Logistics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ISYE 6414 Final Exam Review with complete solution (All)
ISYE 6414 Final Exam Review with complete solution
Document Content and Description Below
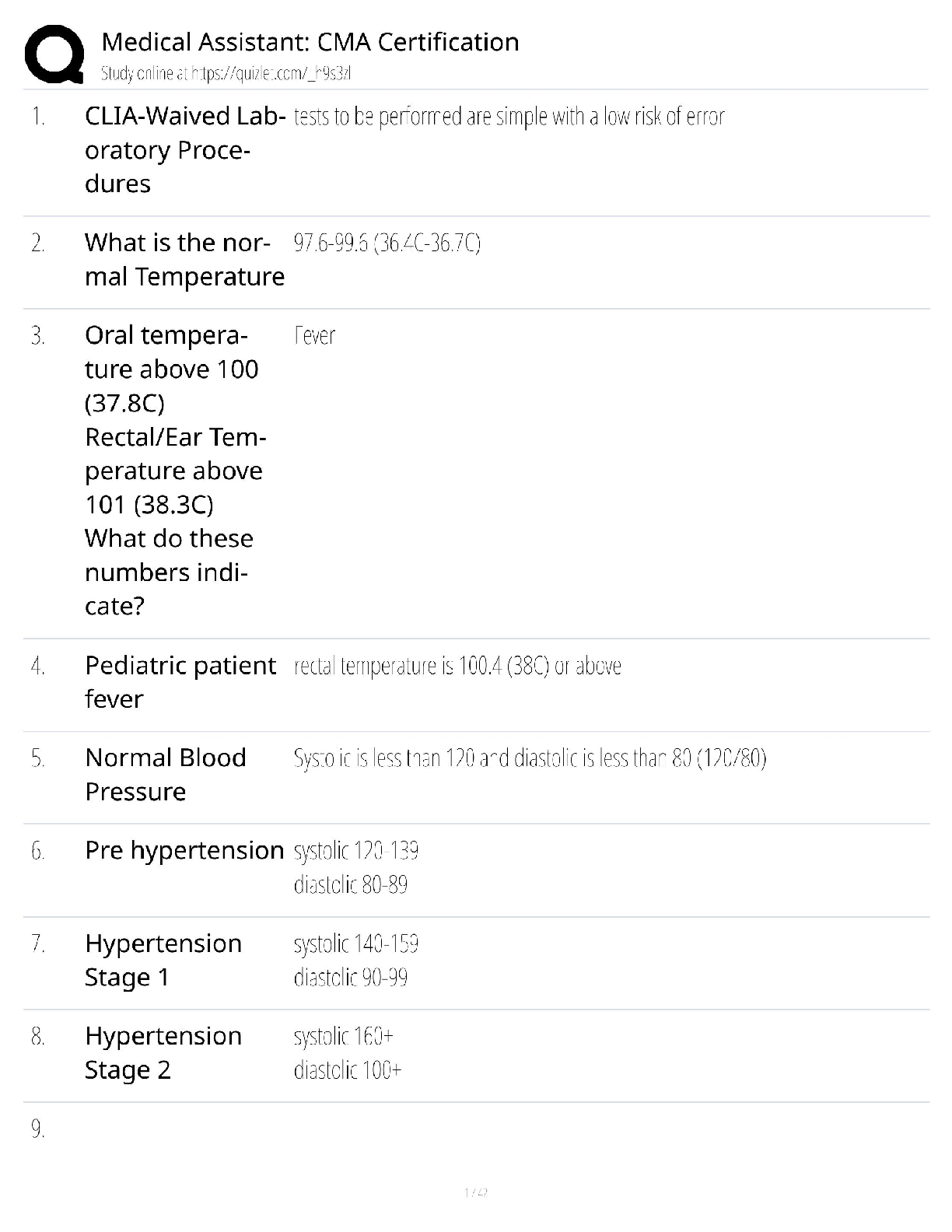
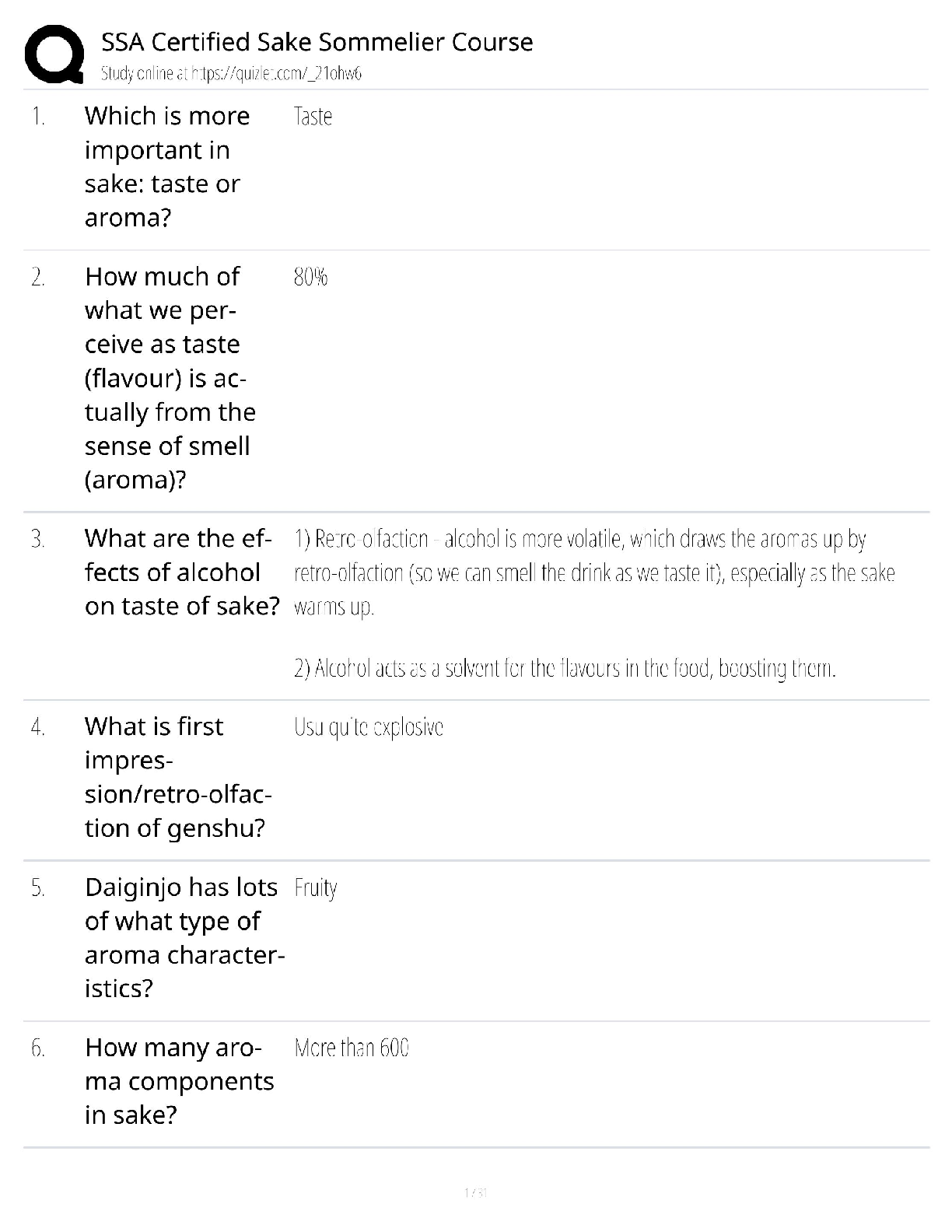
ISYE 6414 Final Exam Review with complete solution Least Square Elimination (LSE) cannot be applied to GLM models. ✔✔ False - it is applicable but does not use data distribution information ful ... ly. In multiple linear regression with idd and equal variance, the least squares estimation of regression coefficients are always unbiased. ✔✔ True - the least squares estimates are BLUE (Best Linear Unbiased Estimates) in multiple linear regression. Maximum Likelihood Estimation is not applicable for simple linear regression and multiple linear regression. ✔✔ False - In SLR and MLR, the SLE and MLE are the same with normal idd data. The backward elimination requires a pre-set probability of type II error ✔✔ False - Type I error The first degree of freedom in the F distribution for any of the three procedures in stepwise is always equal to one. ✔✔ True MLE is used for the GLMs for handling complicated link function modeling in the X-Y relationship. ✔✔ True In the GLMs the link function cannot be a non linear regression. ✔✔ False - It can be linear, non linear, or parametric When the p-value of the slope estimate in the SLR is small the r-squared becomes smaller too. ✔✔ False - When P value is small, the model fits become more significant and R squared become larger. In GLMs the main reason one does not use LSE to estimate model parameters is the potential constrained in the parameters. ✔✔ False - The potential constraint in the parameters of GLMs is handled by the link function. The R-squared and adjusted R-squared are not appropriate model comparisons for non linear regression but are for linear regression models. ✔✔ TRUE - The underlying assumption of R-squared calculations is that you are fitting a linear model. The decision in using ANOVA table for testing whether a model is significant depends on the normal distribution of the response variable ✔✔ True When the data may not be normally distributed, AIC is more appropriate for variable selection than adjusted R-squared ✔✔ True The slope of a linear regression equation is an example of a correlation coefficient. ✔✔ False - the correlation coefficient is the r value. Will have the same + or - sign as the slope. In multiple linear regression, as the value of R-squared increases, the relationship between predictors becomes stronger ✔✔ False - r squared measures how much variability is explained by the model, NOT how strong the predictors are. When dealing with a multiple linear regression model, an adjusted R-squared can be greater than the corresponding unadjusted R-Squared value. ✔✔ False - the adjusted rsquared value take the number and types of predictors into account. It is lower than the r squared value. In a multiple regression problem, a