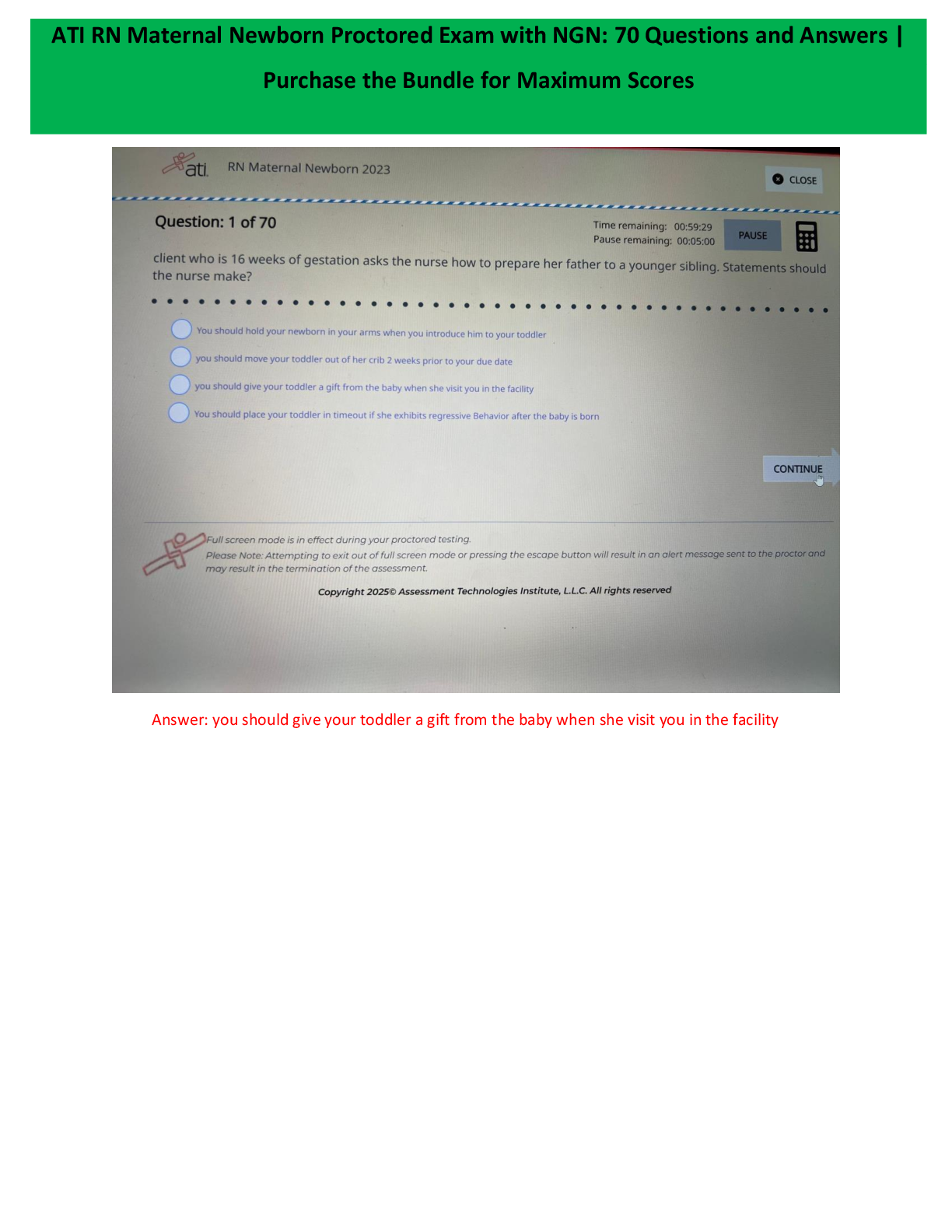
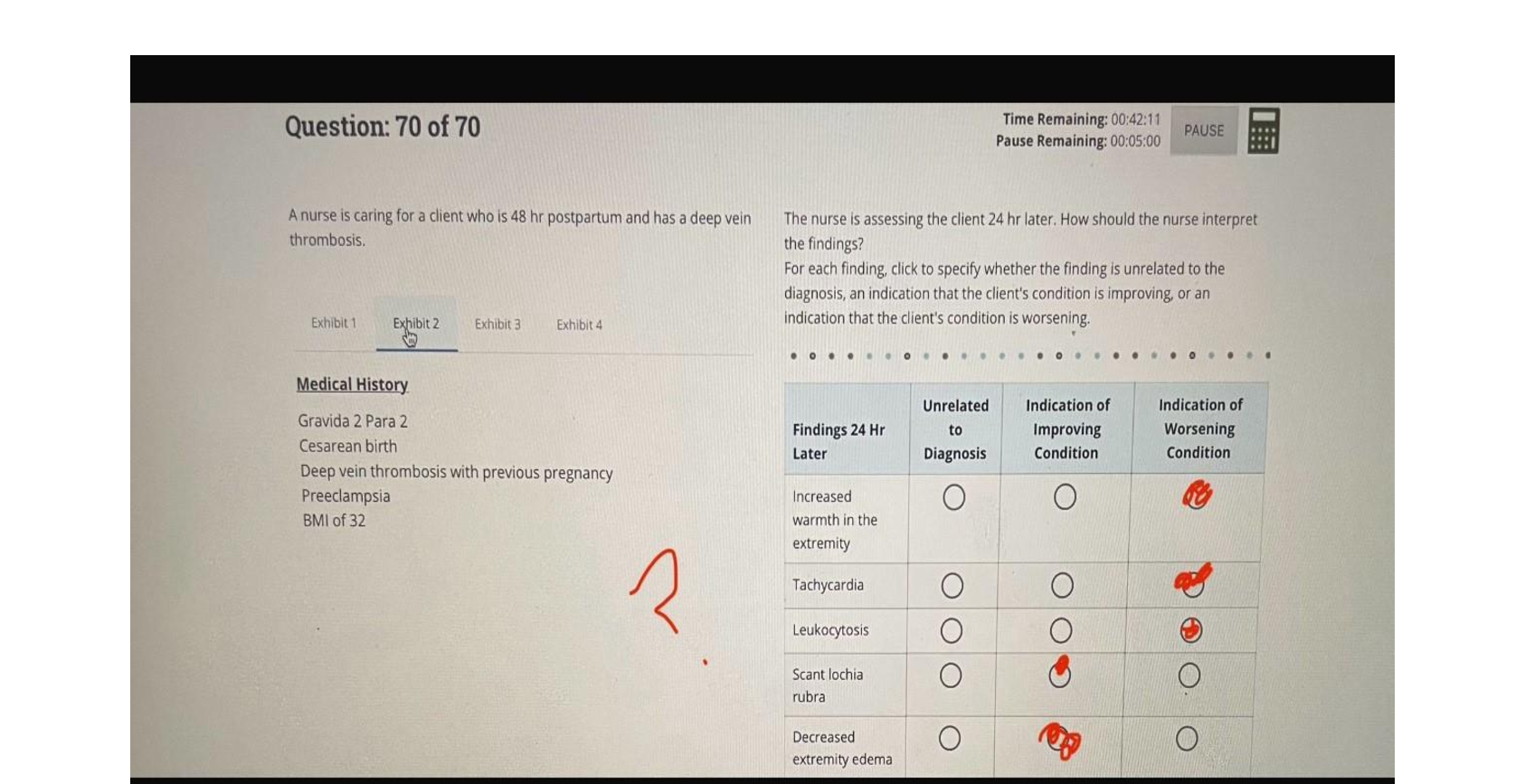
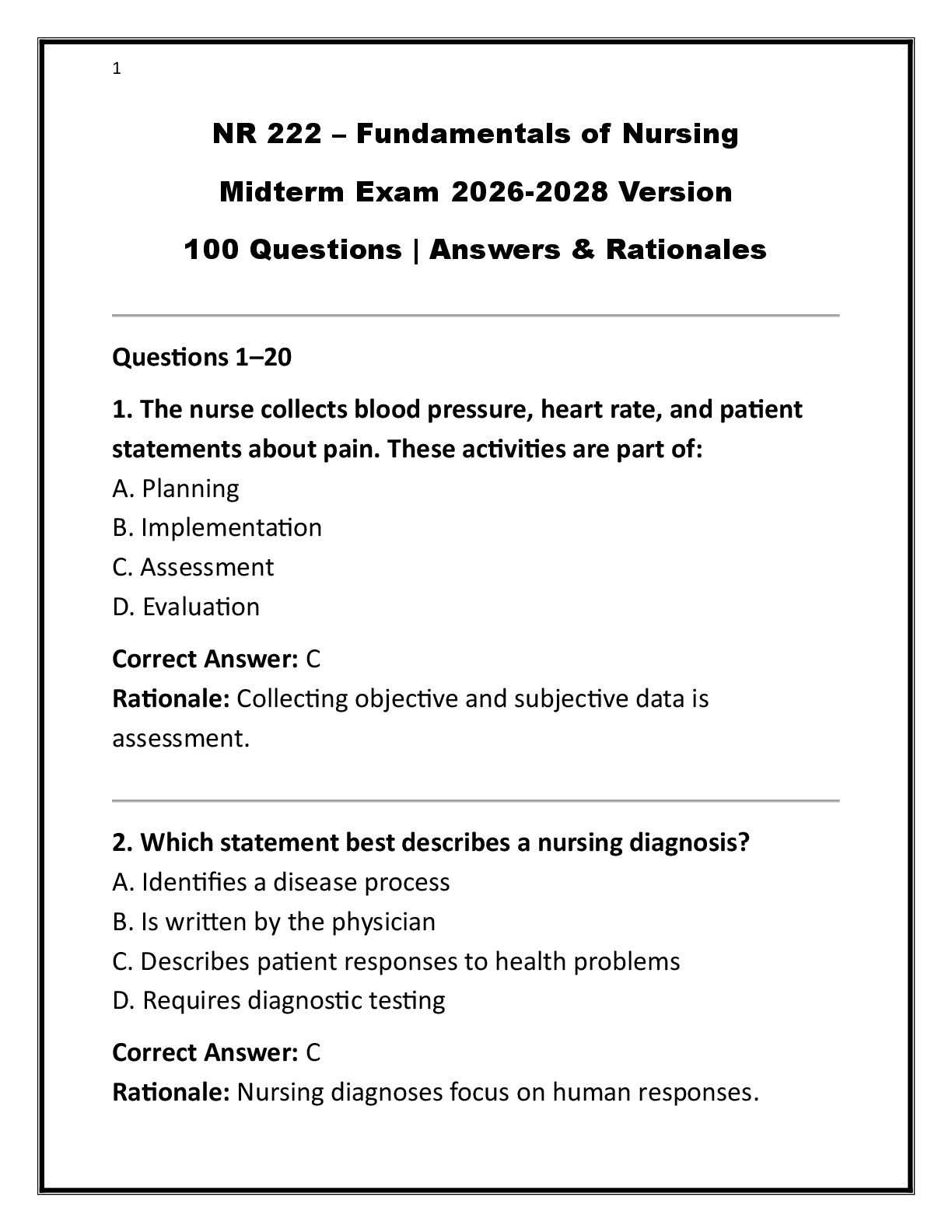
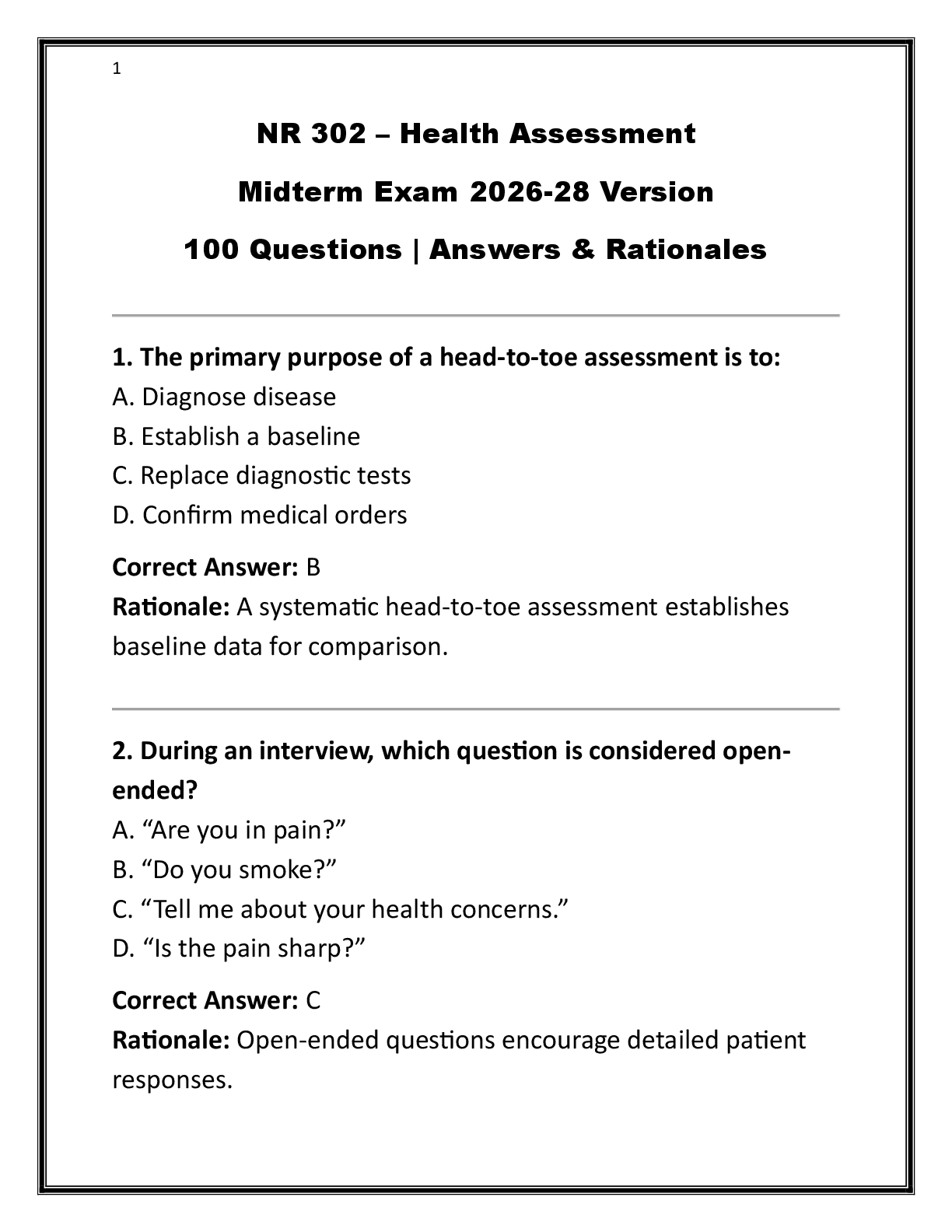
During the birth process, the perineum is stretched significantly to accommodate the emerging fetus; however, lacerations may occur. A laceration that extends through the perineal body into the anal sphincter is a - ANSW
...
During the birth process, the perineum is stretched significantly to accommodate the emerging fetus; however, lacerations may occur. A laceration that extends through the perineal body into the anal sphincter is a - ANSWER third-degree laceration.
The primary factor that would allow a woman to push beyond two hours in the second stage of labor is - ANSWER a fetal heart rate (FHR) within normal limits as the presenting part descends.
Which of these third-stage management strategies would help prevent hemorrhage? - ANSWER Oxytocin administration after infant delivered
