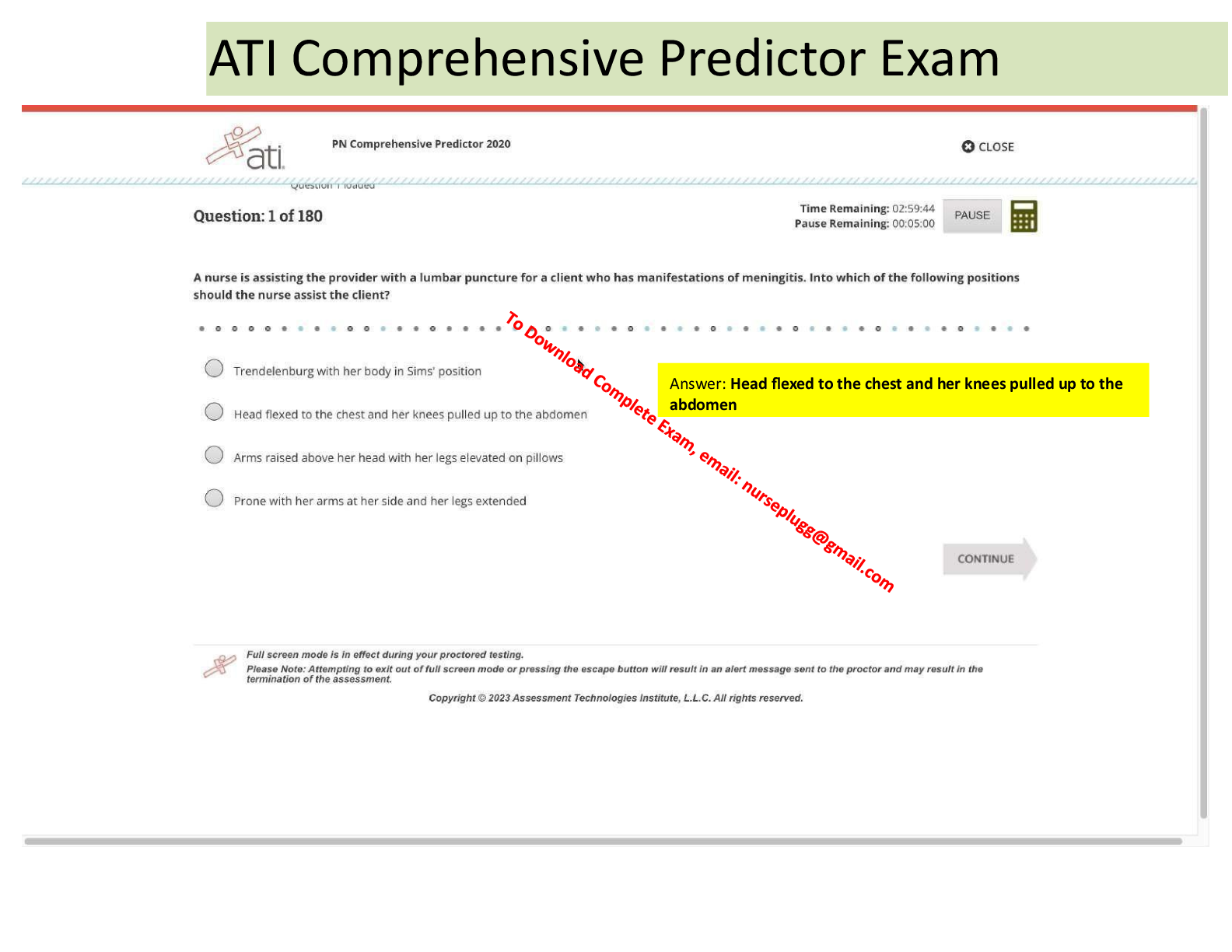
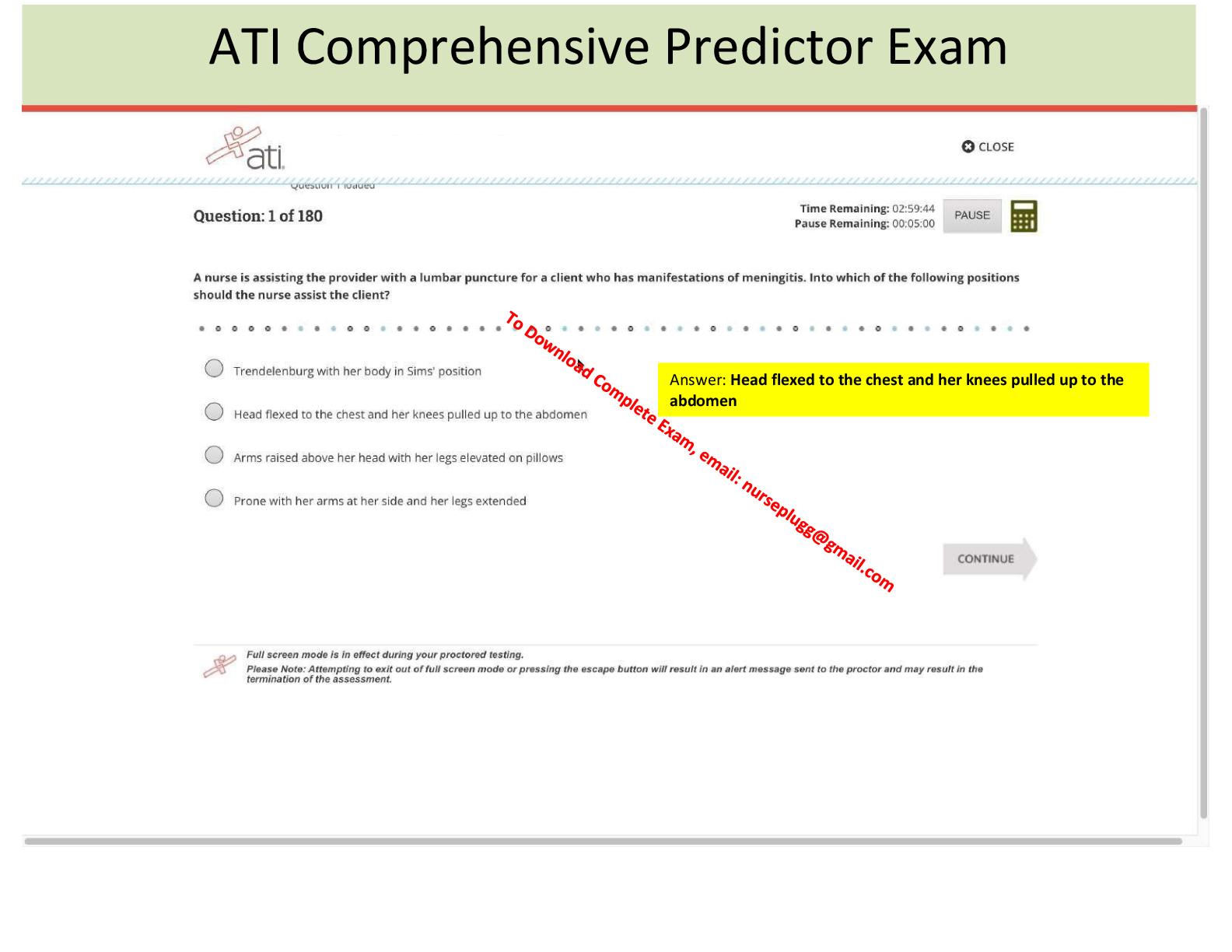
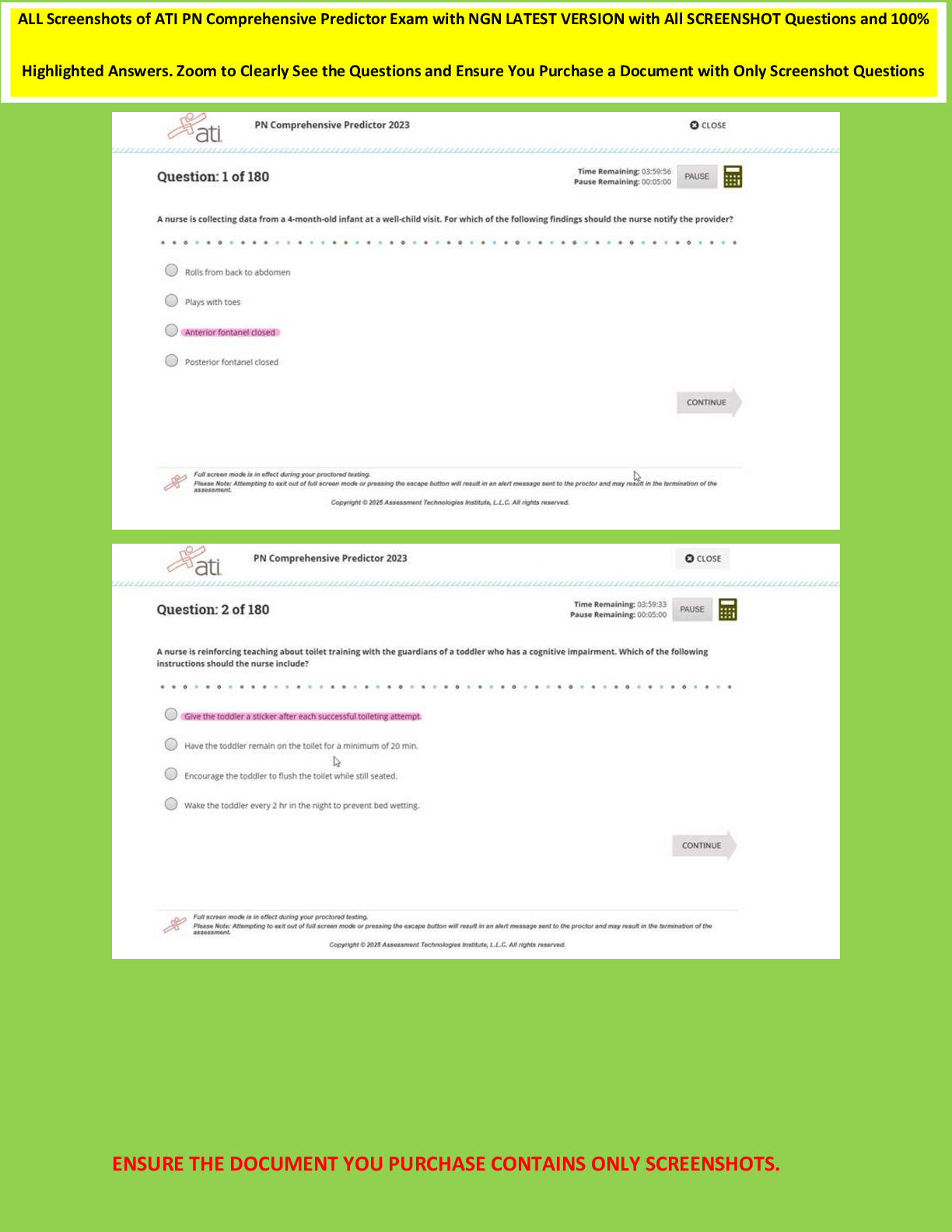
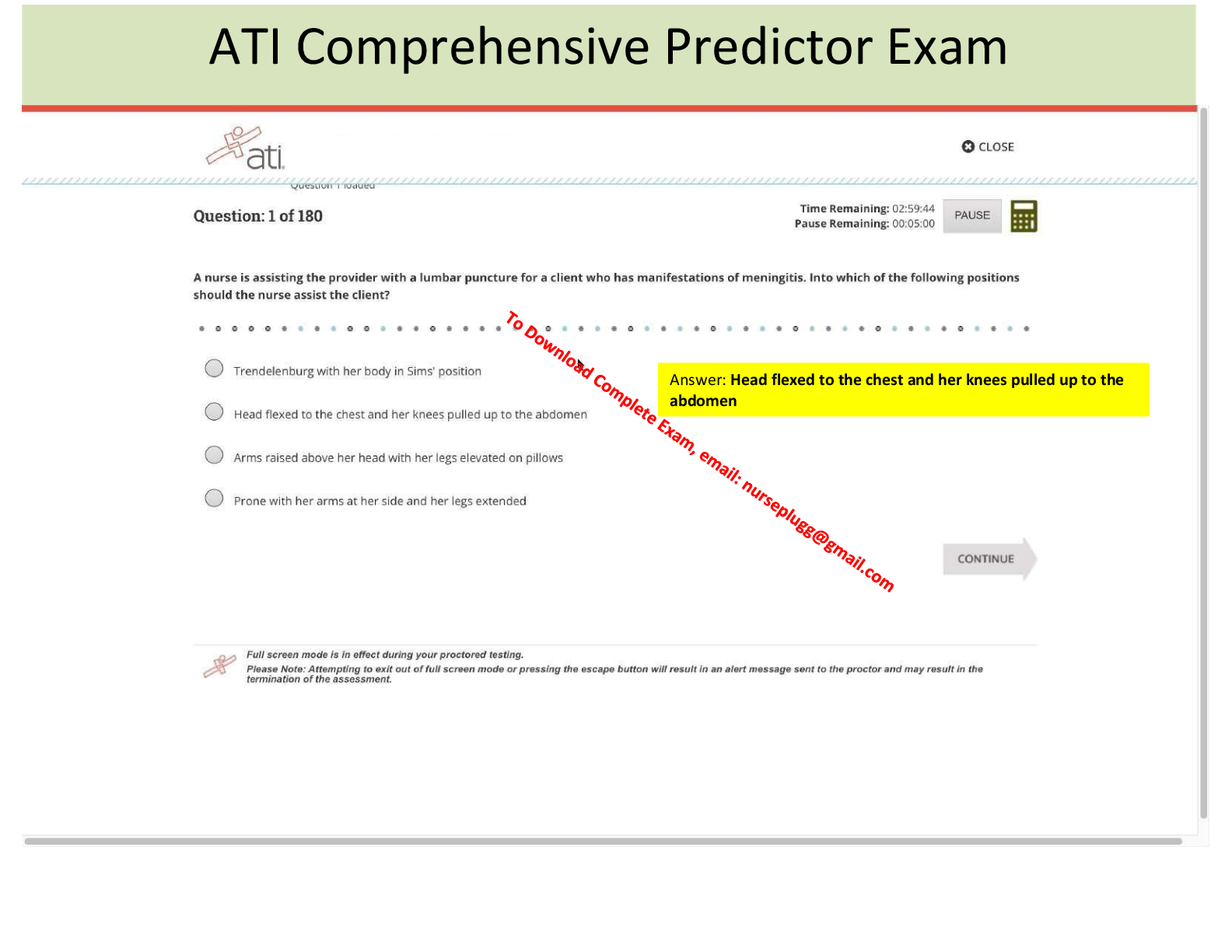
A patient develops acute diarrhea and then comes to clinic two weeks later reporting profuse watery, bloody diarrheal stools 6 to 8 times daily. The provider notes a toxic appearance with moderate dehydration. Which test
...
A patient develops acute diarrhea and then comes to clinic two weeks later reporting profuse watery, bloody diarrheal stools 6 to 8 times daily. The provider notes a toxic appearance with moderate dehydration. Which test is indicated to diagnose this cause?
Stool collection for 24-hour stool pH
Qualitative and quantitative fecal fat
C. difficile toxin
Wright stain of stool for white blood cells - ANSWER C. difficile toxin
A patient reports anal pruritis and occasional bleeding with defecation. An examination of the perianal area reveals external hemorrhoids around the anal orifice as the patient is bearing down. The provider orders a
