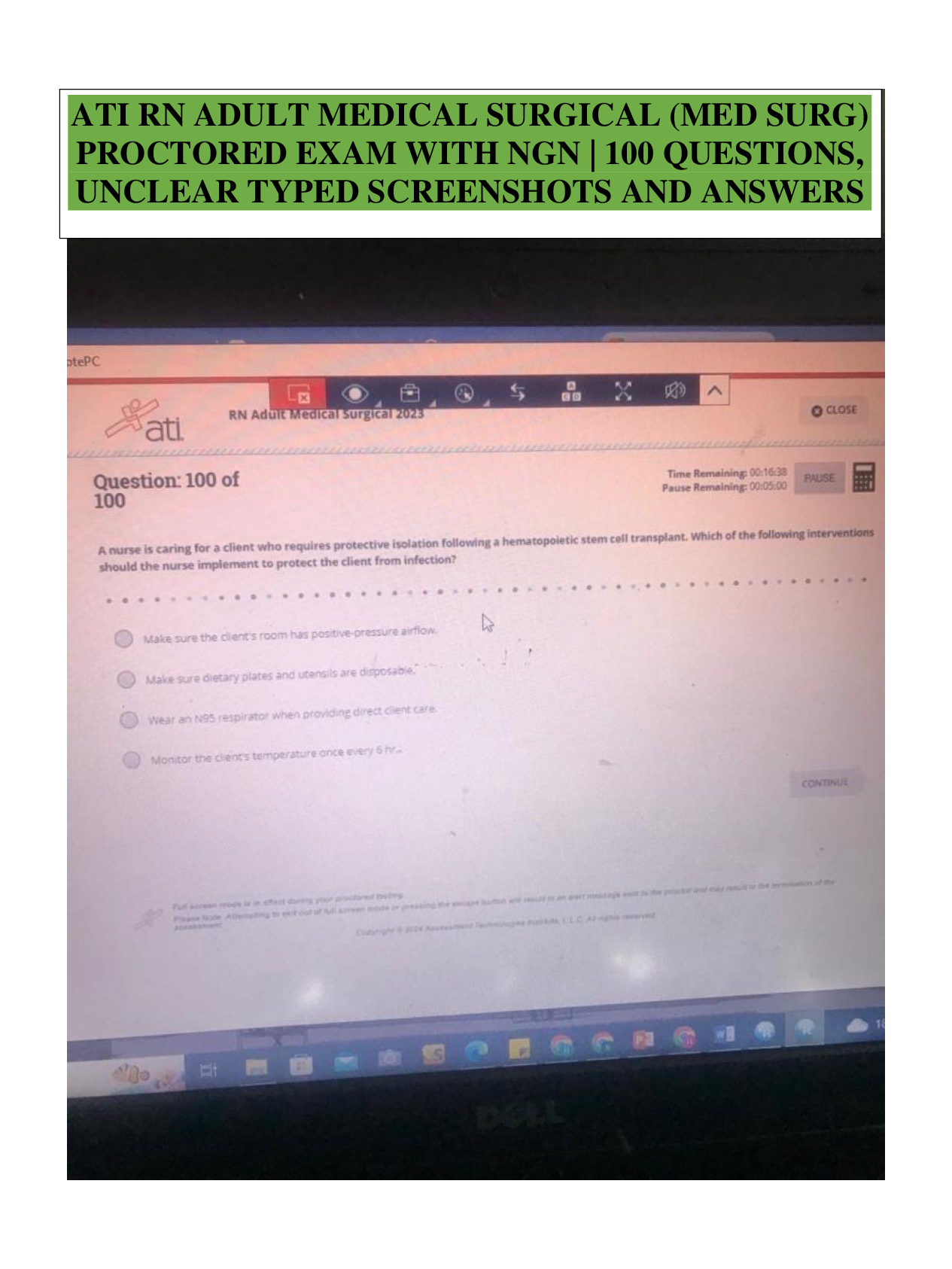
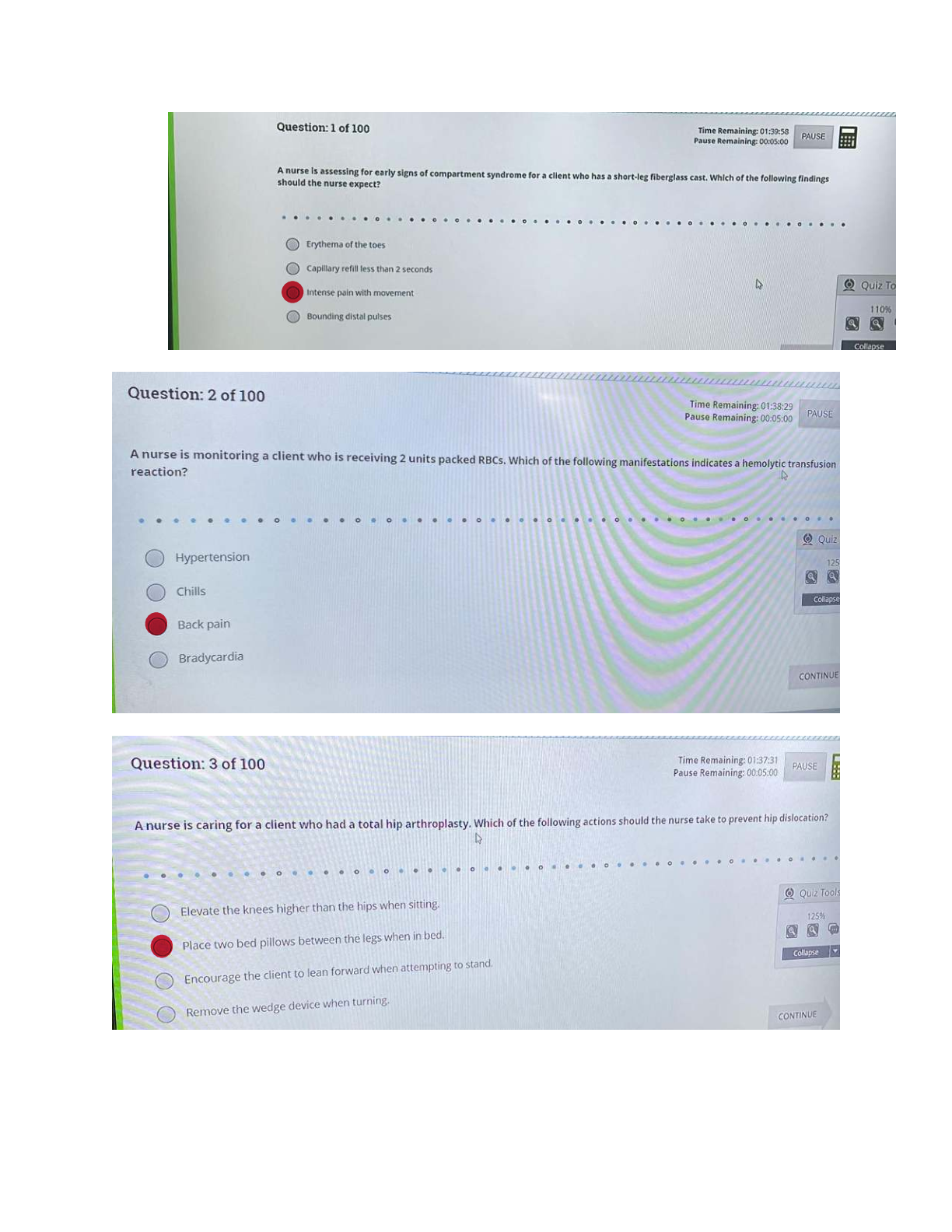
