CBCS Exam Study Guide Latest 2022 update
$ 8

Medtech Laws Exam
$ 18

ICT2622 SEM 2 ASSIGNMENT 2 2023
$ 15

AVIA 245 FINAL EXAM COMPLETE
$ 11

PSYC 503 Interview and Reflection Project.docx PSYC 503 Interview and Reflection
$ 10

IRC Study Guide
$ 8

Neuron function worksheet with complete solution
$ 8

Solution Manual for Introduction to Business Analytics, 1st Edition By Vernon Richardson and Marcia Watson Verified Chapter's 1 - 12 | Complete
$ 7.5

EMT Final Exam(completed)2022
$ 11

Cloud Native Java Designing Resilient Systems with Spring Boot, Spring Cloud, and Cloud Foundry Josh Long and Kenny Bastani
$ 13

NURS 190.
$ 8

CAISS CERTIFICATION SET EXAM
$ 19

OSHA Basic Orientation Plus Test | 50 Questions with 100% Correct Answers | Verified | Updated 2023
$ 9

Physics_mark_2020.pdf
$ 10.5

Ethical Hacking and Countermeasures, Threats and Defense Mechanisms, 2e EC-Council (Review Question Answers)
$ 25

[eBook] [PDF] Python for Programmers By Oswald Campesato
$ 25
.png)
ATI Maternal Newborn, Q&A
$ 10

Anatomy MCQ ( PDFDrive )
$ 30

Informative speech outline.docx
$ 10

Test Bank for Evolutionary Analysis 5th Edition by Herron Jon; Freeman Scott ISBN 9780321998378 Chapter 1-20 A+ Latest
$ 19.5

ACQ 202 Module 2 Exam: Part II Planning - Acquisition Strategy Development Q/A GRADED A
$ 4

ISM 4210 ISM4210 LESSON7 DSC.
$ 4

17-Responsibility-Accounting-Reporting
$ 30

MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE COMPLETED SOLUTIONS
$ 14

Fred O Macintyre V5 PC CASE STUDY
$ 7

DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 STUDY GUIDE COMPLETE WITH ELABORATE AND CLEAR LABELLED DIAGRAMS
$ 10

SAP Commerce Cloud Business User Certification / Score 100% / 2025 Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 9

Arizona State UniversityEET 113Experiment #16_Peak and RMS AC Voltage
$ 8

ATI_Obstetrics
$ 8
.png)
ServSafe Manager Exam with Complete Solutions
$ 9

WGU C213
$ 11
Instructor Solution Manual for Advanced Topics in Applied Mathematics: For Engineering and the Physical Sciences. 1st Edition. 2011, Sudhakar Nair
$ 22

Math 417 homework 2 solutions
$ 13

BCAT Study Guide (Exam Graded A+)
$ 7
.png)
case study | best case study | 2022 | 5 pages
$ 9

[eBook] [PDF] Google Gemini for Python_ Coding with Bard By Oswald Campesato
$ 25

eBook Birds of the Middle East 2nd Edition By Richard Porter Simon Aspinall
$ 30

Physics 17 HW 1
$ 7

MILESTONE 2 RETAKE NEW EXAM STUDY GUIDE SOLUTION
$ 10

RN ATI CAPSTONE COMPREHENSIVE STUDY GUIDE
$ 21.5

SPD 510 Module 5 Assignment
$ 7

[eBook] [PDF] Communicating Science In Times Of Crisis COVID-19 Pandemic 1st Edition By H. Dan O’Hair, Mary John O’Hair
$ 30
GCSE (9–1) Mathematics J560/04 Paper 4 (Higher Tier) May 2023 QP
$ 4

NR 451 Assignment Week 6 EBP Change Process FORM
$ 11

NRNP – 6531 Week 8 Knowledge Check
$ 14

eBook Electrical Engineering Principles and Applications 7th Edition By Allan R. Hambley
$ 20

Pearson Edexcel Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE In Further Pure Mathematics (4PM1) Paper 2
$ 6
Virginia Business Strategy Coursera Quiz (Questions and Answers) Answer key.
$ 15.5

NR 602 Final Exam Study Guide-comprehensive-2022
$ 16

APEA 3P Exam Pre1
$ 14

Concordia UniversityMECH 412412_Assignment_3_2008F_solution Computer Aided Mechanical Design
$ 11

Definite Integration
$ 15.5

ATI_PHARM_PROCTORED_29
$ 10.5

Matillion Certification / Score 100% / 2025 Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 9

Assignment_2_2_.docx (1).pdf
$ 18.5

The Enlightenment Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 6

Appendicitis/Appendectomy RAPID Reasoning Suggested Answer Guidelines
$ 13
.png)
Pearson Edexcel Question paper + Mark Scheme (Results) [merged] January 2022 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE In Mathematics B (4MB1) Paper 01
$ 7