colonoscopy to further evaluate this patient. What is the treatment for this patient's symptoms?
Referral for possible surgical intervention
A high-fiber diet and increased fluid intake
Daily laxatives to prevent straining with stools
Infiltration of a local anesthetic into the hemorrhoid - ANSWER A high-fiber diet and increased fluid intake
A patient has sudden onset of right upper quadrant and epigastric abdominal pain with fever, nausea, and vomiting. The emergency department provider notes yellowing of the sclerae. What is the probable cause of these findings?
Acute acalculous cholecystitis
Infectious cholecystitis
Common bile duct obstruction
Chronic cholelithiasis - ANSWER Common bile duct obstruction
An 83 year old is diagnosed with diverticulitis. The most common complaint is
Rectal bleeding
Bloating and crampiness
Left lower quadrant pain
Frequent belching and flatulence - ANSWER Left lower quadrant pain
A patient's CBC demonstrated anemia. Which diagnosis is likely based on this patient's laboratory values?
MCV 74.1 fL (normal 80-95)
MCH 24 pg (normal 27-31)
MCHC 33% (normal 32-69)
RDW 12% (normal 11-14.5)
iron deficiency anemia
anemia of chronic disease
vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
thalassemia - ANSWER thalassemia
A patient has fever, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. An ultrasound is negative for gallstones. Which action is necessary to treat this patient's symptoms?
Hospitalization for emergent treatment
Empiric treatment with antibiotics
Supportive care with close follow-up
Prescribing ursodeoxycholic acid - ANSWER Hospitalization for emergent treatment
A patient has both occasional "coffee ground" emesis and melena stools. What is the most probably source of bleeding in this patient?
Upper GI
Hepatic
Lower GI
Rectal - ANSWER Upper GI
An adult patient has intermittent, crampy abdominal pain with vomiting. The provider notes marked abdominal distention and hyperactive bowel sounds. What will the provider do initially?
Prescribe an antiemetic and recommend a clear liquid diet for 24 hours
Obtain upright and supine radiologic views of the abdomen
Schedule the patient for a barium swallow and enema
Admit the patient to the hospital for consultation with a surgeon - ANSWER Obtain upright and supine radiologic views of the abdomen
What choice below is most commonly associated with pancreatitis?
Appendicitis and renal stones
Hypertriglyceridemia and cholecystitis
Gallstones and alcohol abuse
Viral infection and cholecystitis - ANSWER Gallstones and alcohol abuse
What medication may be used to treat GERD if a patient has tried over the counter ranitidine without benefit?
