Business > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > [Solved] Liberty University ECON 214 Exam 2 (All)
[Solved] Liberty University ECON 214 Exam 2
Document Content and Description Below
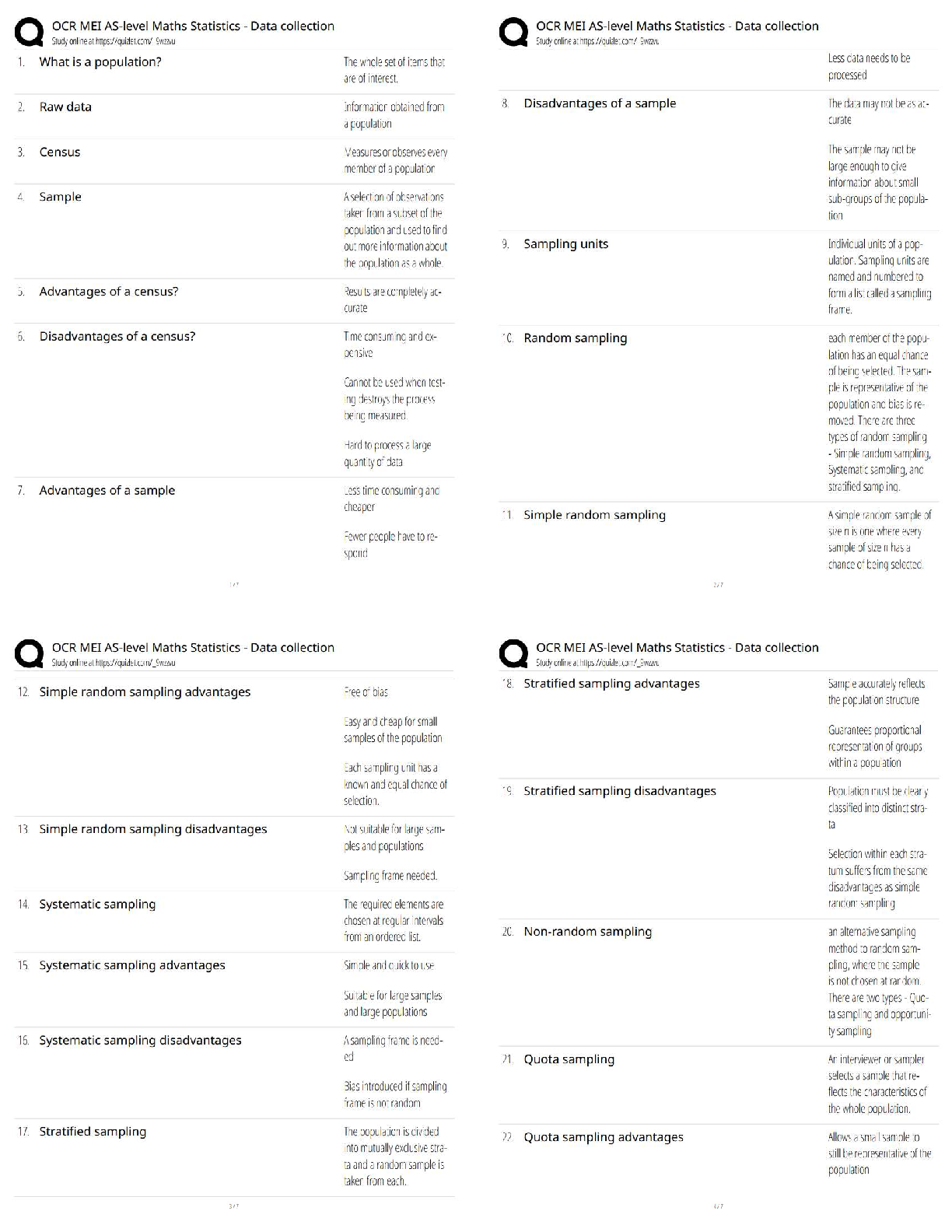
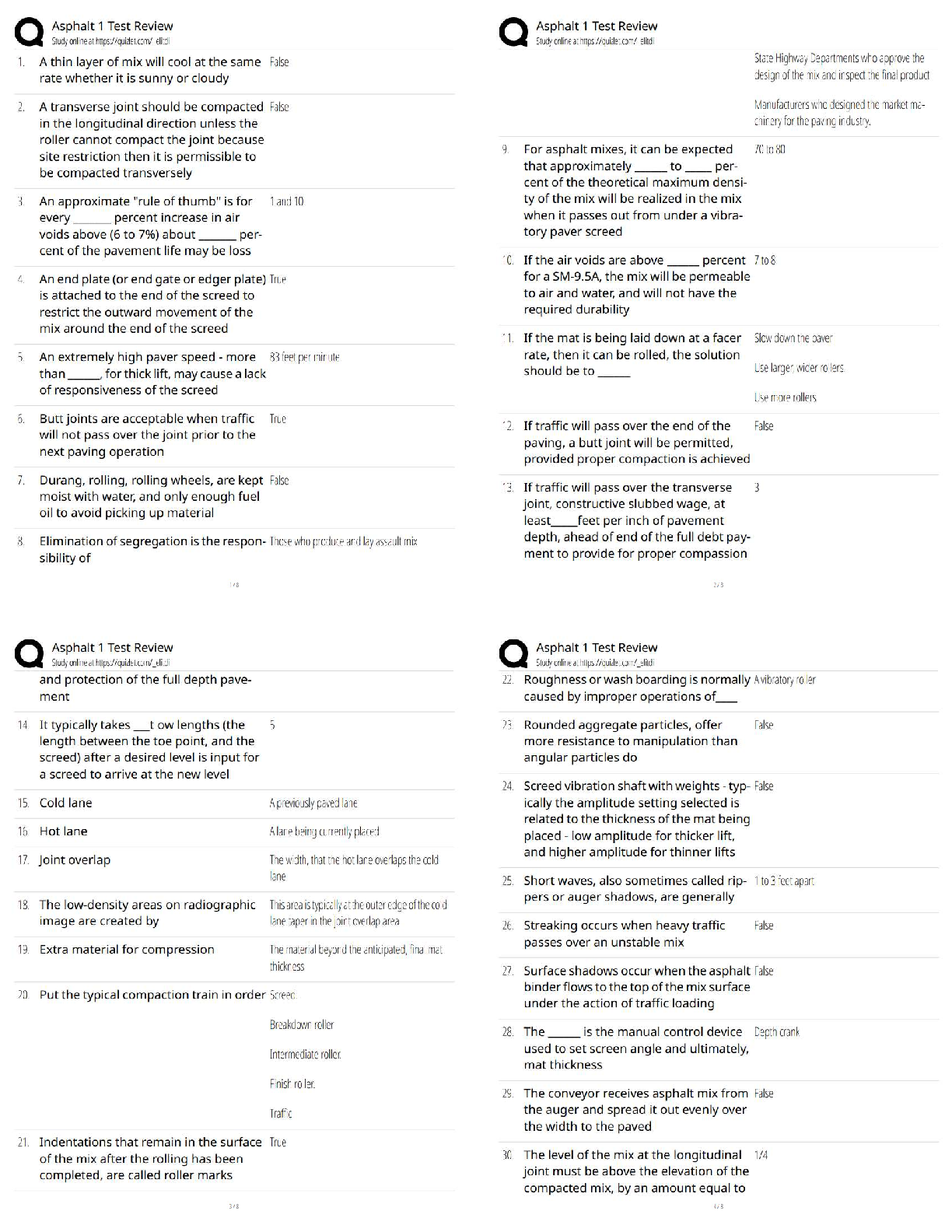
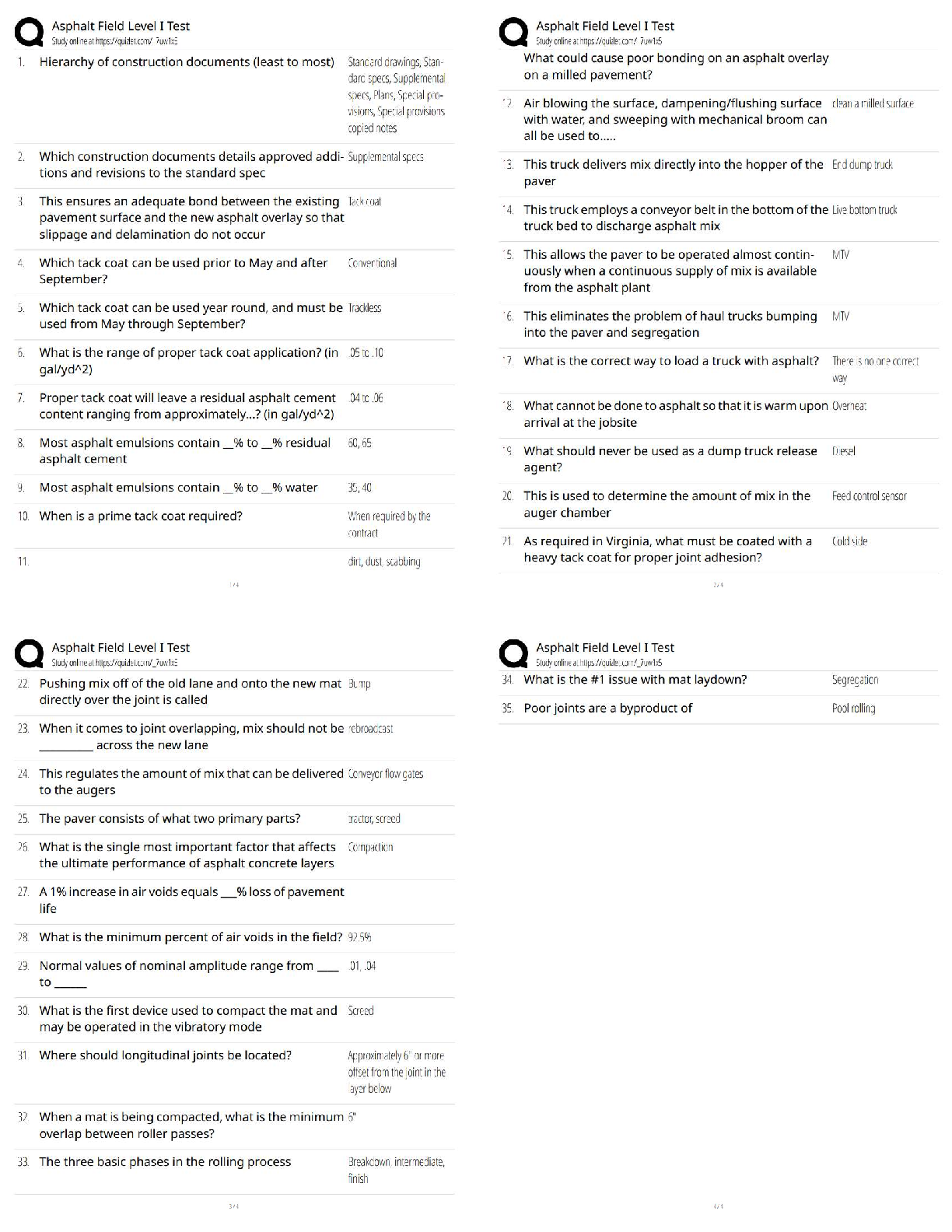
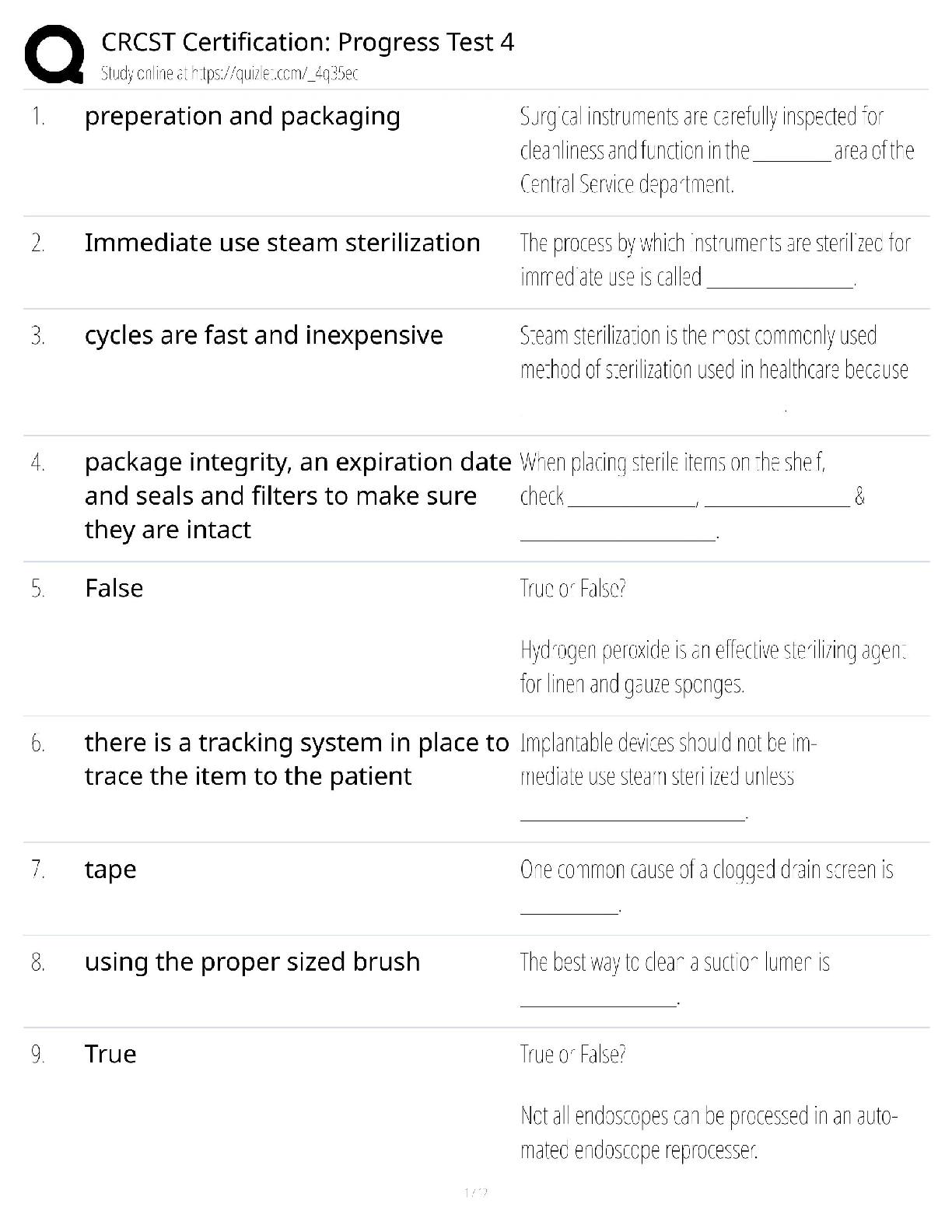
Liberty University ECON 214 Exam 2 ECON 214 Exam 2 · Question 1 2 out of 2 points Use the following graph to answer the questions that follow. The graph depicts an economy where a ... ggregate demand has decreased. Note that long-run aggregate supply remains changed. The graph shows a decrease in the price level due to a decrease in aggregate demand. Real gross domestic product (GDP), however, does not change. If this were an accurate description of how an economy responds during a recession, which of the following would be an appropriate government response to a decrease in aggregate demand? · Question 2 2 out of 2 points During the Great Recession, ___________ caused aggregate demand to decrease. · Question 3 2 out of 2 points Annual real per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in China was roughly $5,200 in 2000. If it grew by 10% the following year, by 2001 the annual real per capita GDP would be: · Question 4 0 out of 2 points Average world income began to increase rapidly during: · Question 5 2 out of 2 points The Great Recession was different from other recessions since World War II in that: · Question 6 2 out of 