.png)
Hesi Exit
$ 9

H431/03: The global business environment Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for November 2020
$ 10

[Solved] NSG 3029 Week 4 Knowledge Check
$ 14

ATI Nutrition Practice Exam B practice docs exam questions with answers solution
$ 12.5

MATH 534 Week 6 Course Project Part B: Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals LATEST 2021 PROJECT WITH ASSURED GRADE A+
$ 17.5

Georgia Institute Of Technology Deep Learning CS7643_Quiz3_1
$ 8
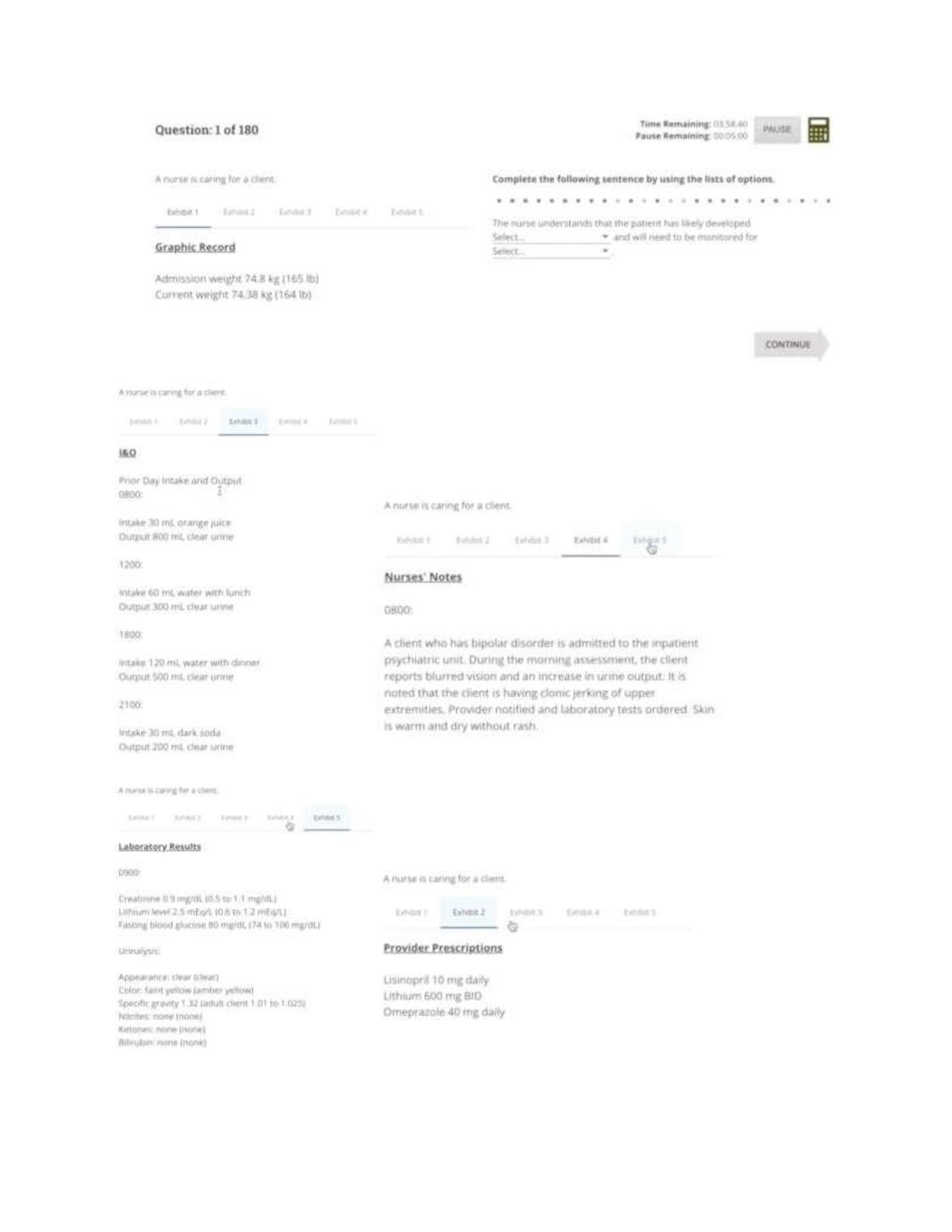
ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM 2023
$ 10

APEA MIDTERM EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT ANSWERS LATEST UPDATE GRADED A+
$ 15

Mark Scheme (Results) October 2020 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Pure Mathematics P1 (WMA11) Paper 01
$ 12

500 MPRE Practice Questions & Answers (100% Guaranteed Pass)
$ 12

ATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020/2021 Form A,B,C
$ 20

Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Business Advanced PAPER 2: Business activities, decisions and strategy QUESTION PAPER 9BS0/02 2021
$ 6

RN COMPREHENSIVE NURSING CARE – SPECIAL SENSES- SUMMARY 2023 [LAB PRACTICE]
$ 10

HSM 543 Week 1 Quiz (100% CORRECT) Questions and Answers.
$ 7.5

EXIT EXAM: NURSING NUR205: Answers 100% Correct
$ 8

AQA A-level PHYSICS Paper 1 QP JUNE 2022
$ 7.5

Unit 4 - Milestone 4.docx. Questions and answers. Rated A Masterpiece. 100% pass rate.
$ 7

NURS 6541 Midterm Exam | 100 Questions and Answers (Walden University)
$ 16

Pearson Edexcel GCE In Mathematics (9MA0) Paper 32 Mechanics Examiners’ Report Principal Examiner Feedback November 2021
$ 5

Field tech 1 Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 10

[NGN] 2023_2024 HESI EXIT RN EXAM VERSION 1_ VERSION 7 LATEST QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS NEW UPDATE %SCORES
$ 14.5

OCR GCE Biology A H020/02 :Depth in biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Mark Scheme
$ 8

Rn comprehensive predictor FORM B 2023 2024 UPDATE

![Loading document previews for Introduction to Audiology, 13th Edition By Frederick Martin, John Clark | eBook [PDF]](https://scholarfriends.com/img/ajax-loader.gif)


 Gary Donell, Clarence Byrd, Ida Chen.png)





















