Wound Care Part 1
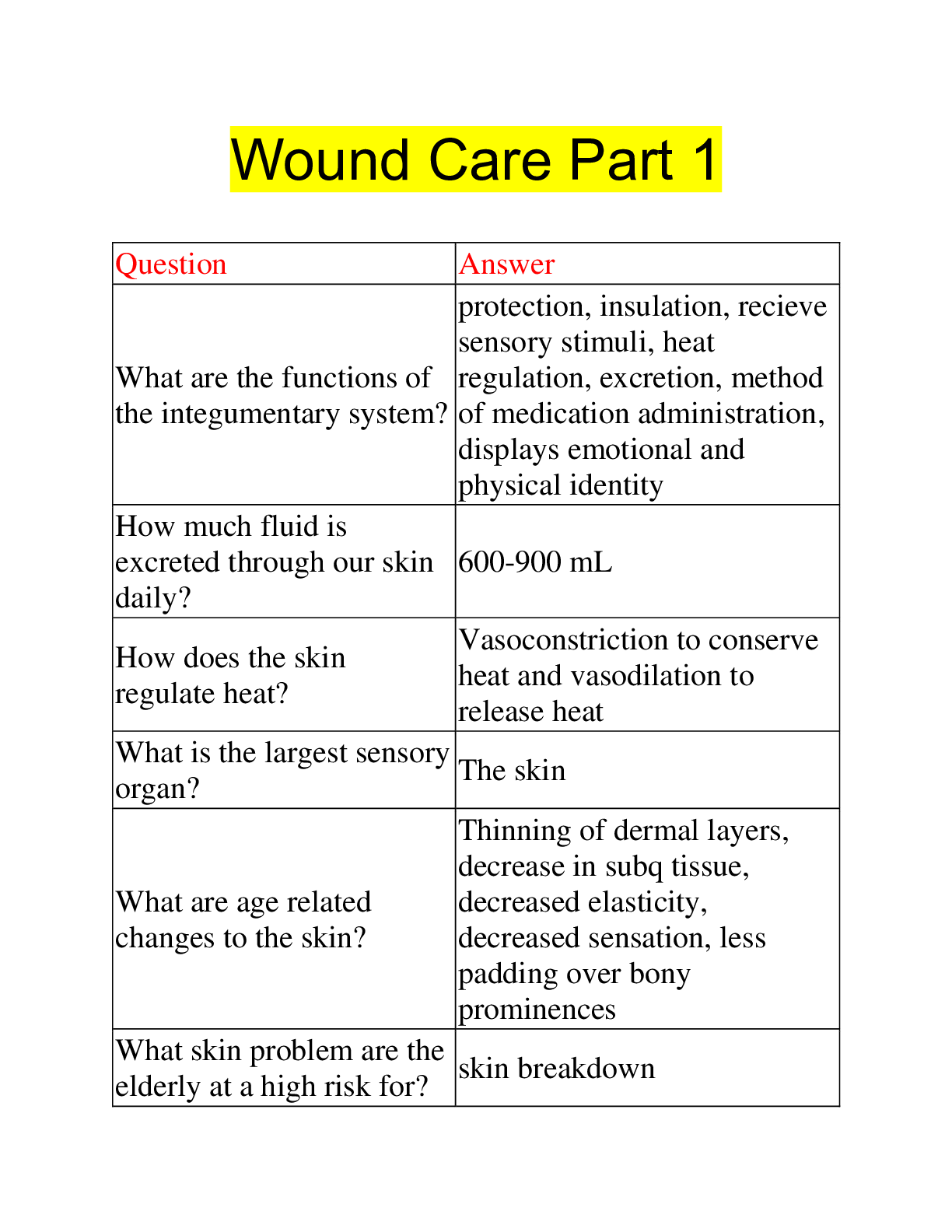
Question Answer
What are the functions of
the integumentary system?
protection, insulation, recieve
sensory stimuli, heat
regulation, excretion, method
of medication administration,
displays emo
...
Wound Care Part 1
Question Answer
What are the functions of
the integumentary system?
protection, insulation, recieve
sensory stimuli, heat
regulation, excretion, method
of medication administration,
displays emotional and
physical identity
How much fluid is
excreted through our skin
daily?
600-900 mL
How does the skin
regulate heat?
Vasoconstriction to conserve
heat and vasodilation to
release heat
What is the largest sensory
organ? The skin
What are age related
changes to the skin?
Thinning of dermal layers,
decrease in subq tissue,
decreased elasticity,
decreased sensation, less
padding over bony
prominences
What skin problem are the
elderly at a high risk for? skin breakdown
How does the skin repair
itself?
Through regeneration and
repair
Tissue regeneration
replacement of lost cells and
tissues with cells of the same
type
Tissue repair
Healing as a result of lost
cells being replaced by
connective tissue. Occurs by
primary, secondary, or tertiary
intention
What are the two
differences between tissue
repair and regeneration?
Regeneration usually occurs
with smaller cuts and will not
leave a scar. Repair happens
with larger/infected wounds
and will leave a scar b/c of the
connective tissue.
Primary wound healing
edges can be brought
together, stitched and healed.
Mostly medical surgeries
Secondary wound healing
wound will heal from bottom
up and from the edges in.
Mostly pressure ulcers and
wounds with infections.
Which nutrients promote
wound healing?
