NURSING RNSG 1205 EXAM 2 FOUNDATIONS GUIDE(2021/2022)
Document Content and Description Below
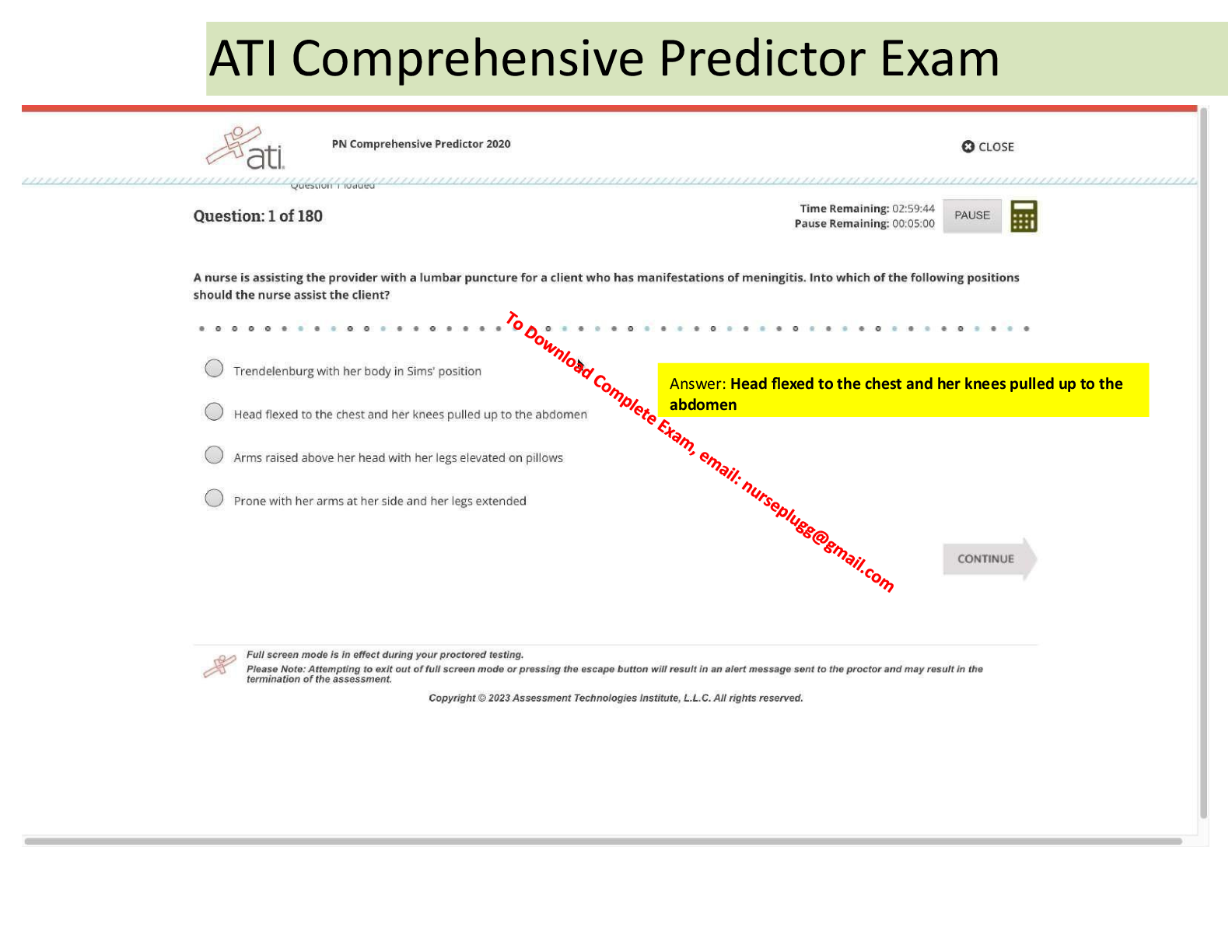
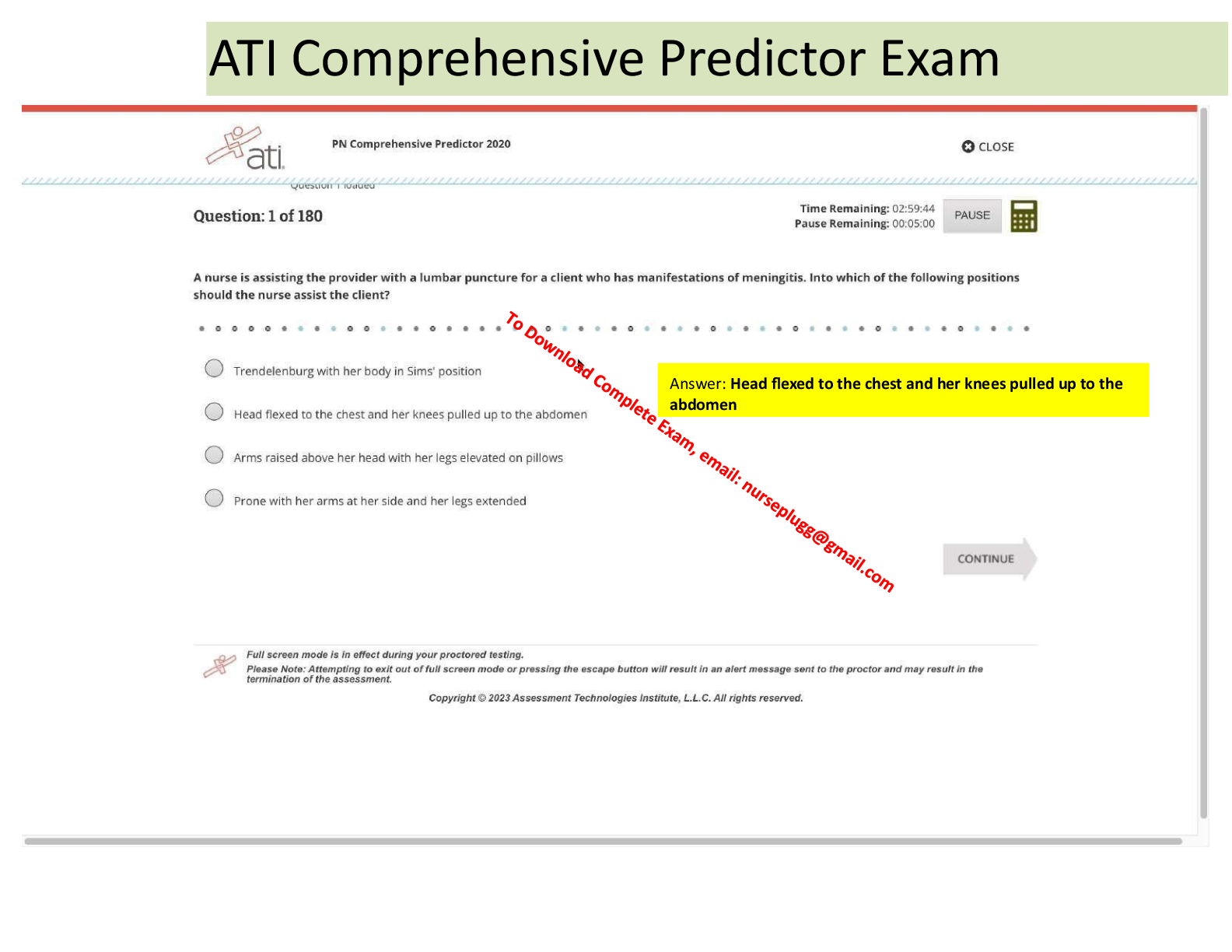
NURSING RNSG 1205 EXAM 2 FOUNDATIONS GUIDE(2021/2022) Chapter 46: Urinary Elimination Chapter 46: Urinary Elimination Potter et al.: Fundamentals of Nursing, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A n ... urse is teaching a patient about the urinary system. In which order will the nurse present the structures, following the flow of urine? 1. Kidney, urethra, bladder, ureters 2. Kidney, ureters, bladder, urethra 3. Bladder, kidney, ureters, urethra 4. Bladder, kidney, urethra, ureters ANS: B The flow of urine follows these structures: kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:1101-1103 OBJ: Explain the function and role of urinary system structures in urine formation and elimination. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 2. A nurse is reviewing urinary laboratory results. Which finding will cause the nurse to follow up? 1. Protein level of 2 mg/100 mL 2. Urine output of 80 mL/hr 3. Specific gravity of 1.036 4. pH of 6.4 ANS: C Dehydration, reduced renal blood flow, and increase in antidiuretic hormone secretion elevate specific gravity. Normal specific gravity is 1.0053 to 1.030. An output of 30 mL/hr or less for 2 or more hours would be cause for concern; 80 mL/hr is normal. The normal pH of urine is between 4.6 and 8.0. Protein up to 8 mg/100 mL is acceptable; however, values in excess of this could indicate renal disease. DIF:Apply (application)REF:1113 OBJ: Describe nursing implications of common diagnostic tests of the urinary system. TOP: Implementation MSC: Reduction of Risk Potential 3. A patient is experiencing oliguria. Which action should the nurse perform first? 1. Assess for bladder distention. 2. Request an order for diuretics. 3. Increase the patient’s intravenous fluid rate. 4. Encourage the patient to drink caffeinated beverages. ANS: A Oliguria is diminished urinary output in relation to fluid intake. The nurse first should gather all assessment data to determine the potential cause of oliguria. It could be that the patient does not have adequate intake, or it could be that the bladder sphincter is not functioning and the patient is retaining water. Increasing fluids is effective if the patient does not have adequate intake or if dehydration occurs. Caffeine can work as a diuretic but is not helpful if an underlying pathology is present. An order for diuretics can be obtained if the patient was retaining water, but this should not be the first action. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:1110 OBJ erform a physical assessment focused on urinary elimination. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Adaptation 4. A patient requests the nurse’s help to the bedside commode and becomes frustrated when unable to void in front of the nurse. How should the nurse interpret the patient’s inability to void? 1. The patient can be anxious, making it difficult for abdominal and perineal muscles to relax enough to void 2. The patient does not recognize the physiological signals that indicate a need to void. 3. The patient is lonely, and calling the nurse in under false pretenses is a way to get attention. 4. The patient is not drinking enough fluids to produce adequate urine output. ANS: A Attempting to void in the presence of another can cause anxiety and tension in the muscles that make voiding difficult. Anxiety can impact bladder emptying due to inadequate relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter. The nurse should give the patient privacy and adequate time if appropriate. No evidence suggests that an underlying physiological (does not recognize signals or not drinking enough fluids) or psychological (lonely) condition exists. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:1102 OBJ:Identify factors that commonly impact urinary elimination. TOP: Evaluation MSC: Basic Care and Comfort 5. The patient is having lower abdominal surgery and the nurse inserts an indwelling catheter. What is the rationale for the nurse’s action? 1. The patient may void uncontrollably during the procedure. 2. Local trauma sometimes promotes excessive urine incontinence. 3. Anesthetics can decrease bladder contractility and cause urinary retention. 4. The patient will not interrupt the procedure by asking to go to the bathroom. ANS: C Anesthetic agents and other agents given during surgery can decrease bladder contractility and/or sensation of bladder fullness, causing urinary retention. Local trauma during lower abdominal and pelvic surgery sometimes obstructs urine flow, requiring temporary use of an indwelling urinary catheter. The patient is more likely to retain urine rather than experience uncontrollable voiding. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:1102 OBJ:Identify factors that commonly impact urinary elimination. TOP: Evaluation MSC: Reduction of Risk Potential 6. The nurse, upon reviewing the history, discovers the patient has dysuria. Which assessment finding is consistent with dysuria? 1. Blood in the urine 2. Burning upon urination 3. Immediate, strong desire to void 4. Awakes from sleep due to urge to void ANS: B Dysuria is burning or pain with urination. Hematuria is blood in the urine. Urgency is an immediate and strong desire to void that is not easily deferred. Nocturia is awakening form sleep due to urge to void. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:1103 | 1110 OBJ: Compare and contrast common alterations associated with urinary elimination. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Adaptation 7. An 86-year-old patient is experiencing uncontrollable leakage of urine with a strong desire to void and even leaks on the way to the toilet. Which priority nursing diagnosis will the nurse include in the patient’s plan of care? 1. Functional Urinary Incontinence 2. Urge urinary incontinence 3. Impaired Skin Integrity 4. Urinary Retention ANS: B Urge urinary incontinence is the leakage of urine associated with a strong urge to void. Patients leak urine on the way to or at the toilet and rush or hurry to the toilet. Urinary retention is the inability to empty the bladder. Functional urinary incontinence is incontinence due to causes outside the urinary tract, such as mobility or cognitive impairments. While Impaired skin integrity can occur, it is not the priority at this time, and there is no data to support this diagnosis. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:1113 | 1115 OBJ: Identify nursing diagnoses associated with alterations in urinary elimination. TOP iagnosisMSC:Management of Care 8. A patient has fallen several times in the past week when attempting to get to the bathroom. The patient gets up 3 or 4 times a night to urinate. Which recommendation by the nurse is most appropriate in correcting this urinary problem? 1. Limit fluid and caffeine intake before bed. 2. Leave the bathroom light on to illuminate a pathway. 3. Practice Kegel exercises to strengthen bladder muscles. 