Applied Science > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Tcfp HazMat Operations Possible Questions and Correct Answers (Complete Solution) Graded A+ (All)
Tcfp HazMat Operations Possible Questions and Correct Answers (Complete Solution) Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
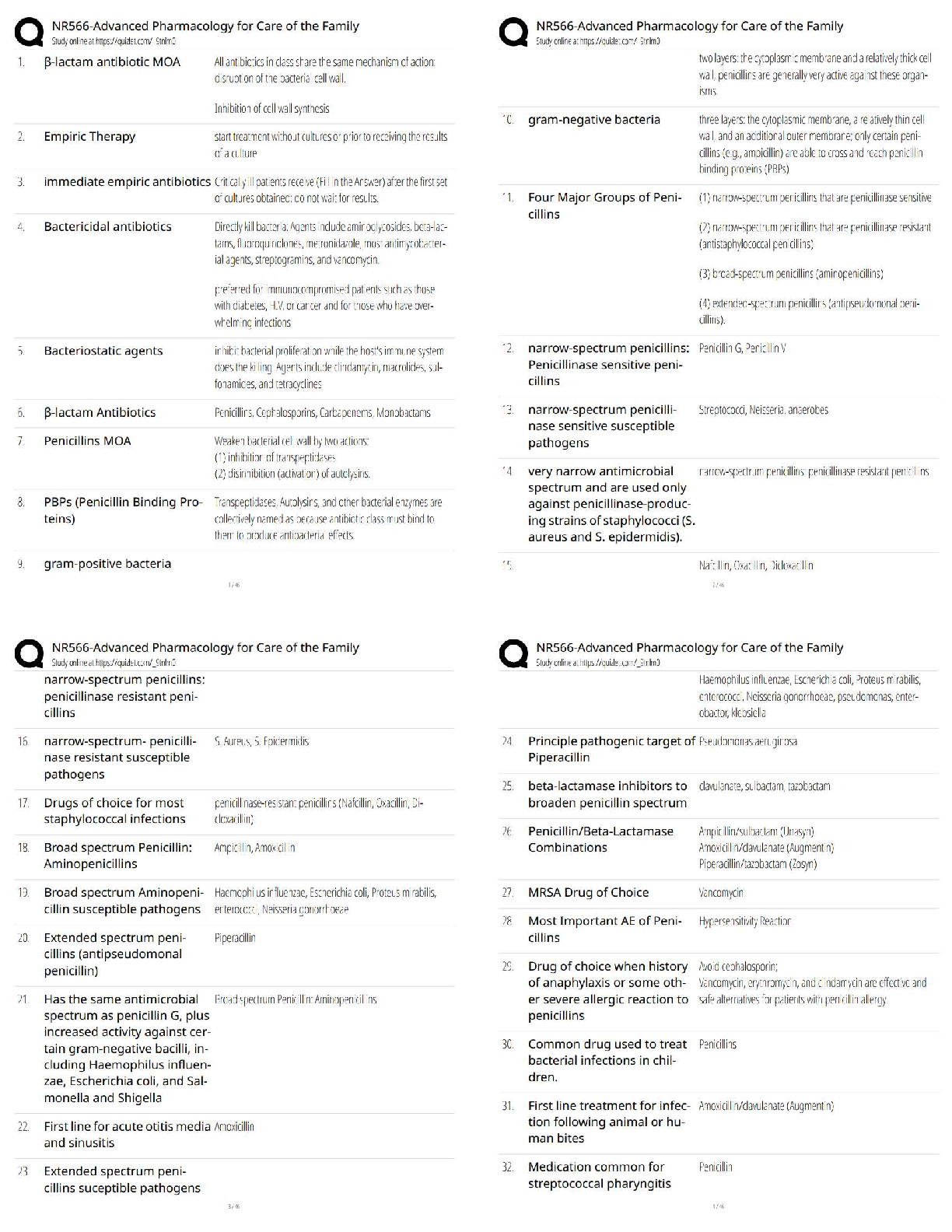
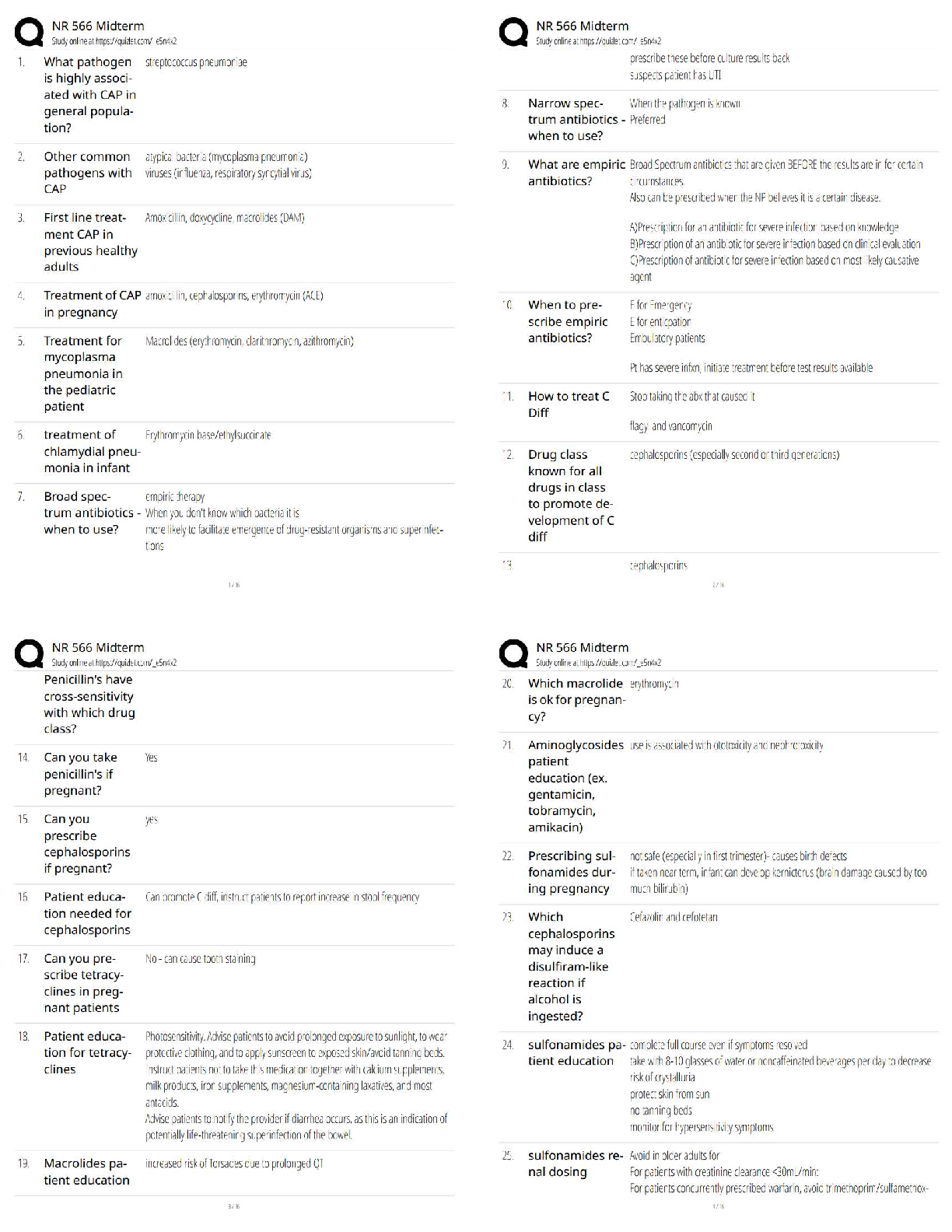
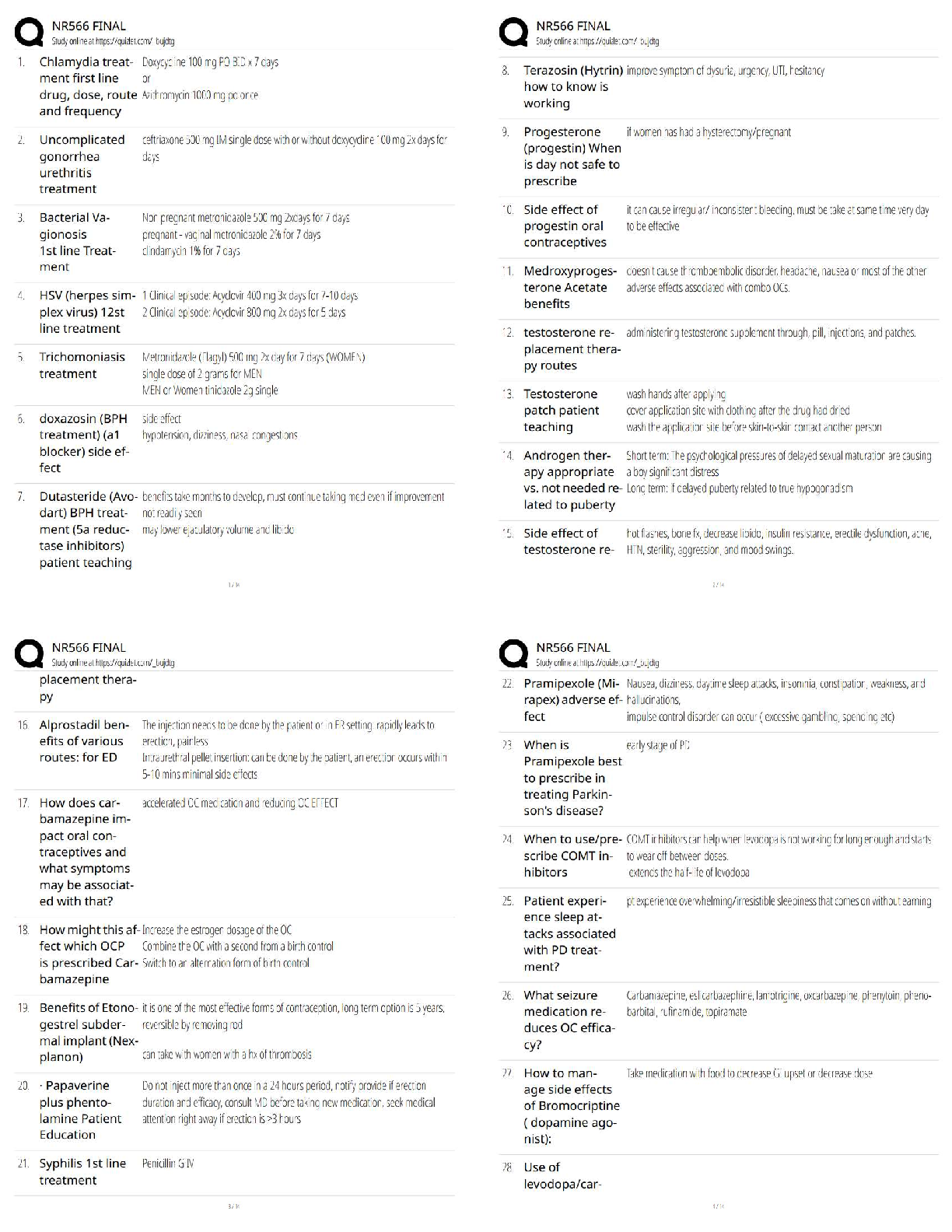
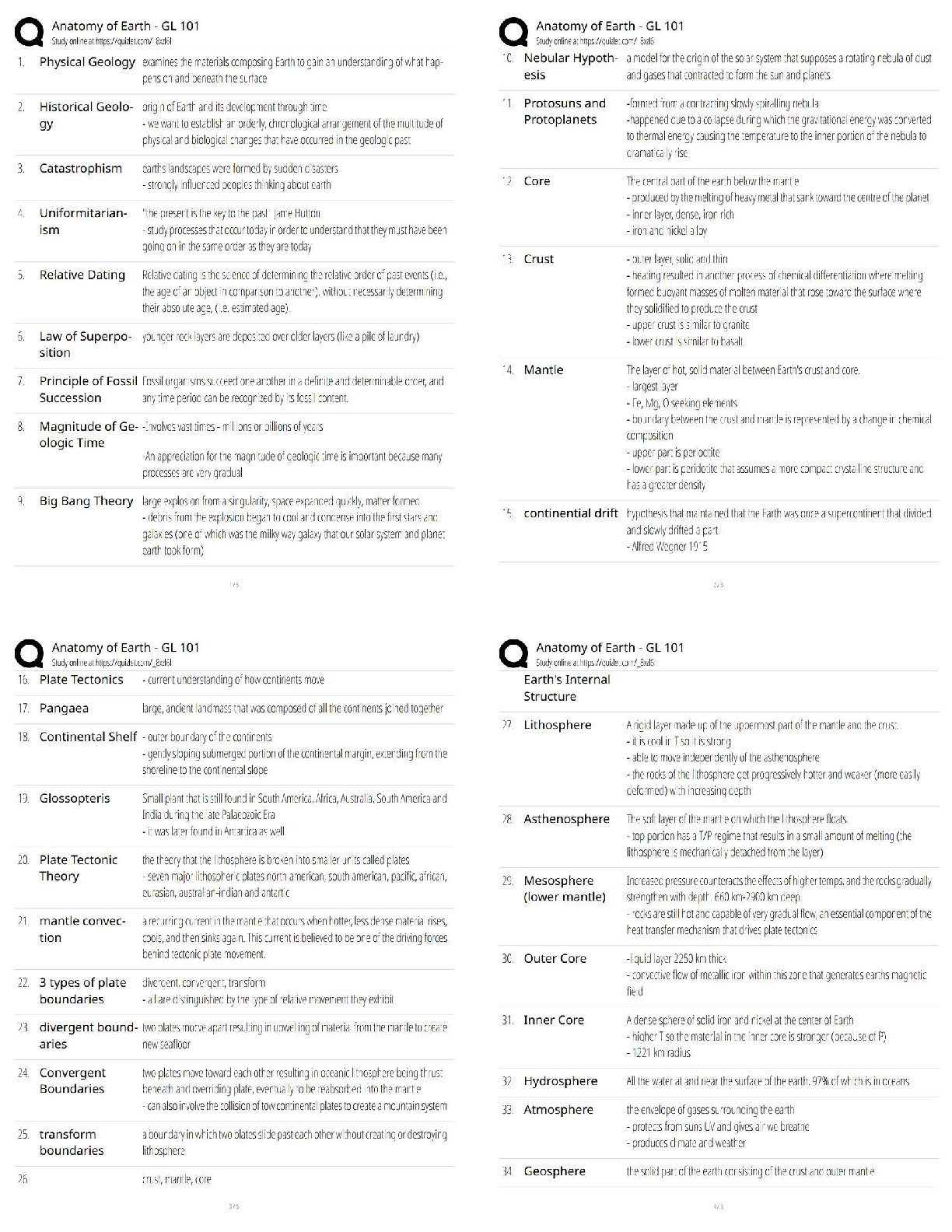
Tcfp HazMat Operations Possible Questions and Correct Answers (Complete Solution) Graded A+ When responding to hazardous materials/WMD incidents Operations level responders shall be able to preform ... the following task... ✔✔ 1. Analyze a HazMat incident to determine the scope of the problem 2. Plan an initial response 3. Implement a planned response 4. Evaluate the progress Analyzing a hazardous material incident to determine the scope of the problem involves... ✔✔ 1. Surveying the incident to identify containers and materials involved, determine if wether hazardous material has been released and evaluate the surrounding conditions 2. Collect hazard and response