Solutions Manual For Building Java Programs A Back to Basics Approach 4th Edition By Stuart Reges Marty Stepp (All Chapters, 100% Original Verified, A+ Grade)
$ 25

APEA-GI
$ 7

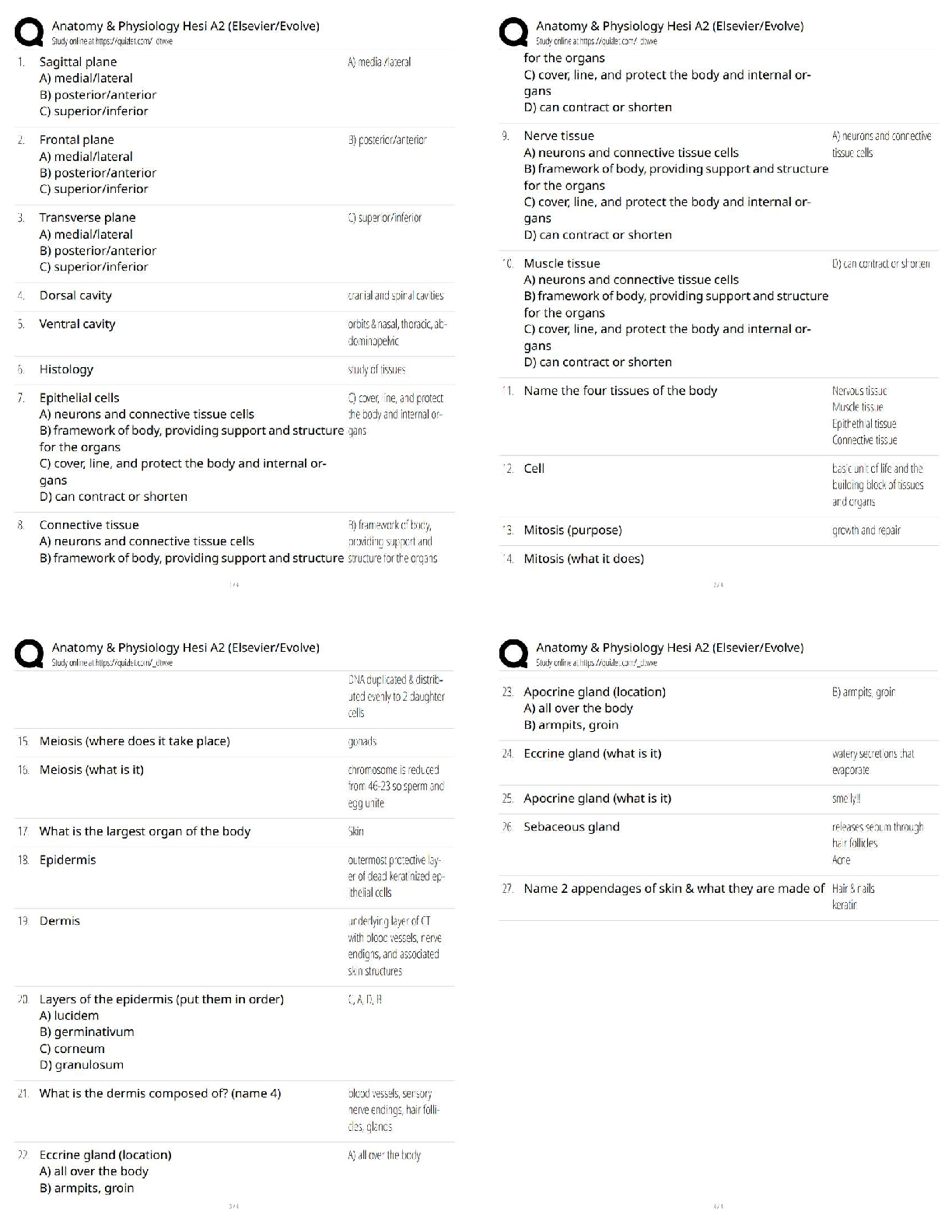
ATI PEDS FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
$ 8