2 points During the Great Depression, the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifted to the left, in part, because: · Question 7 2 out of 2 points In 1950, residents in Liberia were wealthier than those in Taiwan. Today, per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in Taiwan is more than 20 times that of Liberia. Which of the following best explains why Taiwan is now so much wealthier than Liberia? · Question 8 2 out of 2 points A severe drought hits a country and reduces farm output by 50%. This will impact: · Question 9 2 out of 2 points Why do institutions such as private property rights promote economic growth? · Question 10 2 out of 2 points An economy has experienced a rightward shift of its long-run aggregate supply curve and is now producing on that new long-run aggregate supply curve. It is reasonable to expect that: · Question 11 2 out of 2 points Annual real per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in the United States was roughly $44,000 in 2000. If it grew by 3% the following year, by 2001 the annual real per capita GDP would be: · Question 12 2 out of 2 points The Great Recession was similar to other recessions since World War II in that: · Question 13 2 out of 2 points From 2009 to 2010, nominal gross domestic product (GDP) in the United States grew by 3.8%. Given that the population grew by 1% and per capita real GDP grew by 1.8%, we know that prices increased by: · Question 14 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is true? · Question 15 2 out of 2 points During the Great Recession, the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifted to the left, in part, because: · Question 16 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is true about recessions in the United States? · Question 17 2 out of 2 points Suppose that many countries in Europe sink into recession. In the short run, output in the United States will __________ and the price level will __________. · Question 18 2 out of 2 points From 2006 to 2010, per capita real gross domestic product (GDP) in Poland grew an average of 4.71% per year. At that rate, according to the Rule of 70, in roughly how many years will the Polish economy double in size? · Question 19 2 out of 2 points __________ would cause a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve. · Question 20 2 out of 2 points During the Great Recession, the U.S. long-run aggregate supply curve shifted to the left, in part, because: · Question 21 2 out of 2 points The Great Recession is characterized by a decrease in aggregate demand. __________ would have caused such a decrease. · Question 22 2 out of 2 points From 2009 to 2010 per capita real gross domestic product (GDP) in the United States grew by 1.8%. At that rate, according to the Rule of 70, in roughly how many years will per capita real GDP double? · Question 23 2 out of 2 points An increase in the value of the dollar will __________ exports and __________ imports. · Question 24 2 out of 2 points Which of the following