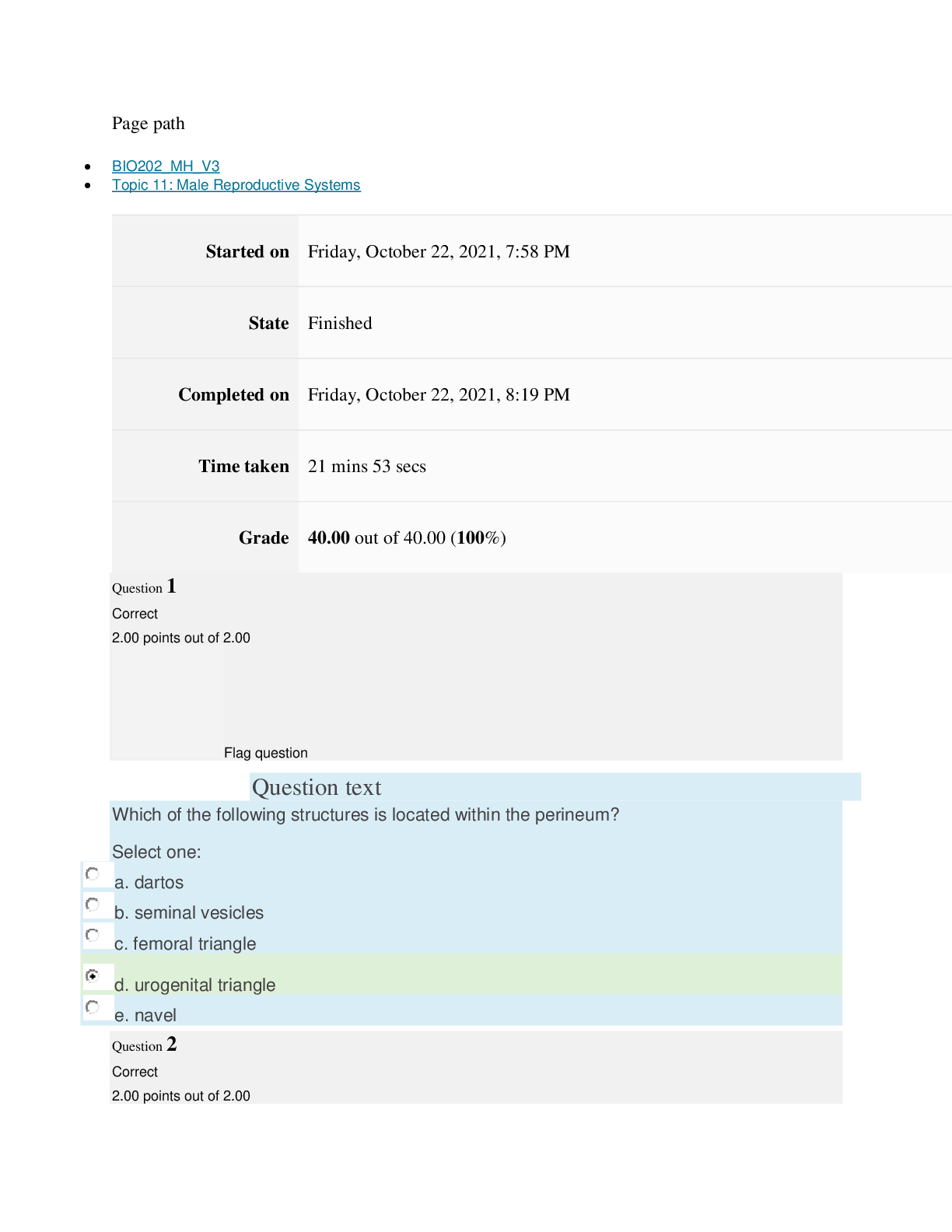
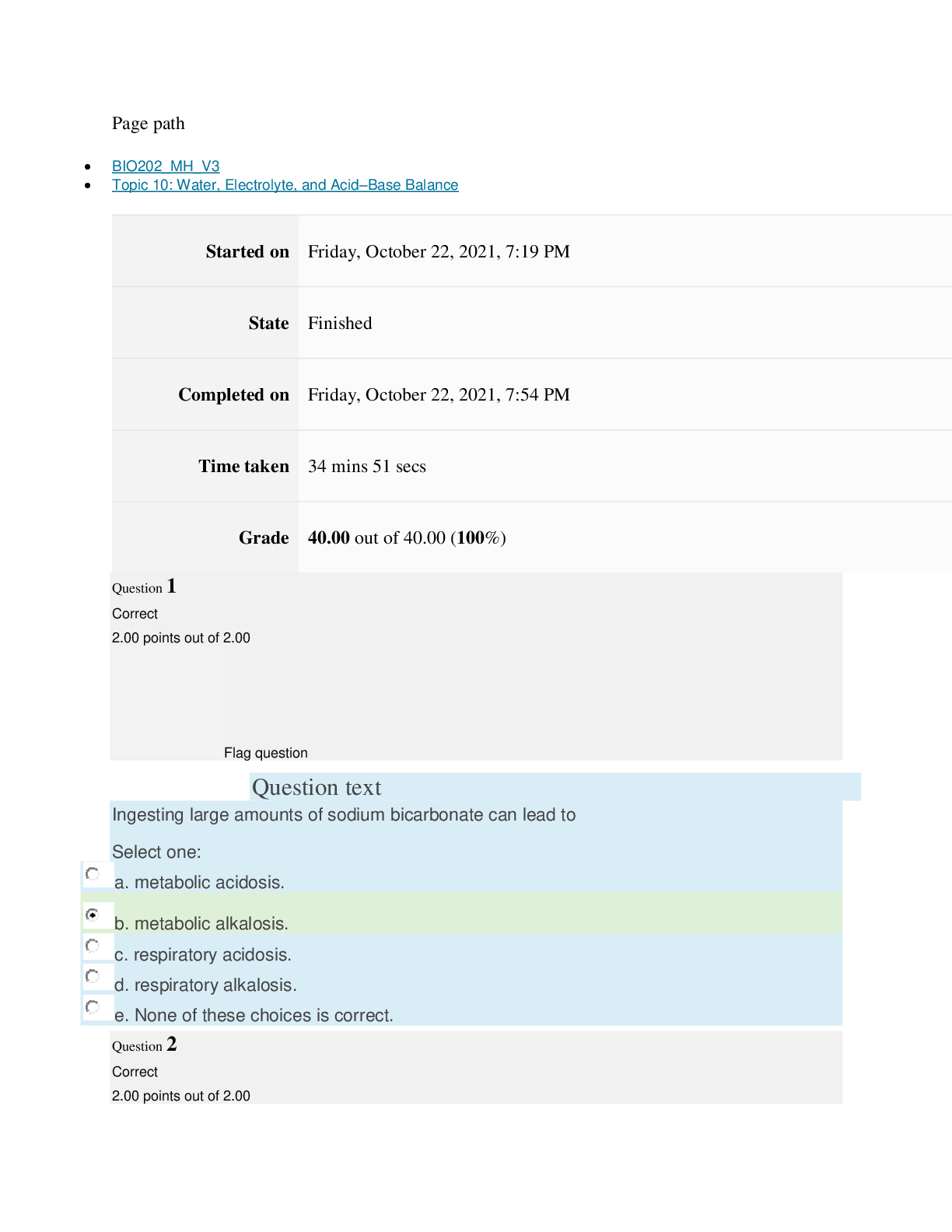
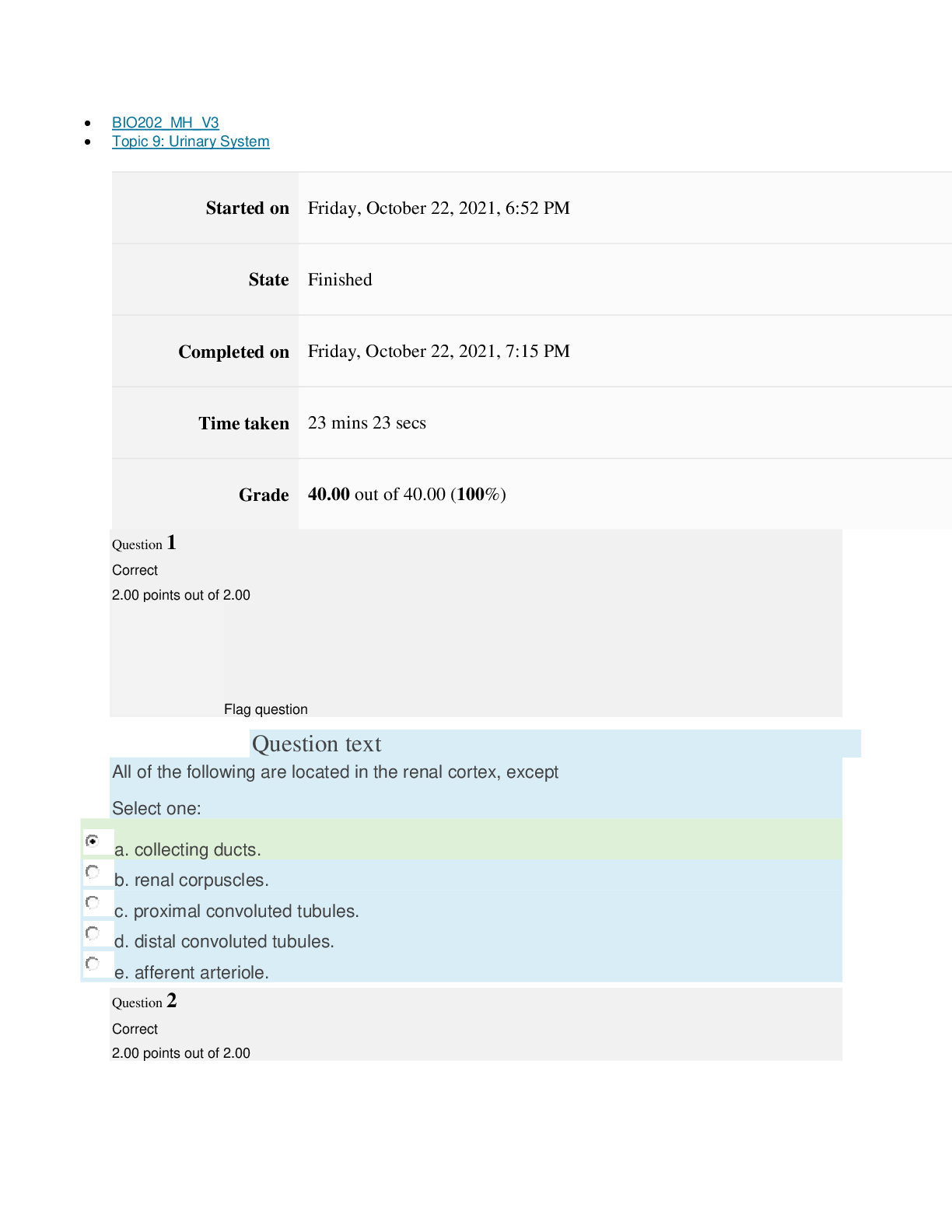
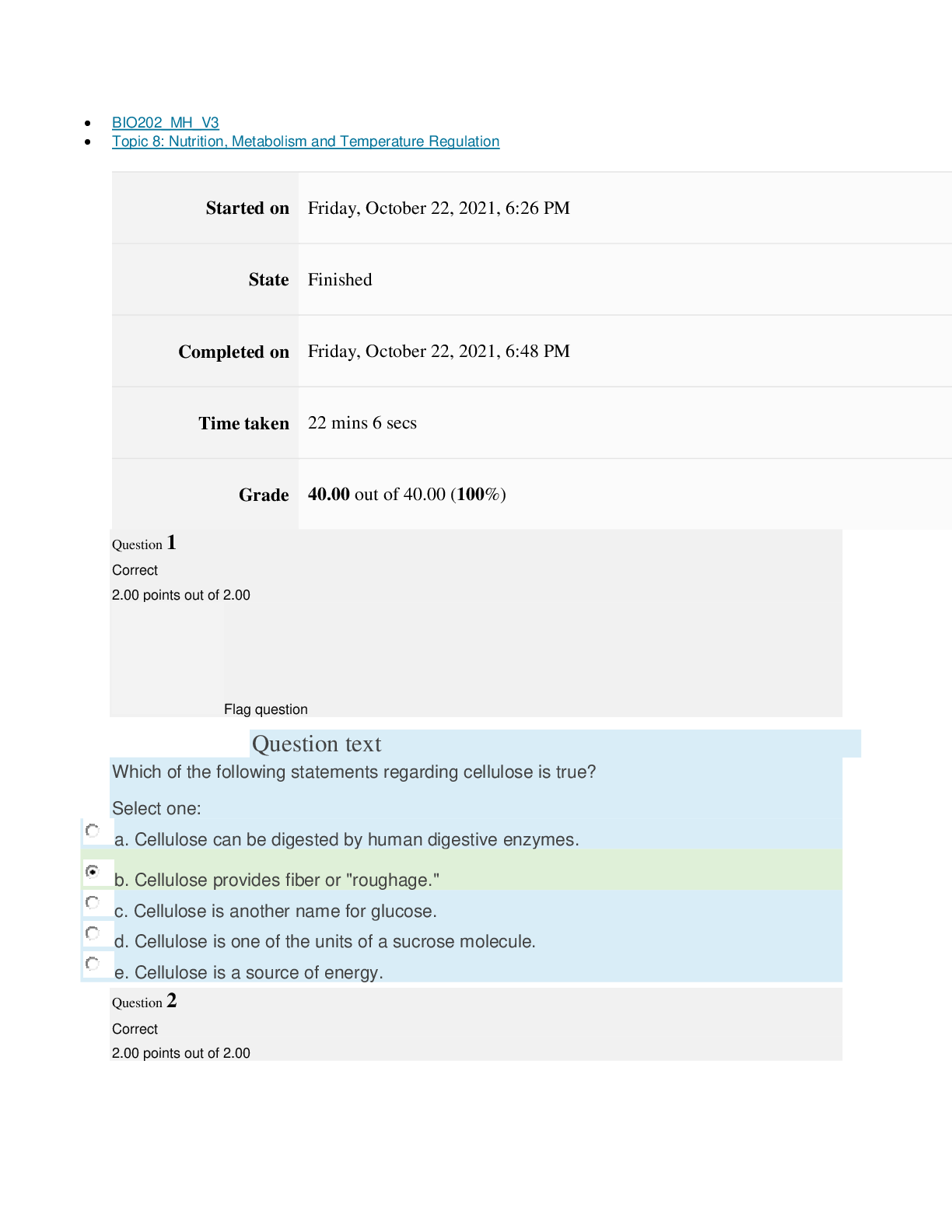
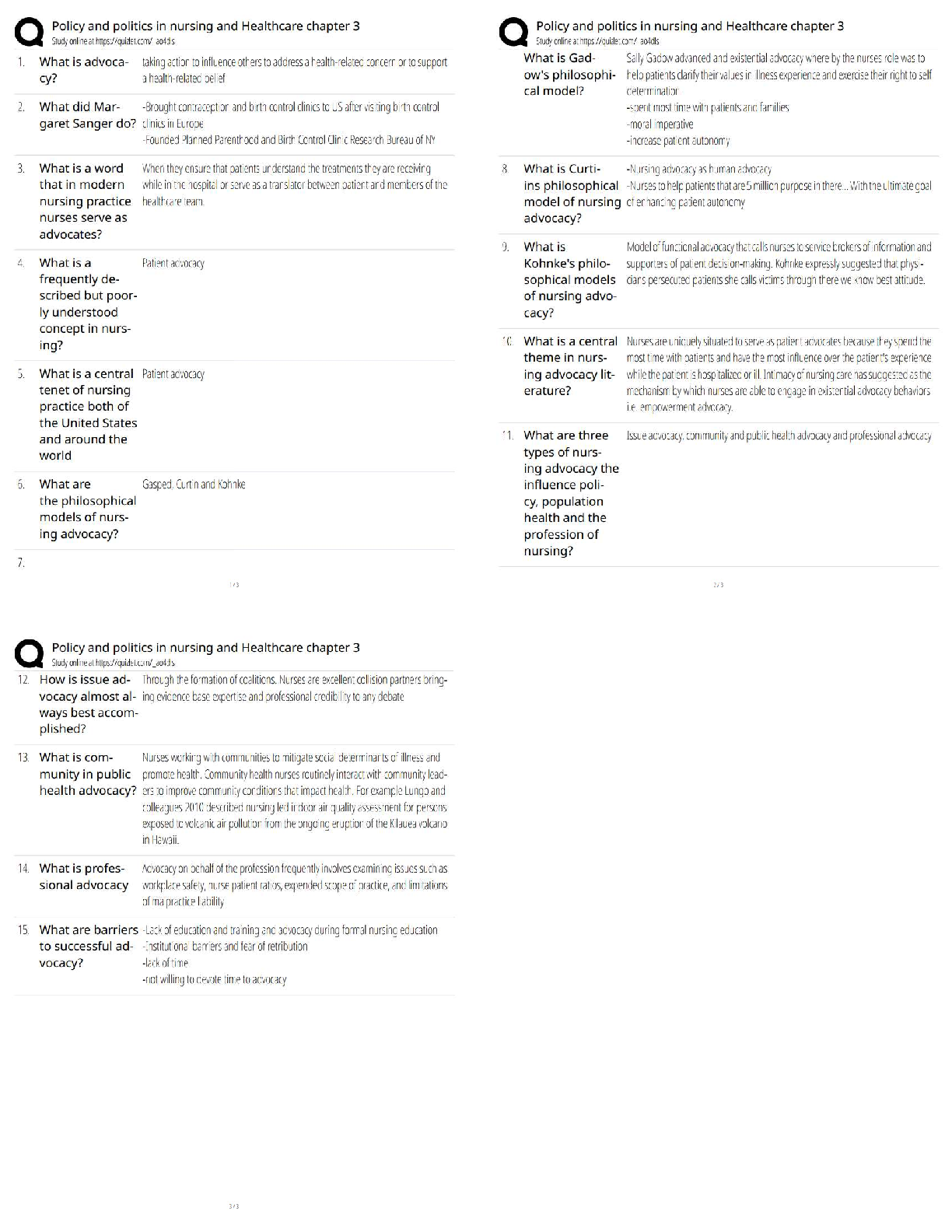