information from SDS, CHEMTREC and shipping/manufacturer contracts 3.Predict the behavior of Hazardous materials and its container 4.Estimate the potential harm through TRACE-MP What does TRACE-MP stand for? ✔✔ Types of potential harm at Hazardous Material/WMD incidents. Thermal Radiation Asphyxiation Chemical Etiological Mechanical Psychological/ Psychogenic The initial response at a HazMat incident is determined by.. ✔✔ The capabilities and competencies of available personnel and personal protective equipment The response objectives at a hazardous material/WMD incident include... ✔✔ 1.Evacuation 2. Search and Rescue 3. Exposure protection/ Isolating the Area 4. Defensive control techniques 5. Crime scene management and evidence preservation 6. Recovery and termination Describe the response options available for Evacuation ✔✔ 1. Full scale evacuation 2. Shelter-in-place 3. Combination Describe the response options available for Search and Rescue ✔✔ 1. Based on training and equipment 2. Risk-benefit analysis (risk a lot to save a lot, risk a little to save a little) Describe the response options available for Exposure protection/Isolating the Area ✔✔ 1.Establish initial isolation zone 2.Establish protective action distance 3. Establish control zones Describe the response options available for Defensive Control Techniques ✔✔ 1. Damming (Overflow or Underflow) 2. Diking 3. Retention 4. Dispersion 5. Absorption 6. Adsorption 7. Dilution 8. Dissolution 9. Diversion 10. Vapor dispersion 11. Vapor suppression 12. Ventilation 13. Remote valve shutoff What is Damming... ✔✔ Physical method of confinement by which barriers are constructed to prevent or reduce the quantity of liquid flowing into the environment. Consists of constructing a barrier across a waterway to stop/control the product flow and pick up liquid or solid contaminants What is Underflow Damming ... ✔✔ Spill control tactic used to trap floating lighter than water materials behind the dam. Dam is constructed in a manner that allows uncontaminated water to flow unobstructed under the dam while keeping the contaminant behind the dam. What is Overflow Damming... ✔✔ Spill control tactic used to trap sinking heavier than water materials behind the dam. With the product