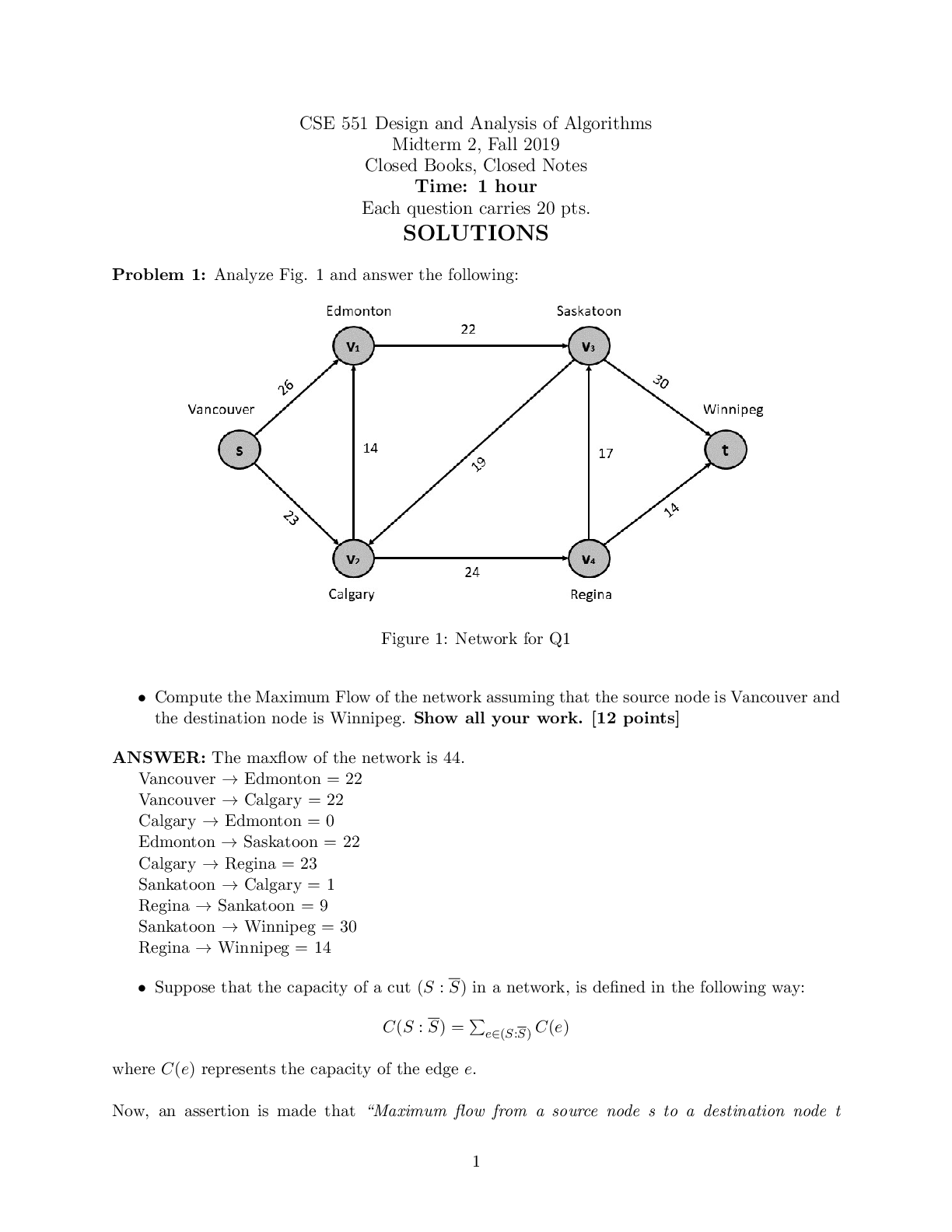
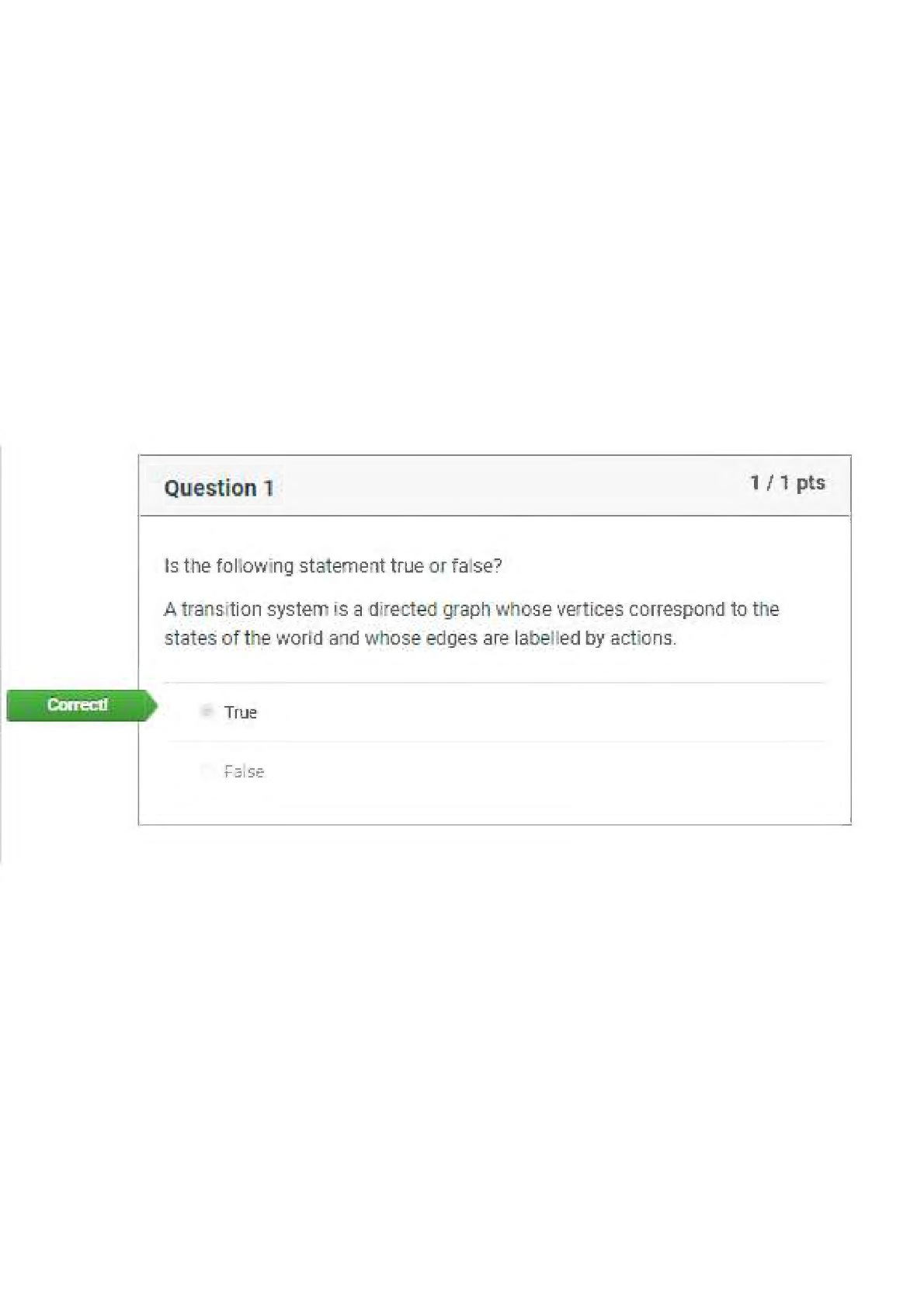
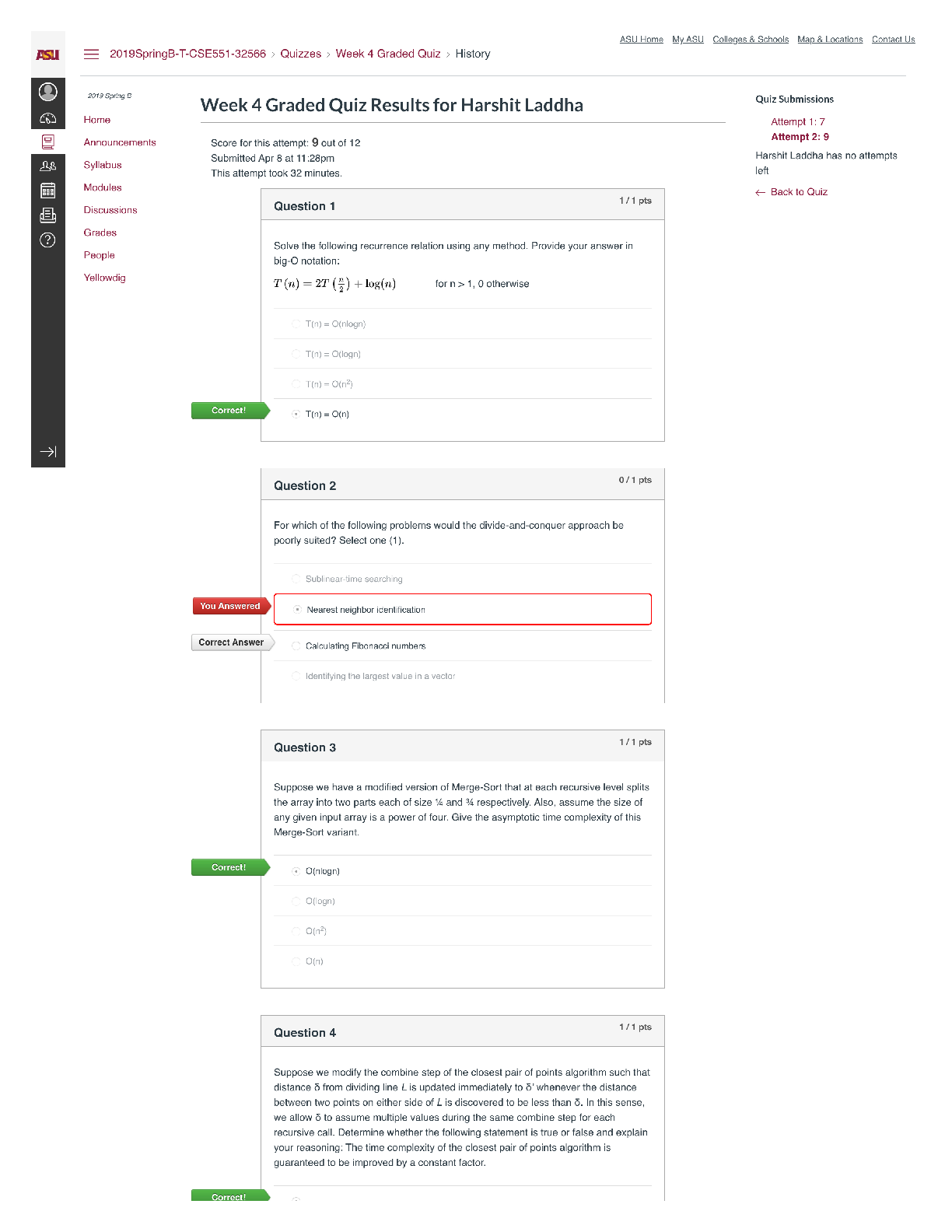
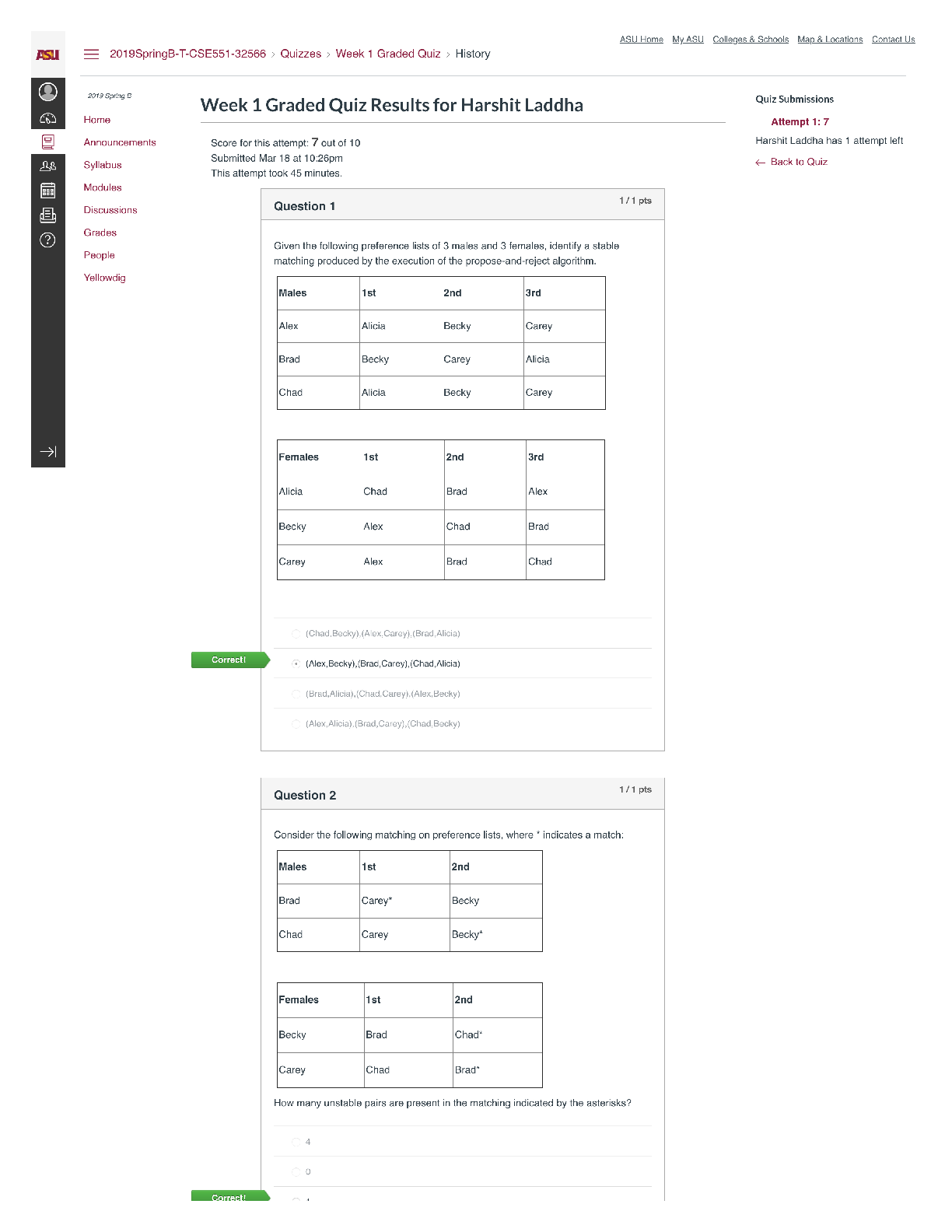
ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT
1. Management is:
A. An art
B. Both science and art
C. A science
D. Neither art nor science
2. Engineering is:
A. An art
B. Both science and art
C. A science
D. Neither art nor science
3
...
ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT
1. Management is:
A. An art
B. Both science and art
C. A science
D. Neither art nor science
2. Engineering is:
A. An art
B. Both science and art
C. A science
D. Neither art nor science
3. Engineers can become good managers only through __________.
• A. Experience
• B. Taking master degree in management
• C. Effective career planning
• D. Trainings
4. If you are an engineer wanting to become a manager, what will you do?
• A. Develop new talents
• B. Acquire new values
• C. Broaden your point of view
• D. All of the above
5. When engineer enters management, what is the most likely problem he
finds difficult to acquire?
