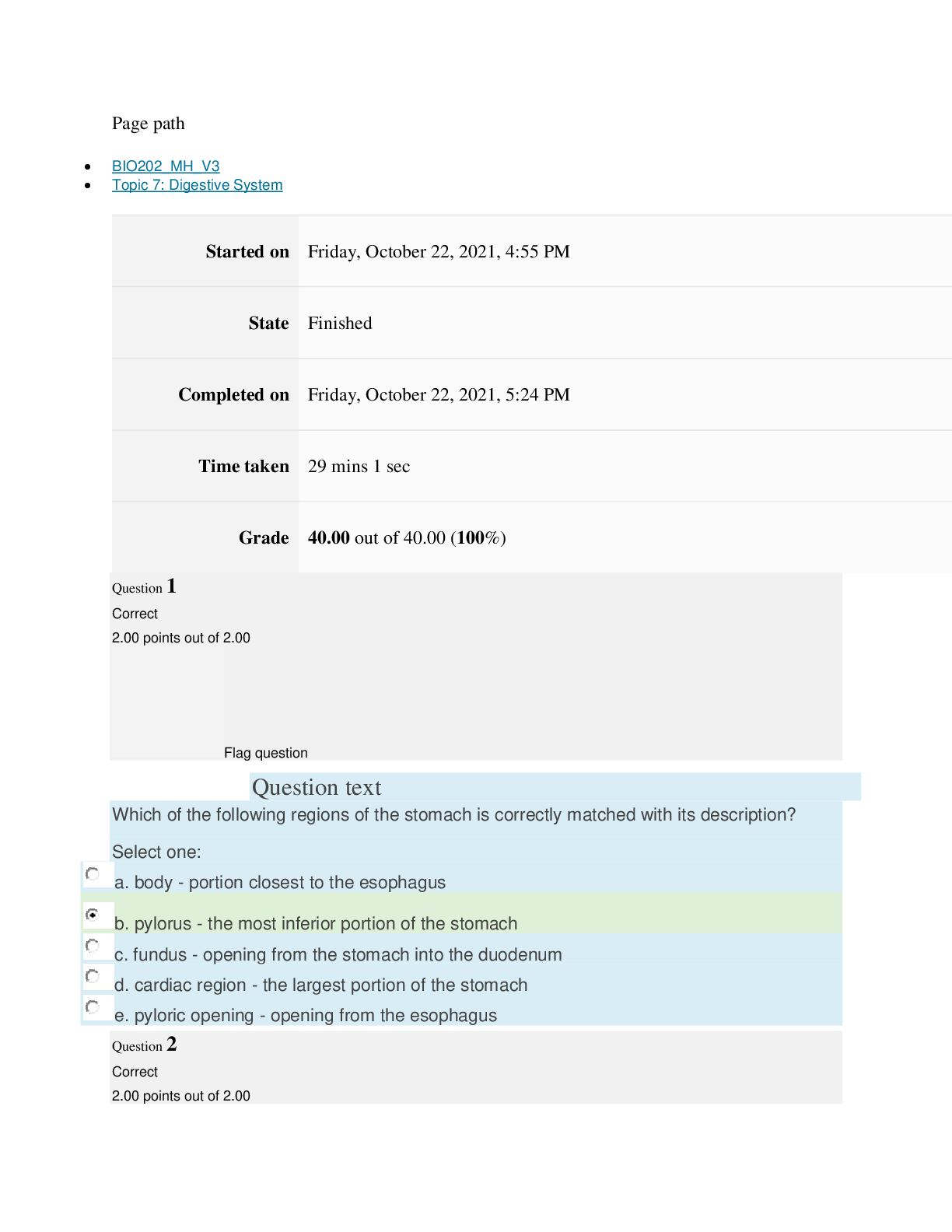
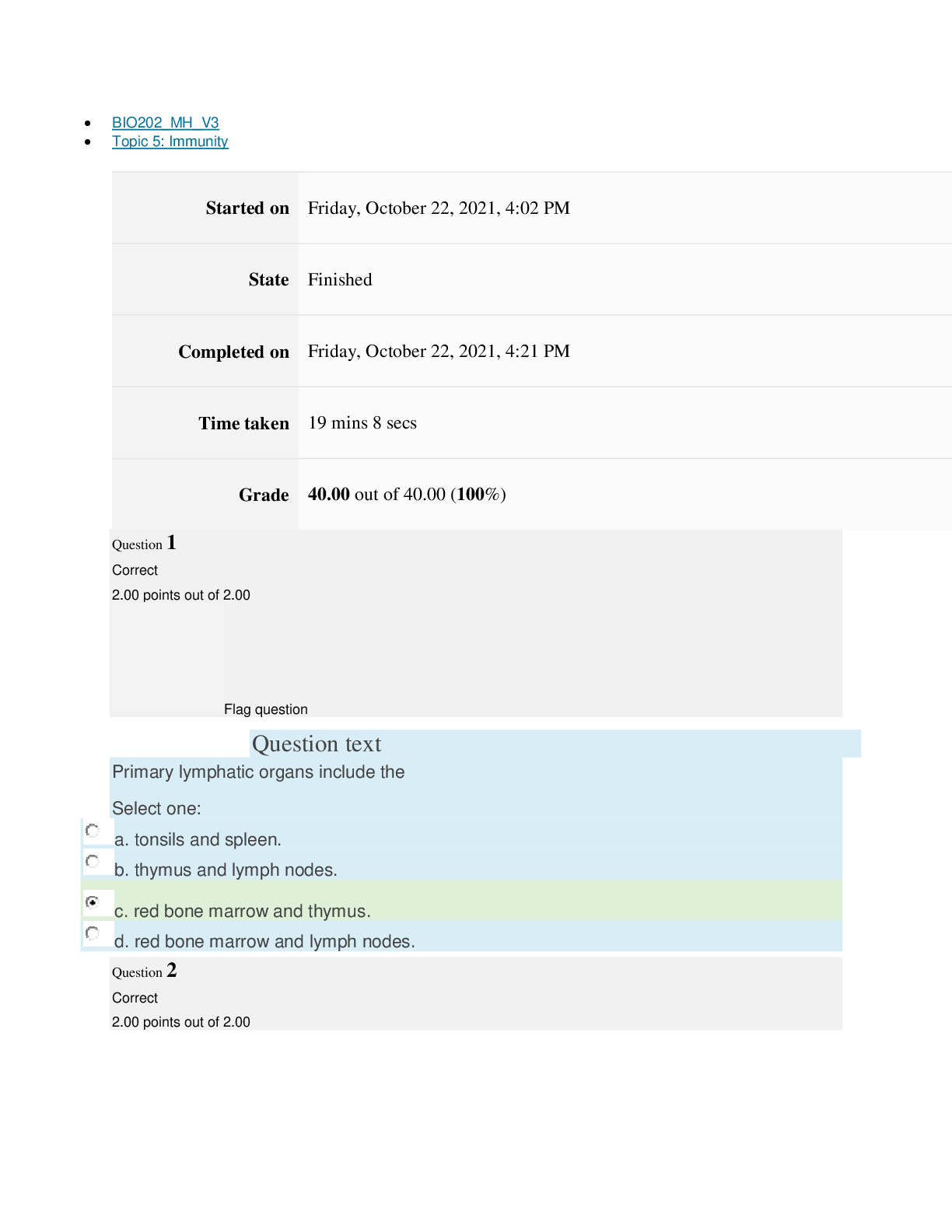
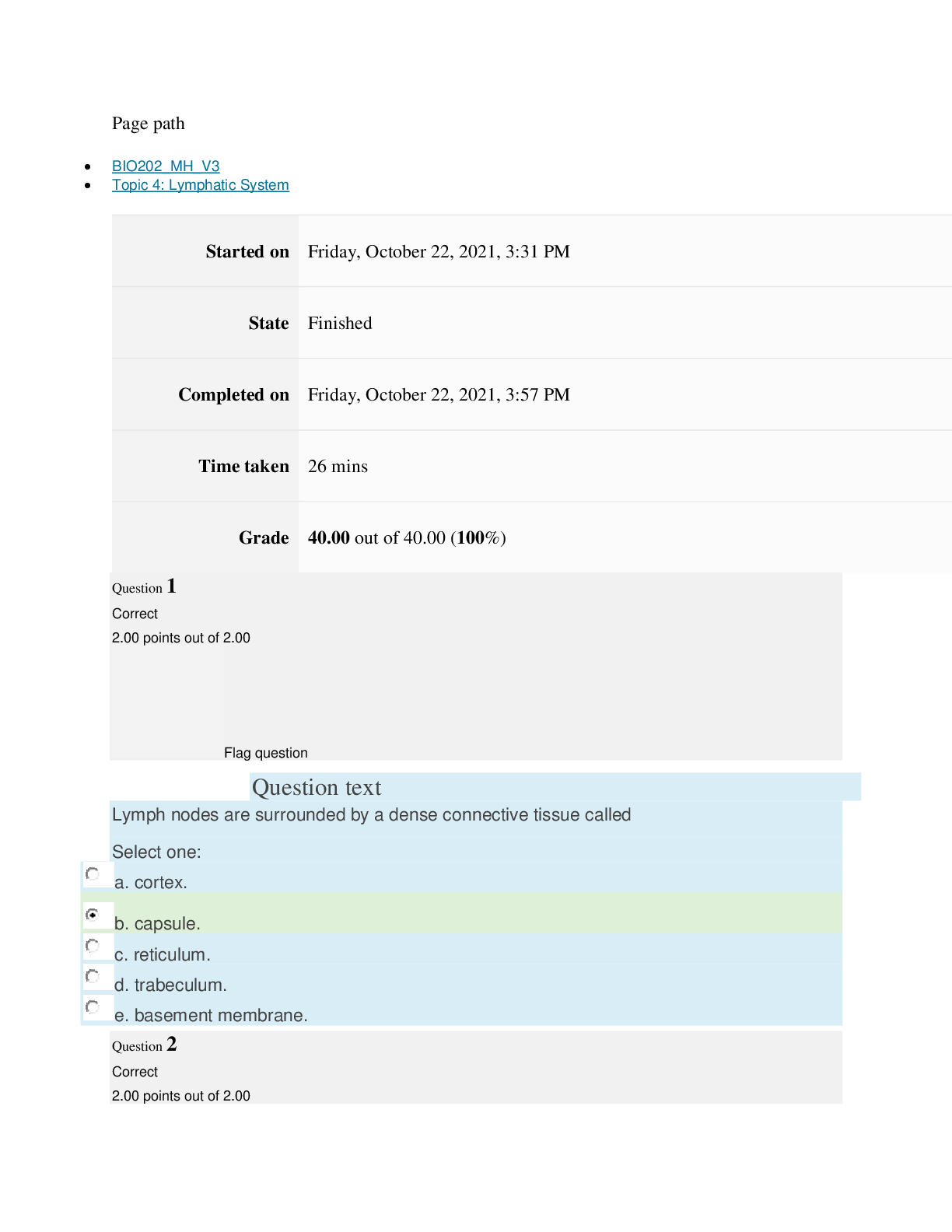
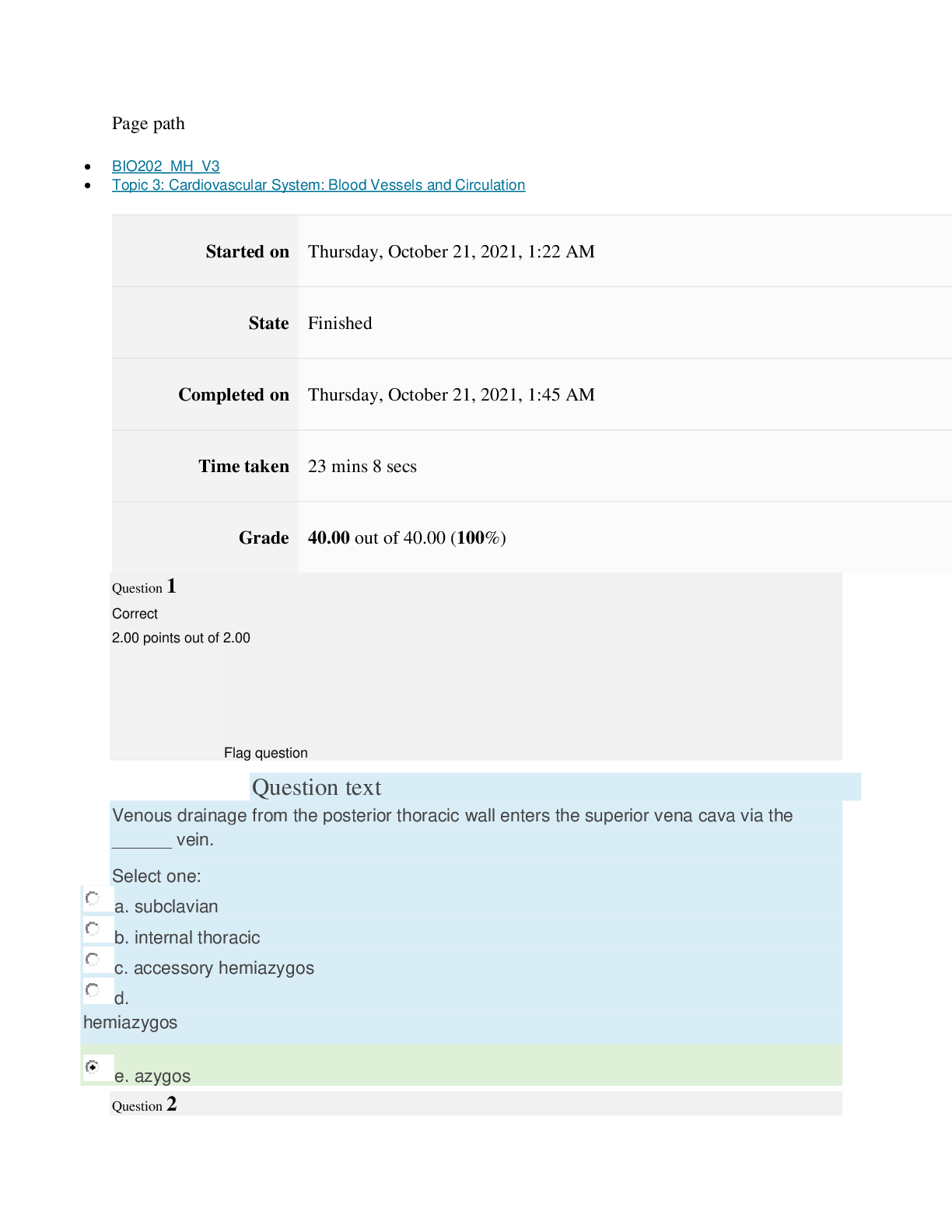
Instructions
Multiple Choice Exam
Exam questions are comprised of topics presented in this course. It is recommended that you
go through all of the content each week before taking the exam. You may take the exam no
...
Instructions
Multiple Choice Exam
Exam questions are comprised of topics presented in this course. It is recommended that you
go through all of the content each week before taking the exam. You may take the exam no