CYSE 101 FINAL REVIEW | with COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 10
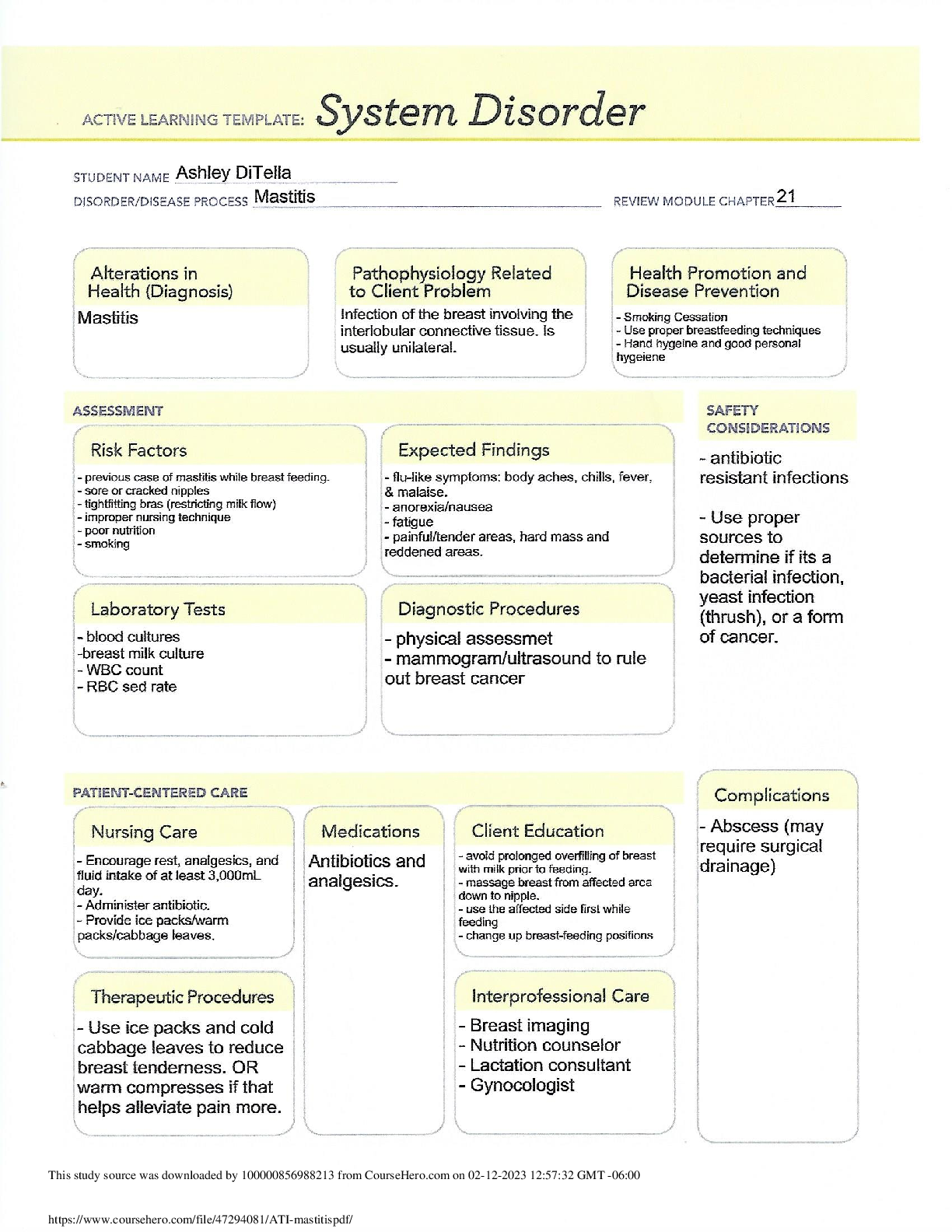
ATI_mastitis
$ 8.5

