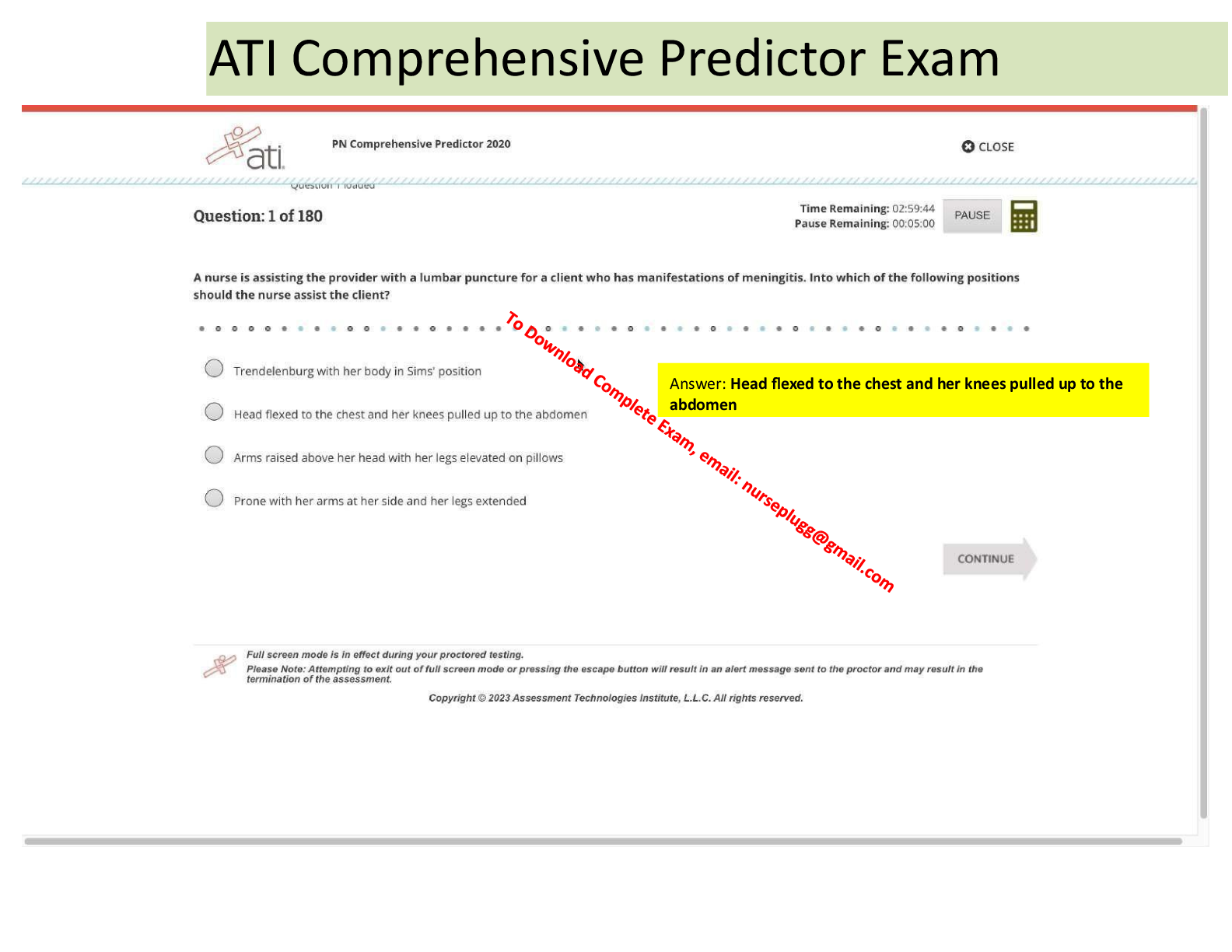
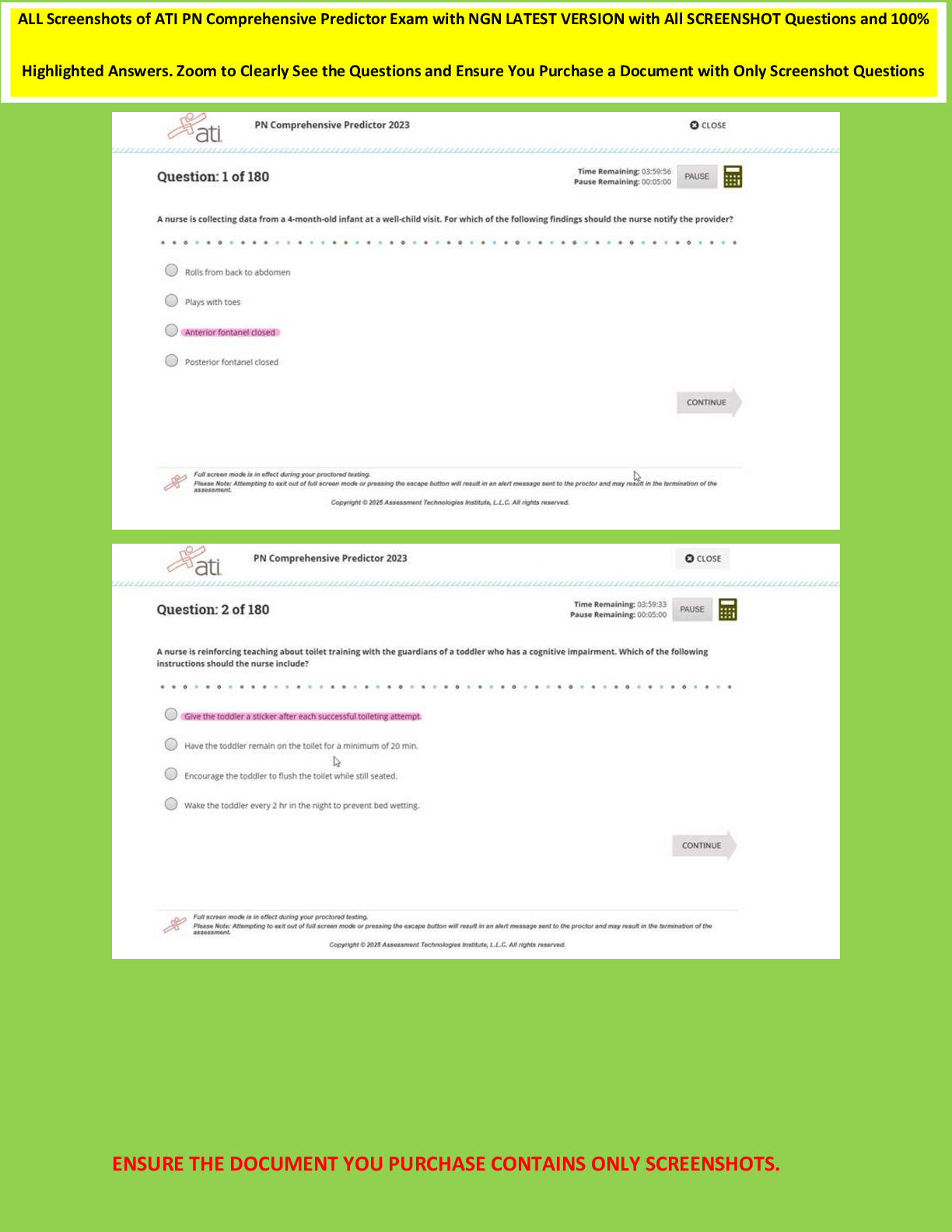
phoneme - ANSWER in language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
Grapheme - ANSWER the written or printed representation of a phoneme
Phonics - ANSWER The predictable relationship between phonemes and graphemes
...
phoneme - ANSWER in language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
Grapheme - ANSWER the written or printed representation of a phoneme
Phonics - ANSWER The predictable relationship between phonemes and graphemes
Phonemic Awareness - ANSWER The ability to hear, identify,and manipulate the individual sounds, phonemes, in oral language.
phonological awareness - ANSWER the ability to reflect on and manipulate the sound structure of spoken language
syllable - ANSWER a word part that contains a vowel, or, in spoken language, a vowel sound.
Onset and Rime - ANSWER -Parts of spoken language that are smaller than syllables but larger than phonemes
-Onset is the initial consonant(s) sound of a syllable (the b- of bag; the sw- of swim)
-Rime is the part of the syllable that contains the vowel and all that follows it (the -ag of bag; the -im of swim)
Phoneme Isolation - ANSWER —recognizing the individual sounds in words. For example, "Tell me the first sound you hear in the word top (/t/)."
