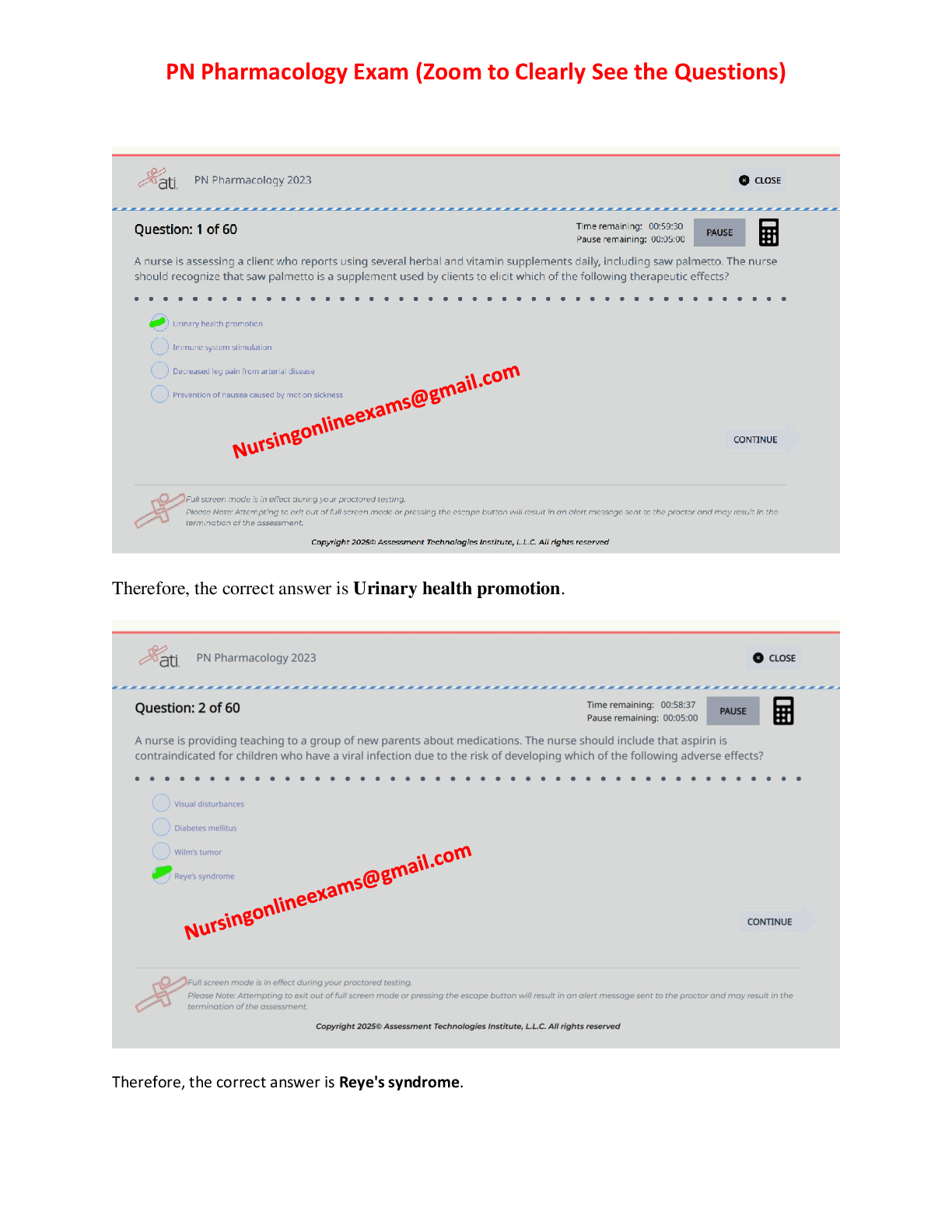
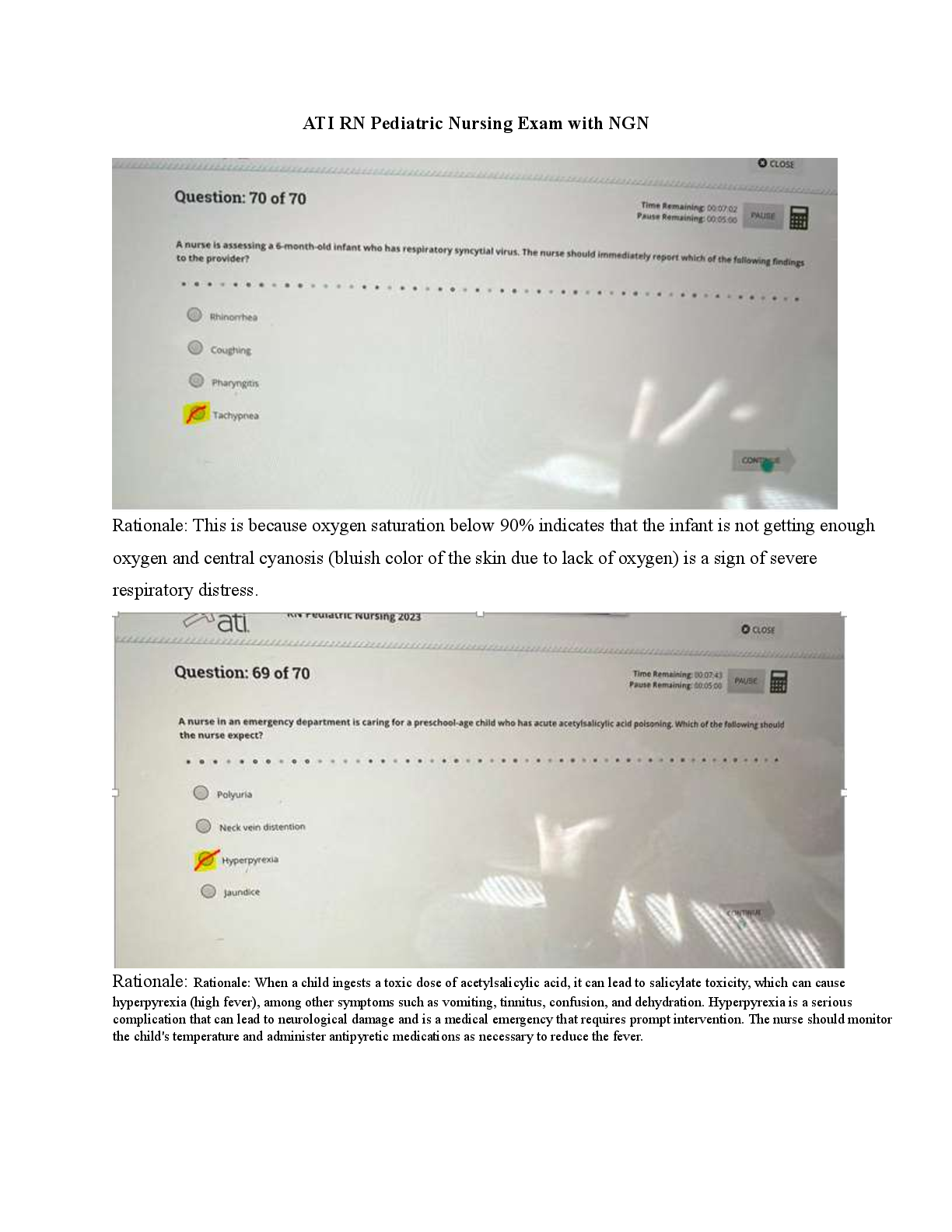
MIDTERM EXAMINATION #2
OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS
03-60-330-01 Fall 2009
UN I V E R S I T Y O F WI N D S O R
S C H O O L O F CO M P U T E R S C I E N C E
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
1. This is a CLOSED bo
...
MIDTERM EXAMINATION #2
OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS
03-60-330-01 Fall 2009
UN I V E R S I T Y O F WI N D S O R
S C H O O L O F CO M P U T E R S C I E N C E
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
1. This is a CLOSED book test; no notes, textbooks, calculators or computer aids are allowed.
2. PRINT your name legibly and clearly with your Student ID in the spaces indicated on the
Scantron sheet.
