PECT PreK-4 All Modules Questions and
Answers Already Passed
Explicit instruction ✔✔Direct, skill-based, holistic, in context, developmentally appropriate,
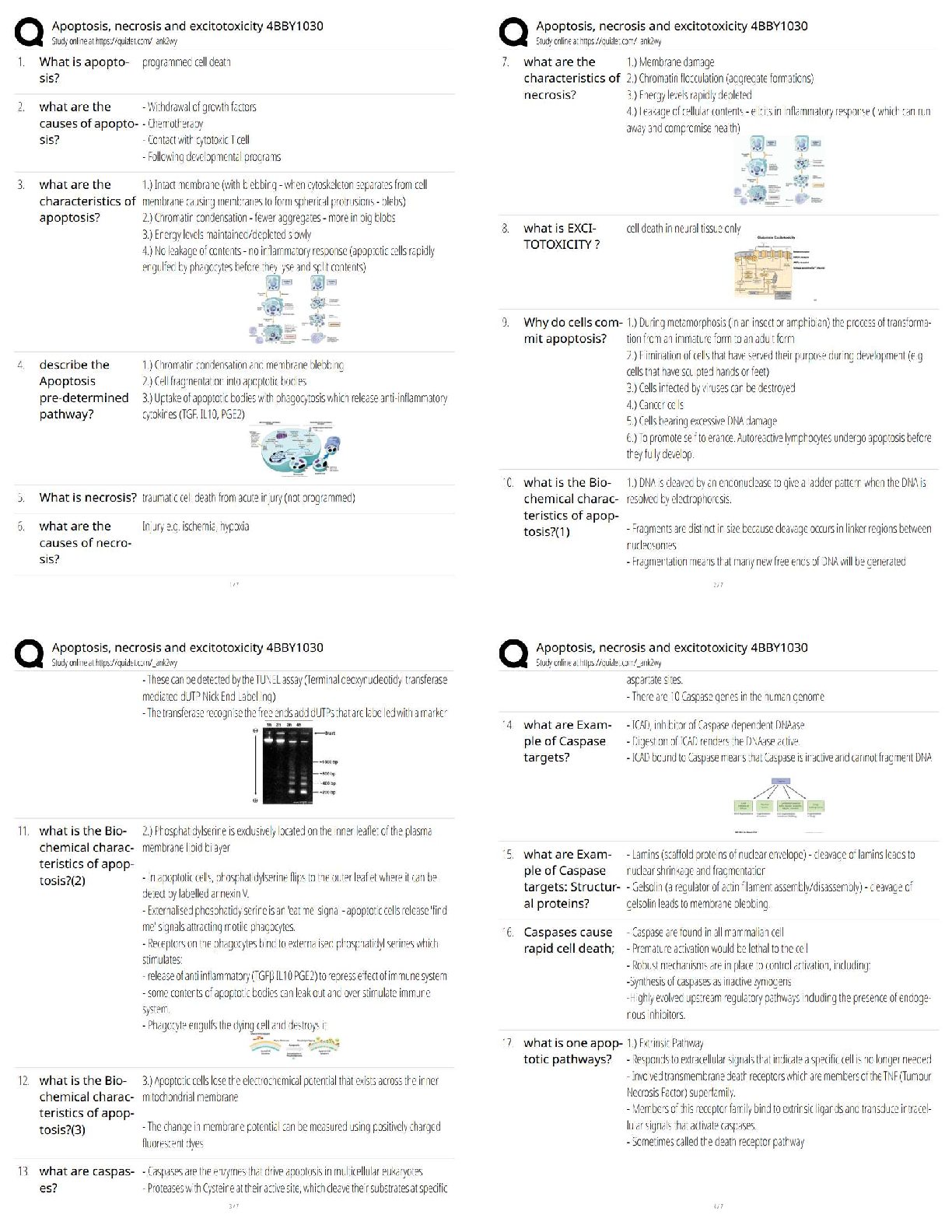
student centered and directed
Formative assessment ✔✔provide
...