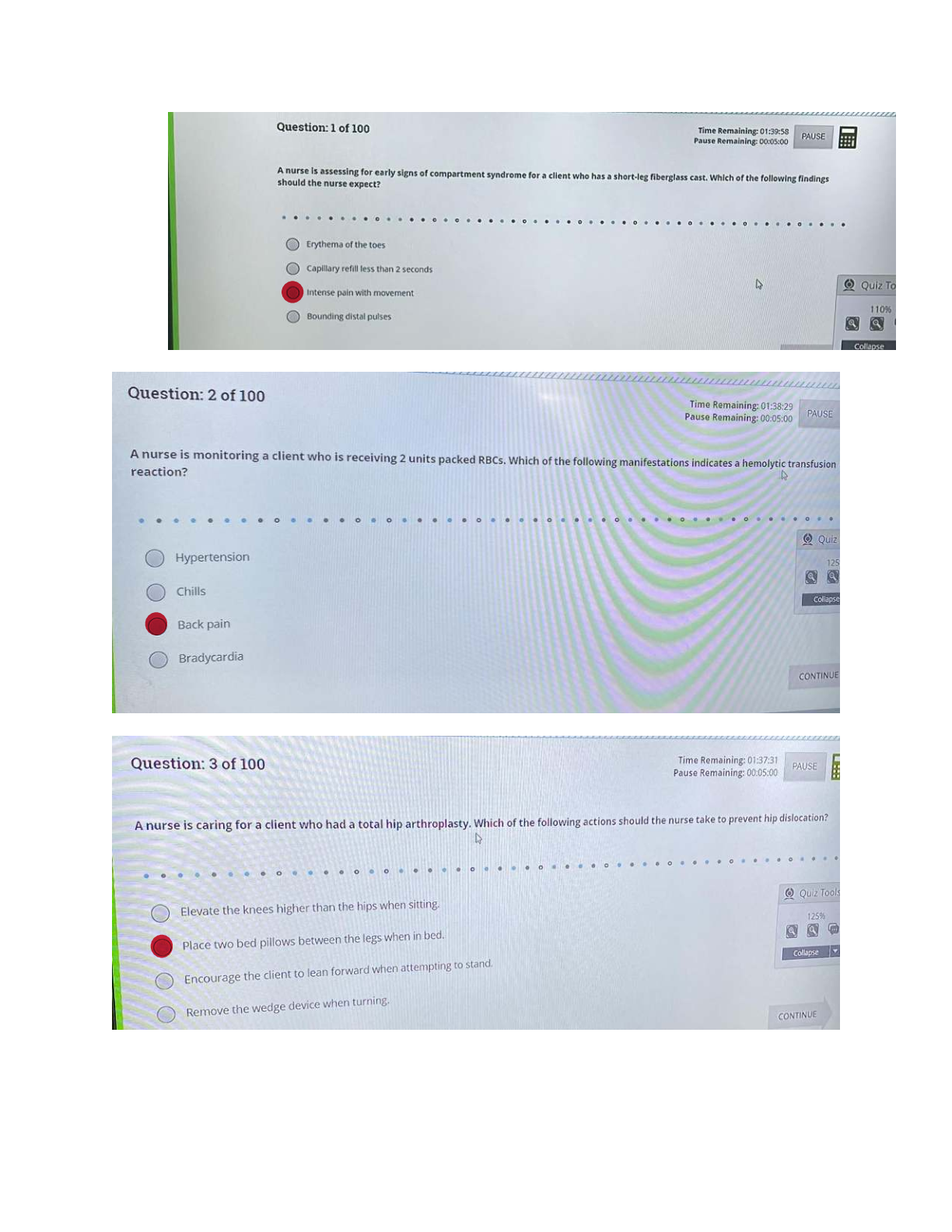
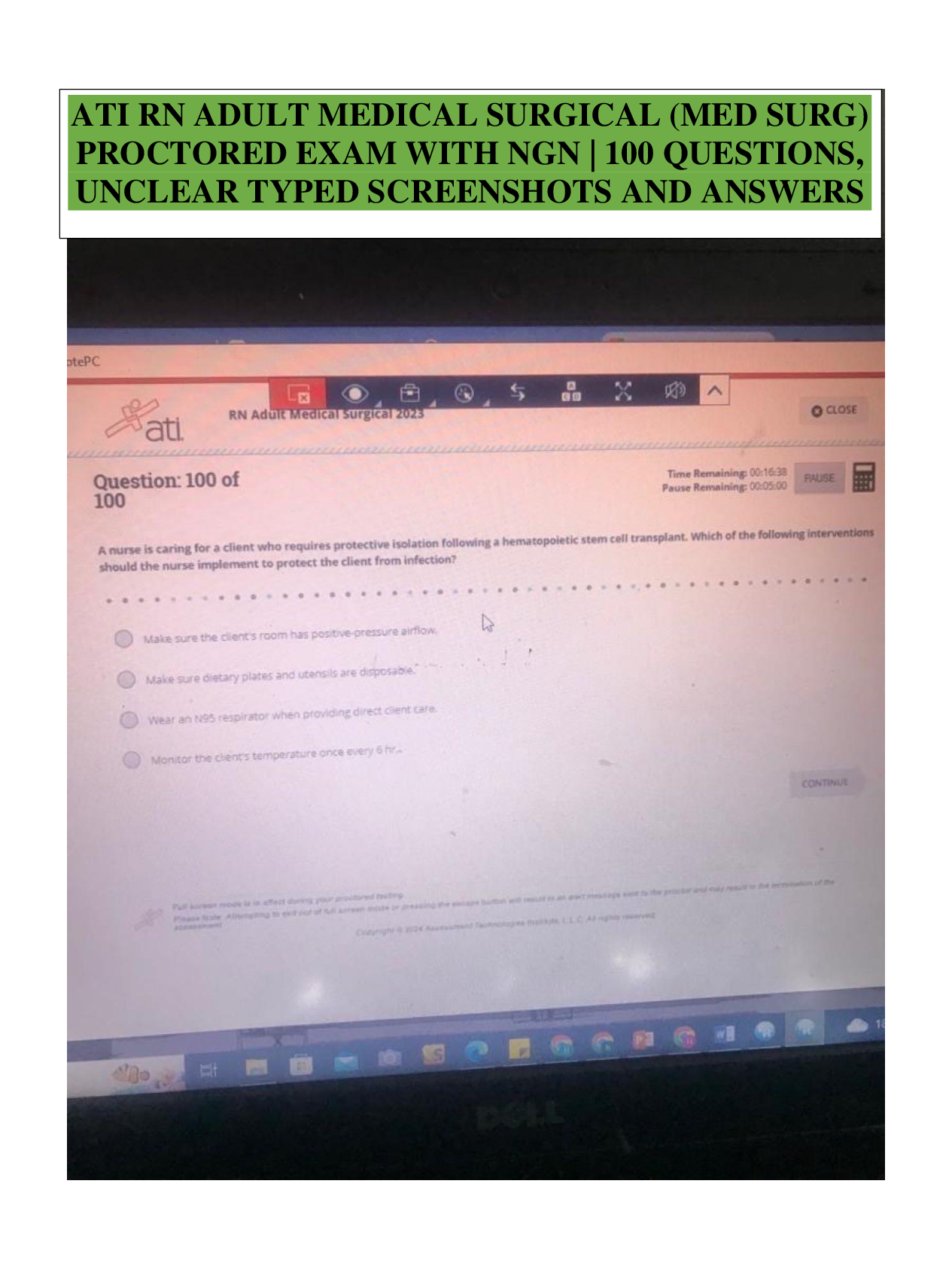
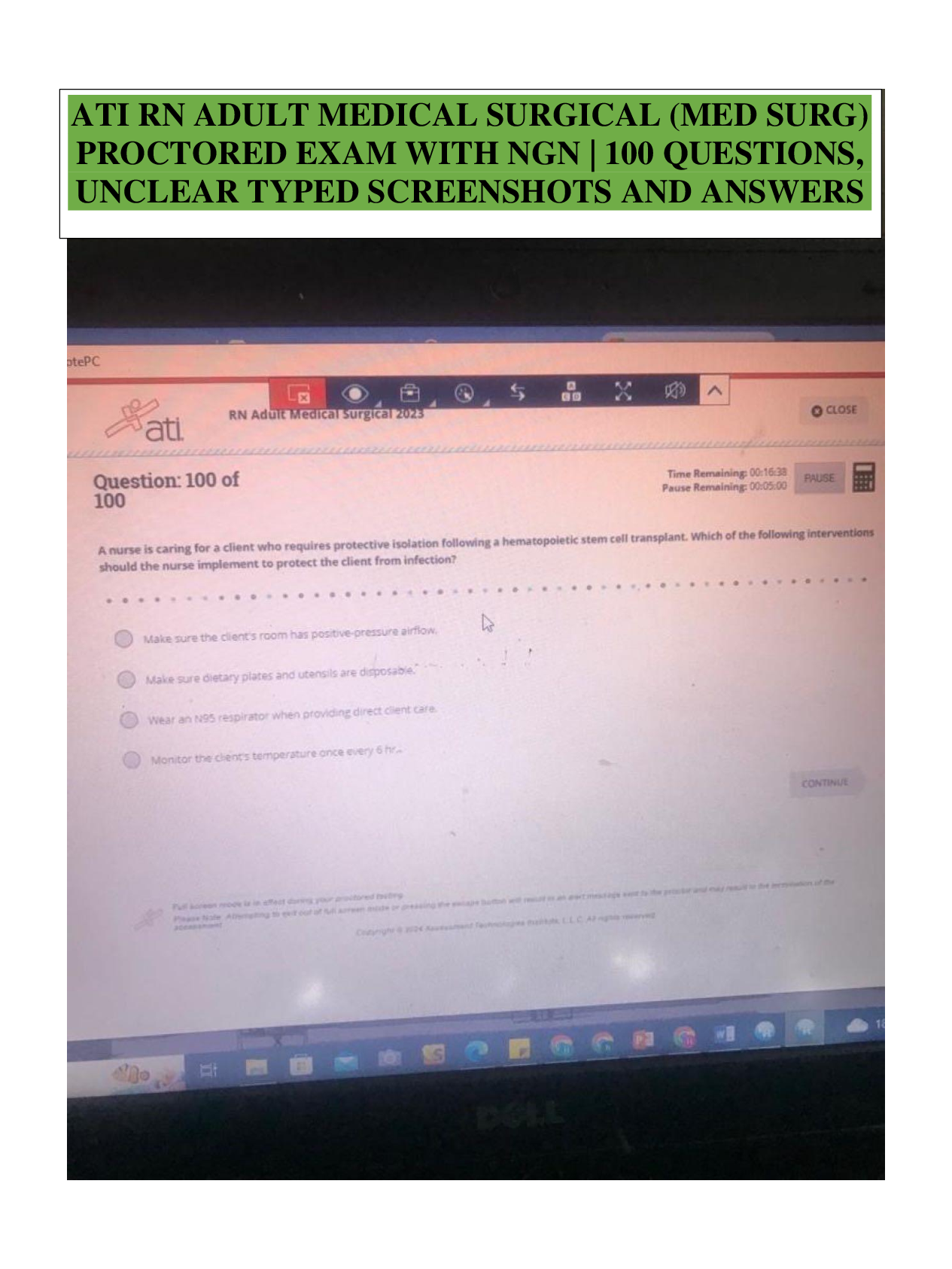