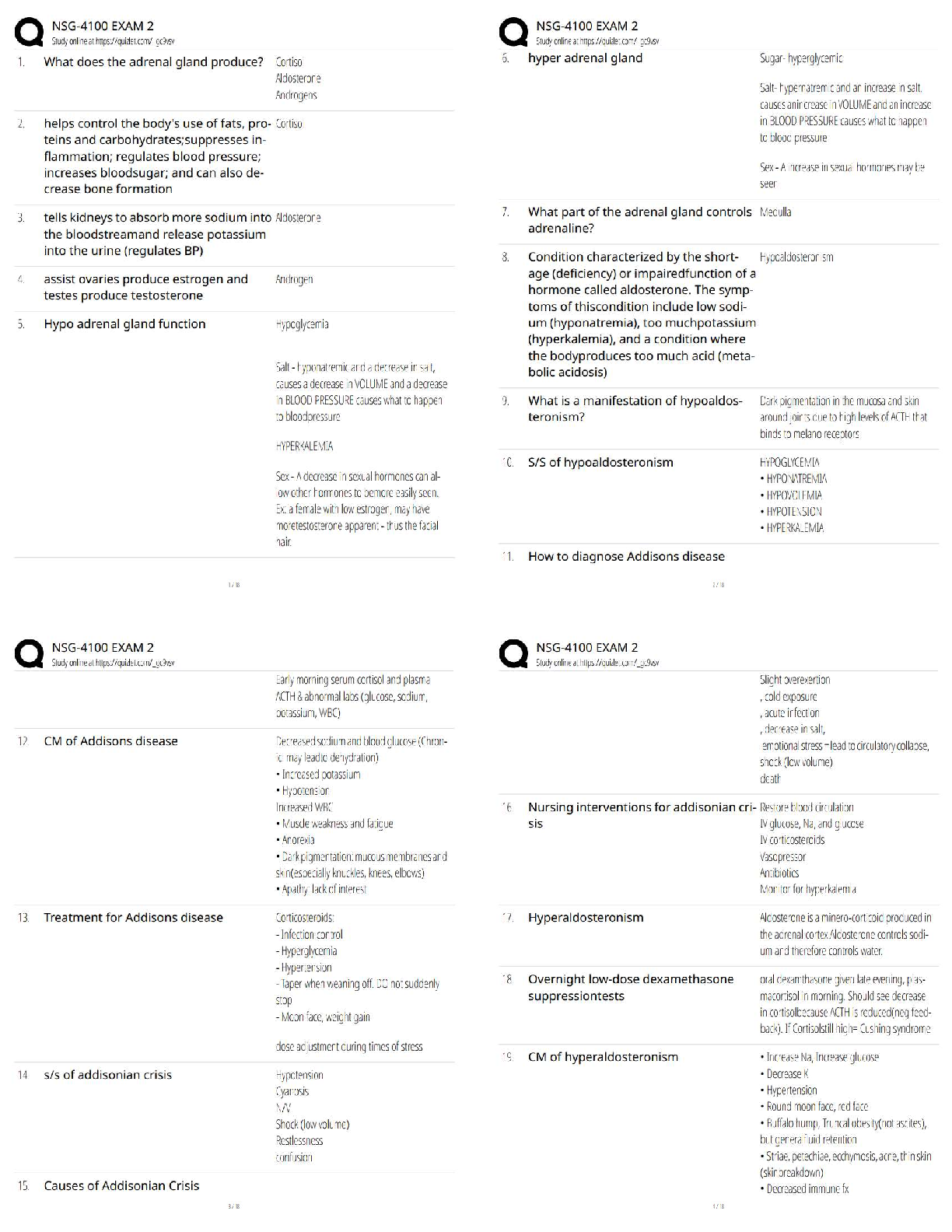
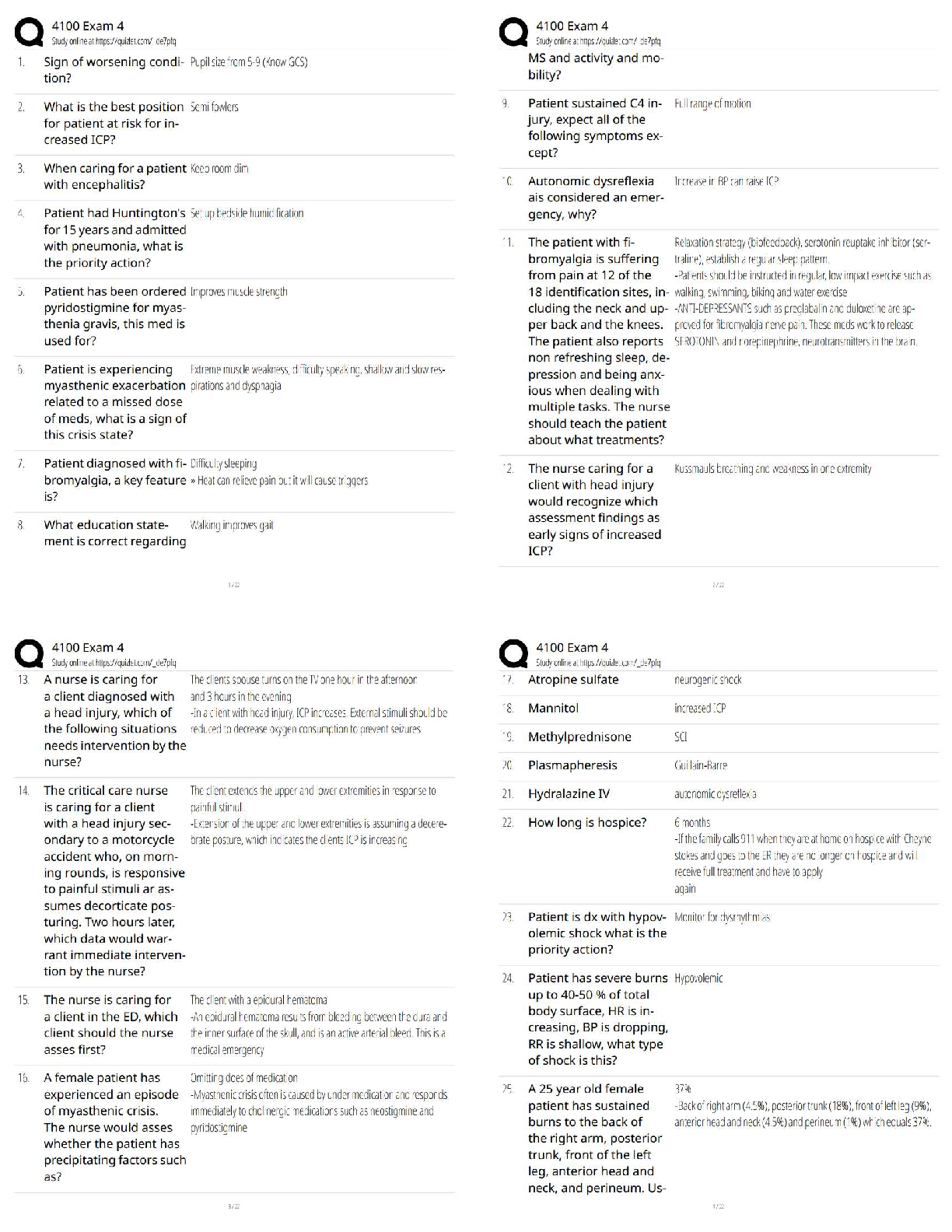
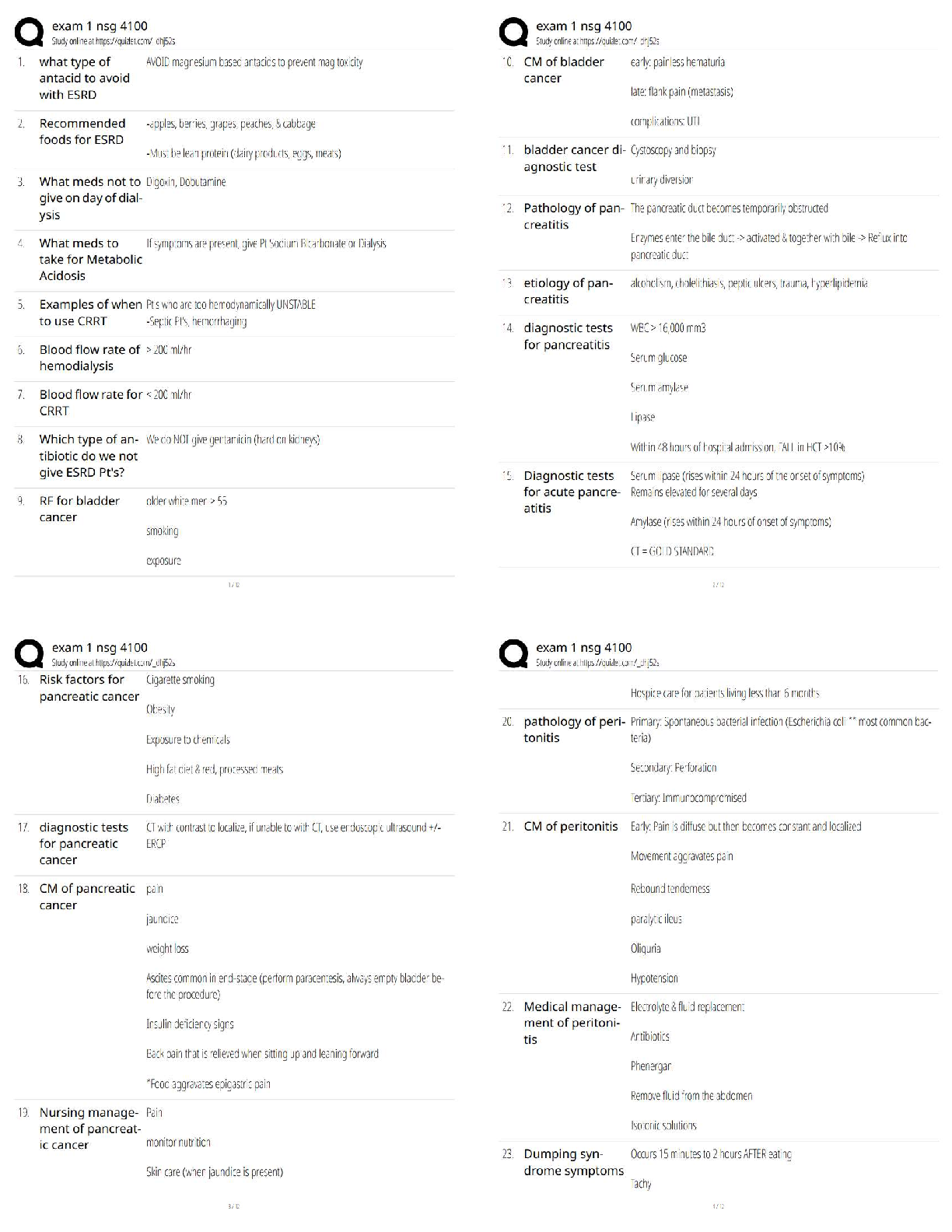
Cell & Tissue Function/Dysfunction
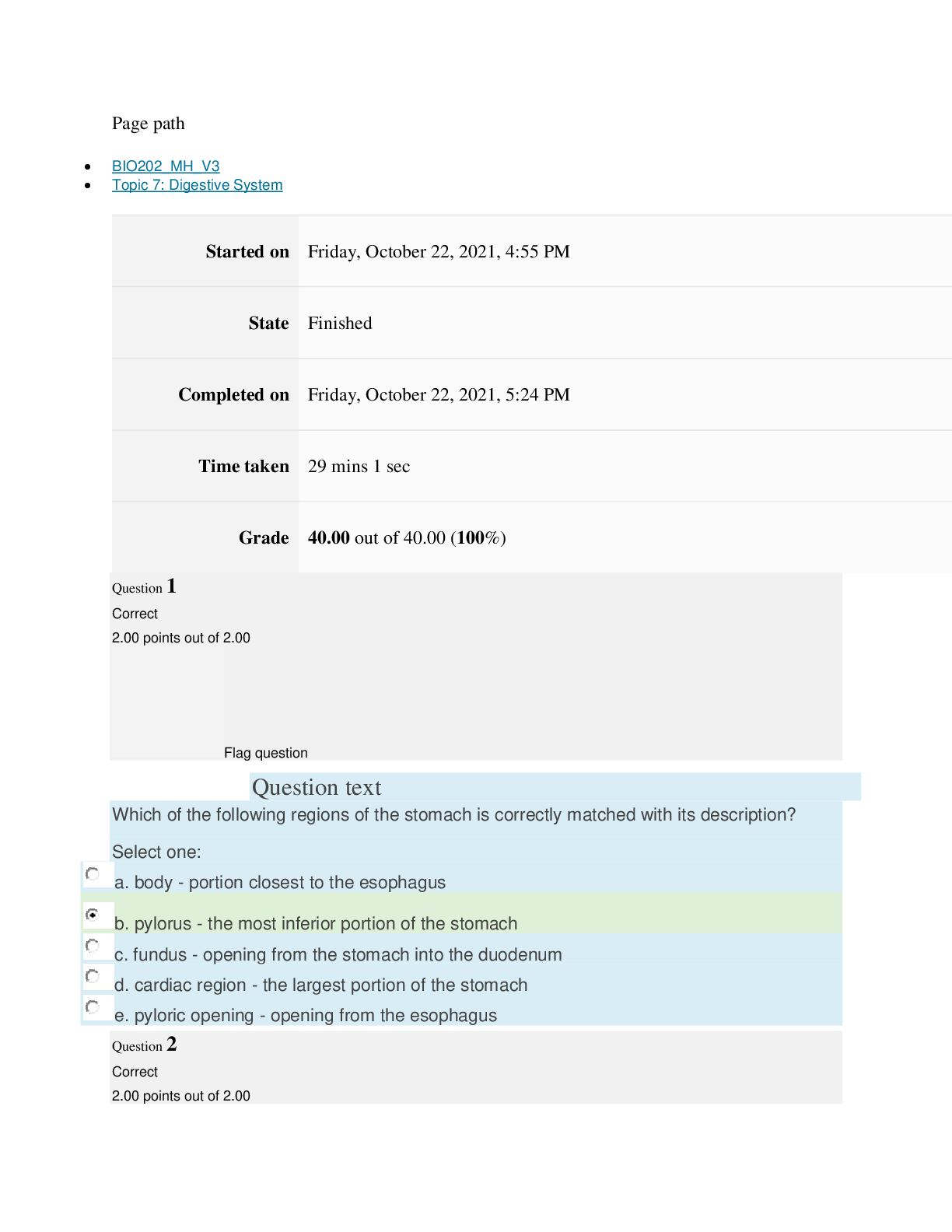
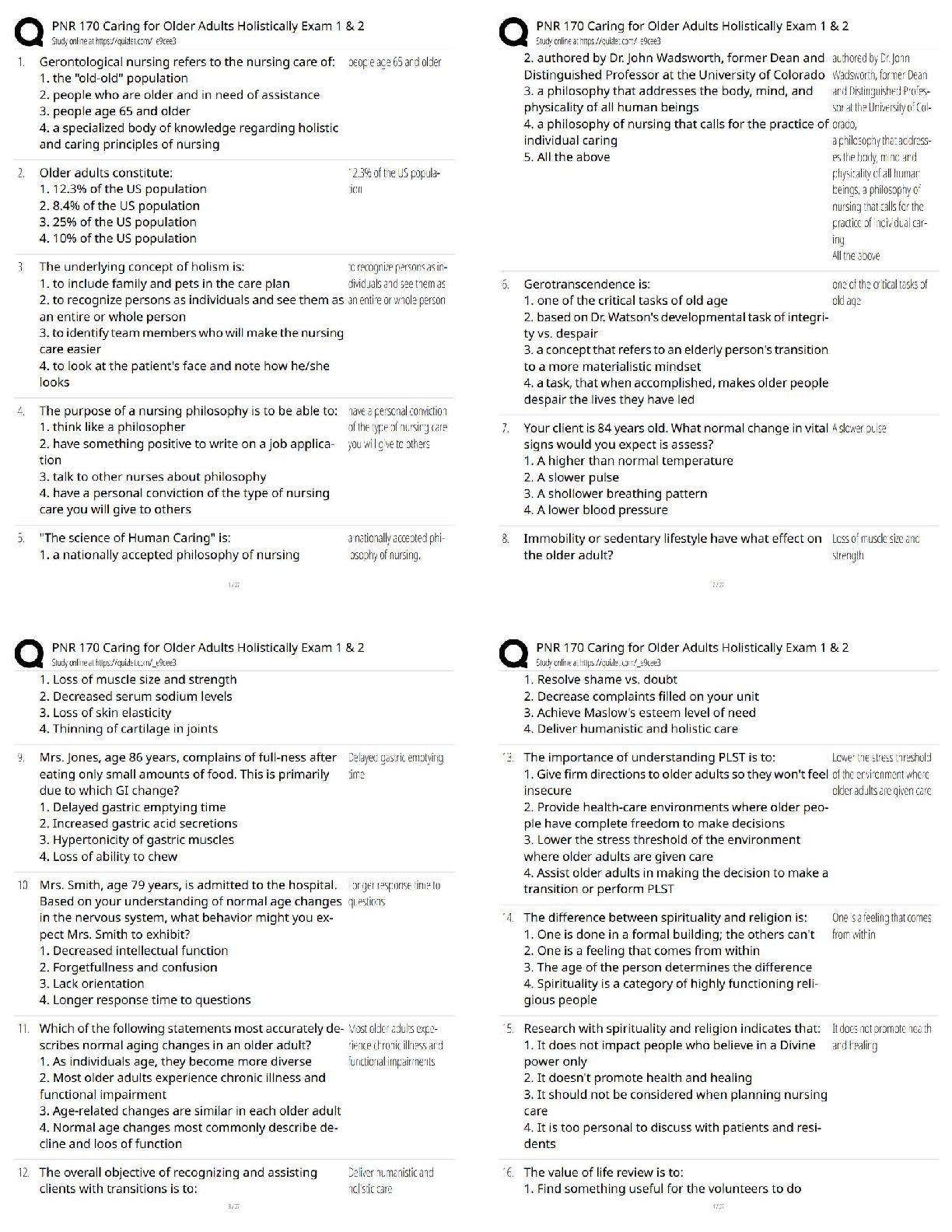