PECT PreK-4 All Modules Questions and
Answers Already Passed
Explicit instruction ✔✔Direct, skill-based, holistic, in context, developmentally appropriate,
student centered and directed
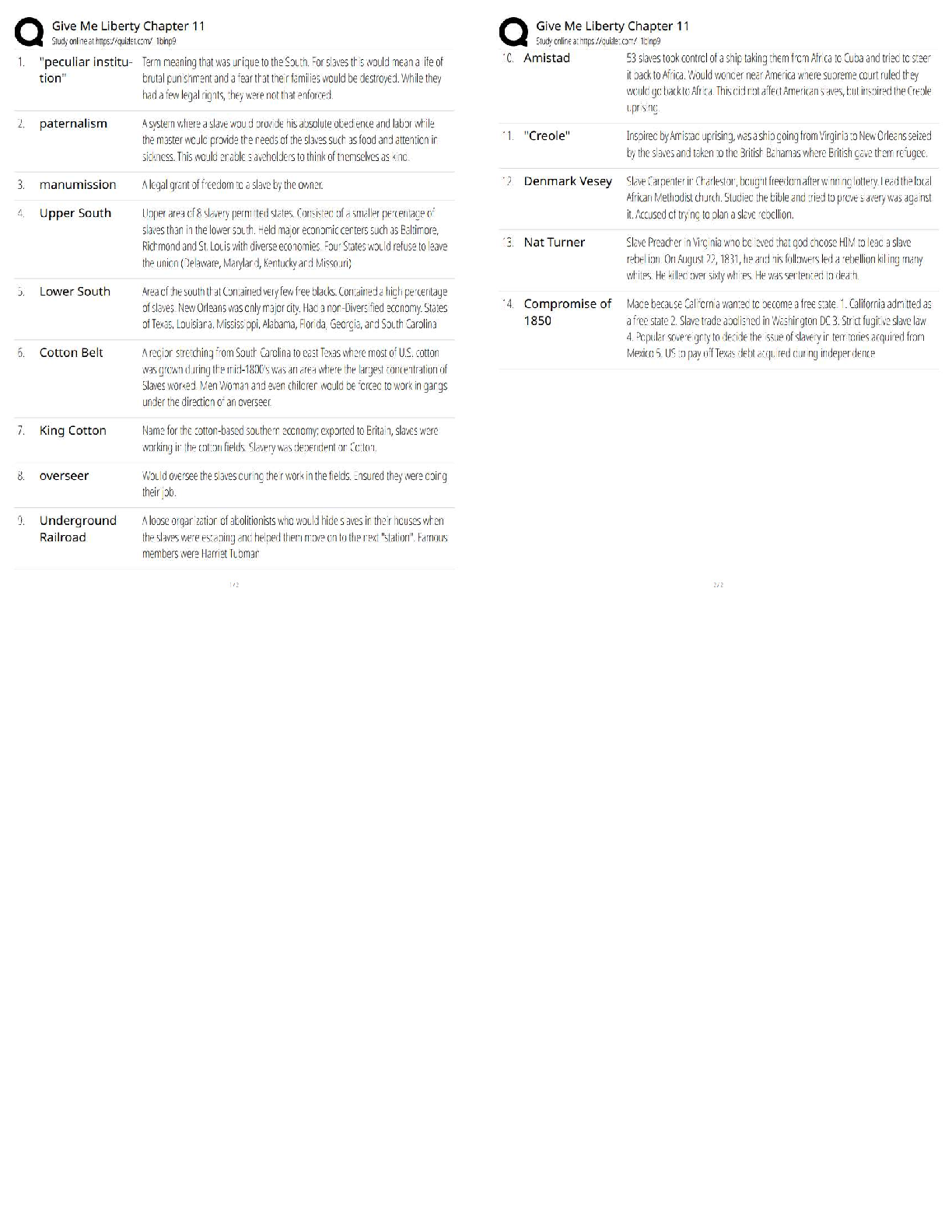
Formative assessment ✔✔provides ongoing feedback, identifies strengths, weaknesses, and
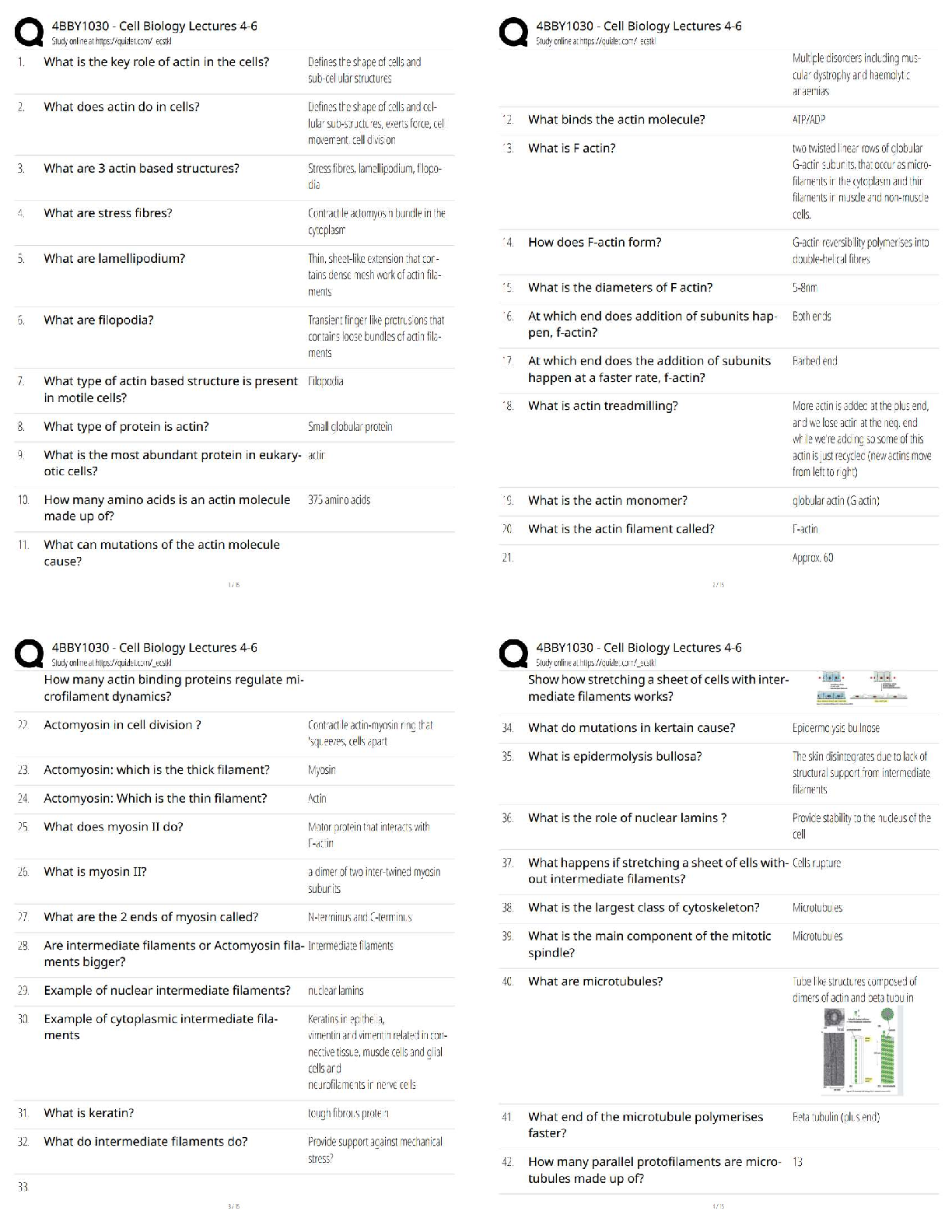
target areas, low stakes, addresses problems immediately
Summative assessment ✔✔evaluates learning at the end of a unit and compares it against some
standard or benchmark, high stakes, (midterm, final, paper)
Scaffolding ✔✔Promotes deeper level of learning, support tailored to needs of student
(modeling, coaching) that is gradually removed
Inquiry-based learning ✔✔poses questions, problems or scenarios - rather than simply presenting
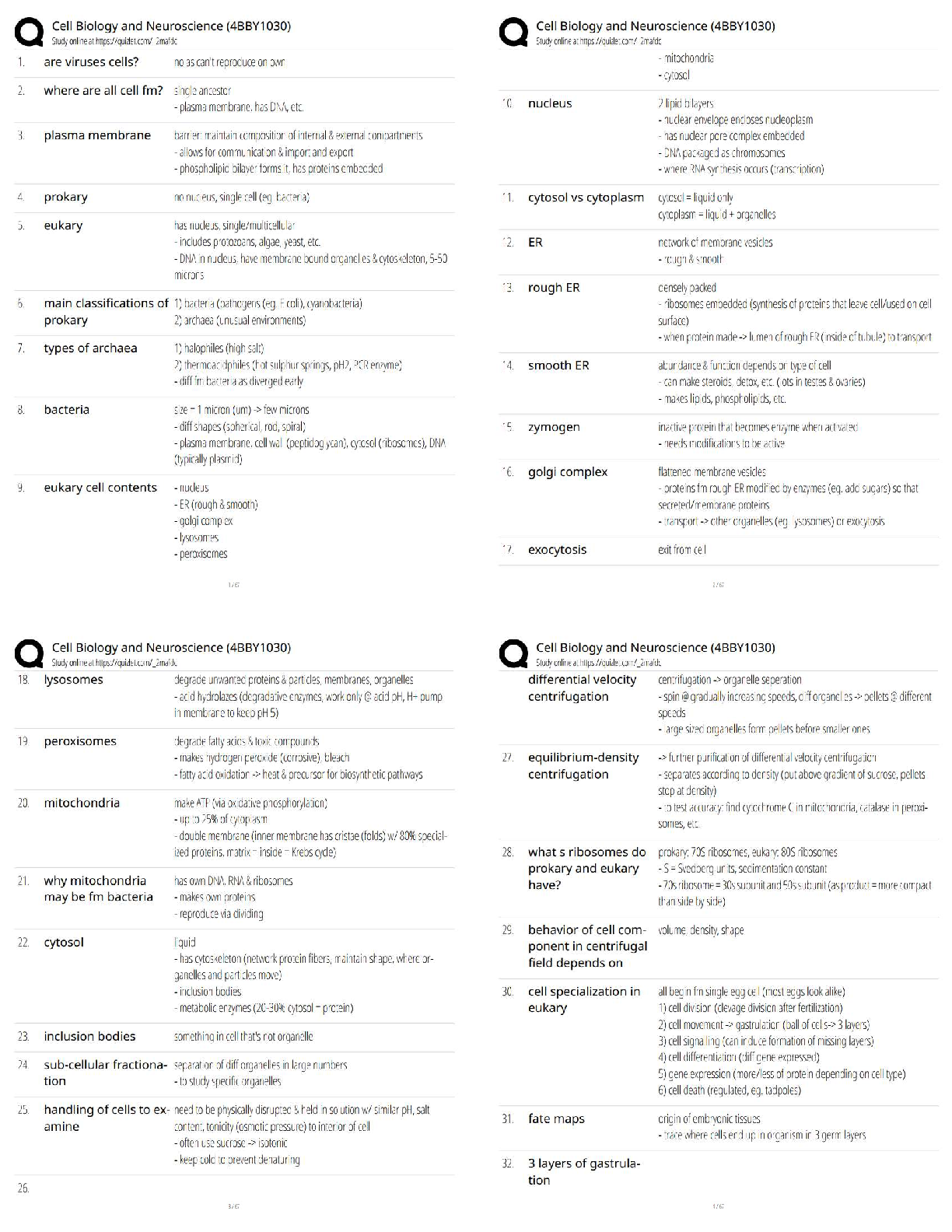
established facts; assisted by a facilitator
Assessment anchors ✔✔tools to better align curriculum, instruction, and assessment practices
LEA (Language Experience Approach) ✔✔combines all 4 language skills, aids fluency, centered
