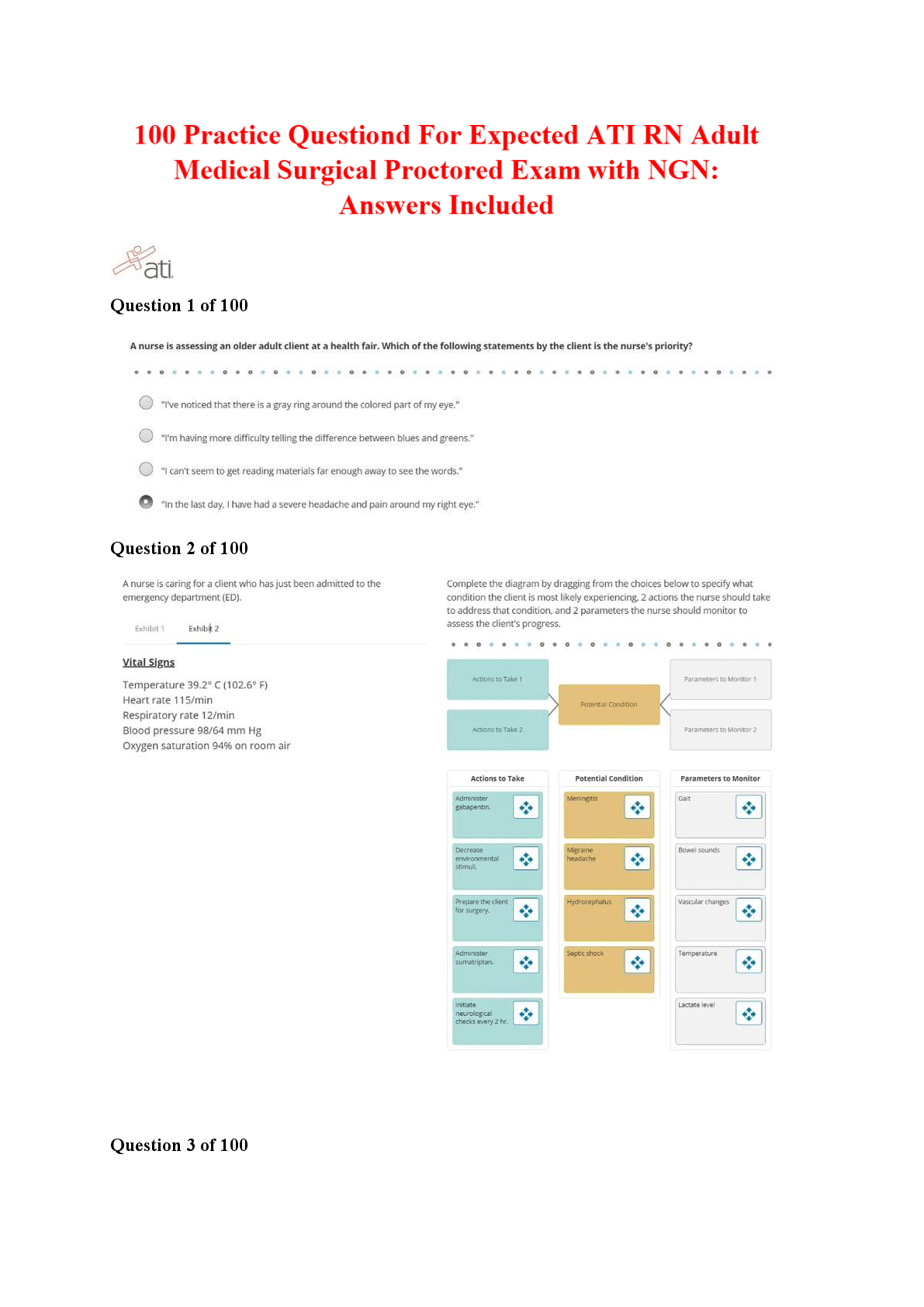
AUDITORY SYSTEM - ANSWER Responsible for hearing, balance, equilibrium, and communication skills
cardiovascular system - ANSWER THE HEART IS A MUSCLE THAT INITIATES SYSTEMIC ARTERIAL PULSE WAVES, CAUSING BLOOD TO CIRC
...
AUDITORY SYSTEM - ANSWER Responsible for hearing, balance, equilibrium, and communication skills
cardiovascular system - ANSWER THE HEART IS A MUSCLE THAT INITIATES SYSTEMIC ARTERIAL PULSE WAVES, CAUSING BLOOD TO CIRCULATE
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - ANSWER RESPONSIBLE FOR THE DIGESTION, ABSORPTION, METABOLISM, AND EXCRETION OF FOOD
endocrine system - ANSWER PRODUCTION AND SECRETION OF HORMONES FROM THE GLANDS.
