static compliance with acceptable oxygenation - ANSWER Increasing oxygenation with increasing plateau pressures
All of the following could be recommended to treat a patient with a severely decreased static compliance problem, EXCEPT:
A. inverse positive pressure ventilation
B. optium PEEP therapy
C. pressure control ventilation
D. expiratory resistance - ANSWER expiratory resistance
Which of the following is NOT a primary ventilation parameter measured and displayed to create airway graphics of continuous mechanical ventilation?
A. Flow
B. PEEP
C. Tidal volume
D. Airway pressure - ANSWER PEEP
A "broken" flow/volume loop and/or volume/pressure loop will occur with:
A. airway resistance
B. overdistension
C. auto PEEP
D. airway leak - ANSWER airway leak
A 32 year old female who weighs 100 kg (220 lbs.) and is 165 cm (5 ft. 6 inches) tall has chest trauma due to a motorcycle accident. The patient has just been intubated, sedated and paralyzed with morphine sulfate and pancuronium bromide. The physician asks for your immediate recommendation in ventilator settings for this patient. You would recommend:
A. A/C mode, rate 10, tidal volume 1000 ml
B. SIMV mode, rate 8, tidal volume 900 ml
C. IMV mode, rate 14, tidal volume 800 ml
D. Control mode, rate 12, tidal volume 600 ml - ANSWER Control mode, rate 12, tidal volume 600 ml
A respiratory care practitioner reviews a ventilator parameter sheet and finds that the peak inspiratory pressure has been gradually rising for the past several hours. Which of the following could be the cause for this change?
I. Bronchospasm
II. Increasing pulmonary compliance
III. Accumulation of secretions
IV. Increasing airway resistance
A. III only
B. I & III only
C. I, III & IV
D. I, II, III &IV - ANSWER I, III & IV
A 29 year old female post-operative mitral valve replacement patient is combative on a volume-cycled ventilator in the assist/control mode. The peak pressure alarm is sounding with each breath. The nurse practitioner has a STAT call into the cardiovascular surgeon. She asks for your immediate recommendation. You would recommend which of the following?
A. Increase the peak pressure alarm limit
B. Order a STAT chest x-ray
C. Change to SIMV mode and evaluate the patient
D. Order a STAT arterial blood gas - ANSWER Change to SIMV mode and evaluate the patient
A 44 year old male patient is being mechanically ventilated with a volume cycled ventilator. You observe that there is insufficient time for the patient to exhale completely. You would now do which of the following to correct the problem?
A. increase the flow
B. decrease the minute volume
C. add expiratory retard
D. remove mechanical deadspace - ANSWER increase the flow
A 58 year old male patient is hypoxic on a volume cycled ventilator and is receiving 15 cmH2O of PEEP on an FIO2 0.60. Shortly after increasing the PEEP therapy to 18 cmH2O, the respiratory care practitioner notes the systemic blood pressure has fallen from 110/72 torr to 94/50 torr and the cardiac output has fallen from 4.3 L/min. to 2.5 L/min. The most appropriate action at this time would be to:
A. maintain the present therapy and re-evaluate the patient in thirty minutes
B. decrease the PEEP to 15 cmH2O and increase the FIO2 to 0.70
C. decrease the PEEP to 12 cmH2O and maintain the FIO2 at 0.60
D. discontinue the PEEP and increase the FIO2 to 0.80 - ANSWER decrease the PEEP to 15 cmH2O and increase the FIO2 to 0.70
A 80 kg (176 lb) post-operative hepatic turmor removal patient is being mechanically ventilated on a volume cycled ventilator at the following settings:
Mode: A/C
Mandatory rate: 12 br/min
Total rate: 18 br/min
Tidal volume (set): 800 ml
Tidal volume (spontaneous): 0
FIO2: 0.50
Peak flow: 60 LPM
Arterial blood gas results:
pH: 7.34
PaCO2: 41 torr
PaO2: 94 torr
HCO3: 21 mEq/L
BE: -2
Which of the following should the respiratory care practitioner recommend at this time?
A. increase the tidal volume to 900 ml
B. increase the rate setting to 14 br/min
C. maintain current ventilator settings
D. add a pressure support of 10 cmH2O - ANSWER maintain current ventilator settings
Which of the following clinical combinations would indicate that you have exceeded the optimum level of PEEP therapy and that you should reduce the PEEP and increase the FIO2?
A. BP decreases, QT decreases, PWP increases and PAP increases
B. BP decreases, QT decreases, PWP decreases and PAP decreases
C. BP stable, QT stable, PWP decreases and PAP decreases
D. BP stable, QT increases, PWP stable and PAP stable - ANSWER BP decreases, QT decreases, PWP increases and PAP increases
A 74 year old female who weighs 65 kg (132 lbs) is being mechanically ventilated with a volume cycled ventilator following hip replacement surgery. Ventilator settings and arterial blood gas results are as follows:
Ventilator settings
Mode: A/C
Set rate: 14 br/min
Total rate: 14 br.min
Tidal volume: 750 ml
Peak flow: 50 lpm
FIO2: 0.35
Arterial blood gas
pH: 7.50
PaCO2: 29 torr
PaO2: 118 torr
HCO3: 23 mEq/L
The respiratory care practitioner should do which of the following?
A. decrease the peak flow setting
B. decrease minute ventilation
C. decrease the FIO2
D. initiate pressure support therapy - ANSWER decrease minute ventilation
A 80 kg (176 lb) male patient with alpha 1 protease inhibitor deficiency is being mechanically ventilated on a volume cycled ventilator at the following settings:
Mode: SIMV
Set rate: 12 br/min.
Total rate: 16 br/min.
Tidal volume (set): 850 ml
Tidal volume (spontaneous): 320 ml
Peak flow: 55 lpm
FIO2: 0.30
His vital signs are stable and he is asleep. An arterial blood gas has been drawn with the following results:
pH: 7.37
PaCO2: 51 torr
PaO2: 68 torr
HCO3: 32 mE/1L
Which of the following should the respiratory care practitioner recommend?
A. increase the rate setting
B. increase the tidal volume setting
C. increase the FIO2 setting
D. maintain current settings - ANSWER maintain current settings
A 6 year old child who weighs 20 kg (44 lbs) is intubated and being mechanically ventilated on the following settings:
Mode: A/C
FIO2: 0.80
Set rate: 12 br/min.
Total rate: 15 br/min.
Tidal volume: 200 ml
Arterial blood gas results:
pH: 7.48
PaCO2: 31 torr
PaO2: 54 torr
HCO3: 22 mEq/L
The respiratory care practitioner should recommend which of the following?
A. initiate 6 cmH2O PEEP
B. decrease the rate to 10
C. increase the tidal volume to 300 ml
D. increase the FIO2 to 0.85 - ANSWER initiate 6 cmH2O PEEP
[Show More]