more than three times. After the third try, the exam will be locked and your highest score will be
factored into your average final grade. Remember that in addition to meeting the attendance
requirement, your average final grade must be 70% or greater to pass this course. This
average is calculated by totaling your best score from each exam and dividing the total by the
number of exams in this course.
Attempt History
Attempt Time Score
KEPT Attempt 2 32 minutes 95 out of 100
LATEST Attempt 3 12 minutes 90 out of 100
Attempt 2 32 minutes 95 out of 100
Attempt 1 82 minutes 70 out of 100
Score for this attempt: 90 out of 100
Submitted Oct 19 at 7:43am
This attempt took 12 minutes.
The average number of accidents on an interstate highway each month
should be tracked using the
P chart
Question 1 5 / 5 pts
11/20/2022 Required Exam - Unit 10 and Unit 11: VIL61 [November 2022]
2/9
Correct! U chart
C chart
Np chart
Correct! All of the above
Make the correct decision
Make a type II error
Make a type I error
When drawing our hypothesis conclusion based on comparing our test
statistic to the critical value, we can
Question 5 / 5 pts 2
If you were performing a one-tailed, left-tailed hypothesis test, and your
critical value was -4.26 and your test statistic was -3.57, what would your
conclusion be?
Reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis
orrect Answer Fail to reject the null hypothesis
ou Answered Accept the null hypothesis
None of the above
Question 3 0 / 5 pts
11/20/2022 Required Exam - Unit 10 and Unit 11: VIL61 [November 2022]
3/9
When making a statistical decision to develop a conclusion when hypothesis
testing, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis
when
The test stat is in the opposite tail from the single critical value
[Show More]