around learner generated text.
Step 1) A shared experience, 2) creating the text, 3) read and revise, 4) read and reread, 5)
extension
Receptive language ✔✔the ability to understand or comprehend language heard or read
Expressive language ✔✔being able to put thoughts into words and sentences that make sense
and are grammatically accurate
Family systems theory ✔✔(Dr. Murray Bowen) individuals cannot be understood in isolation
from one another, but rather as a part of their family, which is an emotional unit
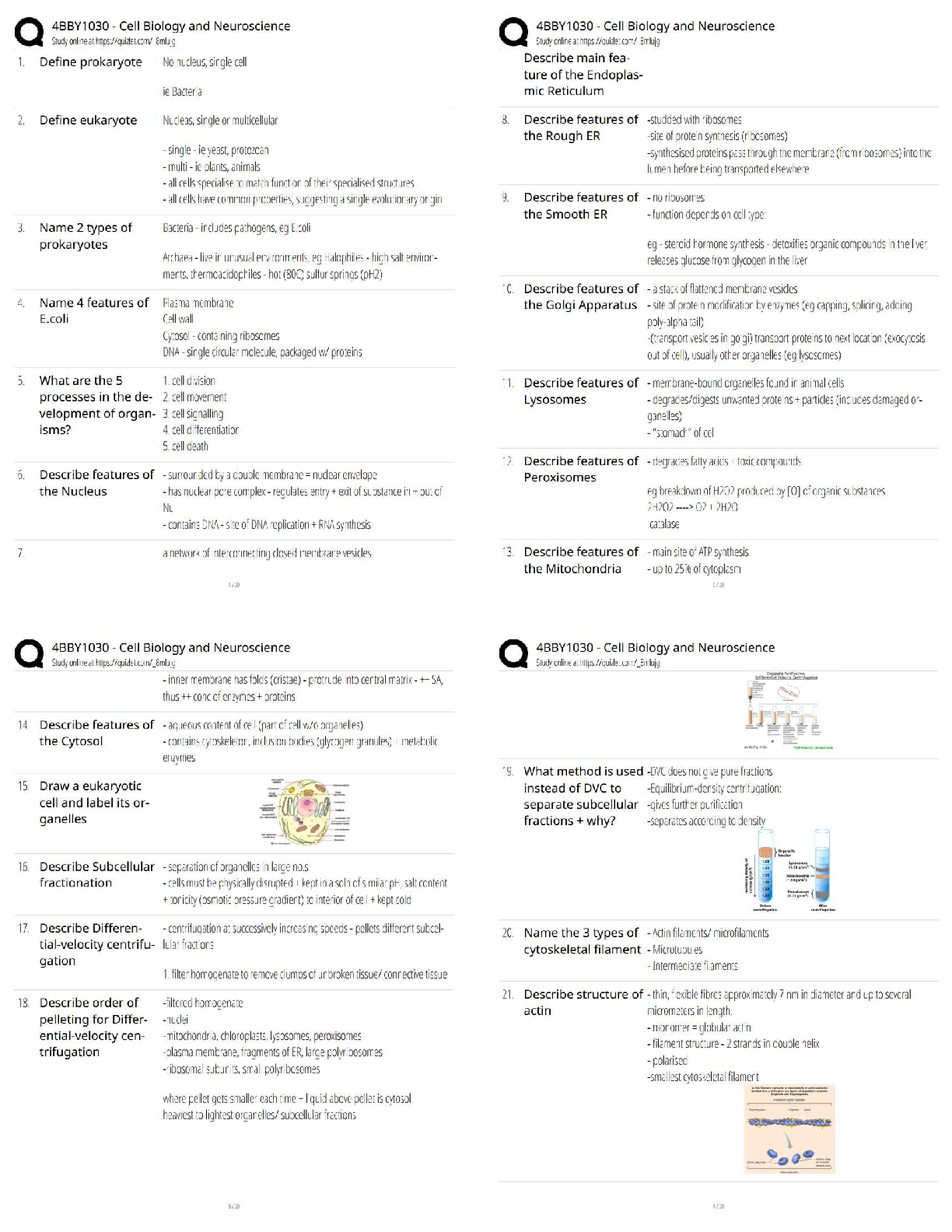
Constructivist Approach ✔✔the learner is an active participant in building understanding and
knowledge. Use hands-on exploration with concrete materials. Realistic and relevant learning
situations. Uses scaffolding
Alphabetic principle ✔✔the understanding that the letters used in writing represent the
component sounds in spoken words
Informal assessment ✔✔Sometimes referred to as criterion referenced measures. Performance is
