Unit 2: Tableau Desktop Specialist Exam
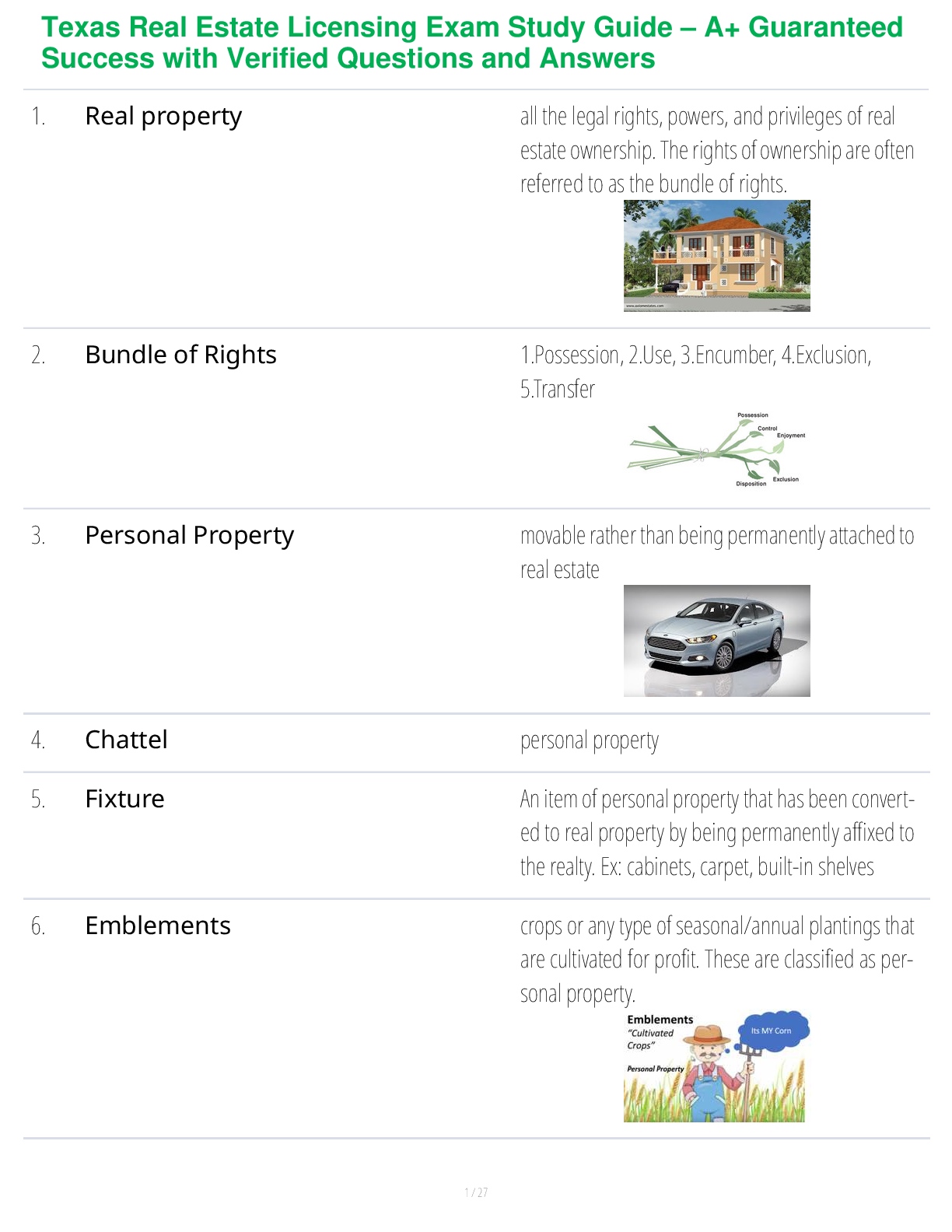
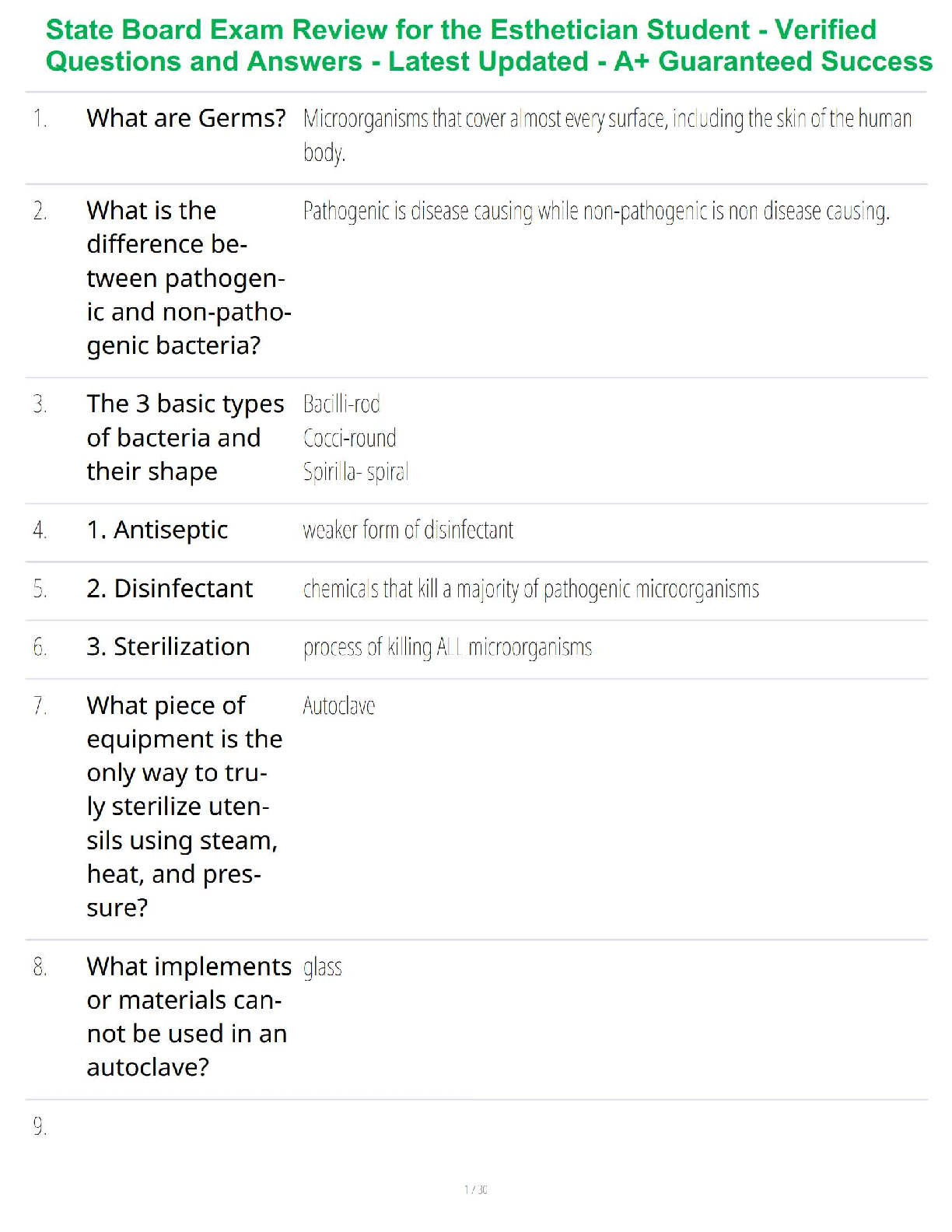