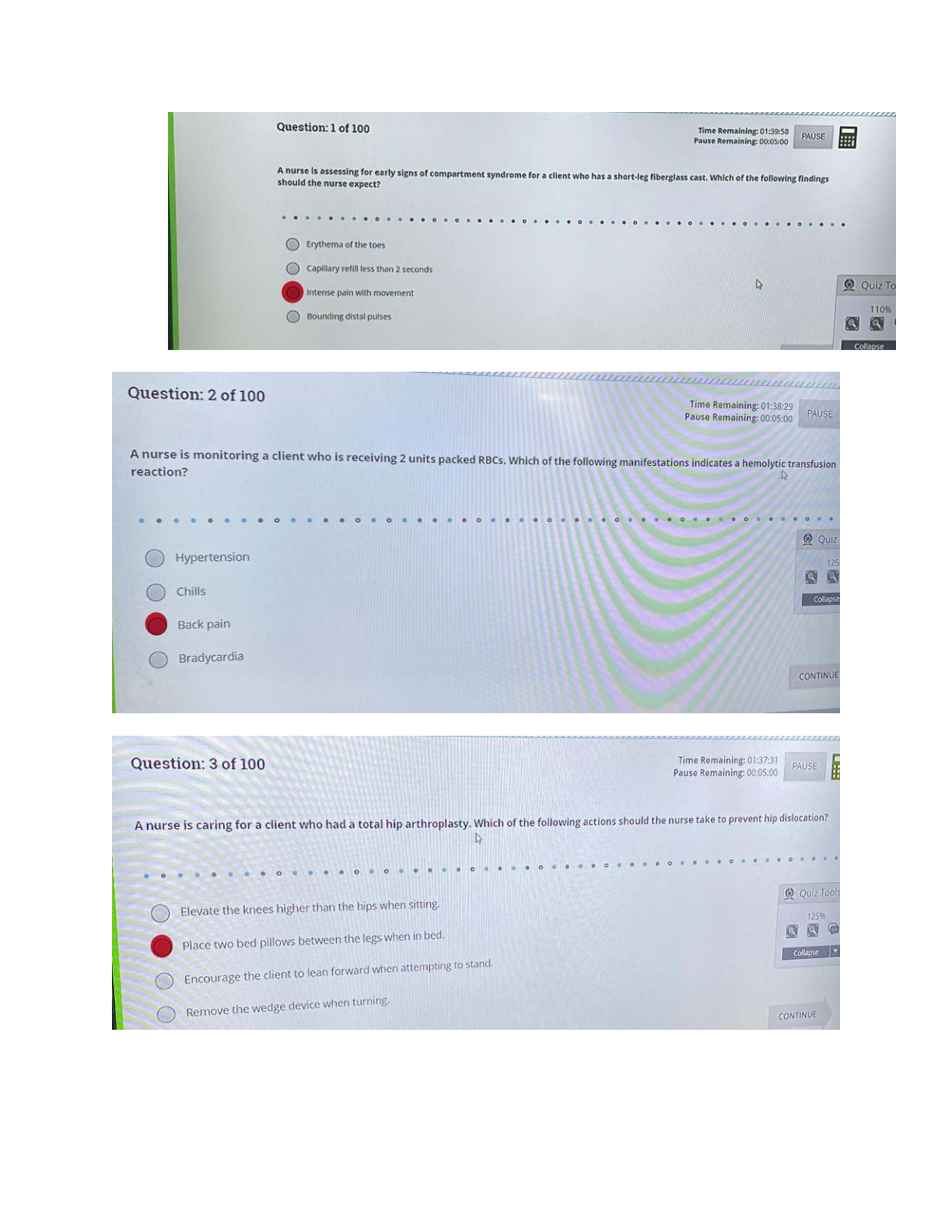
What is the basic structure of an amino acid? What do they look like? - ANSWER amino group (NH2 or NH3), carboxyl group (COO or COOH), alpha carbon (C), and variable group
How do you identify the 3 different types of
...