not being evaluated against established standards or rubrics, not data driven. Content and
performance driven. (anecdotal notes, teacher observations, running records, rubric scores, etc.)
Used to inform instruction.
Formal assessment ✔✔Assess overall achievement, compare student performance with others at
their grade or rangeHave data which support the conclusions made from the test (standardized
measures). Use statistics. Data is mathematically computed and summarized. Scores are
percentiles, stanines, or standard scores.
Diphthong ✔✔a sound made by combining two vowels, specifically when it starts as one vowel
sound and goes to another (oy in oil). Refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the
same syllable.
Phonological awareness ✔✔Student should be able to recognize and use rhyme, break words
into syllables, blend phonemes into syllables and words, identify the beginning and ending
sounds in a syllable, and see smaller words within larger words ("cat" in "catalog").
Phonemic awareness ✔✔Student will demonstrate the ability to hear rhyme and alliteration, find
the different sound in a set of words, and blend and segment phonemes
Complex morpheme ✔✔a morpheme that contains a lexical morpheme (words that have
meaning by themselves) and at least one grammatical morpheme (function to specify the
relationship between two lexical morphemes). (ex. strong irregular verbs like swim, swam,
swum)
Inflected endings ✔✔a subcategory of suffixes that indicate tense and number. To apply these
rules, students will need an understanding of consonant and vowel patterns in the base word
Criterion-referenced tests ✔✔Determines whether each student has achieved specific skills or
concepts, how much they know before instruction begins and after it ends, measures specific
curricular skills expressed as instructional objectives, each skill is tested by at least 4 items, each
individual is compared with a preset standard for acceptable achievement (performance of others
is irrelevant), score is expressed as a percentage.
