BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MCAT Biochemistry Review Questions and Answers Already Passed (All)
MCAT Biochemistry Review Questions and Answers Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
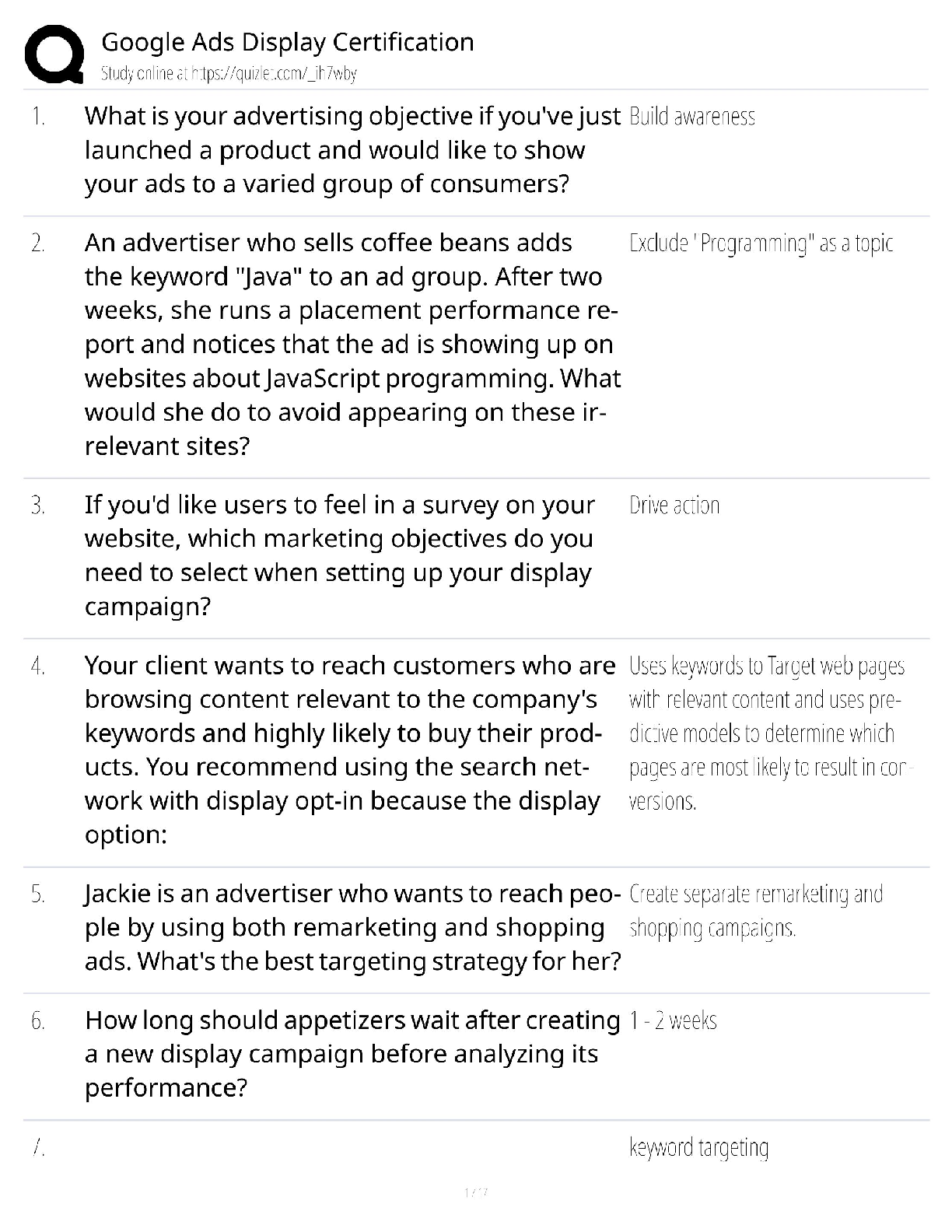
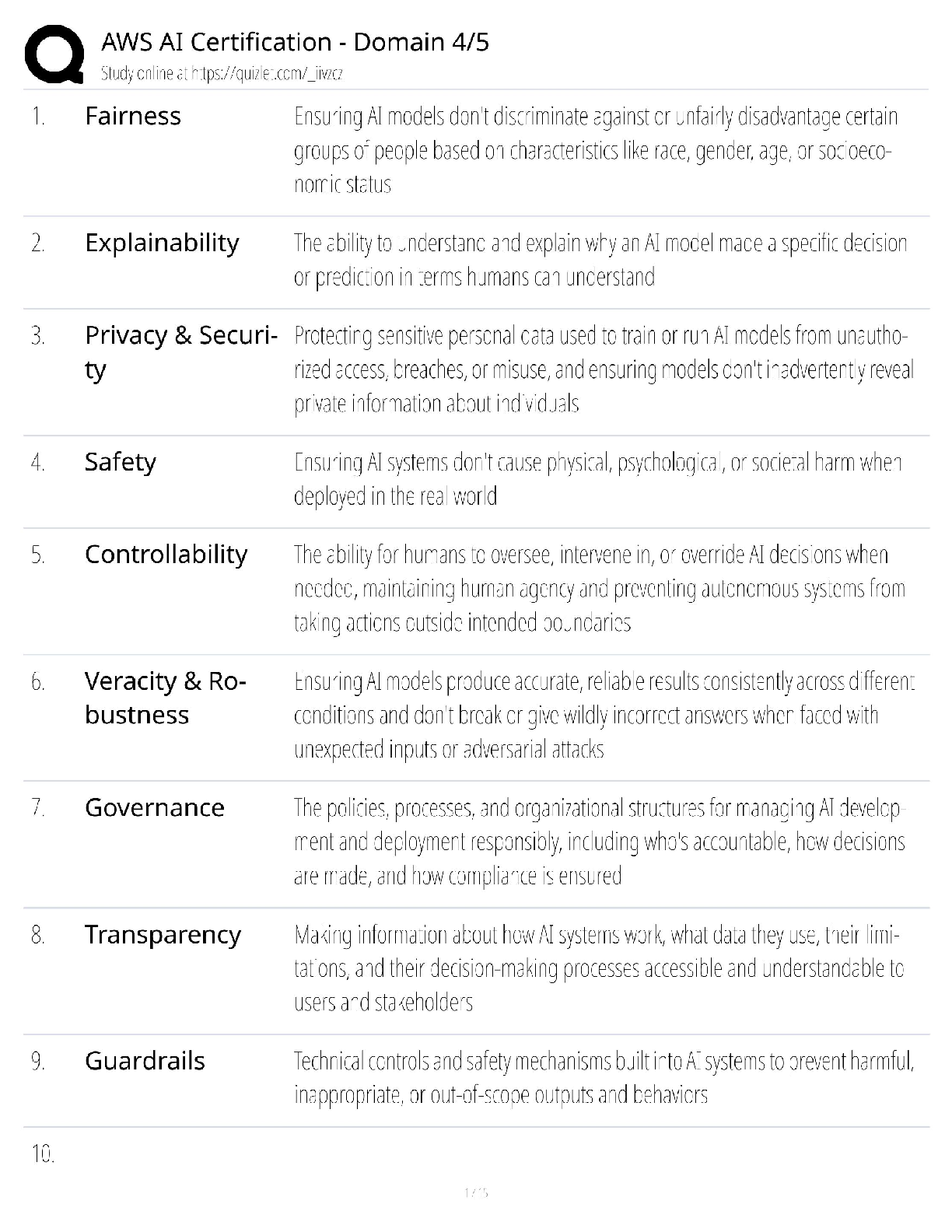
MCAT Biochemistry Review Questions and Answers Already Passed Amino Acid ✔✔Dipolar compound containing an amino group and a carboxyl group Amino Group ✔✔-NH2 Carboxyl Group ✔✔-COOH Al ... pha Carbon ✔✔Central carbon atom in amino acid Attached to amino & carboxyl groups, H atom, and side chain Side Chain ✔✔The variable component of an amino acid that gives the amino acid its identity and chemical properties also called R-group Chiral ✔✔A molecule with a nonsuperimposable mirror image All amino acids (except glycine) are chiral (S) Absolute Configuration ✔✔All amino acids (except cysteine) have an (S) absolute configuration L-amino Acid ✔✔All amino acids found in eukaryotes Nonpolar, Nonaromatic Amino Acids ✔✔Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline Glycine ✔✔Single H atom as side chain Achiral Smallest amino acid Alanine ✔✔Alkyl side chain (1C) Valine ✔✔Alkyl side chain (3C) Leucine ✔✔Alkyl side chain (4C) Isoleucine ✔✔Alkyl side chain (4C) Methionine ✔✔Methyl side chain (-CH3) Contains S atom in side chain Proline ✔✔Cyclic amino acid N from amino group becomes part of side chain, forming five-part ring, limiting where is can appear on a protein Rigid/constraints on flexibility Aromatic Amino Acids ✔✔Tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine Aromaticity ✔✔The ability of a molecule to delocalize pi electrons around a conjucated ring, creating exceptional stability Tryptophan ✔✔Double-ring system Contains N atom in one ring Largest of aromatic amino acids Phenylalanine ✔✔Benzyl side chain (benzene ring + -CH2 group) Smallest aromatic amino acid Relatively nonpolar Tyrosine ✔✔Phenylalanine + -OH group Relatively polar Polar Amino Acids ✔✔Serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, cysteine Polarity ✔✔An uneven sharing of electrons in a molecule, creating a slightly positive side and a slightly negative side Serine ✔✔-OH group in side chain Highly polar - participate in H-bonding Threonine ✔✔-OH group in side chain Highly polar - participate in H-bonding Asparagine ✔✔Amide (-NH2) side chain Amide N do not gain or lose protons with changes in pH - do not become charged Glutamine ✔✔Amide (-NH2) side chain Amide N do not gain or lose protons with changes in pH - do not become charged Cysteine ✔✔Thiol (-SH) side chain - weaker than OH bond Prone to oxidation Negatively-charged (Acidic) Amino Acids ✔✔Aspartic acid (aspartate), glutamic acid (glutamate) Aspartic Acid (Aspartate) ✔✔Carboxylate (-COO(-)) group in side chain Deprotonated form of asparagine Glutamic Acid (Glutamate) ✔✔Carboxylate (-COO(-)) group in side chain Deprotonated form of glutamine Positively-charged (Basic) Amino Acids ✔✔Lysine, arginine, histidine Lysine ✔✔Terminal primary amino group Arginine ✔✔Has 3 N atoms in side chain Charge delocalized over all three N atoms Histidine ✔✔Has arom [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 109 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)
.png)
MCAT BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALL RATED A+
MCAT BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALL RATED A+
By Nutmegs 3 years ago
$19
9
Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 30, 2022
Number of pages
109
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 30, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
125








.png)