What is the basic structure of an amino acid? What do they look like? - ANSWER amino group (NH2 or NH3), carboxyl group (COO or COOH), alpha carbon (C), and variable group
How do you identify the 3 different types of side chains: non-polar/hydrophobic, polar, and charged? - ANSWER Non-polar/hydrophobic - end with CH or "can't have" water. Polar - end with OH, SH, or NH. Charged - end with a charge
what kinds of bonds do each of the 3 different types of side chains make? - ANSWER ionic, hydrophobic/non-polar, charged
What are the 4 levels of protein structure? - ANSWER Primary - linear structure, Secondary - Folded into helix or pleated sheet caused by hydrogen bonding, tertiary - 3D structure caused by side chain interactions, quaternary - 1+ amino acid chains combine = multiple subunits MUST have 1+ subunit
What enviormental change breaks each type of bond? - ANSWER hydrophobic - temperature change, ionic - salt or decreased pH, hydrogen - temperature, change in pH, disulfide - reducing agents
what type of amino acid side chain leads to protein aggregration? - ANSWER hydrophobic bonds
how do environmental changes affect protein folding? - ANSWER Extreme temp can cause hydrogen bonds to break apart = malformation of protein folding
how do mutations affect protein structure? - ANSWER Can cause structure to change. Protein loses form = loses function. May form a different protein.
What is an electron? - ANSWER Negatively charged atom on outer ring for bonding
What is energy: - ANSWER Power derived fro chemical interaction
what are covalent bonds? - ANSWER chemical bond, atoms share 1+ valence electrons
what is an ionic bond? - ANSWER bond between positive and negative
what is a hydrogen bond? - ANSWER weak bond between positive and negative
with an amino? - ANSWER piece of amino acid, NH2 or NH3
what is a carboyxl? - ANSWER piece of amino acid, COO or COOH
What is hydrophobic? - ANSWER Doesn't like water, end with CH
what is hydrophilic? - ANSWER Water Lovering, end with OH, NH, or SH
what is disulfide bond? - ANSWER strongest bond between reduction agents, formed between SH's.
what are zwitterions? - ANSWER amino with positive and negative charges = overall charge of zero
what is a polypeptide - ANSWER polymer of amino acids
What is dehydration synthesis? - ANSWER Process of forming peptide bonds
what is hydrolysis? - ANSWER adding water to destroy bonds
what is an alpha helix? - ANSWER twisted secondary structure, formed by hydrogen bonds
what is a beta sheet? - ANSWER folded second structure shape, formed by hydrogen bonds
what is denaturation? - ANSWER loss of shape duet o interruption of chemical bonds; occurs via extreme salt, temp, pH
what is aggregation? - ANSWER clumping of inner or outer cellular proteins caused by misfolded proteins leading to diseases such as Alzheimers, ALS, Parkinson's
how do enzymes catalyze reactions? - ANSWER bind with substrates to decrease activation energy required and decrease reaction rate
how do enzymes affect reaction rate and activation energy? - ANSWER decrease activation energy and decrease reaction rate
what are the 4 steps of the enzymatic cycle? - ANSWER enzyme recognizes substrate, substrate attracts the enzyme; enzyme-substrate complex is formed; enzyme-product complex formed; product is released, enzyme recycled
how do environmental changes affect enzymes? - ANSWER High heat, pH change, high salt concentration, and reducing agents can cause an enzyme to lose its form/lose function
what is a competitive inhibitor? - ANSWER Mimics substrate and takes its place on the active binding site
what is a noncompetitive inhibitor? - ANSWER Binds to allosteric site causing active site to change shape = preventing substrate from binding with enzyme
what molecules increase/build up or decrease given a specific inhibitor? A -> (enzyme 1) -> B -> (enzyme 2) -> C -> (enzyme 3) -> D. Pretend Enzyme 2 is inhibited. - ANSWER Inhibitor would cause a build up for product B, decrease product C. Enzyme 3 and product D would not be created.
what is substrate? - ANSWER the substance on which an enzyme acts
what is a product? - ANSWER result of a reaction
what is an intermediate? - ANSWER products produced in an enzyme pathway before final product
what is an active site? - ANSWER location where substrate binds with enzyme
what is enzyme specificity? - ANSWER Enzymes bind with certain substrate or type of substrate to create a certain reaction
what is induced fit? - ANSWER Enzyme changes shape in enzyme-substrate complex to facilitate formation of enzyme-product complex
what is kinase? - ANSWER Enzyme, adds phosphate group via phosphorlation
what is phosphatase? - ANSWER enzyme, removes phosphate group via dephosphorylation
with is an allosteric site? - ANSWER secondary site on an enzyme an inhibitor binds to via non-competitive inhibition
what is competitive inhibition? - ANSWER enzyme substrate and inhibitor complex compete to bind with enzyme's active site. no product formed when inhibitor binds with enzyme.
what is non-competitive inhibition? - ANSWER inhibitor binds to allosteric site, not active site. Changes shape of active site, preventing substrate from binding and making product
what is feedback inhibition? - ANSWER End product sends feedback to beginning of enzyme pathway inhibiting 1st enzyme via noncompetitive inhibition
what nucleotides/bases are used in DNA? what are their abbreviations/full names? - ANSWER C - cytosine, G - guanine, A - adenine, T - thyamine
what nucleotides/bases are used in RNA? - ANSWER C - cytosine, G - guanine, U - uracil, A - adenine
which nucleotides base-pair together in DNA? - ANSWER T-A, G-C
which nucleotides base-pair together in RNA? - ANSWER U-A, G-C
how to we make complementary DNA? (i.e. coding to temple et reverse) - ANSWER Taking coding DNA, write in reverse, then pair them up to make template.