MATH 225N Week 7 Hypothesis Testing..RATED ASSIGNMENT!GOOD LUCK
$ 8

PDF(eBook) The Numerical Method of Lines and Duality Principles Applied to Models in Physics and Engineering,Fabio Silva Botelho,1e
$ 25
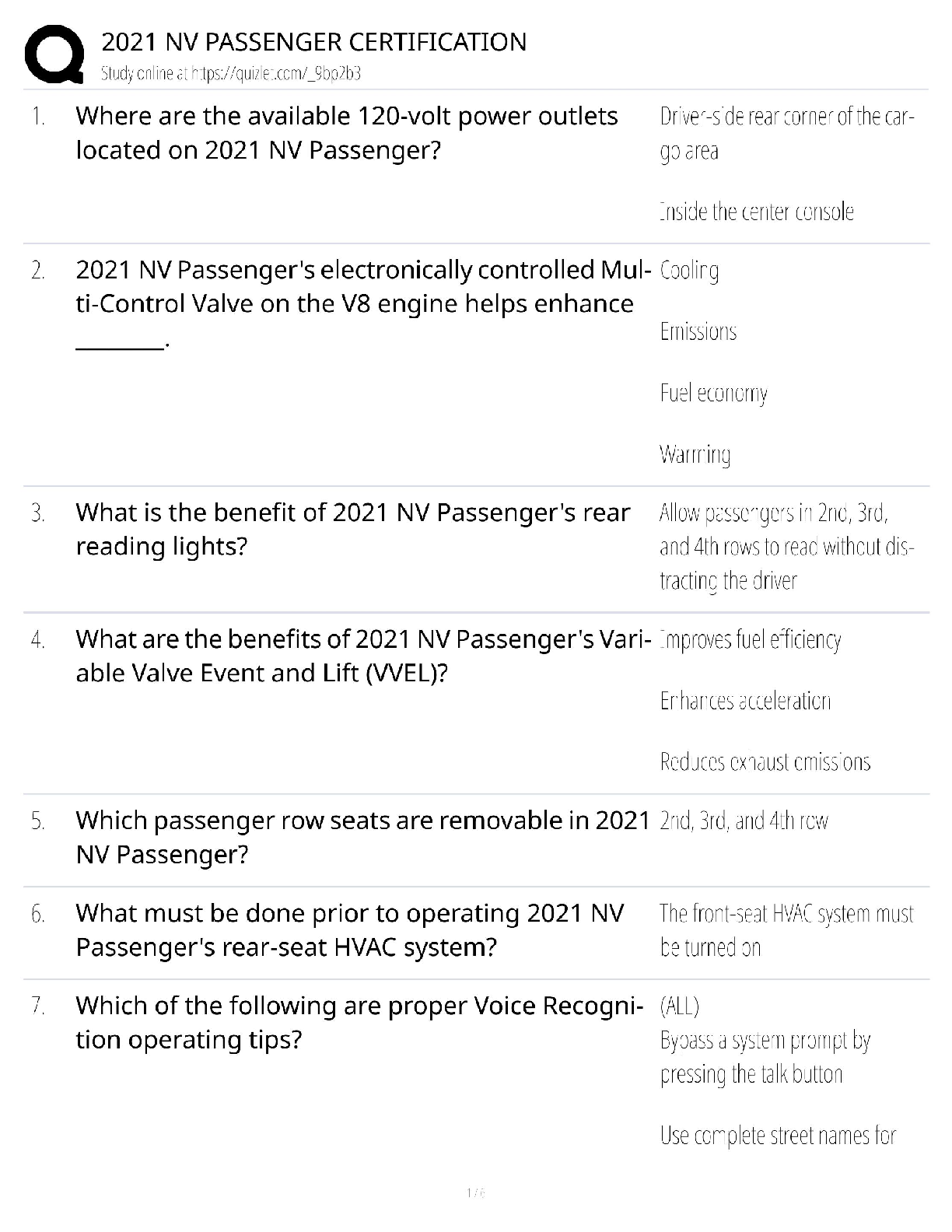
2021 NV Passenger Certification / Latest Study Guide / DMV Test Prep / Pass Guaranteed
$ 14.5

Hospice HESI Case Study – Latest Exam with Verified Detailed A+ Answers
$ 8

NURS 231Patho Portage Learning -[Graded A+ ] Questions And Answers-Portage Learning
$ 20

[eTextBook] [PDF] Source Separation in Physical-Chemical Sensing By Christian Jutten, Leonardo Tomazeli Duarte, Saïd Moussaoui
$ 25