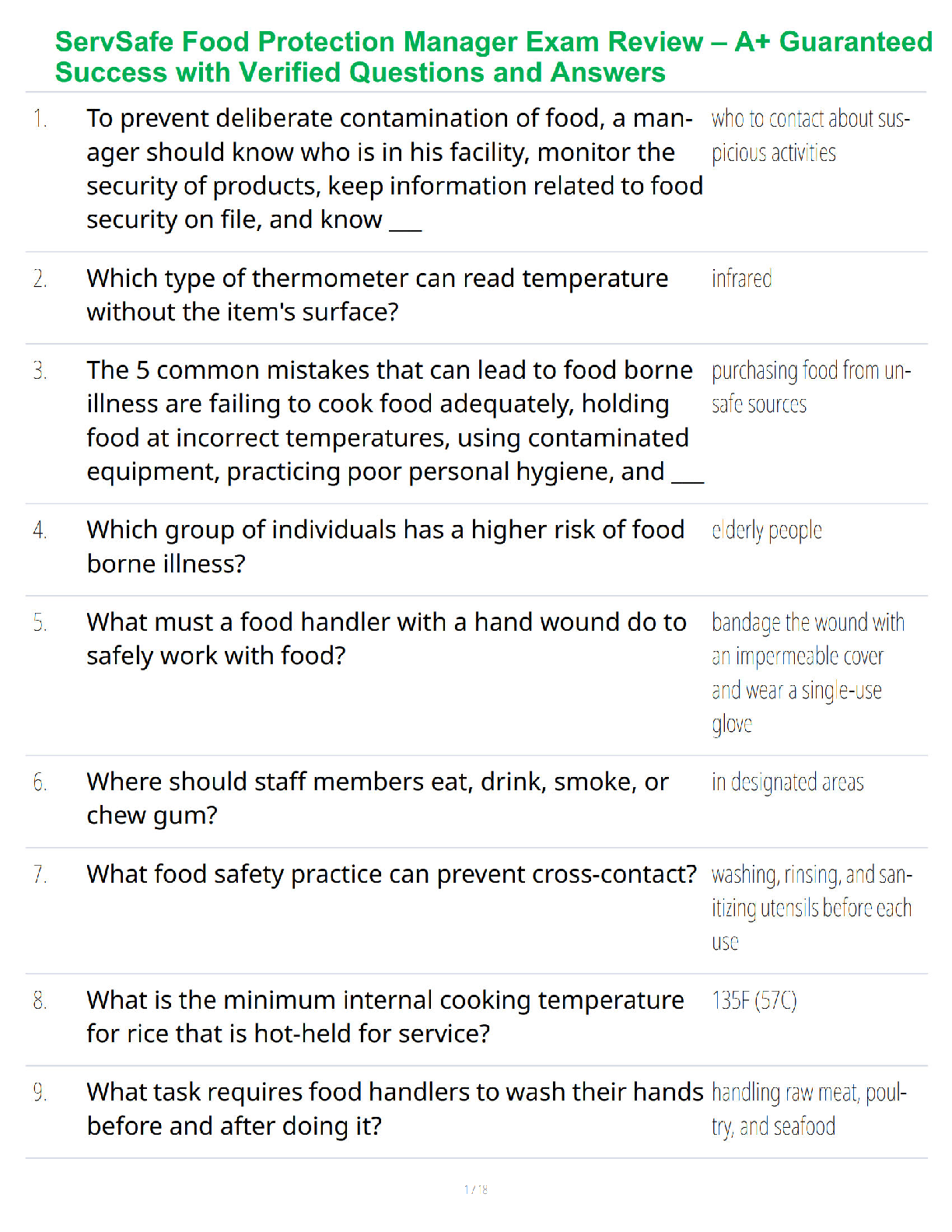
How do you group dimensions? ✔✔3 options:
1. Group in the dimension pane. Right click then select Group.
2. Group in the viz by mark (color coding each bar within a group). Pres
...