Atrophy: decrease in size of cells.
Hypertrophy: increase in cell size.
Hyperplasia: increase in number of cells.
Metaplasia: mature cell type is replaced by a different mature cell
...
Cell & Tissue Function/Dysfunction
Atrophy: decrease in size of cells.
Hypertrophy: increase in cell size.
Hyperplasia: increase in number of cells.
Metaplasia: mature cell type is replaced by a different mature cell type.
Dysplasia: cells vary in size & shape within a tissue.
Anaplasia: undifferentiated cells with variable nuclear & cell structure.
Neoplasm: tumor.
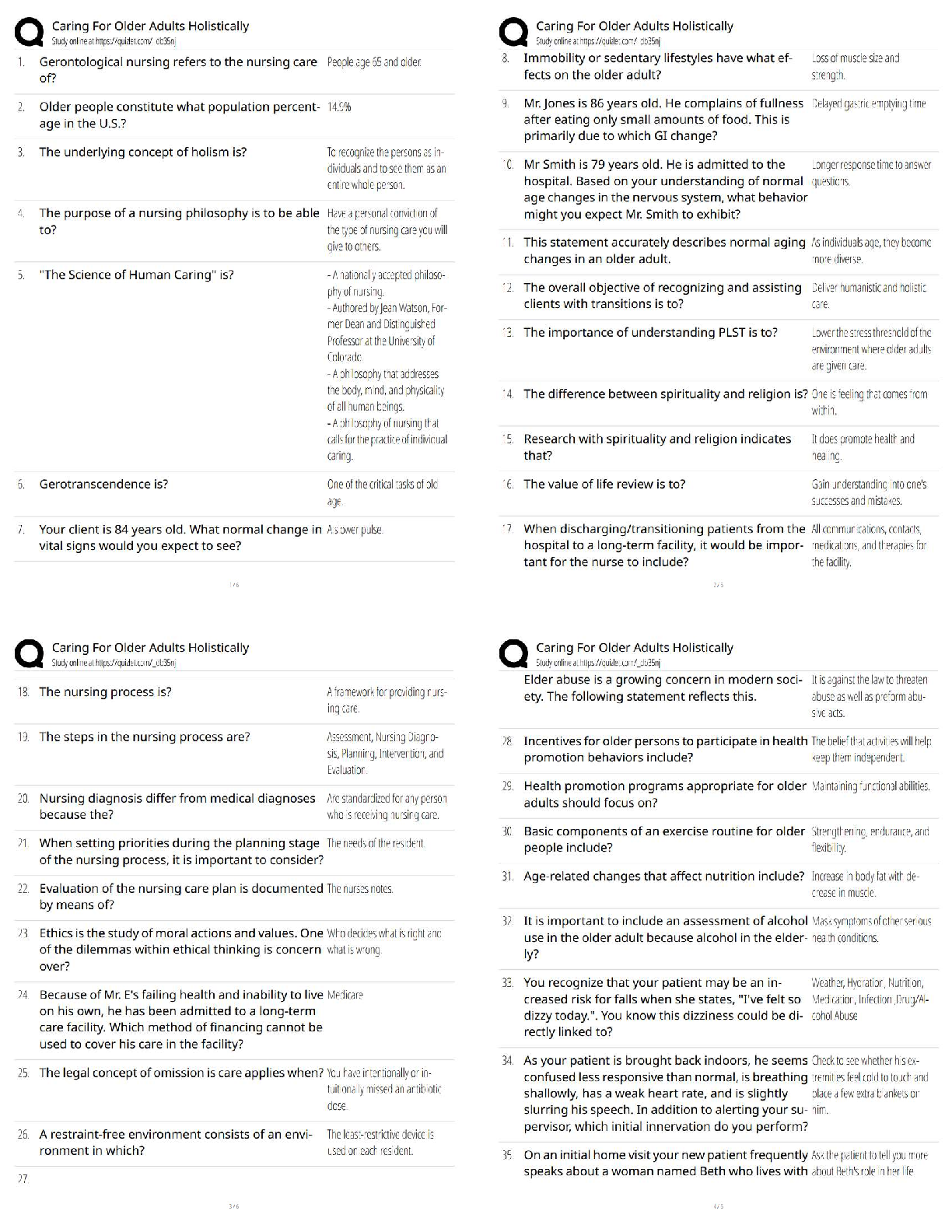
Cell Damage
Ischemia: oxygen deficit due to respiratory or circulatory problems.
