UNCP Genetics Exam 2
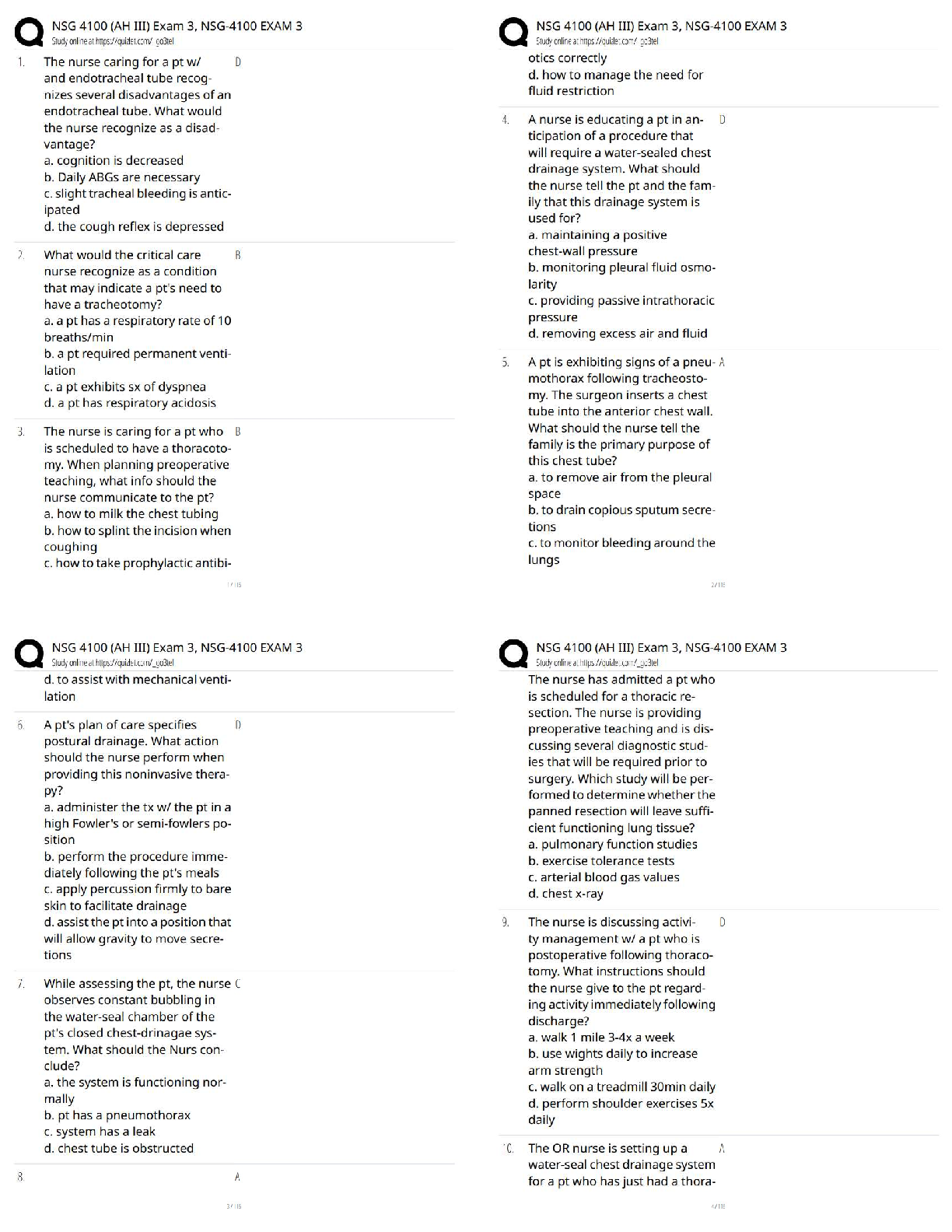
We discussed how transfer RNA's undergo substantial posttranscriptional base modification.
Which of the following is correct relative to this phenomenon? - ANS - without base
modification a tRNA w
...