A contraindication to the administration of regional analgesia and anesthesia includes - ANSWER coagulation disorders
Natalie has been 4 cm dilated for over three hours and is expressing frustration over her slow progress. Based on your knowledge of contemporary labor curves, inform her that - ANSWER it may take up to six hours to dilate from 4-5 cm, and this is normal in the latent phase of labor.
Some of the benefits of 1:1 nursing care include all except - ANSWER increased need for augmentation with oxytocin.
Your patient, Anne-Elise, has arrived in L&D for a labor evaluation. After a full assessment and cervical examination, she is informed that she is 50 percent effaced and two cm dilated. Effacement is described as the - ANSWER thinning and shortening of the cervix.
Planning culturally sensitive care includes - ANSWER noting patterns of decision-making and roles within the family.
Insufficient relaxation of the uterus is defined as hypertonus. Which of the following would be indicative of hypertonus? A tracing with - ANSWER a uterine resting tone of 30 mm Hg pressure between contractions.
AWHONN's staffing guidelines recommend a nurse to patient ratio of 1:1 for all of the following except - ANSWER for the woman with a prolonged latent phase of labor.
While supporting a woman through the second stage of labor with non-directed pushing, she should not be encouraged to - ANSWER NOT: push in hard pulses of 1-2 seconds for the duration of the contraction or pant and bear down during contractions
It is important to document frequent maternal and fetal assessments during labor. Tachysystole is defined as ____________ averaged over a 30-minute window - ANSWER greater than five uterine contractions in 10 minutes.
There are three phases during the first stage of labor. During which phase does the cervix efface while there is little to no descent of the presenting part? - ANSWER Latent phase
During a cervical examination, the physician states that the infant is in a cephalic presentation with the fetal head fully flexed. This position should be documented as - ANSWER occiput presentation.
The initial physical examination should include a cervical exam to assess effacement and dilation, position of the presenting part, and station of the presenting part. Which of the following is a contraindication to cervical examination? - ANSWER placent previa
After two hours of ambulation, Anne-Elise is re-examined and her cervix is found to be unchanged and her contractions have spaced out and become irregular. Based on these findings, the plan for her should be - ANSWER send her home with instructions on when to return to L&D, as she is not in true labor.
Several theories are proposed to explain the onset of labor. Which of the following fetal factors may influence the onset of labor? - ANSWER The production of prostaglandin by the fetal membranes causes the uterus to contract.
[Show More]

 1.png)