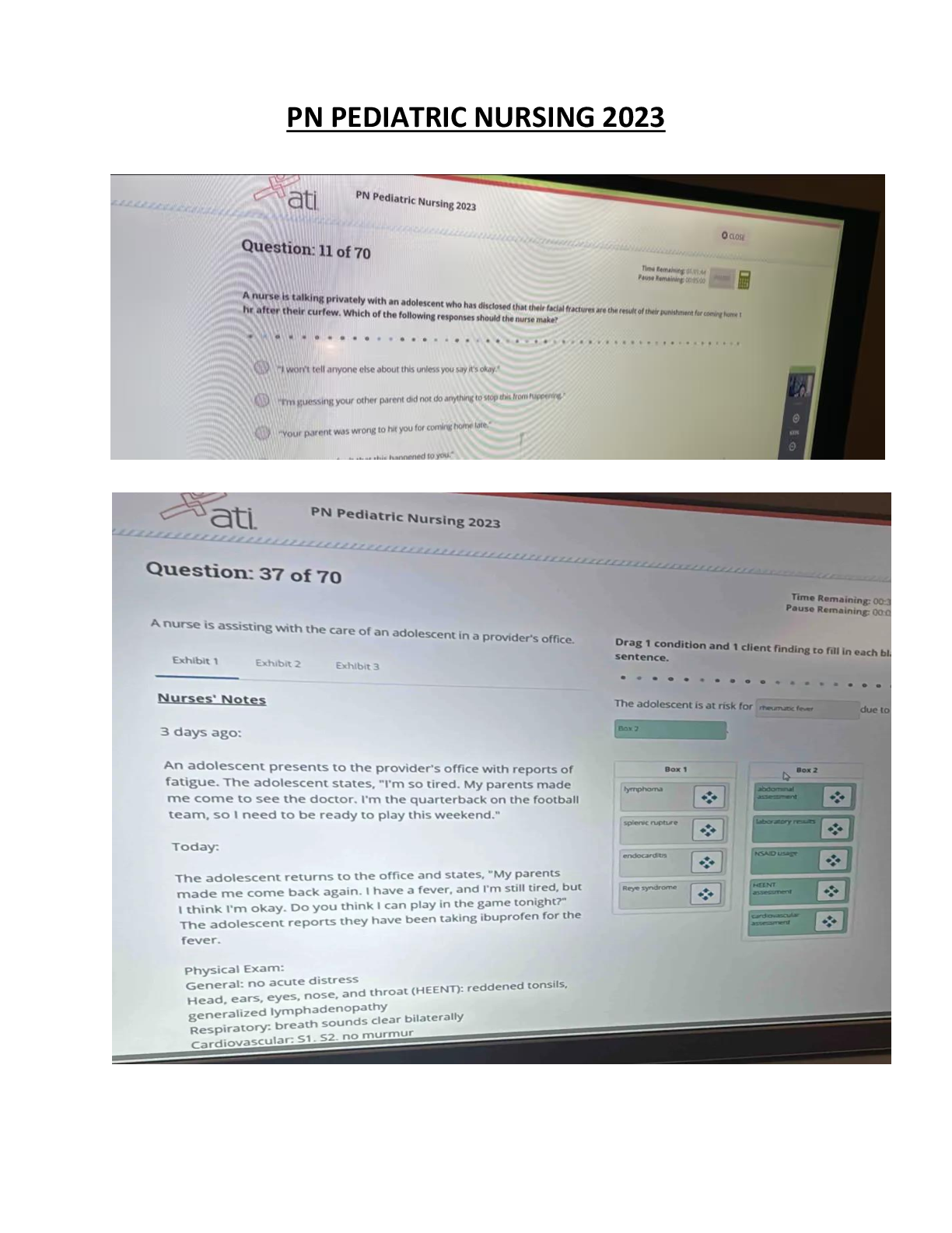
PN PEDIATRIC NURSING
$ 20

eBook Applied Behavior Analysis Research Made Easy A Handbook for Practitioners Conducting Research Post-Certification 1st Edition By Amber L. Valentino PsyD BCBA-D, Patrick C. Friman PhD ABPP
$ 29

Test Bank for Introduction to Data Analytics for Accounting 1st Edition by Vern Richardson
$ 15

Thermal characteristics of Thermistors and Thermocouples
$ 12

Database Management System-An Evolutionary Approach by Jagdish Chandra Patni, Hitesh Kumar Sharma, Ravi Tomar & Avita Katal - Complete Elaborated and Latest Solution Manual. ALL Chapters(1-8) included-Updated for 2023
$ 31.5

Test Bank For Java Software Solutions, Foundations of Program Design, 10th Edition by John Lewis William Loftus Chapter 1-13
$ 19