Prescription strength ranitidine
Calcium carbonate
Prescription strength ranitidine
Pantoprazole - ANSWER Pantoprazole
A 30-year-old woman has right upper quadrant abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Which diagnostic test will the provider order?
Abdominal ultrasound
MRI of the abdomen
Abdominal CT with contrast
Plain abdominal radiographs - ANSWER Abdominal ultrasound
Which medications may increase the prevalence of GERD? (Select all that apply.)
Calcium antagonists
Aspirin
Oral contraceptives
Hormone replacements
Benzodiazepines - ANSWER Calcium antagonists
Aspirin
Benzodiazepines
What is the best treatment for H. pylori-related peptic ulcer disease?
H2RA, bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline for 10 to 14 days
PPI, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin for 10 days
PPI and clarithromycin for 14 days
H2RA and clarithromycin for 14 days - ANSWER PPI and clarithromycin for 14 days
An 8-month-old girl is brought by her grandmother to see the nurse practitioner because of intermittent, random episodes of vomiting, abdominal bloating, currant jelly stools, and irritability with poor appetite. The infant is stranding in the 10th percentile on the growth chart and appears lethargic. During the abdominal exam, a sausage like mass is palpated on the right side of the abdomen. The infant's presentation is highly suggestive of which condition?
Lactose intolerance
Intussusception
Inflammatory bowel disease
Irritable bowel syndrome - ANSWER Intussusception
The classic triad of intussusception is currant jelly stools, a sausage like mass, and pain. A sausage-shaped abdominal mass may be palpated on the right side of the abdomen.
A patient is in the clinic with a 36 hrs history of diarrhea and moderate dehydration. Interventions should include:
IV rehydration
Oral rehydration with gatorade or tea
Resumption of usual fluid intake
Oral rehydration with an electrolyte replenishment solution - ANSWER Oral rehydration with an electrolyte replenishment solution
All of the following are true statements about diverticula except:
Most diverticula in the colon are infected with gram negative bacteria
Supplementing with fiber, such as psyllium (Metamucil), is recommended
Diverticula are located in the colon
A low fiber diet is associated with the condition - ANSWER Most diverticula in the colon are infected with gram negative bacteria
A patient has a history of diverticular disease and asks what can be done to minimize acute symptoms. What will the practitioner recommend to this
patient?
Taking an anticholinergic medication
Consuming a diet high in fiber
Avoiding saturated fats and red meat
Using bran to replace high-fiber foods - ANSWER Consuming a diet high in fiber
A patient has a recent episode of vomiting and describes the vomitus as containing mostly gastric juice. What does this symptom suggest?
Small bowel obstruction
Gastritis
Peptic ulcer
Bile duct obstruction - ANSWER Peptic ulcer
A patient present with abdominal pain and has the following laboratory
findings. Would does this mean?
HBsAg positive
anti-HBc positive
IgM Anti-HBc positive
anti-HBs negative
He has immunity to hepatitis B
More data is needed
He has no immunity to hepatitis B
He has acute hepatitis B - ANSWER He has acute hepatitis B
A positive hepatitis B surface antigen and a positive IgM means that
this patient has acute hepatitis B. The first serological marker to be
positive is the surface antigen. It can become positive as soon as 3-4
weeks after exposure to hepatitis B. Positive IgM indicates acute
infection.
A patient who has been taking an NSAID for osteoarthritis pain has newly diagnosed peptic ulcer disease. What is the initial step in treating this patient?
Discontinue the NSAID
Order prostaglandin therapy
Prescribe a proton pump inhibitor
Recommend an H2 receptor antagonist - ANSWER Discontinue the NSAID
Which is the most common cause of pancreatitis in the United States?
Hyperlipidemia
Ethyl alcohol
Trauma
Gallstones - ANSWER Gallstones
Most patient who have an acute hepatitis B infection:
Have varied clinical presentations
Are acutely ill
Are females
Develop subsequent cirrhosis - ANSWER Have varied clinical presentations
Which description is more typical of a patient with acute cholecystitis?
The patient is ill appearing and febrile
The elderly patient is more likely to exhibit Murphy's sign
The patient rolls from side to side on the exam table
Most are asymptomatic until a stone blocks the bile duct - ANSWER The patient is ill appearing and febrile
A patient with acute cholecystitis usually c/o abd pain in upper right quadrant or epigastric pain. Many also have nausea. The patient lies still on the exam table as this condition is associated with peritoneal
inflammation that is worse with movement. Elderly are less likely to exhibit Murphy's sign. Asymptomatic patients have cholelithiasis.