NR 222 Week 5 Edapt
$ 30

NUR 3946L Finals Readiness Exam Q & S (UF) - (Individual Clinical Practice)
$ 12

TIME SERIES ANALYSIS
$ 8
.png)
PMK-EE for E-5 (Career Information)
$ 7
PSY 140 life span module 3- Portage Learning
$ 14.5

eBook Oncogenic Viruses (Volume 2) 1st Edition By Moulay Mustapha Ennaji
$ 30

eBook Climate Change Alleviation for Sustainable Progression 1st Edition By Moonisa Aslam Dervash , Akhlaq Amin Wani
$ 30

[eBook] [PDF] Managing Machine Learning Projects By Simon Thompson
$ 25

NURS 661 Test 4 Review 2022 with complete solution
$ 7

CBL 1 - Noisy Breathing
$ 14

Danny Rivera.Focused Exam_ Cough _ Subjective Data_ Shadow Health. Complete Solution
$ 16

NATE core Exam | 71 Exam Questions with 100% Correct Answers
$ 5

Test Bank for Management Information Systems 5th Edition by Baltzan
$ 20

MGMT 180 Midterm Practice Questions Fall 2023
$ 13
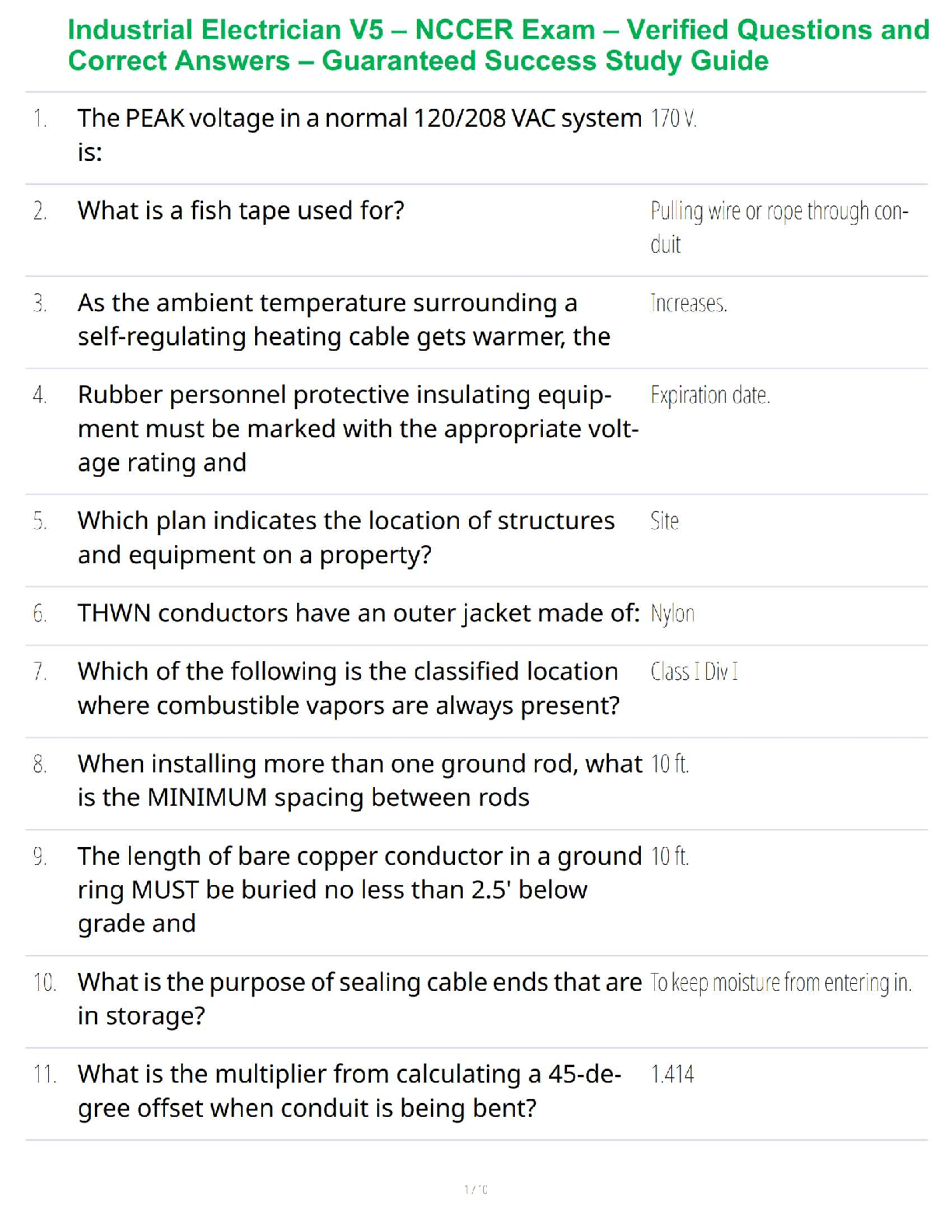
Industrial Electrician V5 – NCCER Exam – Verified Questions and Correct Answers – Guaranteed Success Study Guide
$ 8