Protein, zinc, vitamins A and
C
What is the building block
of new tissue? Protein
What are some factors in
delayed wound healing?
nutritional deficiencies,
inadequate blood supply,
corticosteroids, infection,
smoking, mechanical friction,
obesity, DM, poor general
health, anemia
What effect does smoking
have on the blood vessels? It causes vasoconstriction
What effect does infection
have on the tissues?
Inflammation and tissue
breakdown
Why does friction pose a
problem with wound
healing?
b/c friction can remove new
tissue growth.
Why is anemia a problem
with wound healing?
B/c there is not enough
hemoglobin to carry oxygen
to the wound
What are some factors that
can promote wound
healing?
Using precautions to prevent
wound infections, drug
therapy, nutritional therapy,
rest and immobilization,
elevation, oxygenation, heat
and cold and wound
management
How does elevation help
wound healing? It prevents edema
How does heat/cold
therapy effect the blood
vessels?
cold causes vasoconstriction;
heat causes vasodilation
When taking care of a
wound, what is the first
thing you need to do?
Clean the wound
When you assess the
wound, what information
do you need to know?
location, size, drainage, color
of wound and tissue, assess
pain associated with the
wound
When assessing the size,
what information do you
need to gather?
Length, width, depth, extent
of tunneling
When assessing the
drainage, what information
do you need to gather?
color, odor, amount, type
(remember COAT, the
drainage coats the wound)
When assessing color,
what color would indicate
healthy tissue?
Erythema (red)
Erythema indicates what
in wound healing?
typically indicates granulation
tissue; wound is in the
inflammatory or proliferative
phase of wound healing
When a wound is
erythemic, what do you
need to do?
protect the wound and keep it
most
When a wound is yellow,
what does this indicate?
infection or fibrous slough
and indicates that wound is
not ready to heal
eschar scabs or dry crust that result
from trauma or infection
eschar is commonly
referred to as black wound color
Black wound color
indicates
the presence of dead tissue
that is dehydrated; may be
covered w/eschar, the wound
can not be assessed when
eschar is present and it's an
excellent medium for
bacterial proliferation.
Why is eschar a good
medium for bacterial
growth?
It's moist and dark
When can a wound not be
classified?
If the wound contains eschar
it can not be properly
assessed.
When is the only time that
you do not want to remove
necrotic tissue?
When it's on the heel.
Why do you not want to
remove necrotic tissue on
the heel?
It will increases the risk of
osteomyelitis
mechanical debridement wet to moist dressing change
autolytic debridement cover wound and let the body
heal by itself
enzymatic debridement creams and ointments that eat
unhealthy tissue
biological debridement
(maggot therapy) maggots are
placed into the wound and
eats dead tissue
osteomyelitis infection of the bone
When taking a wound
culture, what do you need
to do first?
Clean the wound
Whose responsability is it
to do a tissue biopsy? The doctor
Purulent Pus, yellow, green, tan or
brown
serious fluid clear or light pink
sangionous blood
serousangounous blood and serum
What types of medications
can you give to treat
wounds?
oral, IV, and/or topical
What is the cause of
pressure ulcers?
compression of soft tissue
between two hard surfaces
causing occlusion of
capillaries, the tissue becomes
ischemic and dies
What are the factors to
consider in the cause of
the pressure ulcer?
pressure intensity, pressure
duration and tissue tolerance
What are the risk factors
for development of
pressure ulcers?
friction and sheer, decreased
mobility, decreased sensory
perception, fecal and/or
urinary incontinence, poor
nutrition
What tool do you use to
assess risk for pressure
ulcers?
Braden Scale
What is the braden scale
score that indicates your pt
is at risk?
<18
What are some
interventions for
prevention of pressure
ulcers?
assess skin, reposition pt and
shift weight every 15 min
when sitting, limit time at the
HOB, relieve pressure on
heels and keep bony
prominances from direct
contact with each other,
consider pressure relieving
devices, use a lifting device
The greatest pressure is at
which area? The sacral area
What are the two highest
risk areas for pressure
ulcers?
sacral and heels
bogginess/sponginess is an
indicator of? Skin breakdown
When do you change the
stage of a wound?
You can change it going up
(from a stage 1 to a stage 4)
but never going down.
Whose responsability is it
to intervene when a pt is
developing a potential
pressure ulcer?
The nurses
Stage 1 pressure ulcer Skin intact, non-blanching
redness
blanching push on red skin and the
redness goes away
What do you need to do
when you have a stage 1
pressure ulcer?
Relieve pressure
Stage 2 pressure ulcer
small crater, top layer of skin
broken, limited to the dermal
skin
What do you do for a stage
2 pressure ulcer?
use a hydrocoylloid dressing
to protect the skin
Stage 3 pressure ulcer damage goes down to the
subQ tissue
Stage 4 pressure ulccer
through the fascia and
beneath, you may be able to
see the bone
When you are dealing with
a pressure ulcer, when it is
the nurses vs the doctor's
responsability?
Stage 1 and 2 are usually
cared for by a nurse; stage 3
and 4 are usually taken care
of by a MD
Why are diabetics
predisposed to pressure
ulcers?
diabetics lose protective
sensation, they just don't feel
the damage being done and
that is why they get their feet
inspected at each visit.
When you have a wound,
what condition do you
want the wound bed to be
in?
moist (NOT WET)
What is normally used to
clean the wound? Normal saline
What is the purpose of
wound vac therapy?
Remove fluids, promotes
moist wound healing
environment, helps to draw
wound edges together, helps
promote perfusion, removes
infectious materials, helps
protect the wound
environment
[Show More]