IMMUNE SYSTEM - ANSWER DEFENSE SYSTEM THAT IDENTIFIES AND DESTROYS FOREIGN SUBSTANCES THAT INVADE THE BODY
integumentary system - ANSWER protects the body as a whole from the external environment
nervous system - ANSWER CONTROLS BOTH VOLUNTARY AND INVOLUNTARY FUNCTIONS OF THE BODY
OPTHALMIC SYSTEM - ANSWER responsible for providing an individual with vision
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM - ANSWER the production of offspring
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - ANSWER RESPONSIBLE FOR RESPIRATION AND MAINTAINING HOMEOSTASIS
URINARY SYSTEM - ANSWER RESPONSIBLE FOR THE EXCRETION OF CHEMICALS AND SUBSTANCES FROM THE BODY SYSTEM
drug-drug interactions: ADDITION - ANSWER the combined effect of two drugs; it is equal to the sum of the effects of each drug taken alone
drug-drug interactions: ANTAGONISM - ANSWER one drug works against the action of another drug
drug-drug interactions: POTENTIATION - ANSWER One drug increases or prolongs the effect of another drug; the total effect is greater than the sum of the effects of each drug alone.
Example: Vistaril and Demerol.
drug-drug interactions: SYNERGISM - ANSWER The joint action of drugs in which their combined effect is more intense or longer in duration than the sum of the effects of two drugs.
Drug-Disease Interactions - ANSWER Various diseases may inhibit the absorption, metabolism, and elimination of different drugs.
DRUG DISEASE INTERACTIONS EXAMPLE - ANSWER TAKING DECONGESTANTS IF THE PATIENT HAD HYPERTENSION OR DIABETES
Drug-Dietary Supplement Interactions - ANSWER Many herbal and dietary supplements have developed drug interactions with prescription drugs (ex: warfarin)
drug-over-the-counter drug interactions - ANSWER various over-the-counter (OTC) medications may either increase or decrease the effects of a prescription medication
Drug-OTC drug interactions example - ANSWER aspirin can increase the effect of warfarin
Drug-laboratory interactions - ANSWER Many drugs used today have demonstrated they may have an effect on serum potassium and creatine levels in the body. These interactions can result in additional testing to detect abnormalities.
Drug-Nutrient Interactions - ANSWER poor nutrition may affect the metabolism of various drugs
Drug-Related Problems - ANSWER an event or situation involving drug therapy that actually or potentially interferes with the optimum outcome - include: untreated indication, improper drug selection, sub-therapeutic dosage (dosage too low to produce a therapeutic effect), failure to receive a drug, over-dosage, and drug use without an indication
pregnancy category a - ANSWER no risk to fetus
pregnancy category b - ANSWER drug studies have not been performed in pregnant women; animal studies have not demonstrated fetal risk
pregnancy category c - ANSWER animal studies show risk, caution is advised, benefits may outweigh risks
pregnancy category d - ANSWER Positive evidence of human fetal risk BUT benefits outweigh risks
Pregnancy Category X - ANSWER Studies in animals or humans show abnormalities; use in pregnancy is contraindicated
chemical name - ANSWER Determined by chemical structure of the drug entity
proprietary name - ANSWER Assigned by the drug manufacturer and is protected through a patent
nonproprietary name - ANSWER generic name
astine - ANSWER antihistamine
azepam - ANSWER Antianxiety
caine - ANSWER local anesthetic
cillin - ANSWER penicillin
conazole - ANSWER systemic antifungal
estr - ANSWER estrogen
-glitazone - ANSWER Antidiabetic
micin - ANSWER Aminoglycosides (antibiotics)
thromycin - ANSWER macrolide antibiotic
olol - ANSWER beta blocker
olone - ANSWER steroid
profen - ANSWER NSAIDS (anti-inflammatory)
prazole - ANSWER proton pump inhibitor
pril - ANSWER ACE inhibitor
sartan - ANSWER Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist
semide - ANSWER loop diuretic
setron - ANSWER Serotonin (5-HT3) antagonist
sulfa - ANSWER antibiotic; anti-infective; anti-inflammatory
terol - ANSWER Bronchodilator
tidine - ANSWER H2 receptor antagonists
-e-triptyline; -amine - ANSWER tricyclic antidepressant
-oxetine - ANSWER Antidepressant
vastatin - ANSWER antihyperlipidemics
bacterial infections - ANSWER occur when the body's immune system is unable to resist bacteria. symptoms: fever greater than 101 F and an increase in white blood cells
multidrug resistant infections - ANSWER An infection caused by bacteria that is resistant to one or more drug classifications.