A patient is in clinic for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain. The provider palpates a pulsatile, painful mass between the xiphoid process and
the umbilicus. What is the initial action?
Schedule the patient for an aortic angiogram
Perform an ultrasound examination to evaluate the cause
Transfer the patient to the emergency department for a surgical consult
Order a CBC, type and crossmatch, electrolytes, and renal function tests - ANSWER Transfer the patient to the emergency department for a surgical consult
A patient has intermittent left-sided lower abdominal pain and fever associated with bloating and constipation alternating with diarrhea. The provider suspects acute diverticulitis. Which tests will the provider order? (Select all that apply.)
Stool for occult blood
CT scan of abdomen and pelvis
Rigid sigmoidoscopy
Plain abdominal radiographs
Barium enema examination - ANSWER Stool for occult blood
CT scan of abdomen and pelvis
Extreme tenderness and involuntary guarding at McBurney's point is a significant finding for possible:
Acute gastroenteritis
Acute appendicitis
Acute diverticulitis
Acute cholecystitis - ANSWER Acute appendicitis
A 24 year old female with pain and tenderness in the right lower abdominal quadrant. Pelvic exam and UA are normal. WBC is elevated. Urine pregnancy test is negative. What is part of the differential diagnosis?
UTI
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Ectopic pregnancy
Appendicitis - ANSWER Appendicitis
Which factors increase the risk of renal stones? (Select all that apply.)
Excess antacid use
Vitamin D excess
Strenuous exercise
Snow skiing
Surgical menopause - ANSWER Excess antacid use
Strenuous exercise
Surgical menopause
A pregnant woman at 30 weeks gestation has proteinuria. What will the
provider do next?
Reassure her that this normal at this stage of pregnancy
Evaluate her blood pressure
Monitor serum glucose for gestational diabetes
Perform a 24-hour urine collection - ANSWER Evaluate her blood pressure
A patient who has diabetes has symptoms consistent with renal stones.
Which type of stone is most likely in this patient?
Uric acid
Citrate
Oxalate
Cysteine - ANSWER Uric acid
A 50-year-old male patient reports that he has a sensation of scrotal
heaviness. He reports that the sensation is worse at the end of the day. He denies pain. What is likely etiology of these symptoms?
Strangulated hernia
Inguinal hernia
Epididymitis
Hydrocele - ANSWER Inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernias are common in males. typical symptom reported by
man with an inguinal hernia is scrotal heaviness, especially at the end
of the day. If pain is severe, it may indicated strangulated hernia.
This is a medical emergency. Epididymitis can produce scrotal pain,
not usually heaviness. Hydrocele results in fluid in the scrotum.
A female patient who is 45-year-old states that she is having urinary
frequency. She describes episodes of "having to go right now" and not being
able to wait. Her urinalysis results are within normal limits. What this part of
the differential?
Stress incontinence
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Lupus
Diabetes - ANSWER Diabetes
Patients with diabetes can present with polyuria. In assessment of
patient's risk factors should be done with strong consideration even to
checking glucose level. Other possible diagnoses include urge
incontinence and vaginitis. A urinalysis would show bacteriuria.
A 3-month-old male infant has edema and painless swelling of the scrotum.
On physical examination, the provider is able to transilluminate the scrotum.
What will the provider recommend?
A short course of empiric antibiotic therapy
Observation and reassurance that spontaneous resolution may occur
A Doppler ultrasound to evaluate the scrotal structures
Immediate referral to a genitourinary surgeon for repair - ANSWER Observation and reassurance that spontaneous resolution may occur
An asymptomatic pregnant woman has a positive leukocyte esterase and
positive nitrites on a urine dipstick screening. What will the provider do next?
Admit to the hospital
Obtain a urine culture
Prescribe trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Order a renal ultrasound - ANSWER Obtain a urine culture
A patient has acute renal colic, nausea, and vomiting and a urinalysis reveals
hematuria, but is otherwise normal. A radiographic exam shows several
radiopaque stones in the ureter which are less than 1 mm in diameter. What
will the primary provider do initially to manage this patient?
Order a narcotic pain medication and increased oral fluids
Obtain a consultation with a urology specialist
Prescribe desmopressin and a corticosteroid medication
Prescribe nifedipine and hospitalize for intravenous antibiotics - ANSWER Order a narcotic pain medication and increased oral fluids
17-year-old boy reports feeling something on his left scrotum. On palpation, soft and movable blood vessels that feel like "a bag of worms" are noted underneath the scrotal skin. The testicle is not swollen or reddened. The most likely diagnosis is:
Testicular torsion
Varicocele
Chronic orchitis
Chronic epididymitis - ANSWER Varicocele
Palpation of varicose veins, described as "a bag of worms", is a
classic symptom of varicocele.