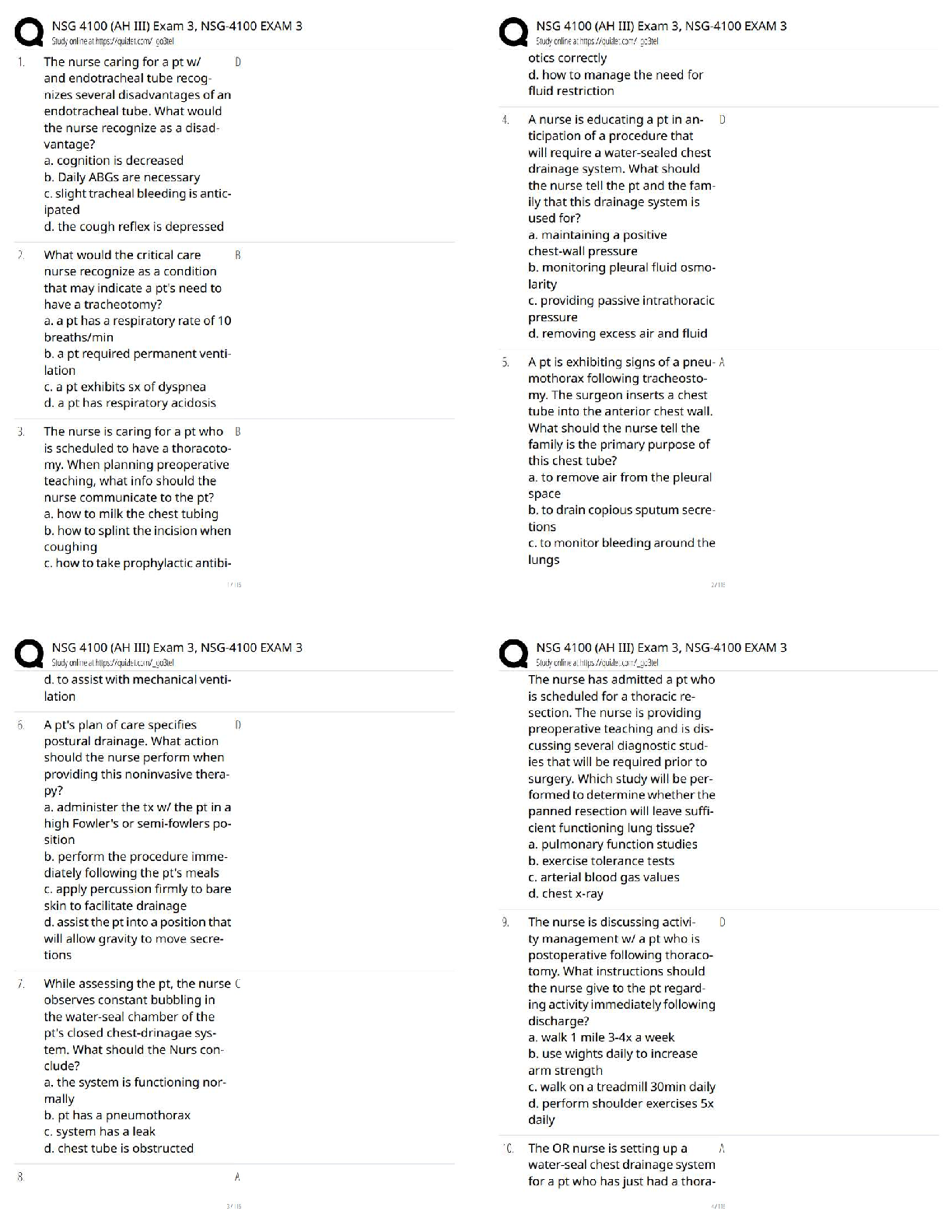
UNCP Genetics Exam 2
We discussed how transfer RNA's undergo substantial posttranscriptional base modification.
Which of the following is correct relative to this phenomenon? - ANS - without base
modification a tRNA will not function
There is several nucleic acid molecules involved in polypeptide synthesis, however, only one is
physically connected to an amino acid. Which one is this? - ANS - tRNA
We have frequently discussed the complementary nature of nucleic acid strands. Which of the
following sequences show complementarity between them? - ANS - anticodon & partner DNA
The ShineDalgarno sequence: - ANS - is complimentary to 3' end of the 16S rRNA strand.
In our discussion of the genetic code, we learned that three codons are known as termination or
stop codons. How many tRNA's normally recognize these codons? - ANS - 0
All of the following are involved in the process of tRNA charging EXCEPT __________. - ANS
- rRNA
What signals termination of translation in bacteria? - ANS - RF1 & RF2
A mutation in EF-Tu would have a direct effect on which part of translation? - ANS - The next
tRNA would not be able to enter the A site of the ribosome.
In bacteria, the methionine that initiates the formation of a polypeptide chain differs from
subsequently added methionines in that _______. - ANS - a formyl group is attached to the
initiating methionine
Translation in bacteria is directly dependent on all of the following associations except _______.
- ANS - Complementary base pairing between mRNA & DNA
Which of the following best describes the first step in the formation of the translation initiation
complex? - ANS - The small ribosomal subunit binds to an mRNA sequence near the 5' end of
the transcript
Identify the correct sequence of steps in protein synthesis.
A peptide bond formation
B binding of fmettRNA to mRNAribosome complex
C binding of mRNA to ribosome
D release of fmettRNA and translocation
E binding of charged tRNA to A site - ANS - CBEAD
Once elongation is underway, tRNAs involved in the process occupy a series of sites on the
complexed ribosome. The occupation of sites occurs in the following order. - ANS - A site, P
site, E site
catalyses the formation of the peptide bond linking two amino acids during translation. - ANS -
23S RNA
When a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids, one is attached to the tRNA occupying
the P site and the other _______. - ANS - is attached to the tRNA occupying the A site
The correct sequence of events involving a given amino acid in protein synthesis is:
1 pairing of charged tRNA with mRNA
2 binds with aminoacyl synthetase
3 peptide bond formation.
4 attached to tRNA - ANS - 2413
A mad cartoonist has all the molecules necessary for protein synthesis in a test tube. He has
inadvertently mixed up some of the components. Included in his test tube are: partner DNA from
Fred Flintstone, tRNA molecules from Bugs Bunny, ribosomes from Tweedy Bird, mRNA from
George Jetson, and amino acids from Wiley Coyote. Assuming this concoction is functional and
translation occurs, the first proteins generated will be the same proteins produced by which of the
above mentioned critters? - ANS - George Jetson
Identify the correct sequence of steps in protein synthesis in prokaryotes:
A binding of large ribosomal subunit to initiation complex
B peptide bond formation
C binding of mRNA to small subunit of ribosome
D binding of charged tRNA to A site
E release of fmettRNA and translocation - ANS - CADBE
Translation in bacterial and eukaryotic cells has many similarities, but there are also several key
differences. Which of the following is one of those differences that is seen in eukaryotes? - ANS
- Eukaryotes use the 5 G-cap and Poly-A-tail on their mRNAs to initiate translation.
Explain why the one-gene:one-enzyme hypothesis is no longer considered to be totally accurate.
- ANS - Some genes do not code proteins.
Overlapping genes and alternative splicing were discovered.
Some enzymes consist of different subu
[Show More]