3. You will be asked to sign your name once before leaving the exam room (sign-out). By doing so
you state agreement to the terms below
I agree to the above terms and will neither receive nor give
unauthorized help on this exam.
4. All questions are multiple choice. Circle the single response which best answers each question.
5. Place all responses on the approved Scantron marking sheet using PENCIL.
6. You are not allowed to give or receive unauthorized help with your test. Any misconduct, as
outlined by the Senate bylaw 31 article I, will be reported accordingly.
7. You have 75 minutes to complete this test.
8. You may keep this question paper following the examination. A photocopy of your Scantron
sheet will be returned to you.
9. The maximum mark is 40.
Good Luck!
ANSWER SHEET
Page 1
All questions are Multiple Choice or True/False. In each Multiple Choice question, 4 responses are
provided – you are to choose only one response which best answers the question. On the Scantron sheet
provided, carefully fill in the circle corresponding to the response letter A, B, C or D (one only).
If an error is made you must carefully erase your response on the Scantron sheet, and then fill in the
circle you intend to choose.
1. Two short methods that implement the simple semaphore wait() and signal() operations
on global variable S include:
signal (S) {
S++;
}
and _______________ .
A) wait (S) {
while (S <= 0);
S--;
}
B) wait (S) {
while (S >= 0);
S--;
}
C) wait (S) {
S--;
while (S <= 0);
}
D) None of these are correct solutions.
2. Race conditions are prevented by requiring that critical regions be protected by
________ .
A) clocks
B) semaphores
C) locks
D) monitors
3. The local variables of a monitor can be accessed by ___________ .
A) only the operating system kernel threads
B) only the local procedures
C) signals
D) licensed developers
Page 2
4. The first readers-writers problem ____.
A) requires that, once a writer is ready, that writer performs its write as soon as
possible.
B) is not used to test synchronization primitives.
C) requires that no reader will be kept waiting unless a writer has already obtained
permission to use the shared database.
D) requires that no reader will be kept waiting unless a reader has already obtained
permission to use the shared database.
5. The second readers-writers problem _____________ .
A) requires that, once a writer is ready, that writer performs its write as soon as
possible.
B) is not used to test synchronization primitives.
C) requires that no reader will be kept waiting unless a writer has already obtained
permission to use the shared database.
D) requires that, once a writer is ready, that writer performs its write as soon as
possible.
NOTE: Either A or D are correct. Noted in class to ignore D, however.
6. A deadlocked state occurs whenever ____.
A) a process is waiting for I/O to a device that does not exist
B) the system has no available free resources
C) every process in a set is waiting for an event that can only be caused by another
process in the set
D) a process is unable to release its request for a resource after use
7. One necessary condition for deadlock is ____, which states that at least one resource
must be held in a non-sharable mode.
A) hold and wait
B) mutual exclusion
C) circular wait
D) no preemption
8. In a system resource-allocation graph, ____.
A) a directed edge from a process to a resource is called an assignment edge
B) a directed edge from a resource to a process is called a request edge
C) a directed edge from a process to resource is called a request edge
D) None of the above
Page 3
9. A cycle in a resource-allocation graph is ____.
A) a necessary and sufficient condition for deadlock in the case that each resource has
more than one instance
B) a necessary and sufficient condition for a deadlock in the case that each resource
has exactly one instance
C) a sufficient condition for a deadlock in the case that each resource has more than
once instance
D) is neither necessary nor sufficient for indicating deadlock in the case that each
resource has exactly one instance
10. Which of the following is most often used by operating systems to handle deadlocks?
A) Pretend that deadlocks never occur
B) Use protocols to prevent or avoid deadlocks
C) Detect and recover from deadlocks
D) None of the above
11. Which of the following statements is true?
A) A safe state is a deadlocked state.
B) A safe state may lead to a deadlocked state.
C) An unsafe state is necessarily, and by definition, always a deadlocked state.
D) An unsafe state may lead to a deadlocked state.
12. Suppose that there are 10 resou
[Show More]


 (Penn State University).png)


.png)