Template DNA, write in reverse, then pair up to make coding
how do we make mRNA? - ANSWER template DNA to mRNA by switching back and forth OR coding DNA to mRNA by switching out T's for U's
which strand of DNA is complementary to mRNA? - ANSWER Template DNA
how do we make protein? - ANSWER DNA -> RNA -> Protein
which type of nucleotide sequence is used and in which direction? - ANSWER RNA is used 5' to 3'
what is the relationship between mRNA and tRNA? - ANSWER tRNA is complementary to mRNA
how does mRNA splicing allow use to create multiple proteins from a single gene/mRNA? - ANSWER Alternative splicing allows for all introns to be cut and some exons = multiple proteins form from same MRNA
what factors increase gene expression? - ANSWER Decreased methylation, increased acetylation, Widely spaced neucleosomes, exposed promoter, use of transcription factors, use RNA polymerase
what factors decrease gene expression? - ANSWER Increased methylation/decreased acetylation, tightly packed nucleosomes, hidden promoter, no transcription factors, no RNA polymerase
what steps do you take to determine what type of mutation occurred between a normal and mutated DNA/RNA sequence? - ANSWER look between the two strands, determine what changed, name the mutation
What are the types of mutations? - ANSWER silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift
what type of DNA damage does each repair pathway fix? - ANSWER base excision - single nucleotide, nucleotide excision repair - multiple nucleotides, missmatch - mistakes made in DNA replication, homologous recombination/nonhomologous end joining - double stranded breaks
what are the steps of excision repair? - ANSWER Recognize damage, cut damage out, recreate DNA strand, glue DNA strand back together
what are the steps of mismatch repair? - ANSWER Remove mismatched base, try again
what are the steps of homologous recombination and nonhomologous end joining? - ANSWER HR uses DNA from unbroken strand to fix broken strand, NHEJ reconnects broken pieces, may have pieces missing
what are the steps of PCR? - ANSWER denature, anneal, elongation/extension
how do we denature DNA in PCR? - ANSWER heat to 95 degrees C to separate DNA strands
how do we anneal DNA? - ANSWER primers base pair with DNA strands
how do we elongation/extend DNA? - ANSWER DNA polymerase attach primers and synthesize new DNA strands
what are the components of PCR? - ANSWER target DNA, heat stable DNA polymerase, nucelotides (dNTP), primers
how are primers used to assist in a PCR reaction? - ANSWER Primers allow DNA polymerase to bind to target DNA
how do you calculate the number of copies of DNA produced by specific number of PCR cycles? - ANSWER Each cycle produces doubles the amount of DNA
how does PCR compare to normal DNA replication in the cell? - ANSWER RNA primers used instead of DNA in normal replication. Helicase enzymes separate DNA strands instead of heat in normal replication. DNA polymerase is not heat stable in normal replication.
what is gene expression? - ANSWER process by which info coded in DNA creates proteins and RNAs
What are nucleotides? - ANSWER building blocks of nucleic acids
what is antiparallel? - ANSWER refers to arrangement of DNA double helix (run in opposite directions)
what is complementary? - ANSWER predictable counterparts
what is template DNA? - ANSWER DNA strand, provides pattern for ordering via complementary base pairing in RNA transcript
what is coding DNA? - ANSWER nontemplate strand of DNA, same sequence as mRNA except has T instead of U
what is replication? - ANSWER processing of copying DNA molecules via DNA synthesis
what is transcription? - ANSWER creation of RNA using info from DNA
What is RNA polymerase? - ANSWER enzyme, links ribonucleotides to growing RNA chain during transcription
what is a promoter? - ANSWER sequence of DNA that binds with RNA, encourages RNA transcription
what is a transcription factor? - ANSWER proteins that bind to promoter regions, help initiate transcription
what is mRNA? - ANSWER type of RNA, created via DNA template, specifies primary structure of protein
what is translation? - ANSWER creation of polypeptide using info in the mRNA
what is tRNA? - ANSWER RNA that brings amino acids to ribosomes during creation of polypeptide
what are ribosomes? - ANSWER molecular complex, assist with orderly linking of amino acids/polypeptide chains
what are codons? - ANSWER nucleotide triplet of DNA or RNA. Basic genetic code. Specifies type of amino acid or termination signal
what are anticodons? - ANSWER nucleotide triplet at one end of tRNA. Base pairs with complementary codon on mRNA
what is splicing? - ANSWER parts of transcript are removed and others are reconncected
what are introns? - ANSWER pieces of noncoding that are removed during RNA processing
what are exons? - ANSWER pieces of coding that stay with RNA during processing - ARE NOT DISCARDED
what are histones? - ANSWER Protein; high proportion and charged amino acid that binds with DNA. Plays key role in chromatin structure.