NURS 6660 Midterm Exam
$ 14

Chandigarh University COMPUTER S DBMS anayaranjan
$ 4.5

BIO201L Lab 7 Upload Document.pdf
$ 17

Certified Ethical Hacker -WGU C701 Already Passed
$ 10.5

eBook Solving Optimization Problems with the Heuristic Kalman Algorithm New Stochastic Methods 1st Edition By Rosario Toscano
$ 30

Arizona State UniversityCSE 340CSE340_S14_Final_Solution.
$ 8

Sophia Intro to Ethics Unit Final Milestone (A Graded) Latest Questions and Complete Solutions
$ 10

eBook Web Scraping with Python Data Extraction from the Modern Web 3rd Edition By Ryan Mitchell
$ 30
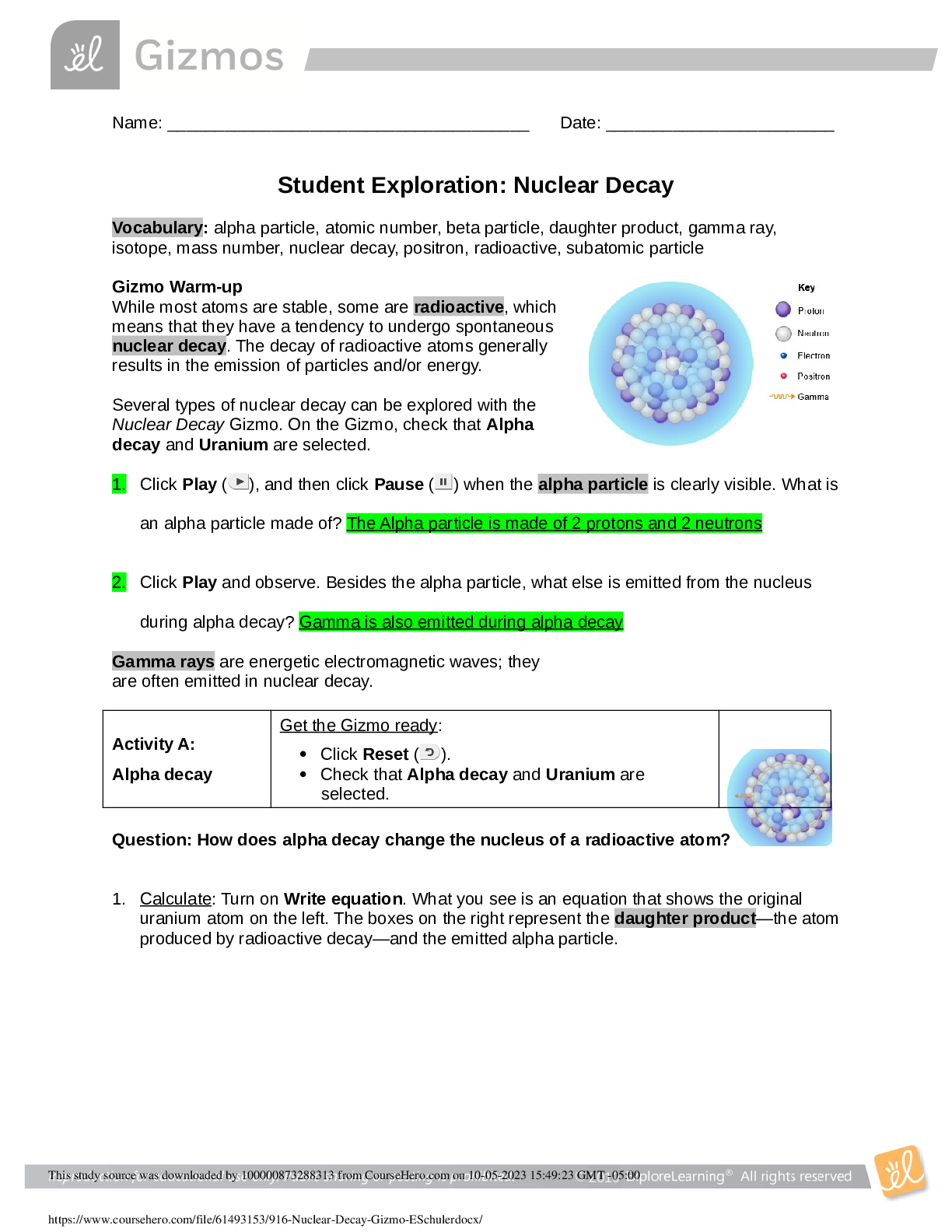
Student Exploration: Nuclear Decay Vocabulary: alpha particle, atomic number, beta particle, daughter product, gamma ray, isotope, mass number, nuclear decay, positron, radioactive, subatomic particle Gizmo Warm-up
$ 21.5

IT C170 C170 58 Question Multi-Choice OA Study Guide SQL Commands
$ 7

CSE 205 GradebookReader.java (//Complete Code)
$ 8

Lab B-03: Programming Exercise 1- McMaster University DEPARTMENT ee340