quantitative input variable x is replaced by x − mean(x). The R-squared for the fitted model will be the same ✔✔ True The estimated coefficients of a regression line is positive, when the coefficient of determination is positive. ✔✔ False - r squared is always positive. If the outcome variable is quantitative and all explanatory variables take values 0 or 1, a logistic regression model is most appropriate. ✔✔ False - More research is necessary to determine the correct model. After fitting a logistic regression model, a plot of residuals versus fitted values is useful for checking if model assumptions are violated. ✔✔ False - for logistic regression use deviance residuals. In a greenhouse experiment with several predictors, the response variable is the number of seeds that germinate out of 60 that are planted with different treatment combinations. A Poisson regression model is most appropriate for modeling this data ✔✔ False - poisson regression models rate or count data. For Poisson regression, we can reduce type I errors of identifying statistical significance in the regression coefficients by increasing the sample size. ✔✔ True Both LASSO and ridge regression always provide greater residual sum of squares than that of simple multiple linear regression. ✔✔ True If data on (Y, X) are available at only two values of X, then the model Y = \beta_1 X + \beta_2 X^2 + \epsilon provides a better fit than Y = \beta_0 + \beta_1 X + \epsilon. ✔✔ False - nothing to determine of a quadratic model is necessary or required. If the Cook's distance for any particular observation is greater than one, that data point is definitely a record error and thus needs to be discarded. ✔✔ False - must see a comparison of data points. Is 1 too large? We can use residual analysis to conclusively determine the assumption of independence ✔✔ False - we can only determine uncorrelated errors. It is possible to apply logistic regression when the response variable Y has 3 classes. ✔✔ True . A correlation coefficient close to 1 is evidence of a cause-and-effect relationship between the two variables. ✔✔ False- cause and effect can only be determined by a well designed experiment. Multiplying a variable by 10 in LASSO regression, decreases the chance that the coefficient of this variable is nonzero. ✔✔ False - I am not sure why anyone would think this would be true. In regression inference, the 99% confidence interval of coefficient \beta_0 is always wider than the 95% confidence interval of \beta_1. ✔✔ False- can only compare beta1 with beta1 and beta0 with beta0 The regression coefficients for the Poisson regression model can be estimated in exact/closed form. ✔✔ False - MLE is NOT closed form. Mean square error is commonly used in statistics to obtain estimators that may be biased, but less uncertain than unbiased ones. And that's preferred. ✔✔ True Regression models are only appropriate for continuous response variables. ✔✔ False - logistic and poisson model probability and rate The assumptions in logistic regression