what is a nucleosome? - ANSWER basic bead like unit of DNA.
what is methylation? - ANSWER presence of methyl groups on DNA bases, adding of methyl groups to DNA bases
what is acetylation? - ANSWER attachment of acetyl groups to certain amino acids of proteins (mainly histones)
what is the structural difference between myoglobin and hemoglobin? - ANSWER myoglobin - primary, secondary, tertiary, single subunit protein (1 heme, 1 iron, 1 O2). hemoglobin - primary, secondary, teriary, quaternary, 4 subunit protein (4 heme, 4 iron, 4 O2)
what are the functional differences between myoglobin and hemoglobin? - ANSWER myoglobin - found in muscle, stores O2 in muscle, higher affinity for O2. hemoglobin - found in blood, delivers O2 to tissues in need, decreased affinity for O2
what are the structural properties of the tense state of hemoglobin? - ANSWER deoxygenated hemoglobin = deep purple color. heme is bent; subunits move farther apart. decreased affinity of O2 binding.
what is the structural properties of hemoglobin in the relaxed state? - ANSWER Bright red color. Heme is planar with subunits moved closer, increased affinity of O2 binding
what causes hemoglobin to change between relaxed and tense state? - ANSWER O2 binding with hemoglobin in tense state causing subunits to move in closer and change hemoglobin to relaxed state
how does carbon monoxide affect the structure of hemoglobin? - ANSWER locks HgB in R-state, and takes up space on HgB for binding to O2
how does it cause carbon monoxide poisoning? - ANSWER keeps HgB in R-state, HgB does not release O2. HgB has higher affinity for O2, but CO has higher affinity than HgB for O2.
steps of DNA replication to protein? - ANSWER DNA -> transcribed -> mRNA -> translation -> protein
what is an okazaki fragment? - ANSWER Okazaki fragments are short molecules of single-stranded DNA that are formed on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
how does 2,3-BPG (2,3-DPG) affect structure of hemoglobin? - ANSWER reduces hemoglobin's affinity for O2
what is the natural function of 2,3-BPG? - ANSWER increases release of O2 in atmosphere with decreased oxygen. efficiently deliver oxygen to fetus.
what are we measuring when we measure pH? - ANSWER number of H+ protons in blood
what level of pH is blood considered acidic? - ANSWER Below 7.2
what level of pH is blood considered basic? - ANSWER above 7.4
what factors change pH in blood? - ANSWER Increased or decreased CO2, increased or decreased H+
how to do changes in pH affect hemoglobin's structure? - ANSWER Increased CO2/Increased pH = T-state, Decreased CO2/Decreased pH = R-state
what is a heme? - ANSWER subunit of hemoglobin/myoglobin
what is affinity - ANSWER stickiness of oxygen binding
what is cooperativity? - ANSWER binding of O2 to deoxygenated blood
what is bicarbonate? - ANSWER carbon dioxide in disguise, outcome of CO2/H2O + carbonic anhydrase
what is carbonic anhydrase? - ANSWER enzyme; converts CO2 into bicarb and proton
what do chaperones do? - ANSWER assist with protein folding
difference between fetal and adult hemoglobin? - ANSWER fetal hemoglobin has higher affinity for oxygen than maternal hemoglobin. fetal has alpha and gamma forms of hemoglobin while adults have alpha and beta
Right left shift curve for decreased pH? increased pH? - ANSWER Decreased pH = right shift curve. Increased pH = left shift curve.
what can show an MI? - ANSWER myoglobin - can show muscle damage
Examples of monosaccharides - ANSWER glucose, fructose, galactose
examples of disaccharides - ANSWER sucrose, lactose, maltose
examples of polysaccharides - ANSWER starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
how do the different linkages between monomers of polysaccharrides affect how they are digested? - ANSWER B linkages - enzymes that break down B linkages, unable to break down A linkages. A linkages - enzymes only able to break down A linkages.
structure and function of ATP? - ANSWER 3 phosphate groups + adenosine. provide energy to cell
real-life scenarios that would like to insulin release from pancreas? - ANSWER eating carb rich meal, eating something excessively sugary
how does insulin help reduce blood sugar level? - ANSWER promote glycogen formation from excess glucose, stimulates gl
[Show More]