Hypoxia: reduced oxygen in tissue.
Oxygen Deficit: decreased energy production, loss of Na pump ↑ intracellular Na.
Temperature: inactivation of some enzymes, damages organelles, protein coagulation,
disruption of cell membrane.
Micro-organisms
Abnormal Metabolites: caused by genetic disorders or altered metabolism.
Nutritional Deficits
Cell Death
Apoptosis:programmed cell death controlled by genetics.
Necrosis:lysis of a cell, cell components leak into blood.
Liquification:dead cells liquefy due to release of enzymes.
Coagulation:cell proteins are altered or denatured causing coagulation.
Caseous:form of coagulation necrosis, thick, yellowish, cheesy.
Fat: fatty tissue is broken down into fatty acids.
Tissue Damage from Chemicals
Exogenous: from environment.
Endogenous: from inside the body,
Tissue Damage from Physical Agents
Hypothermia: vasoconstriction, ↑ blood viscosity, hypovolemic shock ↓ blood
pressure.
Hyperthermia: causes general vasodilatation, decrease in circulating blood
volume.
Radiation: primarily affects actively dividing cells
Biological Agents
Insects/Animals: direct injection of toxin, transmission of infectious agent,
allergic reaction to insect proteins.
Food Poisoning
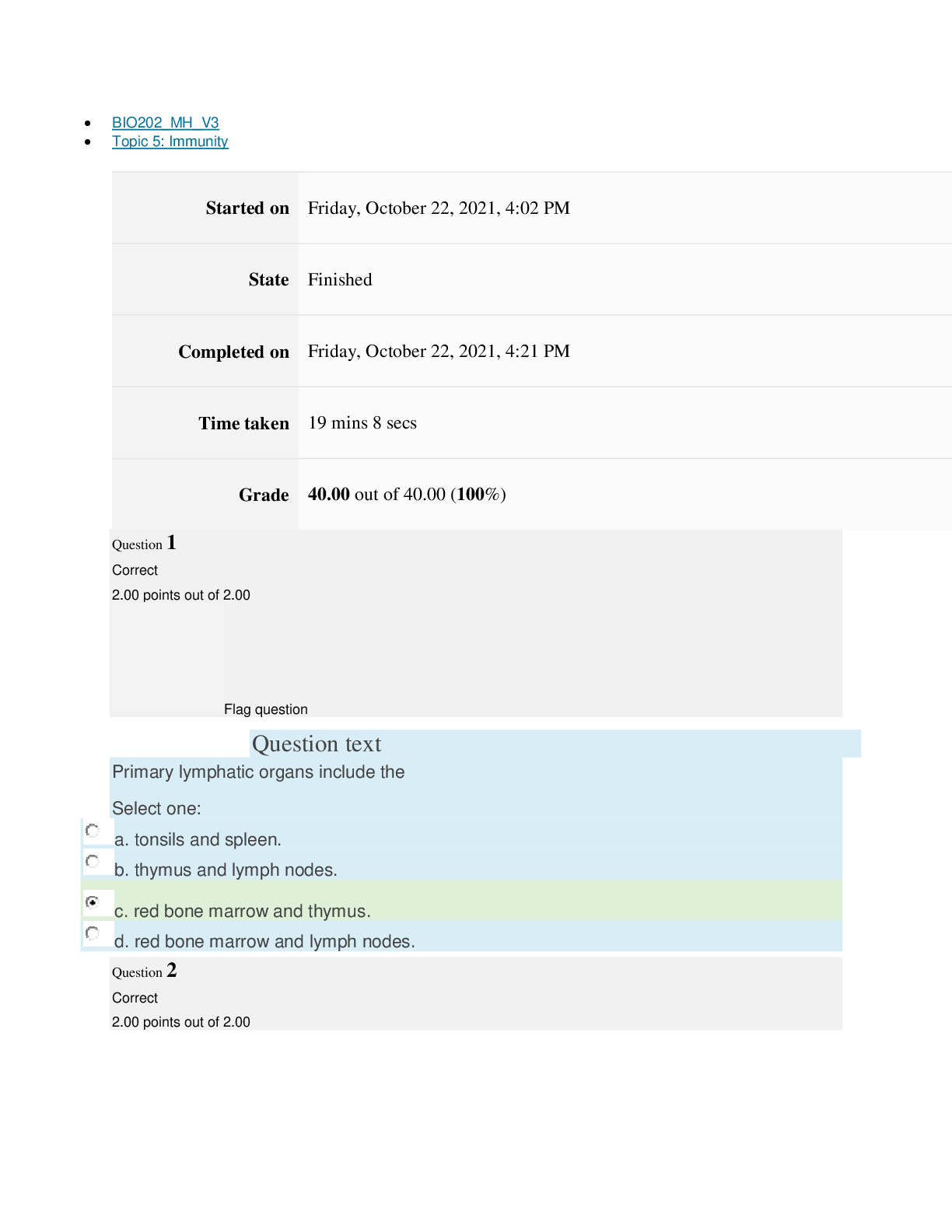
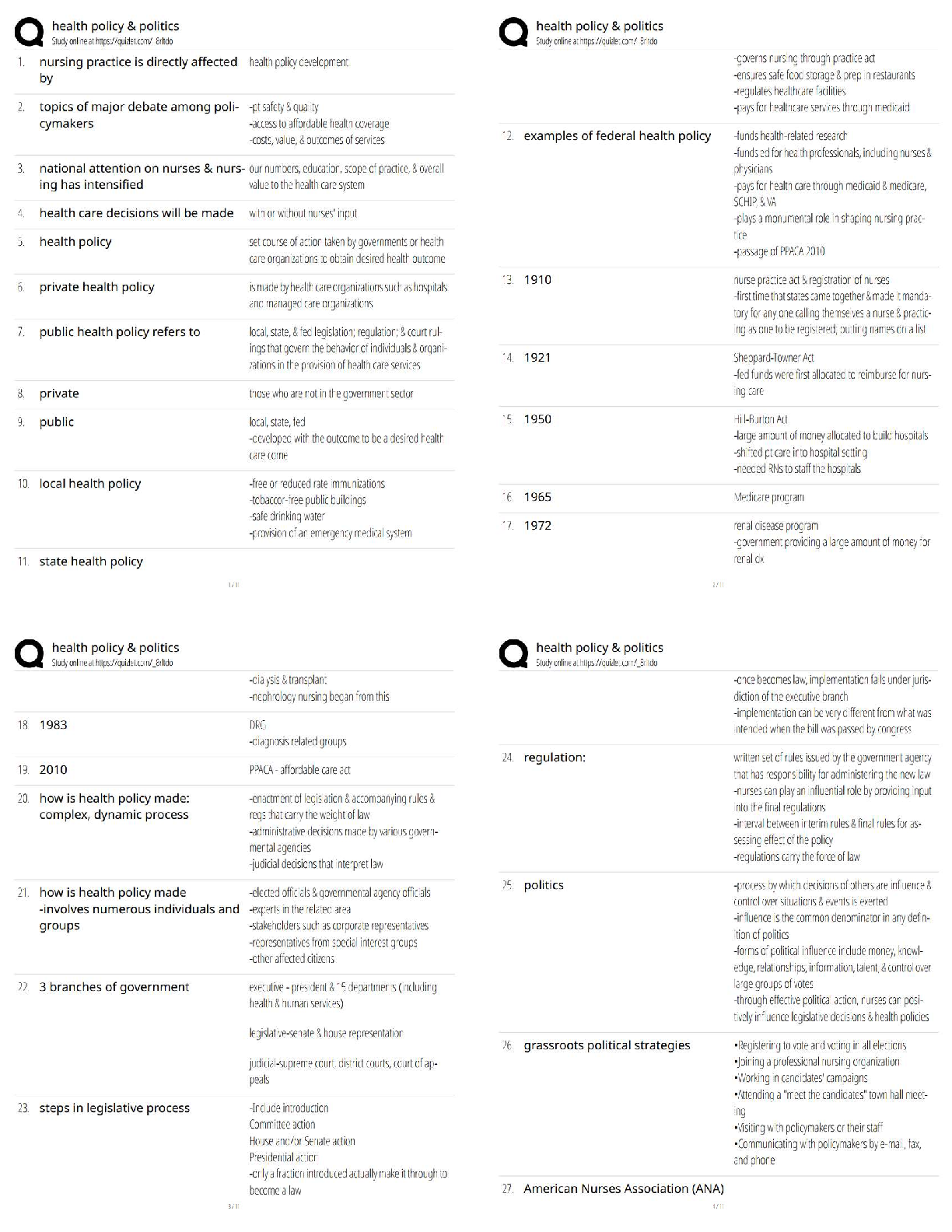
Normal Defenses of the Body
1
st Line Defense
Physical Barriers: unbroken skin, mucous membranes, nasal hair, clots.
Fluids: may contain enzymes or chemicals:saliva, tears, gastric, sweat.
2
nd Line Defense-non-specific
Phagocytosis:neutrophils & macrophages engulf cells, debris, foreign mat.
Inflammation: automatic response to cell injury.
3
rd Line Defense-specific defense produced by
Antibodies
Cell Mediated Immunity
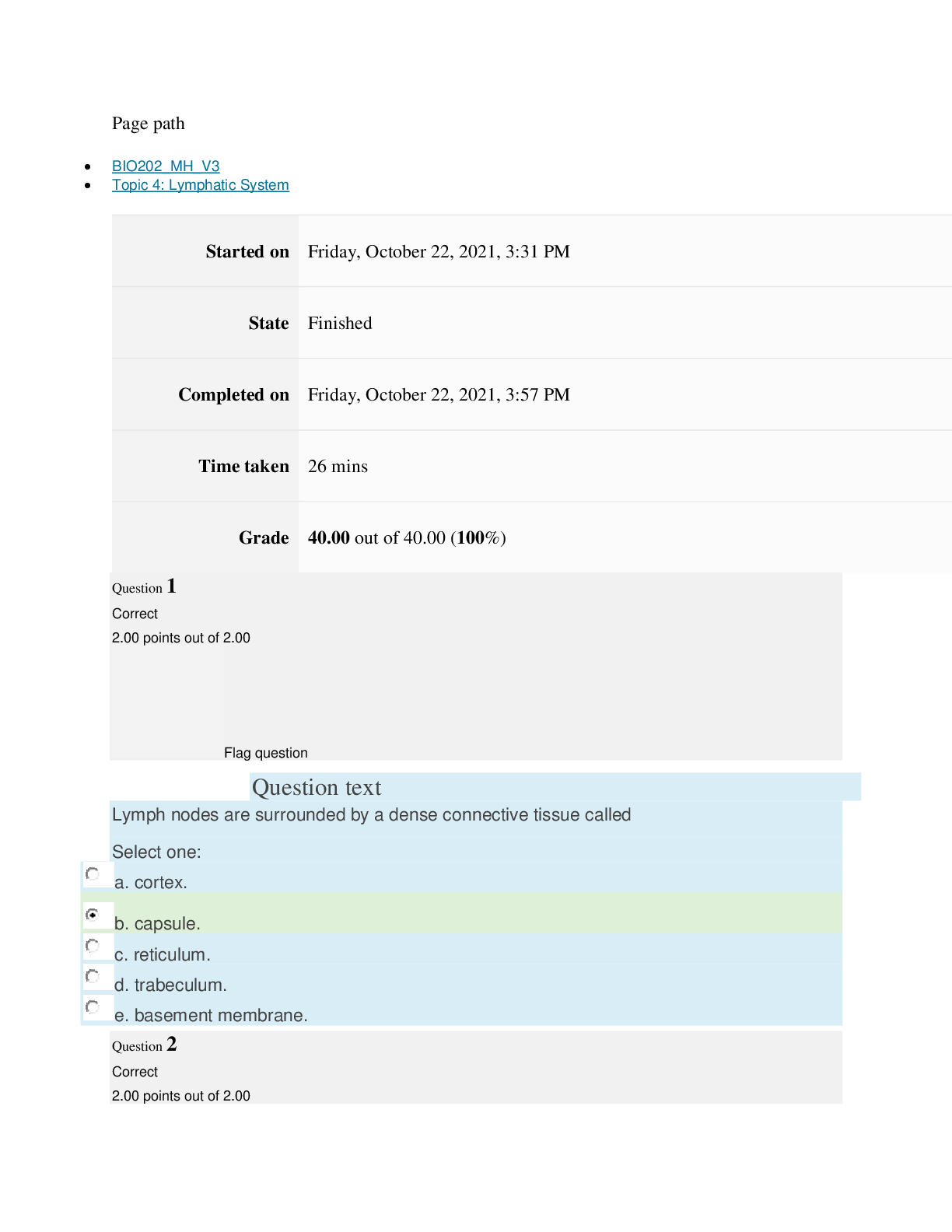
Cellular Defenses
Mast Cells: located in tissue & release histamine & bradykinin.
Macrophages: monocytes that enter tissue & act as phagocytes.
Interferons: small proteins made by lymphocytes to prevent virus replication.
White Blood Cells
Granulocytes
Neutrophils: work by phagocytosis.
Basophils: release histamine leading to inflammation.
Eosinophils:combat the effects of histamine.
Agranulocytes
Monocytes:can enter tissue to become macrophages which
function as phagocyte.