are - Linearity, Independence of response variable, and the link function is the logit function. ✔✔ True - linearity is measured through the link, , the g of the probability of success and the predicted variable. The log odds function, also called the logit function, which is the log of the ratio between the probability of a success and the probability of a failure ✔✔ True In logistic regression we interpret the Betas in terms of the response variable. ✔✔ False - we interpret it in terms of the odds of success or the log odds of success In logistic regression we have an additional error term to estimate. ✔✔ False - there is not error term in logistic regression. The least square estimation for the standard regression model is equivalent with Maximum Likelihood Estimation, under the assumption of normality. ✔✔ True The variance estimator in logistic regression has a closed form expression. ✔✔ False - use statistical software to obtain the variance-co-variance matrix We can use the z value to determine if a coefficient is equal to zero in logistic regression. ✔✔ True - z value = (Beta-0)/(SE of Beta) In testing for a subset of coefficients in logistic regression the null hypothesis is that the coefficient is equal to zero ✔✔ True Like standard linear regression we can use the F test to test for overall regression in logistic regression. ✔✔ False - It's 1-pchisq(null deviance-residual deviance, DFnull-DFresidual) For logistic regression we can define residuals for evaluating model goodness of fit for models with and without replication. ✔✔ False - can only be with replication under the assumption that Yi is binary and n1 is greater than 1 The deviance residuals are the signed square root of the log-likelihood evaluated at the saturated model ✔✔ True From the binomial approximation with a normal distribution using the central limit theorem, the Pearson residuals have an approximately standard chi-squared distribution. ✔✔ False - Normal distribution Visual Analytics for logistic regression Normal probability plot of residuals Residuals vs predictors Logit of success rate vs predictors ✔✔ True Normal probability plot of residuals - Normality Residuals vs predictors - Linearity/Independence Logit of success rate vs predictors - Linearity Under the null hypothesis of good fit for logistic regression, the test statistic has a Chi-Square distribution with n- p- 1 degrees of freedom ✔✔ True - don't forget, we want large P values For the testing procedure for subsets of coefficients, we compare the likelihood of a reduced model versus a full model. This is a goodness of fit test ✔✔ False - it provides inference of the predictive power of the model Predictive power means that the predicting variables predict the data even if one or more of the assumptions do not hold. ✔✔ True [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 28, 2022
Number of pages
9
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 28, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
103




 Answered 2023.png)