4. Clear the path to the bathroom of all obstacles before bedtime. ANS: A Reducing fluids, especially caffeine and alcohol, before bedtime can reduce nocturia. To prevent nocturia, suggest that the patient avoid drinking fluids 2 hours before bedtime. Clearing a path to the bathroom, illuminating the path, or shortening the distance to the bathroom may reduce falls but will not correct the urination problem. Kegel exercises are useful if a patient is experiencing stress incontinence. DIF:Apply (application)REF:1107 | 1118-1119 OBJ: Discuss nursing measures to promote normal micturition and improve bladder control. TOP: Implementation MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 9. A nurse is caring for a male patient with urinary retention. Which action should the nurse take FIRST? 1. Limit fluid intake. 2. Insert a urinary catheter. 3. Assist to a standing position. 4. Ask for a diuretic medication. ANS: C In some patients just helping them to a normal position to void prompts voiding. A urinary catheter would relieve urinary retention, but it is not the first measure; other nursing interventions should be tried before catheterization. Reducing fluids would reduce the amount of urine produced but would not alleviate the urine retention and is usually not recommended unless the retention is severe. Diuretic medication would increase urine production and may worsen the discomfort caused by urine retention. DIF:Apply (application)REF:1111 | 1119 OBJ: Discuss nursing measures to promote normal micturition and improve bladder control. TOP: Implementation MSC: Basic Care and Comfort 10. Upon palpation, the nurse notices that the bladder is firm and distended; the patient expresses an urge to urinate. Which question is most appropriate? 1. “Does your urinary problem interfere with any activities?” 2. “Do you lose urine when you cough or sneeze?” 3. “When was the last time you voided?” 4. “Are you experiencing a fever or chills?” ANS: C To obtain an accurate assessment, the nurse should first determine the source of the discomfort. Urinary retention causes the bladder to be firm and distended; time of last void is most appropriate. Further assessment to determine the pathology of the condition can be performed later. Questions concerning fever and chills, interference with any activities, and losing urine during coughing or sneezing focus on specific pathological conditions. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:1103 | 1109-1111 OBJ: Obtain a nursing history from a patient with an alteration in urinary elimination. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Management of Care [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 74 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 15, 2021
Number of pages
74
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
53

.png)






.png)