Maternal Newborn
Newborn Complications
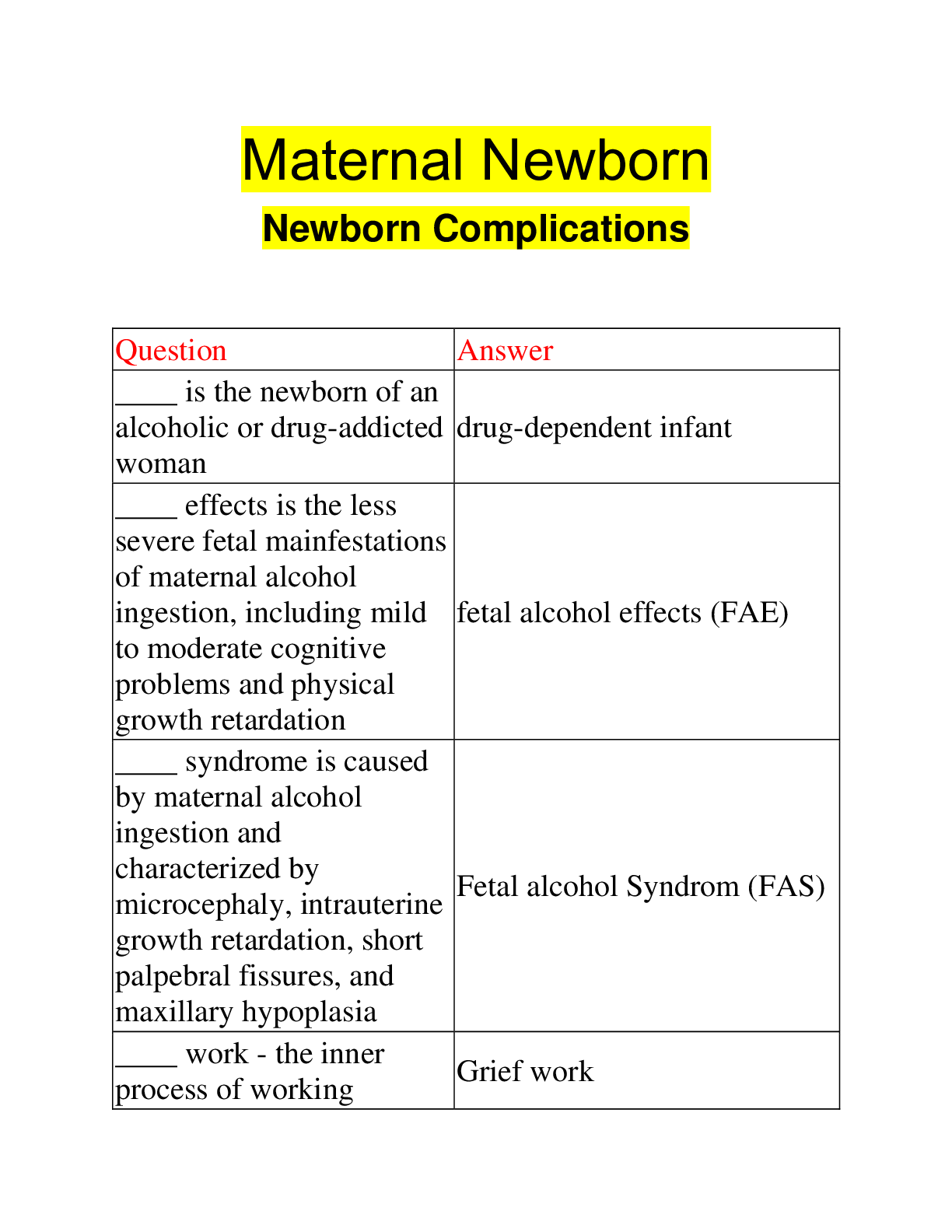
Question Answer
____ is the newborn of an
alcoholic or drug-addicted
woman
drug-dependent infant
____ effects is the less
severe fetal mainfestations
of maternal alcohol
i
...
Maternal Newborn
Newborn Complications
Question Answer
____ is the newborn of an
alcoholic or drug-addicted
woman
drug-dependent infant
____ effects is the less
severe fetal mainfestations
of maternal alcohol
ingestion, including mild
to moderate cognitive
problems and physical
growth retardation
fetal alcohol effects (FAE)
____ syndrome is caused
by maternal alcohol
ingestion and
characterized by
microcephaly, intrauterine
growth retardation, short
palpebral fissures, and
maxillary hypoplasia
Fetal alcohol Syndrom (FAS)
____ work - the inner
process of working Grief work
through or managing the
bereavement
____ - a hereditary
deficiency of a specific
enzyme needed for normal
metabolism of specific
chemicals
Inborn error of metabolism
____ - At-risk infant born
to a woman previously
diagnosed as diabetic, or
who developes symptoms
of diabetes during
pregnancy
Infant of a diabetic mother
(IDM)
____ - Fetal undergrowth
due to an etiology, such as
intrauterine infection,
deficient nutrient supply,
or congenital
malformation.
Intrauterine growth restriction
(IUGR)
____ - excessive growth
of a fetus in relation to the
gestational time period
large for gestational age
(LGA)
____ - number of deaths
of infants in the first 28
days of life per 1000 live
births
neonatal mortality rate
____ - the chance of death
within the newborn period
(first 28 days)
Neonatal mortality risk
____ - a common
metabolic disease caused
by an inborn error in the
metabolism of the amino
acid phenylalanine
Phenylketonuria
____ newborn - any infant
born after 42 weeks'
gestation
Postterm newborn
____ infant - any infant
born before 38 weeks'
gestation
preterm infant
____ - inadequate weight
or growth for gestational
age; birth weight below
the tenth percentile
Small for gestational age
(SGA)
____ dysplasia - chronic
pulmonary disease of
multifactorial etioloty
characterized initially by
alveolar and bronchial
necrosis, which results in
bronchial metaplasia and
interstitial fibrosis.
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
(BPD)
appears in x-ray films as
generalized small cysts
____ stress - excessive
heat loss resulting in
compensatory mechanisms
(increased respirations and
nonshivering
thermogenesis) to
maintain core body
temperature
cold stress
____ fetalis - hemolytic
disease of the newborn
characterized by anemia,
jaundice, enlargement of
the liver and spleen, and
generalized edema.
Caused by
isoimmunization due to
Rh incompatability or
ABO incompatibility
Erythoblastosis fetalis
____ - hyperbilirubinema
secondary to Rh
incompatibility
Hemolytic disease of the
newborn
____ - yellow
pigmentation of ody
tissues caused by the
presence of bile pigments
jaundice
____ - an encephalopathy
caused by deposition of
unconjugated bilirubin in
brain cells; may result in
impaired brain function or
death
kernicterus
____ syndrome -
respiratory disease caused
by inhalation of meconium
in amniotic fluid in the
lungs, respiratory distress,
hyperexpansion of chest,
hyperinflated alveoli and
secondary atelectasis
Meconium aspiration
syndrome
____ - respiratory disease
resulting from right to left
shunting of blood away
from the lungs and
through the ductus
arteriosus and patent
foramen ovale
Persistent pulmonary
hypertension of the newborn
(PPHN)
phototherapy is treatment
of ____ by exposure to
light
jaundice
Polycythemia is an
abnormal increase in the RBC
[Show More]