Phoneme Identity - ANSWER recognizing the common sound in different words. For example, "Tell me the sound that is the same in pig, pot, and pie (/p/)."
phoneme categorization - ANSWER recognize a word with a sound that does not match the sounds in other words (bus,bun,rug) = rug
phoneme blending - ANSWER combining phonemes to make a word (b-i-g)
phoneme segmentation - ANSWER breaking a word into separate sounds and counting them
phoneme deletion - ANSWER being able to identify a sound that has been deleted from a word (smile without s is mile)
phoneme addition - ANSWER make a new word by adding a phoneme to an existing word park-spark adding s
phoneme substitution - ANSWER Substitute one phoneme for another to make a new word (Example- the word is 'bug'. Change the /g/ to /n/. What's the new word? Bun)
Phonemic reversal - ANSWER Reversing the first and last sound
Phonology - ANSWER the study of speech sounds in language
Syntax - ANSWER The arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language.
Semantics - ANSWER the set of rules by which we derive meaning from morphemes, words, and sentences in a given language; also, the study of meaning
orthography - ANSWER a method of representing the sounds of a language by written or printed symbols
Pragmatics (use) - ANSWER the rules of language governing how language is used for social purposes
Hourglass Concept - ANSWER Phonological awareness, Sentences, words, syllables, onset/rime, phonemes
voiced sounds - ANSWER are produced, in part by the vibrations of the vocal chords (v, z, th)
unvoiced sound - ANSWER a sound where no voice is used, e.g. /p/ in pad, /t/ in tomorrow. No movement or vibration can be felt in the throat.
Nasals - ANSWER m, n, ŋ
Fricatives - ANSWER produced by a constant flow of air through the vocal tract (f and v)
Affricates - ANSWER ch/j
Glides - ANSWER w, y
Liquids - ANSWER l, r
diphthong - ANSWER n. The sound produced by combining two vowels in to a single syllable or running together the sounds.
Dialect - ANSWER A regional variety of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
RTI - ANSWER Response to Intervention
Teaching Phonological Awareness - ANSWER Clapping sounds in words, saying blended phonemes, singing songs, nursery rhymes, reading patterned texts, environmental sounds, following directions, rhyming games, alliterative texts, grouping objects using beginning sounds, reordering words in a sentence to make silly phrases.
Screening and prediction instruments - ANSWER DIBELS, TPRI, AIMS, PALS, CPLA, IDEL
Diagnostic Inventories - ANSWER LAC, CTOPP, RAN/RAS, phonological awareness test, really great reading assessments
breve - ANSWER Represents short or unstressed vowel û
macron - ANSWER horizontal mark indicating that the vowel over which it is placed is long ū
Alphabetic Principle - ANSWER an understanding that letters and letter patterns represent the sounds of spoken words.
Floss Rule - ANSWER Words of one syllable, ending in f, l, or s - after one vowel, usually ending in ff, ll, or ss (sounds /f/, /l/, /s/).
6 syllable types - ANSWER Closed, open, vowel-consonant-silent e, vowel pair, R-controlled, and consonant-le.
Hourglass top and bottom - ANSWER Phonology, orthography
C and g as soft sound - ANSWER Before I, e, y
C and g as hard sound - ANSWER Before o, a,u
Spoken Syllable - ANSWER unit of speech organized around a vowel sound
Why teach syllables? - ANSWER Knowing the syllable types helps readers know whether a vowel is long, short, a dipthong, r controlled or whether endings have been added.
Morphophonology - ANSWER The rules governing sound changes that accompany the combination of morphemes in a language.
inflectional endings - ANSWER Sounds, which are added to words to indicate tense, possession, number of comparison
Reccomended key words for short vowels - ANSWER Apple, echo, itch, octopus, up
Key words for selected consonants - ANSWER Dog, tent, box, goat, rope
word families - ANSWER groups of words that have the same ending soudn (rime) but a different beginning sound (onset), such as can, man, fan.
Sight Words - ANSWER Words that are recognized immediately. It can also refer to high frequency words and words that are learned only through memorization. Very few words can be learned through memory. Most are learned through phonics.
Steps of effective phonics instruction - ANSWER State goal, review previous lesson, teach lesson, practice word reading, word practice activities, dictation, reinforce word meaning, practice text reading
[Show More]