trapped, uncontaminated water is allowed to flow unobstructed over the top of the dam. What is Diking... ✔✔ Physical method of confinement by which barriers are constructed on ground used to control the movement of liquids, sludges, solids, or other materials. Prevents the passage of hazmat from entering an area where it will produce more harm. What is retention... ✔✔ Physical method of confinement by which a liquid is temporarily contained in an area where it can be absorbed, neutralized, or picked up for proper disposal What is dispersion... ✔✔ Chemical method of confinement by which certain chemical and biological agents are used to disperse or break up the material involved in liquid spills on water may result in spreading the hazardous material over a large area. What is absorption... ✔✔ Absorption occurs when one material enters the cell structure of another and is retianed within. Absorbents retain the properties of the materials they absorb and must be treated and disposed of as hazardous material What is adsorption... ✔✔ Adsorption is different from absorption in that the molecules of the hazardous materials physically adhere to the adsorbent material Adsorbents do not swell like absorbents Produces heat and can cause spontaneous combustion must be disposed of properly. Examples: activated charcoal, silica, aluminum gel, fuller's eath, POROUS clay and other clays What is dilution.. ✔✔ Dilution involves applying water to a water soluble material in order to reduce the hazard. It is a useful way to preform decontamination but it is not a practical practical spill control method as it typically requires so much water that it creates a runoff problem [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

TCFP EXAMS Bundled Together with complete solutions Questions and Answers (Verified Answers)(Full Solution Pack)
TCFP & GFD HAZMAT AWARENESS/OPS TEST 2023 GRADED A+ Fire Investigator - Master for TCFP Full Test Bank TCFP Possible Questions and Answers Randomized Practice Final TCFP FF2 Questions and Correc...
By Crescent 2 years ago
$15
6
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 06, 2023
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 06, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
180




 Answered 2023.png)