Lymphocytes: B & T
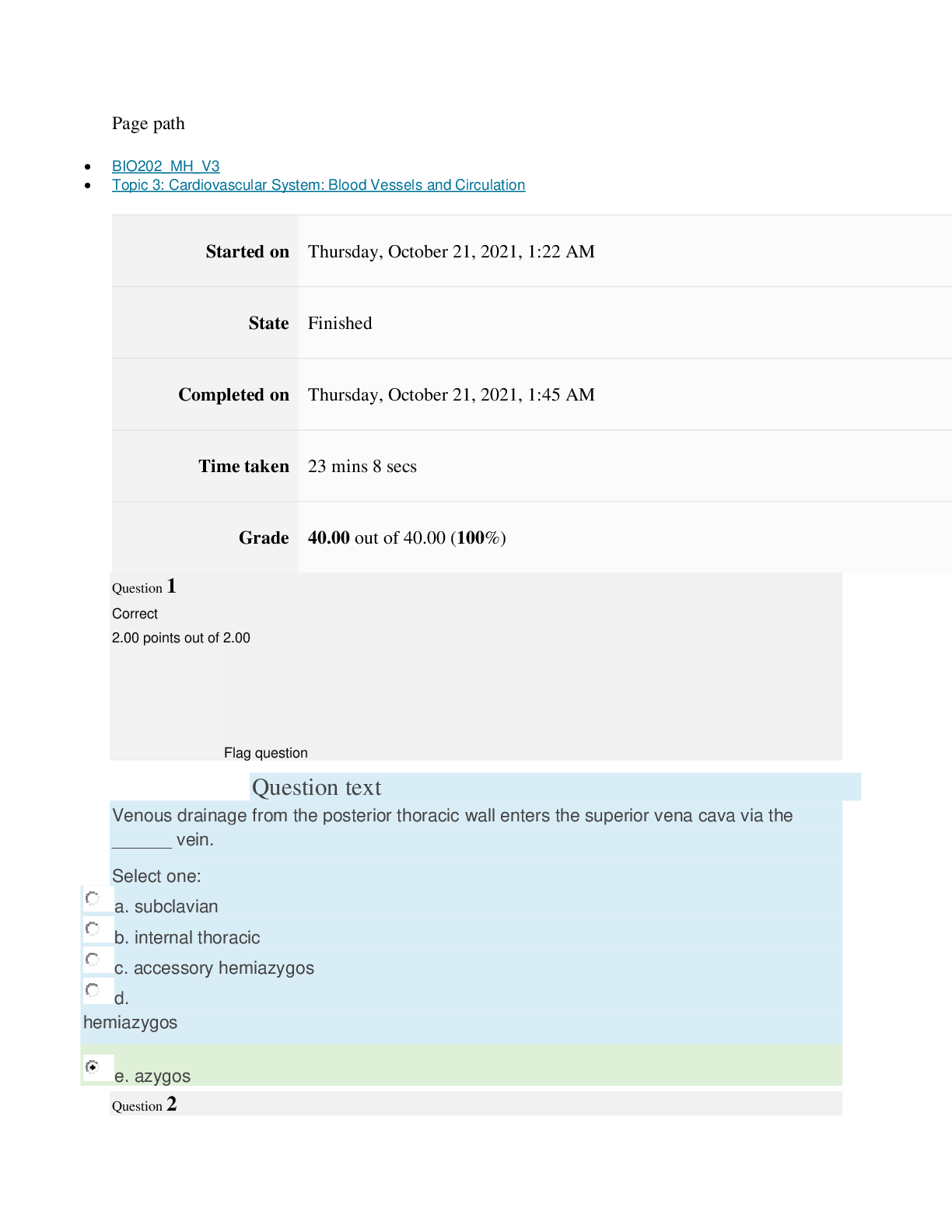
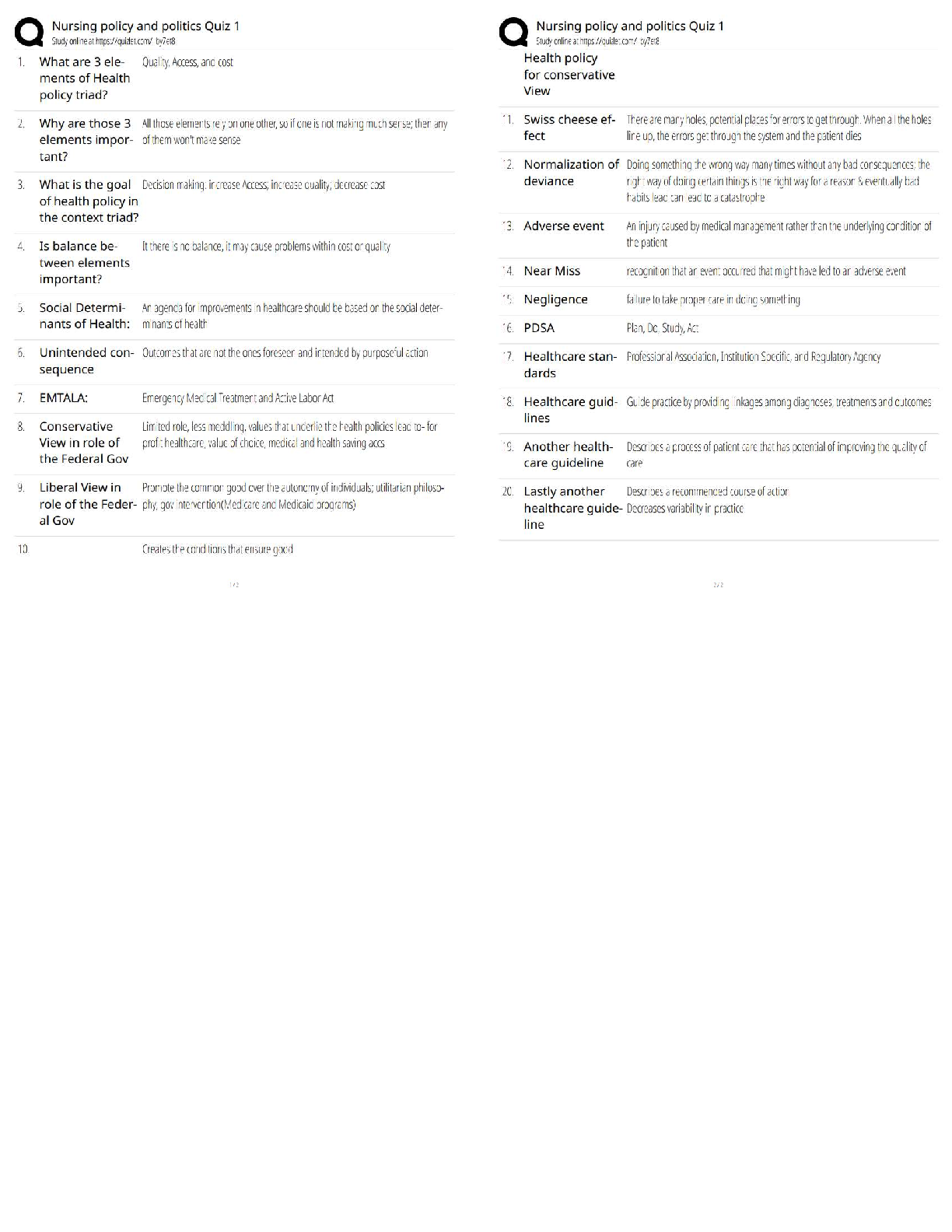
Acute Inflammation
Vascular Response: vasodilatation & increased capillary permeability.
Cellular Response: migration of inflammatory cells through chemotaxis to injury site to
destroy ineffective organism, remove damaged cells, released inflammation mediators.
Exudate
Serous: watery, mostly fluids, some proteins and WBC’s.
Fibrinous: thick, sticky, high fibrin content.
Purulent: thick, yellow-green, contains leukocytes, cell debris & microorganisms.
Abscess: Pocket of purulent exudates or pus in a solid tissue.
Local Effects of Inflammation-Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
Redness & Warmth: due to increased blood flow to area.
Swelling: shift of protein & fluid into interstitial space.
Pain: pressure on free nerve endings, chemical mediators irritate nerves.
Loss of Function: edema may restrict movement.
Systemic Effects of Inflammation
Mild Fever: due to resetting of hypothalamic thermoregulatory set point, release of
endogenous pyrogens.
Malaise
Fatigue
Headache
Anorexia
Treatment of Inflammation: drugs may decrease capillary permeability, reduce number of
leukocytes & mast cells.
Types of Healing
Resolution: minimal tissue damage, cells can repair themselves.
Regeneration: damaged tissue is replaced by identical tissue.
Replacement: functional tissue replaced by scar or fibrous tissue.
[Show More]