Test Bank For Operations Management Processes and Supply Chains, 12th Edition By Krajewski, Malhotra, Ritzman
$ 20.5

NUR 635 Week 1 Discussion Question # 1/COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 11

Capella UniversityPM FPX 5334_Assesment_2_1 Risk Management Plan Taylor Kitchen Remodel
$ 13

Gen 499 Critical Thinking Quiz
$ 5

EXIT_HESI_EXAM_2022
$ 18

(EPUB) eBook Evolutionary Large-Scale Multi-Objective Optimization and Applications 1st Edition By Xingyi Zhang, Ran Cheng, Ye Tian, Yaochu Jin
$ 29

hesi_exit_v2_2022
$ 11

[eBook] [PDF] How Machine Learning is Innovating Today's World By Arindam Dey, Sukanta Nayak, Ranjan Kumar, Sachi Nandan Mohanty
$ 25
.png)
NUR 2063 Essentials of Pathophysiology Final Winter 2021
$ 14

EMT FINAL exam solution 2022 100% latest solution
$ 8.5

eBook [PDF] Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles By James Haslderman, Curt Ward
$ 30
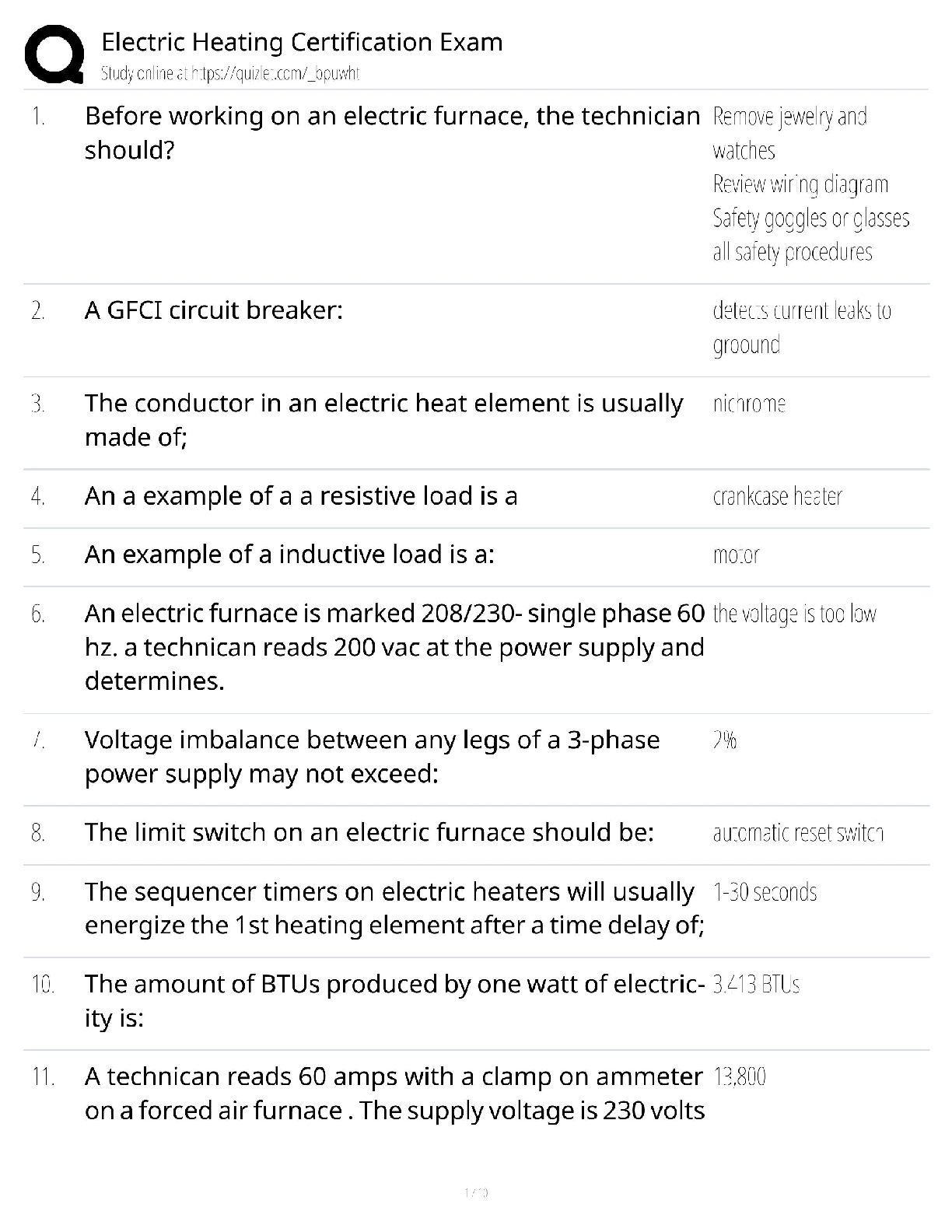
Electric Heating Certification Exam / Electrical Heating Systems / 2026 Update / Practice Test & Study Guide
$ 11.5