The daughter of an elderly, confused female patient reports that her mother is having urinary incontinence several times each day. What will the provider do initially?
Perform a bladder scan to determine distention and retention
Tell the daughter that this is expected given her mother's age and confusion
Obtain a urine sample for urinalysis and possible culture
Order serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen tests - ANSWER Obtain a urine sample for urinalysis and possible culture
An adolescent male reports severe pain in one testicle. The examiner notes
edema and erythema of the scrotum on that side with a swollen, tender
spermatic cord and absence of the cremasteric reflex. What is the most
important intervention?
Immediate referral to the emergency department
Doppler ultrasound to assess testicular blood flow
Prescribing anti-infective agents to treat the infection
Transillumination to assess for a "blue dot" sign - ANSWER Immediate referral to the emergency department
A 20-year-old male has epididymitis. His most common complaint will be:
Scrotal pain
Burning with urination
Penile discharge
Testicular pain - ANSWER Scrotal pain
The most common complaint for epididymitis is scrotal pain. Usually
develops over a period of days. Burning with urination is possible if
the underlying cause is a urinary tract infection. However, this is more
common in older males. Testicular pain is not a common complaint
with epididymitis. Penile discharge may occur with gonorrhea or
Chlamydia infections.
A 16-year-old female patient is being treated for her first UTI. She had an
allergic reaction with hives after taking sulfa as a child. Which of the following antibiotics would be contraindicated?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Cephalexin
Nitrofurantoin
Ampicillin - ANSWER Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
A young adult male reports a gradual onset 3/10 dull pain in the right scrotum
and the provider notes a bluish color showing through the skin on the affected side. Palpation reveals a bag of worms on the proximal spermatic
cord. What is an important next step in managing this patient?
Consideration of underlying causes of this finding
Referral to an emergency department for surgical consultation
Reassurance that this is benign and may resolve spontaneously
Anti-infective therapy with ceftriaxone or doxycycline - ANSWER Consideration of underlying causes of this finding
A 30-year-old male patient has a positive leukocyte esterase and nitrites on a
random urine dipstick during a well patient exam. What type of urinary tract
infection does this represent?
Unresolved
Uncomplicated
Isolation
Complicated - ANSWER Complicated
An older male patient reports gross hematuria but denies flank pain and
fever. What will the provider do to manage this patient?
Obtain a urine culture
Monitor blood pressure closely
Refer for cystoscopy and imaging
Perform a 24-hour urine collection - ANSWER Refer for cystoscopy and imaging
A male patient complaints of dysuria. His urinalysis is positive for nitrates, leukocytes, and bacteria. What medication should be given and for how
many days?
Ciprofloxacin for 3 days
Nitrofurantoin for 14 days
Doxycycline for 7 days
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 7-10 days - ANSWER Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 7-10 days
A patient's recent blood work indicates acute kidney injury. You know that acute kidney injury can be caused from:
Heart failure exacerbation
GERD
Increase in metoprolol dose
atrial fibrillation - ANSWER Heart failure exacerbation
Heart failure exacerbation and cause decreased perfusion to the
kidneys, leading to acute kidney injury. Changes in medications or
nephrotoxic can cause acute kidney injury, metoprolol is not one of
them. While patients with atrial fibrillation can have decreased
cardiac output, it is often compensated to preserve renal perfusion
The provider is evaluating a patient for potential causes of urinary
incontinence and performs a postvoid residual (PVR) test which yields 30 mL of urine. What is the interpretation of this result?
The patient may have overflow incontinence.
The patient probably has a UTI.
This represents incomplete emptying.
This a normal result. - ANSWER This a normal result.
A female patient reports hematuria and a urine dipstick and culture indicate a urinary tract infection. After treatment for the UTI, what testing is indicated for this patient?
Voiding cystourethrogram
24-hour urine collection to evaluate for glomerulonephritis
No testing if hematuria is resolved
Bladder scan - ANSWER No testing if hematuria is resolved
A physically independent 75 year old was diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment 6 months ago. She resides in an assisted living facility. she is in clinic today for scheduled visit. Her adult daughter reports that about 2 weeks ago her mother had an episode of urinary incontinence, but no episode since then. She is found to have asymptomatic bacteriuria. How should this be managed?