Norm-referenced tests ✔✔Rank each student respective to achievement of others in broad areas
of knowledge, discriminates between high and low achievers, each individual is compared with
other examinees and assigned a score expressed as a percentile, grade equivalent score, or a
stanine.
Prosody ✔✔the defining feature of expressive reading, comprises all the variables of timing,
phrasing, emphasis, and intonation that speakers use to convey meaning and make their speech
lively.
Responsive listening ✔✔saying what you feel you heard the other person say. Listening with the
intent of understanding, instead of replying. Enhances the ability to: obtain information, identify
problems, resolve conflicts, improve the accuracy of communication, solve problems, and
motivate the speaker
Semantic map(ping)/web(bing) ✔✔a method of teaching reading using graphical representations
of concepts and the relationships between them. Maps or webs of words the purpose of which is
to visually display the meaning-based connections between a word or phrase and a set of related
words or concepts
Automaticity ✔✔fast, effortless word recognition that comes from reading practice. Refers to
accurate, speedy word recognition, not to reading with expression. Therefore it is necessary, but
not sufficient, for fluency.
Story map ✔✔a strategy that uses a graphic organizer to help students learn the elements of a
book or story. By identifying story characters, plot, setting, problem and solution, students read
carefully to learn details
Reading rate ✔✔part of the broader umbrella of fluency and is measured in words read per
minute, while fluency is a bit more subjective
Syntactic ✔✔relating to the rules of language
Intonation ✔✔describes how the voice rises and falls in speech. The 3 main patterns of
intonation are: falling intonation, rising intonation, and fall-rise intonation
Structural analysis ✔✔the process of using familiar word parts (base words, prefixes, and
suffixes) to determine the meaning of unfamiliar words
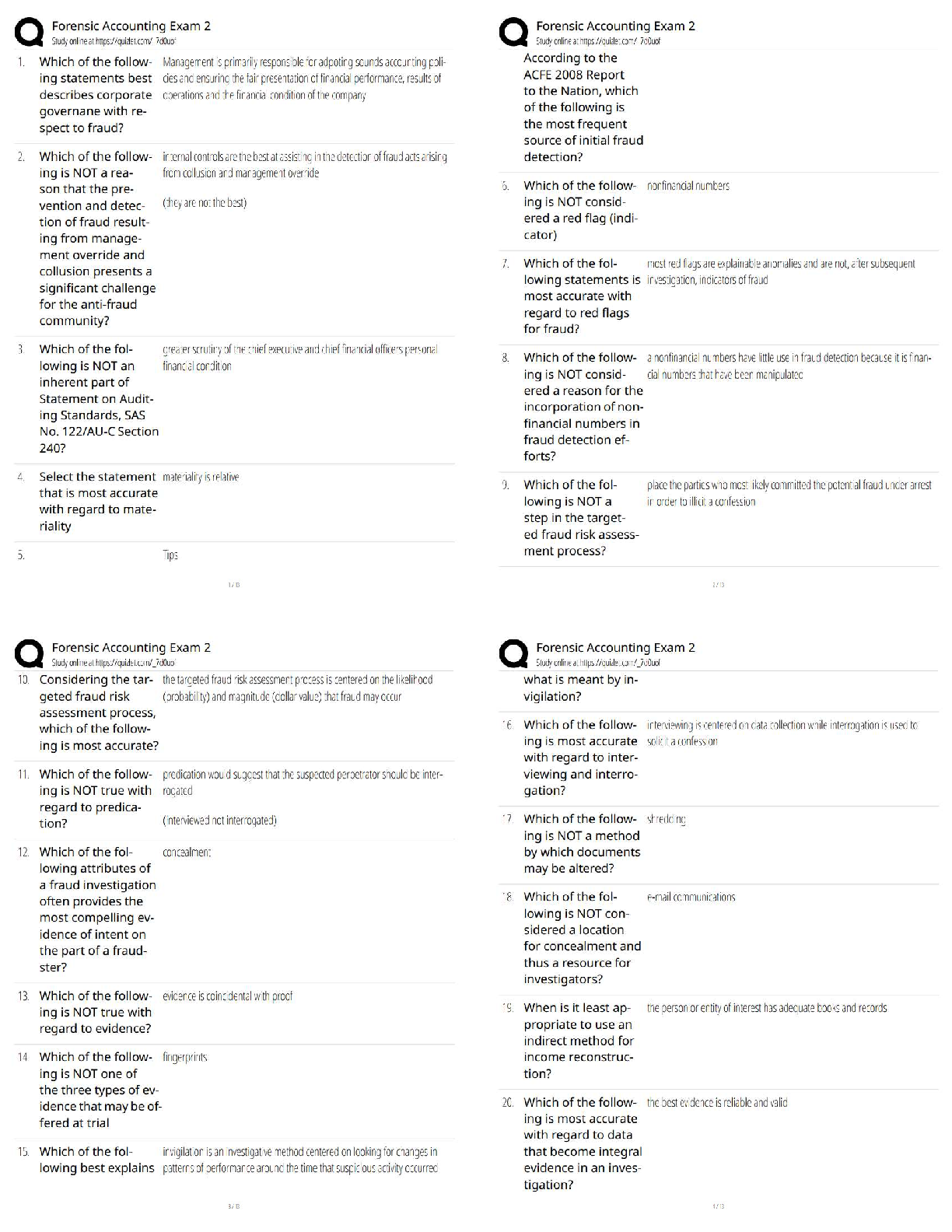
Cultural diffusion ✔✔the spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to
another. The mixing of world cultures through different ethnicities, religions, and nationalities
has increased with advanced communication, transportation, and technology
Institutional development ✔✔the creation or reinforcement of a network of organizations to
effectively generate, allocate and use human, material, and financial resources to attain specific
objectives on a sustainable basis
Bibliography ✔✔complete or selective list of works compiled upon some common principle, as
authorship, subject, place of publication, or printer; a list of source materials that are used or