QMB3302 UF FALL FINAL VERSION 1,2 &3 (3 LATEST VERSIONS) EXAM
$ 23

GCSS-ARMY INTERMEDIATE NAVIGATION TEST 1 WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 8
.png)
Complete solution manual for Database Systems Design Implementation and Management 12th Edition/Top Score
$ 11

Pearson Edexcel A Level 3 GCE (9AA0/01) Arabic Paper 1 question paper + mark scheme 2024
$ 10

NETSUITE ERP CONSULTANT CERTIFICATION STDY GUIDE 2023 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
$ 12

Stationary Engineer Exam - Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions)
$ 24

Instructor’s Solution Manual for INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS
$ 17
.png)
ONCC Practice Tests (OCN - Treatment Modalities)
$ 7.5
.png)
CHAPTER 11 DECISION MAKING AND RELEVANT INFORMATION: answers
$ 6

Research Paper > Methodological recommendations for Summative Assessment “Physics” (advanced level) Grade 11
$ 6

BTEC Applied Science Unit One Biology 128 Questions with Answers,100% CORRECT
$ 11.5
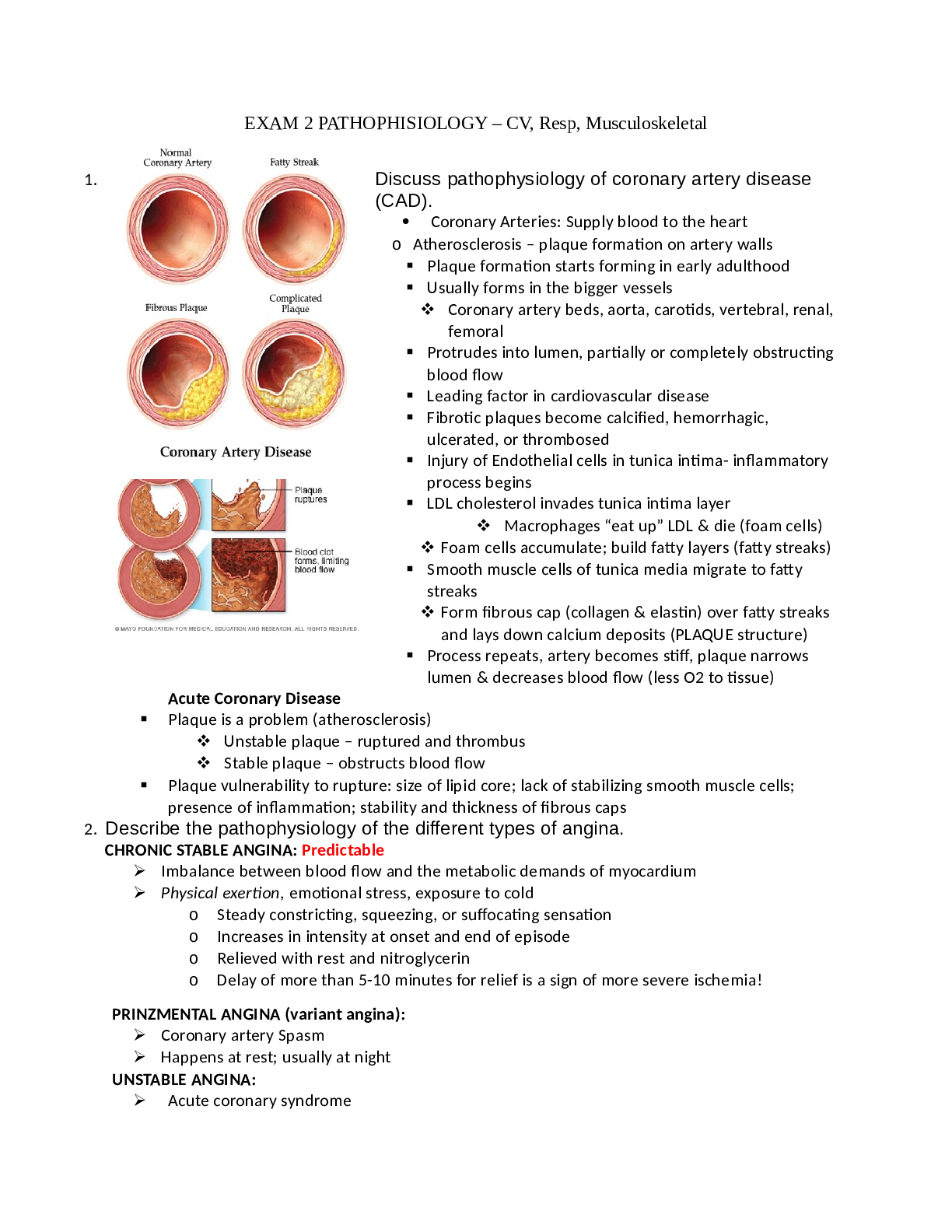
EXAM 2 PATHOPHISIOLOGY – CV, Resp, Musculoskeletal
$ 9

WGU C720 All Competencies Latest 2022 Already Passed
$ 15

Astronomy Assignment #8: CRATERING
$ 12.5

EXIT EXAM ATI 2023 Questions and Answers 100% Verified
$ 10
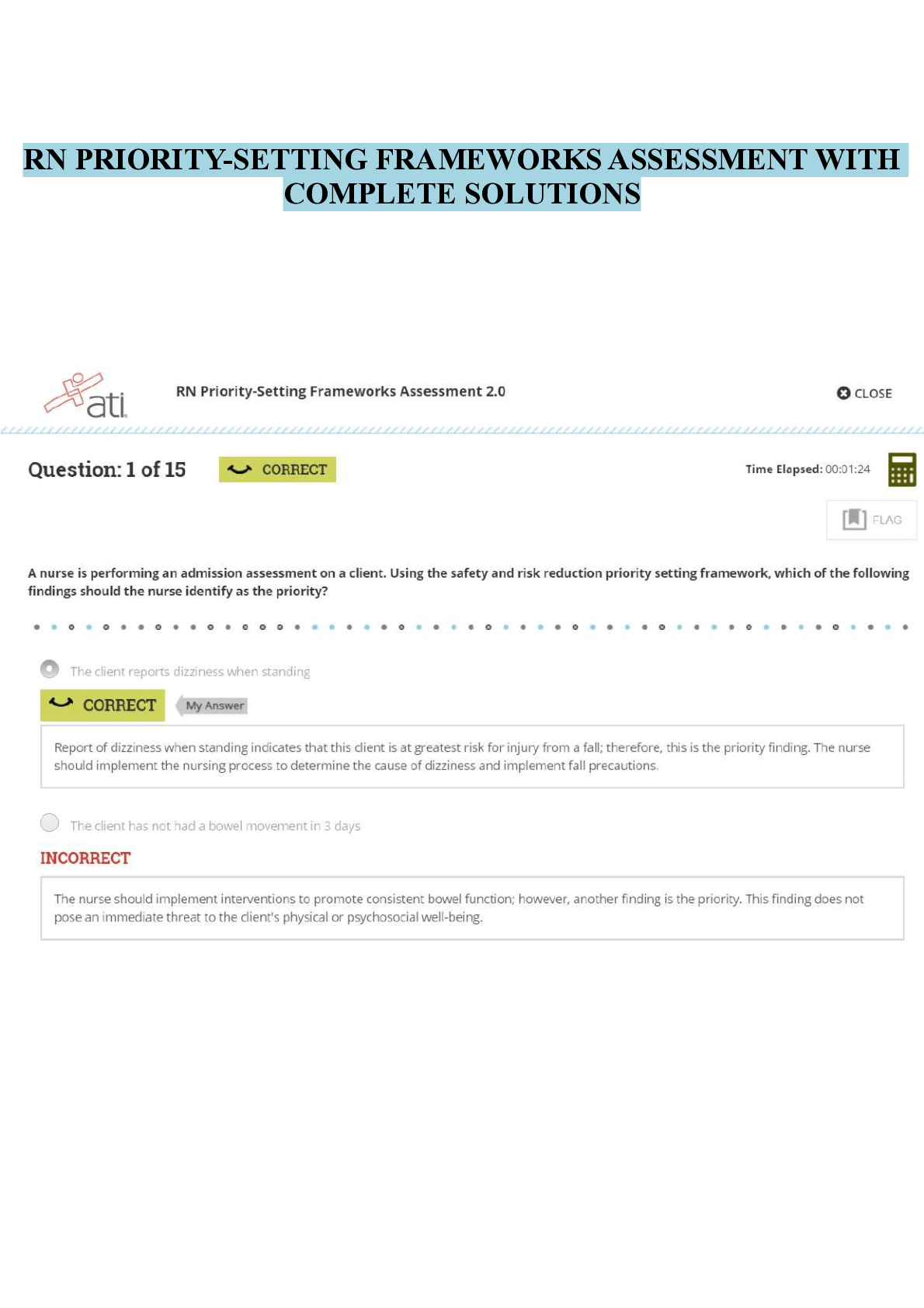
ATI RN Priority-Setting Frameworks Assessment With Complete Solutions
$ 18
PN PEDIATRIC NURSING
$ 30