Repeat the urinalysis in 7 days
Repeat the urinalysis in 4 weeks
Treat her today with one dose of an antibiotic
Monitor her for symptoms of urinary tract infection - ANSWER Monitor her for symptoms of urinary tract infection
Approximately 30-50% of older females living in institutions have
asymptomatic bacteriuria. No data support treatment of patients to prevent future problems or complications. In fact, asymptomatic bacteriuria is not usually treated unless the patient is pregnant, immunocompromised, or is undergoing a urinary procedure.
A pregnant patient has asymptomatic bacteriuria. What is the likely pathogen?
Escherichia coli
Staph aureus
Klebsiella
No pathogen - ANSWER Escherichia coli
Of pregnant patient with asymptomatic bacteriuria should be treated with antibiotics because she is at high risk of developing pyelonephritis and/or preterm labor. The most common pathogen is Escherichia coli.
The provider is counseling a patient who has stress incontinence about ways to minimize accidents. What will the provider suggest initially?
Voiding every 2 hours during the day
Referral to a physical therapist
Increasing fluid intake to dilute the urine
Taking pseudoephedrine daily - ANSWER Voiding every 2 hours during the day
A patient with urolithiasis is more likely to:
Demonstrate RBC casts
Have chills and fevers
Be of male gender
Have frequent UTIs - ANSWER Be of male gender
Males are more likely than females to have urolithiasis. There is no
increased incidence of stone formation among patients with frequent UTIs. Patients with your urolithiasis may exhibit fever and chills of infection if associated with a very large stone, but this is not the usual case. RBC casts are formed in the renal tubules, this generally indicates glomerular injury, not urolithiasis.
A pregnant patient is found to have a urinary tract infection. What is the appropriate course of action?
Prescribe nitrofurantoin
Prescribe ciprofloxacin
Prescribe TMP/SMX
Prescribe no antibiotics - ANSWER Prescribe nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin is considered probably safer to use during pregnancy. It provides coverage for most common UTI pathogens. TMP/SMX is a full of acid antagonist and may be associated with increased risk of congenital malformation. Ciprofloxacin is not to be used first line for any simple UTI, and may not be safe during pregnancy. In some occasions it could still be given if benefits outweigh risks.
An adolescent male reports severe pain in one testicle. The examiner notes edema and erythema of the scrotum on that side with a swollen, tender spermatic cord and absence of the cremasteric reflex. What is the most important intervention?
Prescribing anti-infective agents to treat the infection
Immediate referral to the emergency department
Transillumination to assess for a "blue dot" sign
Doppler ultrasound to assess testicular blood flow - ANSWER Immediate referral to the emergency department
If cervical stenosis is met when performing IUD insertions, which of the following should be used to overcome resistance?
12 - 15 cm
3 - 6 cm
9 - 12 cm
6 - 9 cm - ANSWER 6 - 9 cm
A 45 year old diabetic female presents with c/o vaginal itching and discharge that began after douching post-menstruation approximately one week ago. Upon exam, you find thick, white discharge with a curd-like consistency and erythema generally in the vuvlvogavinal region. Under a wet mount you see the following below (budding, branching hyphae). Which of the following is an appropriate treatment for this patient?
No treatment needed
Rocephin (Ceftriaxone) 250mg IM x 1 and Azithromycin 1 g PO x 1
Diflucan (Fluconazole) 150mg PO x 1
Flagyl (Metronidazole) 500mg PO BID x 7 days - ANSWER Diflucan (Fluconazole) 150mg PO x 1
What is included in your treatment plan for #4?
Flagyl (Metronidazole) 2g PO x 1 of patient only and no report to the county
Rocephin (Ceftriaxone) 250mg IM with partner treatment and report to the county
Flagyl (Metronidazole) 2g PO x 1 with partner treatment and report to the county
Rocephin (Ceftriaxone) 250mg IM of patient only and no report to the county - ANSWER Flagyl (Metronidazole) 2g PO x 1 with partner treatment and report to the county
Syphilis may present as:
Discharge
Painful lesions
Dysuria
A rash - ANSWER A rash
Secondary syphilis can present as a rash, more commonly on the
palms of the hands or soles of the feet. Lesions are usually painless. It usually does not produce significant dysuria or discharge.
A 19-year-old student who is on prescription combined oral contraceptive pills is being seen for lower GI pain. The nurse practitioner has obtained a Pap smear and is about to perform the bimanual exam. She gently remove the plastic speculum from the vagina. While the NP is performing the bimanual vaginal exam, the patient complaints of slight discomfort during palpation of the ovaries. Which with the following is a true statement?
[Show More]