consulted in the preparation of a work, or that are referred to in the text
Periodical index ✔✔provides access to periodical articles by subject or author; can help you find
articles about a specific topic. An index will point you to the correct periodical, the specific date,
volume and issue, and page numbers for the article
Civic ✔✔of or relating to a city; municipal, of or relating to citizenship; civil, of citizens
Universal suffrage ✔✔consists of the extension of the right to vote to adult citizens, although it
may also mean extending that right to minors and non-citizens
Author's Purpose ✔✔3: To entertain, persuade, or inform
Branches of the U.S. Government ✔✔Legislative (Congress), Executive (President and Cabinet),
and Judicial (Supreme Court)
Conservation ✔✔the principle that an object maintains the same size and shape if it is
repositioned or divided in certain ways
Partitioning ✔✔the division of something into parts. In measurement, partitioning is done with
units (meter-centimeter, gallon-quarts, etc.). The level of partitioning used in a measurement
affects the precision of that measurement.
Transitivity ✔✔a mathematical property stating that if A and B satisfy a relation and B and C
satisfy the same relation, then A and C also satisfy the relation. (If A=B and B=C, then A=C)
Transitivity allows objects to be compared indirectly, and allows measurements to be consistent
in comparisons.
Unit iteration ✔✔the repetition of a single unit for a measurement
Array ✔✔a systematic arrangement of similar objects, usually in rows or columns
Cut score ✔✔is the point that sets that predetermined level; it differentiates between those who
pass and those who fail. Multiple cut scores may also be set to more finely separate students into
categories (i.e. advanced, proficient, needs improvement, or unsatisfactory)
Scientific inquiry ✔✔refers to the activities through which students develop knowledge and
understanding of scientific ideas, as well as an understanding of how scientists study the natural
world
Discrepant event ✔✔something that does not turn out as expected. Can be used to challenge
students' beliefs. Makes them more receptive to learning what you want them to learn. Can be
combined with the conceptual change method.
Performance assessment ✔✔also known as alternative or authentic assessment
Quantitative ✔✔a type of information or data that is based on quantities obtained using a
quantifiable measurement process.
Qualitative ✔✔descriptive, subjective, or difficult to measure
Locomotor skills ✔✔physical action that propels an individual from one place to another (i.e.
moving forward, backward. or upwards)
Non-locomotor skill ✔✔a physical action an individual may perform while remaining stationary
[Show More]
.png)

.png)