CP 164 Data Structures _ test_Sorts_array.py
$ 7.5

ATI RN Comprehensive Predictor 2021 Form A
$ 17

ATI Community Health Version 1
$ 13.5
Forensic Quiz Death Investigation / CSI & Medicolegal Exam / 2025 Study Guide / Score 100% / Test Bank
$ 20

Operations Management Creating Value Along the Supply Chain, 2nd Canadian Edition, 2e Roberta Russell, Bernard Taylor, Tiffany Bayley, Ignacio Castillo (Solutions Manual)
$ 25
.png)
RHIA Domain 2 Questions and Answers 100% Verified
$ 10

Nursing 121 Updated Nclex Study Guide 2023
$ 14

Azure Exam Latest 104
$ 8

UIPath RPA Certification 2022
$ 12

ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR RETAKE
$ 8

ENG 105 Quiz 1 Study Test!
$ 4

Ncp on meningitis Handwritten Notes
$ 10

MAJOR ZONE STRATEGY
$ 8

HESI A2 Reading Passages Versions 1 & 2 2022/2023 Real! (with 100% CORRECT ANSWERS)
$ 20

NUR550 Focused Note -Chest Pain – Brian Foster
$ 10

[eBook-PDF] How It Works Book of Amazing Vehicles (11th Edition) – Bookazine by How It Works Team
$ 7.5

USPS Exam 421 Window Clerk Practice
$ 11

PMH-C Final Exam – Complete Questions & Verified Answers (2 Versions)
$ 26

ATI Comprehensive - Predictor review 2019-STUDY GUIDE
$ 12

ATI_comprehensive_predictor_JM
$ 10.5

eBook PDF What's that Sound An Introduction to Rock and Its History 6th Edition By John Covach, Andrew Flory
$ 30

USPAP 15-hour course Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 14

Operations And Supply Chain Management The Core 6th Edition By F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B. Chase TEST BANK
$ 25
.png)
PMP Certification Exam Study Guide A+ Work Latest 2022
$ 10
Comprehensive Preventive Dentistry
$ 20

Pearson Edexcel_A Level Physical Education_9PE0/01 Mark Scheme 2021 | Paper 1: Scientific Principles of Physical Education