• A. Learning to trust others
• B. Learning how to work through others
• C. Learning how to take satisfaction in the work of others
• D. All of the above
6. What management functions refers to the process of anticipating
problems, analyzing them, estimating their likely impact and determining
actions that will lead to the desired outcomes and goals?
• A. Planning
• B. Leading
• C. Controlling
• D. Organizing
7. What refers to the establishing interrelationships between people and
things in such a way that human and materials resources are effectively
focused toward achieving the goal of the company?
• A. Planning
• B. Leading
• C. Controlling
• D. Organizing
8. What management function involves selecting candidates and training
personnel?
• A. Organizing
• B. Staffing
• C. Motivating
• D. Controlling
9. What management function involves orienting personnel in the most
effective way and channeling resources?
• A. Directing
• B. Planning
• C. Organizing
• D. Leading
10. Actual performance normally is the same as the original plan and
therefore it is necessary to check for deviation and to take corrective action.
This action refers to what management function?
• A. Organizing
• B. Planning
• C. Controlling
• D. Staffing
11. What refers to management function which is to encourage others to
follow the example set for them, with great commitment and conviction?
• A. Staffing
• B. Motivating
• C. Controlling
• D. Leading
12. What refers to a principal function of lower management which is to
instill in the workforce a commitment and enthusiasm for pursuing the goals
of the organization?
• A. Directing
• B. Motivating
• C. Staffing
• D. Controlling
13. What refers to the collection of the tolls and techniques that are used on
a predefined set of inputs to produce a predefined set of outputs?
• A. Project Management
• B. Engineering Management
• C. Management
• D. Planning
14. Which is NOT an element of project management process?
• A. Data and information
• B. Research and development
• C. Decision making
• D. Implementation and action
15. What is the most essential attribute of a project manager?
• A. Leadership
• B. Charisma
• C. Communication skill
• D. Knowledge
16. In project management, what provides a simple yet effective means of
monitoring and controlling a project at each stage of its development?
• A. R & D model
• B. Project feasibility
• C. Life cycle model
• D. All of the above
17. What project life cycle model is the most relevant for information
technology project?
• A. Morris model
• B. Waterfall model
• C. Incremental release model
• D. Prototype model
18. In project management, “R & D” stands for:
• A. Retail Distribution
• B. Research and Development
• C. Repair and Develop
• D. Reduce and Deduce
19. In project management O & M stands for:
• A. Operation and Manpower
• B. Operation and Maintenance
• C. Operation and Management
• D. Operation and Mission
20. A project management must be very good in which of the following skills?
• A. Communication skills
• B. Human relationship skills
• C. Leadership skills
• D. All of the above
21. Project integration management involves which of the following
processes?
• A. Project plan development
• B. Project plan execution
• C. Integrated change control
• D. Quality planning
22. Project quality management involves all of the following processes
except:
• A. Quality planning
• B. Quality assurance
• C. Quality Control
• D. Quality feature
23. What is defined as an organized method of providing past, present, and
projected information on internal operations and external intelligence for use
in decision-making?
• A. Electronic Data Processing Systems
• B. Management Information System
• C. Central Processing System
• D. Data Management System
24. Middle management level undertakes what planning activity?
• A. Intermediate planning
• B. Strategic planning
• C. Operational planning
• D. Direct planning
25. Strategic planning is undertaken in which management level?
• A. Lower management level
• B. Middle management level
• C. Top management level
• D. Lowest management level
26. What is the advantage of free-rein style of leadership?
• A. Little managerial control and high degree of risk
• B. Time consuming and cost ineffective
• C. Little ideas from subordinate in decision- making
• D. All of the above
27. If you are appointed as a division manager, your first task is most likely
to
• A. Set goals
• B. Determine the resources needed
• C. Set a standard
• D. Develop strategies and tactics
28. What is defined as the process of planning, organizing, and controlling
operations to reach objective efficiently and effectively?
• A. General Management
• B. Engineering Management
• C. Production Management
• D. Operations Management
29. For a project manager to achieve his given set of goals through other
people, he must have a good __________.