Antepartum NCLEX Test Bank Questions with Answers and Rationales
$ 12
.png)
MSMIT CSC550 Week1_hw Chapter 2_Problems. All Answers Provided.
$ 9.5

CCHT certification preparation test already passed
$ 6

MATH 221 Week 4 Discussion Post
$ 7

Purdue UniversityCS 252HW1-Spring2020
$ 11
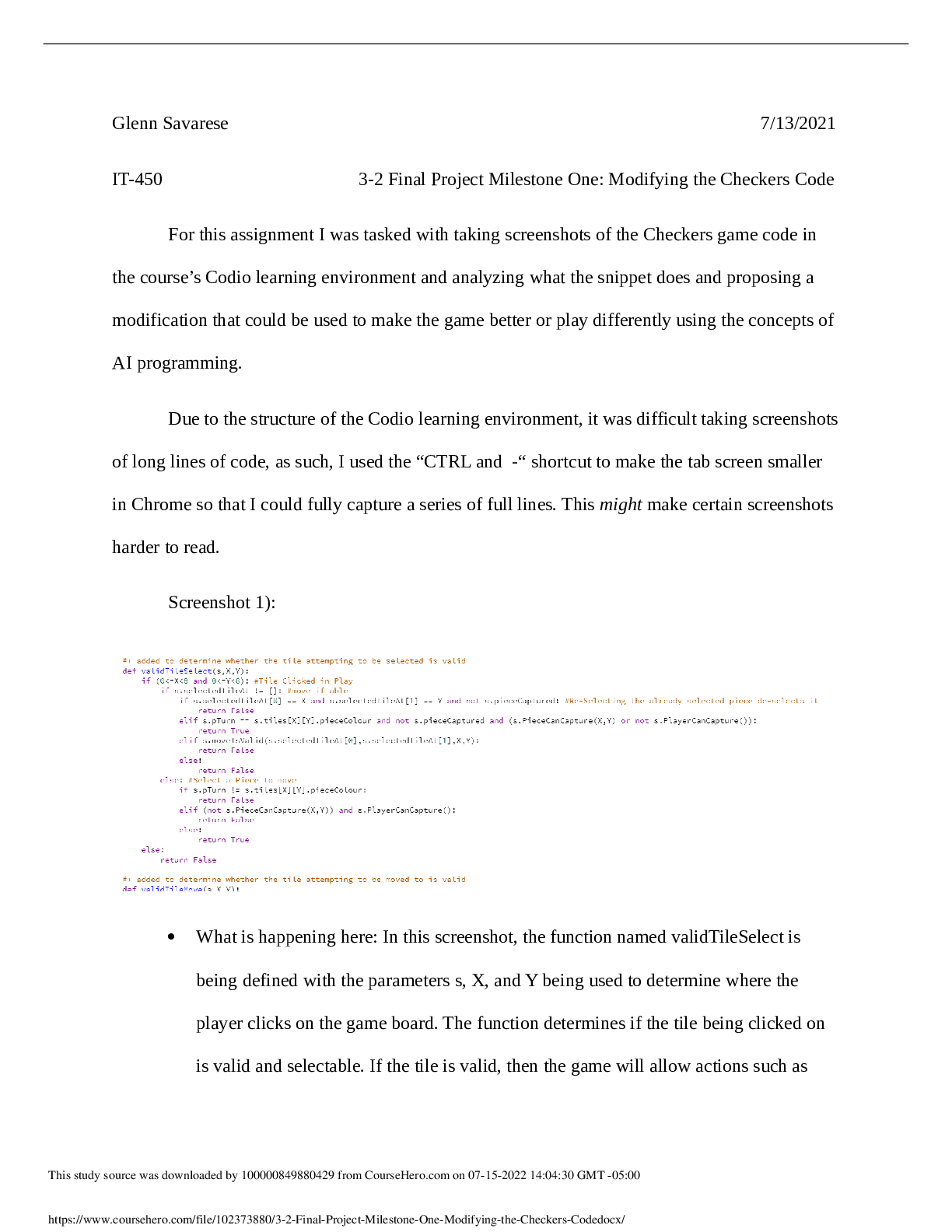
Final Project Milestone One Modifying the Checkers Code
$ 6.5

eBook Free Radical Biology of Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders 1st Editiony Asis Bala
$ 30

[eTextBook] (EPUB) [PDF] Family Law, Cases and Materials 7th Edition By Judith Areen, Marc Spindelman, Philomila Tsoukala, Solangel Maldonado