economic statements would a classical economist tend to support? · Question 25 2 out of 2 points A supply shock is defined as: · Question 26 2 out of 2 points A stock market crash in __________ is generally viewed as the beginning of the Great Depression. · Question 27 2 out of 2 points When an economy experiences economic growth: · Question 28 2 out of 2 points If the price level rises by 10%, then all else being equal, the long-run quantity of aggregate supply will: · Question 29 2 out of 2 points We know that resources are important for economic growth. Which of the following statements about resources is true? · Question 30 2 out of 2 points As they relate to economic growth, institutions are: · Question 31 2 out of 2 points Beginning in the late 1970s, economic reform in China allowed farmers, for the first time, to keep a portion of their crops and to sell them to others. Previously, all food was collectively farmed and shared. How did this basic reform improve China’s economic growth? · Question 32 2 out of 2 points A severe drought hits a country and reduces farm output by 50%. In the short run, this will __________ output and __________ employment. · Question 33 2 out of 2 points Suppose there is a surge in stock market values. In the short run, we would expect the price level to __________ and the unemployment rate to __________. · Question 34 2 out of 2 points During the Great Depression, thousands of U.S. banks failed. As a result: · Question 35 2 out of 2 points Suppose housing values fall during a recession. In the short run: · Question 36 2 out of 2 points In economics, technology is defined as: · Question 37 2 out of 2 points Keynesian economists believe that prolonged recessions are possible because: · Question 38 2 out of 2 points Use the following graph to answer the questions that follow. The graph depicts an economy where aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) have decreased, with no change in short-run aggregate supply (SRAS). During the Great Recession, real gross domestic product (GDP) decreased yet the aggregate price level remained largely unchanged, as depicted in the graph. Unemployment increased to above-normal levels. Which of following best explains why this happened? · Question 39 2 out of 2 points Real per capita gross domestic product (GDP) is defined as: · Question 40 2 out of 2 points From 2006 to 2010, per capita real gross domestic product (GDP) in China grew an average of 10.62% per year. At that rate, according to the Rule of 70, in roughly how many years will Chinese per capita real GDP double in size, beginning in 2006? · [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
![Preview image of [Solved] Liberty University ECON 214 Exam 2 document](https://scholarfriends.com/storage/Liberty-University-ECON-214-Exam-2.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 17, 2021
Number of pages
9
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 17, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
91



.png)