pneumonia - ANSWER an infection that causes acute inflammation in the airways of the lung, blocking them with thick mucus
sulfa moa - ANSWER interfere with paraaminobenzoic acid and folic acid formation and thus destroy bacteria
penicillin moa - ANSWER prevents bacteria from forming a cell wall
Cephalosporins MOA - ANSWER Prevent bacteria from forming a cell wall
Carbapenems & Monobactams MOA - ANSWER inhibit bacterial wall synthesis
Tetracycline MOA - ANSWER inhibit protein synthesis
macrolides - ANSWER inhibit protein synthesis
ketolides moa - ANSWER Block protein synthesis by binding to ribosomal subunits; may inhibit the formation of newly forming ribosomes
streptogramins moa - ANSWER inhibit bacterial protein synthesis
quinolones moa - ANSWER Antagonize an enzyme required for DNA synthesis, causing DNA breakage and finally death
Aminoglycosides MOA - ANSWER inhibit bacterial protein synthesis
Cyclic Lipopeptides moa - ANSWER Bind to bacterial membranes and cause the cell membrane to depolarize, resulting in an inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis
clindamycin moa - ANSWER inhibits protein synthesis
Metronidazole MOA - ANSWER destroys parts of the bacteria's DNA nucleus
Phentamine moa - ANSWER unkown
linezolid moa - ANSWER inhibits bacterial protein synthesis
Vancomycin MOA - ANSWER interferes with bacterial wall formation
fungal infections - ANSWER -caused by single-cell organisms that don't have a cell wall, chlorophyll, and reproduce by spores
-fungus develops in individuals whose immune systems have been compromised by disease, drug therapy, or poor nutrition
Tinea infections - ANSWER a fungal infection of the skin or feet
NRTIs - ANSWER ASSIST IN THE TREATMENT OF HIV
NNRTIs - ANSWER AID IN THE TREATMENT OF HIV DISEASE
Protease inhibitors MOA - ANSWER Prevent the cleavage of certain HIV protein precursors, which are necessary for the replication of new viruses
Fusion Inhibitor MOA - ANSWER Prevents AIDS virus from entering immune cells
ALLERGIES - ANSWER A response of our immune system due to an unrecognized substance
RHINITIS - ANSWER An inflamation of the nose.
Antihistamines - ANSWER medicines that reduce the production of histamines
ANITTUSSIVES - ANSWER prevent or relieve coughing
DECONGESTANTS - ANSWER eliminate or reduce swelling or congestion
EXPECTORANTS - ANSWER TO REMOVE MUCUS FROM BOTH LUNGS AND AIRWAY PASSAGES DURING COUGHING
SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) MOA - ANSWER BLOCK THE REUPTAKE OF SEROTONIN
SSNRIs (selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) MOA - ANSWER INHIBIT NOREPINEPHRINE AND SEROTONIN REUPTAKE
TCAs (tricyclic antidepressants) - ANSWER DEPRESSION, NOCTURIA (BEDWETTING) IN CHILDREN
MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors) - ANSWER DEPRESSION
neurosis - ANSWER a psychologic condition in which anxiety is prominent
phobias - ANSWER irrational fears
psychosis - ANSWER loss of contact with reality
Schizophrenia - ANSWER chronic psychotic disorder that may include hallucinations, disorganized speech and behavior, flat affect, and lack of initiative
antipsychotic agents moa - ANSWER Block Dopamine (D2) receptors in the dopamine pathways of the brain
anti insomnia agents moa - ANSWER interact with acid (gaba)- benzodiazepine receptor complexes
add - ANSWER a physiological disorder found in children showing signs of attention deficit without hyperactivity
adhd - ANSWER a physiological disorder found in which the patient has difficulty focusing their attention in a quiet inattentive manner or displays hyperactivity
Anticonvulsants - ANSWER prevent or control seizures
Antiparkinson's Agents - ANSWER Used in the treatment of parkinson's disease
multiple sclerosis agents - ANSWER autoimmune disease in which the myelin sheaths around nerves degenerate
emphysema - ANSWER destruction of alveoli
cystic fibrosis - ANSWER A genetic disorder that is present at birth and affects both the respiratory and digestive systems.
xanthine derivatives moa - ANSWER Reverse bronchospasm associated with antigens and irritants; improve contractility of diaphragm
H2 anatagonists - ANSWER block gastric acid and pepsin secretion from histamine, gastrin, certain foods
Proton Pump Inhibitors - ANSWER decrease the amount of acid produced by the stomach
Crohn disease (Crohn's) - ANSWER chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract
ulcerative colitis - ANSWER chronic inflammation of the colon with presence of ulcers
[Show More]