Unit 2: Tableau Desktop Specialist Exam
How do you group dimensions? ✔✔3 options:
1. Group in the dimension pane. Right click then select Group.
2. Group in the viz by mark (color coding each bar within a group). Press Ctrl and select each
mark/bar in your desired group. Right click then select Group.
3. Group by label (combining several bars into a single bar). Click each label/title in your desired
group. Right click then select Group.
What are the benefits of using a hierarchy? How do you create one? ✔✔You can group related
dimensions. It also allows you to see data from a high-level overview and get more granular.
(Ex: Category> Subcategory> Product name) You can select several dimensions and right click
to create a hierarchy or drag and drop dimensions onto each other. Then. drag to rearrange if
needed.
What is the benefit of using a filter? ✔✔You can show only a portion of data and hand-pick
which dimensions are shown. You can also apply cool filters like "top" which shows the highest
selling or lowest selling items. You can also filter to see above or below a certain dollar amount
of sales.
When would you filter by dimension? ✔✔When you want to show a subset of data within a
category
When would you filter by measure? ✔✔When you want to show a specific range of values
within your data
How can you show your filter to allow viewers to filter the data as they please? ✔✔Right click
on the measure you filtered and select "Show Filter." This creates a slider that users can play
with.
What logic does Tableau use to apply filters? ✔✔And
How do you create a filter? ✔✔Right click an item and click "Show Filter" and adjust, or Drag a
dimensions/measure into the "Filter" shelf.
How do you remove a filter? ✔✔Simply drag the filter off of the filter shelf and onto the white
space below it
What are some customization options for filters? ✔✔
When you add a filter from a measure, the default filter format is a ______. ✔✔Range of values
slider
To filter by a discrete date part, where do you select it? ✔✔The list that contains "years, months"
etc.
How do you add a filter to context? ✔✔To create a context filter, select Add to Context from the
context menu of an existing categorical filter. The context is computed once to generate the
view. All other filters are then computed relative to the context.
What does it mean to add context to a filter? ✔✔In our example, we found the top 10 selling
products across all categories. By adding a context filter to "categories" we can see the top 10
selling items within each category individually.
How do you sort by a field that's not in a view? ✔✔Right click the dimension you want to filter,
then select sort. Then you choose how you want to arrange that filter. For example, we arranged
the "subcategories" filter by which was most profitable although "sales" was measure in x axis.
What is the benefit of using a set? ✔✔You can monitor key data points and subsets of your data.
Ex: seeing which schools fall above the national average. Once created, you can use it as a filter
or any sheet in your workbook. You can also combine sets to show data that exists in one but not
the other, or the combination of all data found in either set.
What is a combined set? ✔✔It allows you to compare multiple sets to one another. *they both
must be based on the same dimension)
What is an In/Out set? ✔✔They're used to compare members in a set to members out of a set.
Ex: Products with sales under $400K
What is a discrete field? How can you tell it's discrete? ✔✔(Text headers) They have values that
can only fall within a specific bin or category. Ex: pet names: Fluffy or Sammy; countries;
employee IDs.
Continuous fields in Tableau are blue. When added to a view they add categories or headers.
What are continuous fields? How can you tell? ✔✔(Numerical headers) they contain numbers
that can fall anywhere along an axis of an infinite number of values. Ex Temperature is variable
and can be positive or negative. More examples: Height, wind speed, price
Continuous fields in Tableau are green.
When added to a view they create a single line with data plots on it
What does rearranging discrete and continuous fields do? ✔✔It can change which axis your data
is on and if your chart is horizontal or vertical.
It impacts the way your data can be represented (charts vs. bars)
What does changing a field from continuous to discrete do? ✔✔Lets say we're changing the data
field. As a continuous field the date is displayed in numbers therefore we can show the data as a
continuous line. If we change it to discrete, the date becomes arranged categorically and can be
represented in categorical bars by month. This will change the header from a number to text
displaying the month
[Show More]
.png)

.png)