Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BIO 210 - FINAL EXAM REVIEW with complete solution (All)
BIO 210 - FINAL EXAM REVIEW with complete solution
Document Content and Description Below
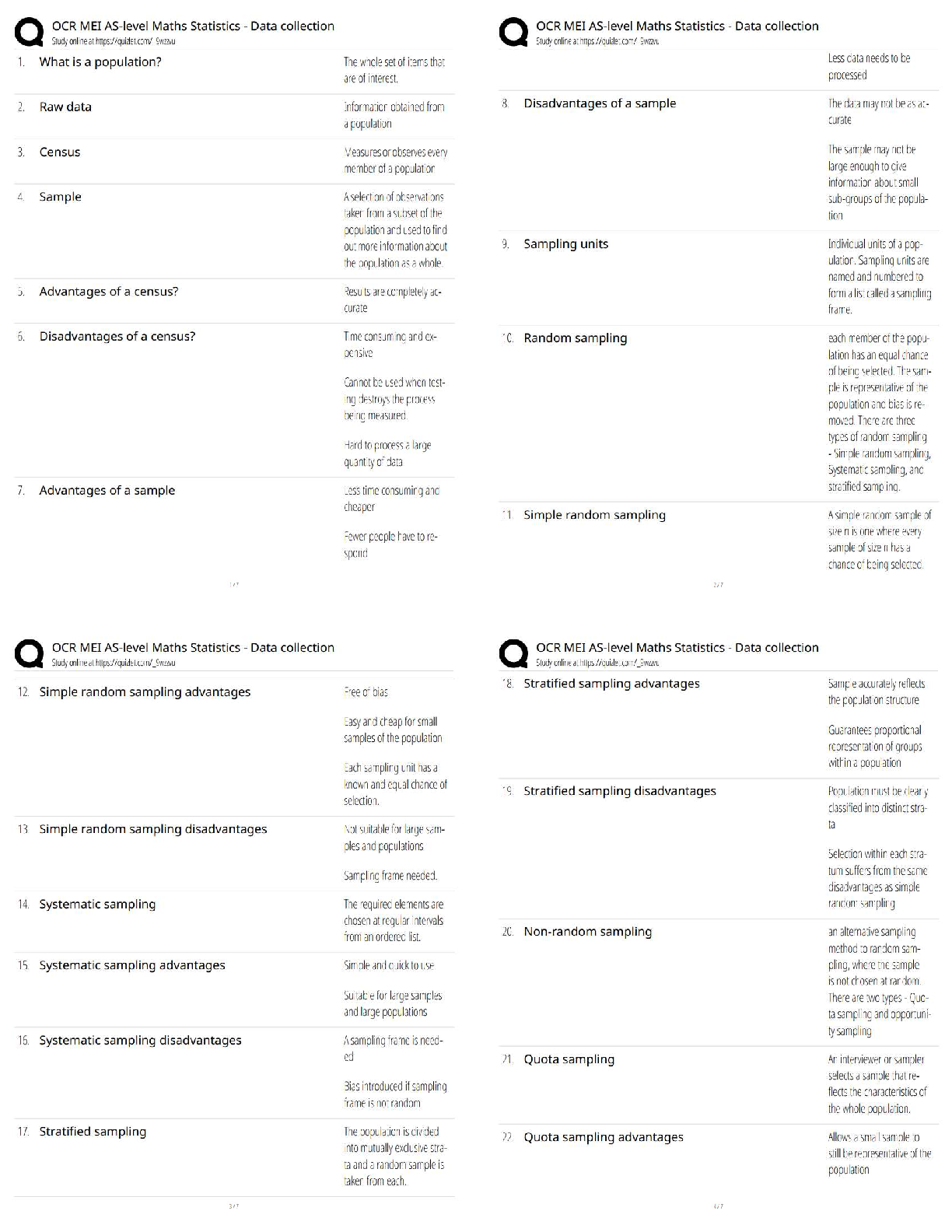
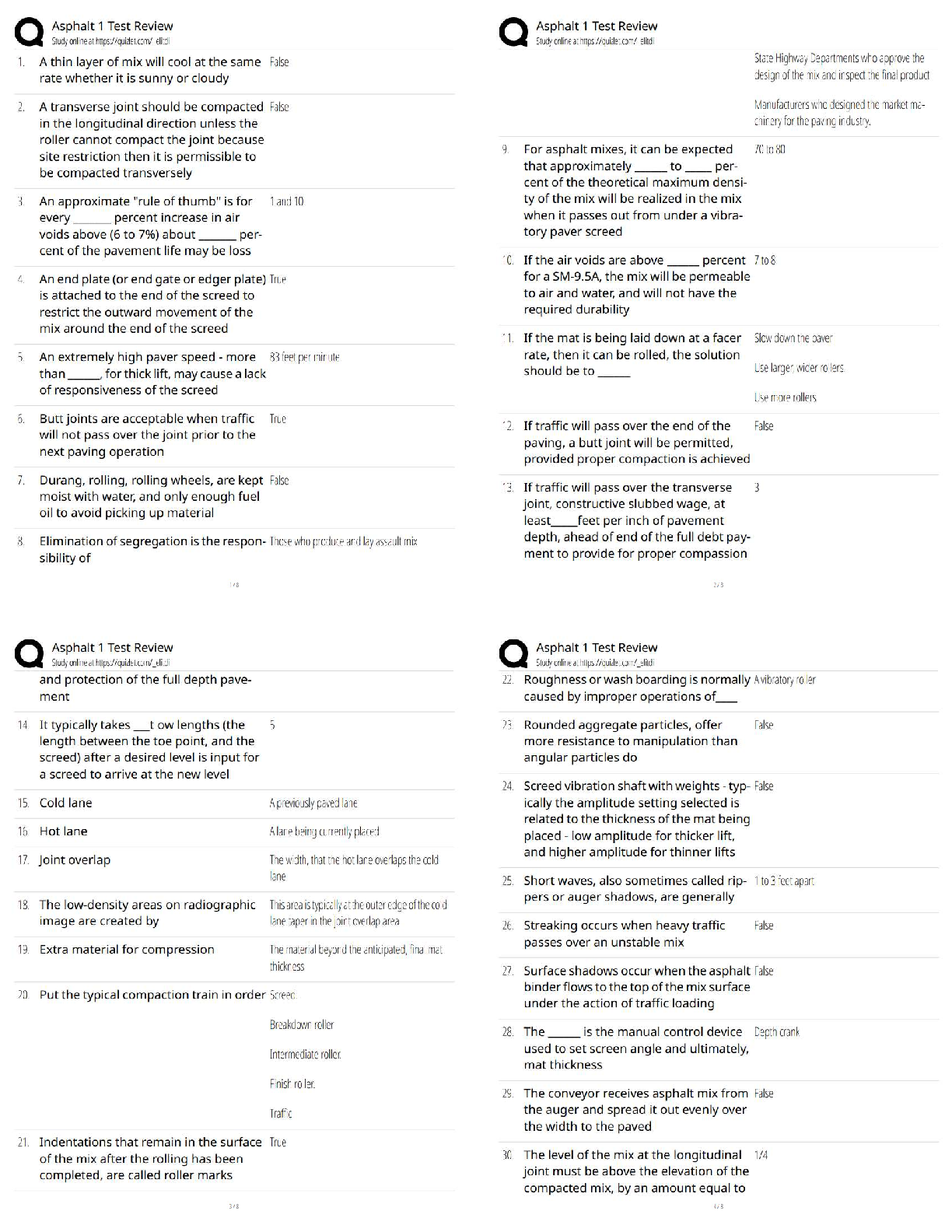
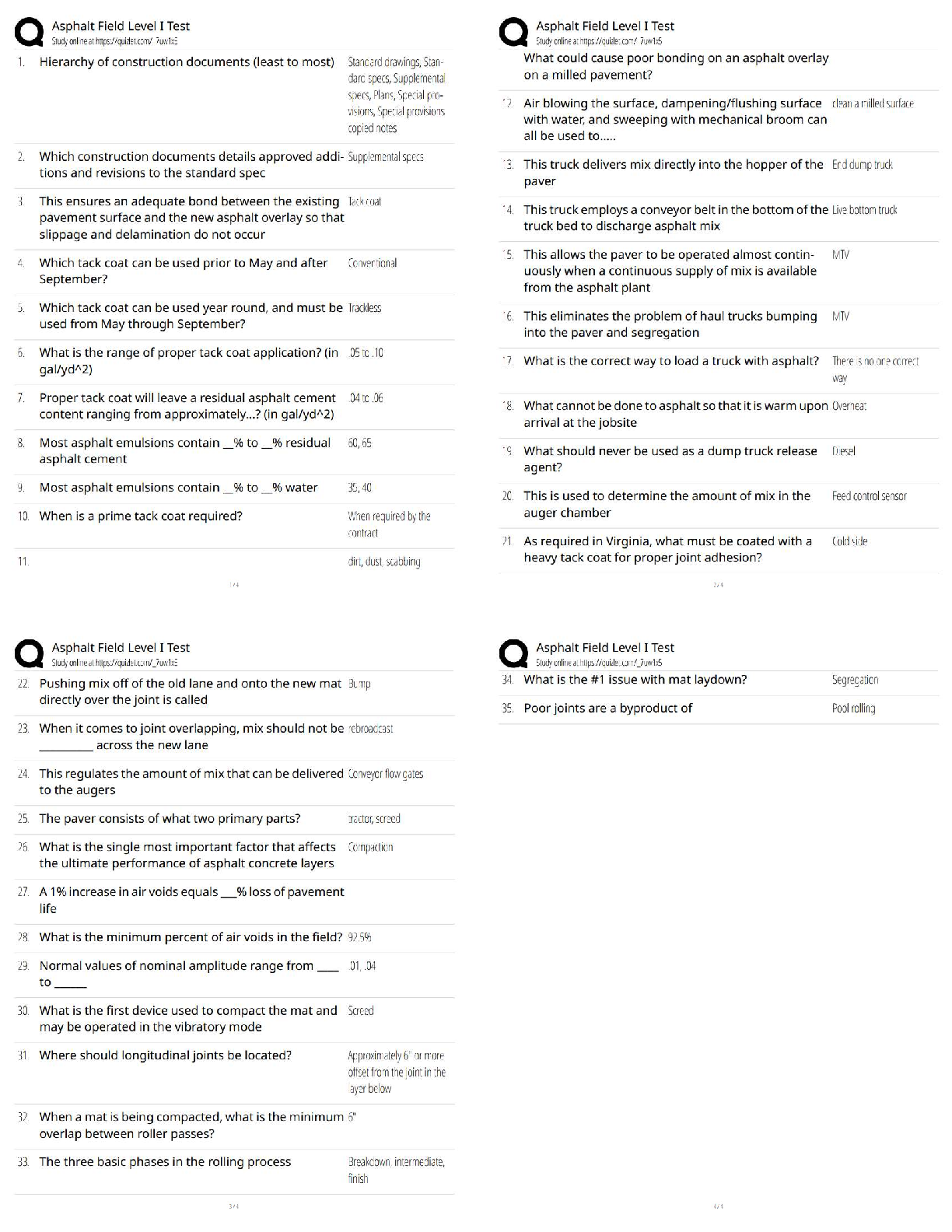
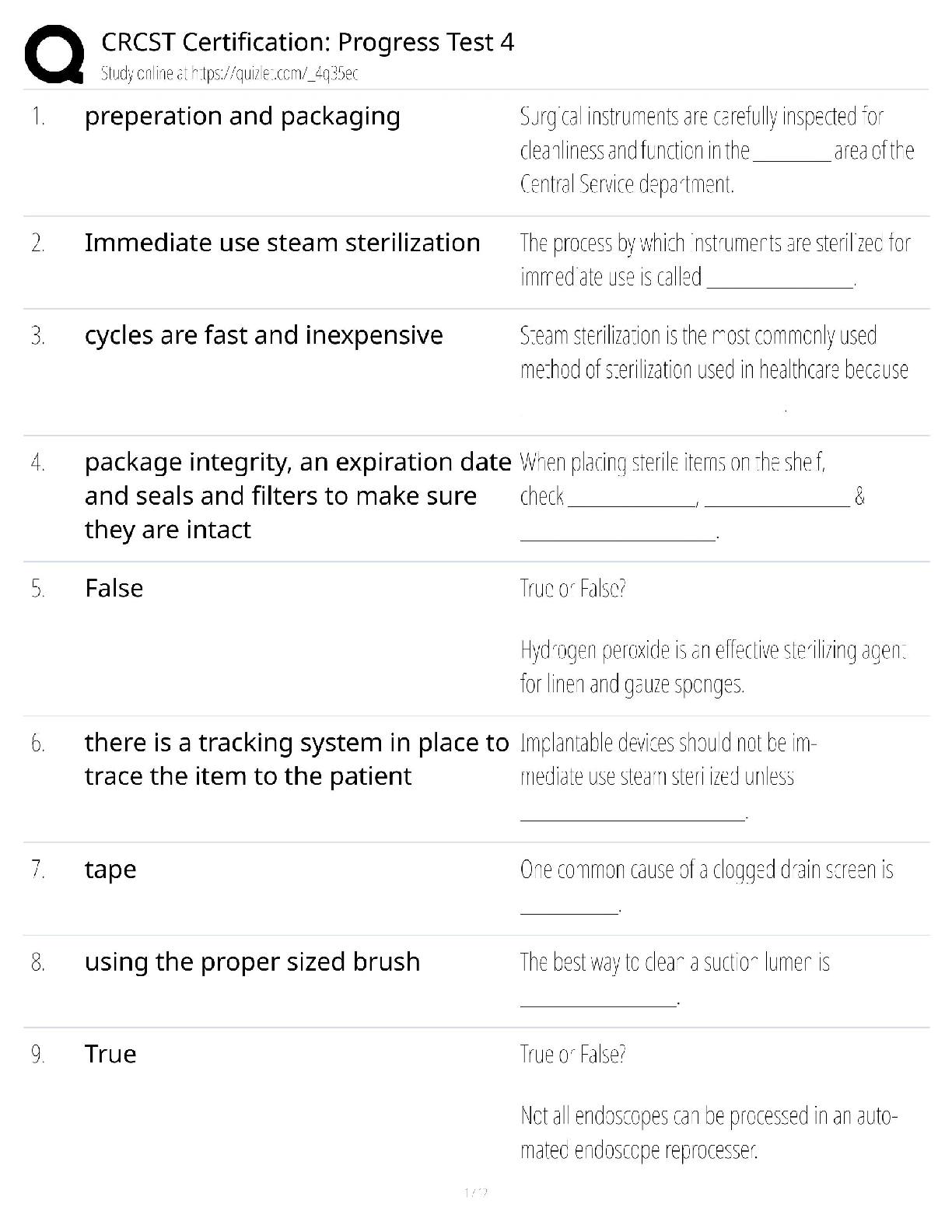
BIO 210 - FINAL EXAM REVIEW with complete solution Anatomy ✔✔the study of structure Physiology ✔✔the study of function Metabolism ✔✔all the chemical reactions that happen in our b ... ody cells Catabolism ✔✔the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones. Catabolic reaction Anabolism ✔✔The building up of complex molecules from simpler ones Levels of Structural Organization ✔✔Atom (chemical), Molecule (chemical), Cell tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism Homeostasis ✔✔The maintenance of the internal environment regardless of external conditions Negative feedback mechanism ✔✔Most feedback mechanisms are this type - regulating body temperature, blood pressure, blood glucose Cranial Cavity ✔✔Brain and spinal cord vertebral cavity ✔✔spinal cord thoracic cavity ✔✔heart and lungs abdominopelvic cavity ✔✔stoach digestive organs parietal membrane ✔✔lines cavity wall visceral membrane ✔✔lines the organs surface ATP ✔✔a form of energy used by all reactions in cells. Made in the mitochondria 4 elements that make up 96% of the human body ✔✔Oxygen, hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen atomic number ✔✔number of protons. Always the same as the number of electrons Atomic mass ✔✔decimal number - number of protons and neutrons together - if you subtract the protons you get the number of neutrons ionic bonds ✔✔the transfer of one or more electrons anion ✔✔negative charge - gains one electron cation ✔✔positive charge - loses one electron covalent bond ✔✔shared electrons 2 types of covalent bonds ✔✔Polar - unequal sharing of electrons Nonpolar - equal sharing of electrons PH ✔✔Acid base concentration - homeostasis of acid base balance is regulated by chemicals called buffers buffers ✔✔acccept hydrogen ions when PH is high and donates when the PH is low Carbohydrates - organic compound ✔✔fructose, glycogen Protiens - organic compound ✔✔amino acids and enzymes Lipids - organic compound ✔✔triglycerides, cholesterol Nucleic acids - organic compound ✔✔DNA, RNA DNA nitrogenous bases ✔✔Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine (AGCT) RNA nitrogenous bases ✔✔Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil (AGSU) Plasma Membrane ✔✔Phospholipid bilayer composed of hydrophilic (phosphate) heads and hydrophobic (lipid) tails Resting membrane potential ✔✔maintained by sodium potassium pump (active transport) - takes 3 sodium out and 2 potassium in K+ Potassium ✔✔10 times higher inside the cell - major intracellular cation Na+ Sodium ✔✔10 times higher outside the cell - major extracellular cation passive transport - osmosis ✔✔Movement of water. Water follows salt, thats what makes it move Hypotonic solution ✔✔cells lyse/burst [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 31, 2022
Number of pages
10
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 31, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
218




 Answered 2023.png)