• A. Interpersonal skills
• B. Communication skills
• C. Leadership
• D. Decision- making skills
30. What type of conflict do managers encounter when there is disagreement
on issues of territorial power or hidden agenda?
• A. Technical opinion conflict
• B. Politics
• C. Ambiguous roles
• D. Managerial procedure conflict
31. The process of partitioning an organization into subunits to improve
efficiency is known as __________.
• A. Division of labor
• B. Segmentation
• C. Departmentalization
• D. Territorialization
32. By departmentalization of an organization, it decentralizes __________?
• A. Authority
• B. Responsibility
• C. Accountability
• D. All of the above
33. What type of committee companies or corporations created for a short
term purpose only?
• A. Interim committee
• B. Temporary committee
• C. Standing committee
• D. Ad hoc committee
34. What refers to a description of whether the objectives are accomplished?
• A. Efficiency
• B. Effectiveness
• C. Ability to manage
• D. Decision- making ability
35. An engineering is required to finish a certain engineering job in 20 days.
He is said to be __________ if he finished the job within the required period of
20 days
• A. Efficient
• B. Effective
• C. Reliable
• D. Qualified
36. If an engineer provides less input (labor and materials) to his project and
still come out with the same output, he is said to be more __________.
• A. Managerial skill
• B. Economical
• C. Effective
• D. Efficient
37. To determine a qualified applicant, the engineer manager will subject the
applicant to a test that is used to measure a person’s current knowledge of a
subject?
• A. Interest test
• B. Aptitude test
• C. Performance test
• D. Personality test
38. What type of training is a combination of on-the-job training and
experience with classroom instruction in particular subject?
• A. On-the-job training
• B. Vestibule school
• C. Apprenticeship program
• D. In-basket
39. What type of authority refers to a specialist’s right to oversee lower level
personnel involved in the project regardless of the personnel’s assignment in
the organization?
• A. Top authority
• B. Line authority
• C. Staff authority
• D. Functional authority
40. When a consultant or specialist gives advice to his superior, he is using
what type of authority?
• A. Top authority
• B. Line authority
• C. Staff authority
• D. Functional authority
41. When structuring an organization, the engineer manager must be
concerned with the determining the scope of words and how it is combined in
a job. This refers to __________.
• A. Division of labor
• B. Delegation of authority
• C. Departmentation
• D. Span of control
42. When structuring an organization, the engineer must be concerned with
the grouping of related jobs, activities, or processes into major organizational
subunits. This refers to:
• A. Division of labor
• B. Delegation of authority
• C. Departmentation
• D. Span of control
43. Which technique will the manager use when evaluating alternative using
qualitative evaluation?
• A. Comparison technique
• B. Intuition and subjective judgment
• C. Rational technique
• D. Analytical technique
44. Which technique will the manager use when evaluating alternative using
quantitative evaluation?
• A. Rational and analytical techniques
• B. Intuition and subjective judgment
• C. Comparison in number technique
• D. Cost analysis
45. What refers to the strategic statement that identifies why an organization
exists, its philosophy of management, and its purpose as distinguished from
other similar organizations in terms of products, services and markets?
• A. Corporate mission
• B. Corporate vision
• C. Corporate character
• D. Corporate identity
46. What refers to a process of influencing and supporting others to work
enthusiastically toward achieving objectives?
• A. Power
• B. Leadership
• C. Teamwork
• D. Charisma
47. What describes how to determine the number of service units that will
minimize both customer’s waiting time and cost of service?
• A. Queuing theory
• B. Network model
• C. Sampling theory
• D. Simulation
48. What refers to the rational way to conceptualize, analyze and solve
problems in situations involving limited or partial information about the
decision environment?
• A. Sampling theory
• B. Linear programming
• C. Decision theory
• D. Simulation
49. What is quantitative technique where samples of populations are
statistically determined to be used for a number of processes, such as
quality control and marketing research?
• A. Sampling theory
• B. Linear programming
• C. Statistical decision theory
• D. Simulation
50. The engineer manager must be concern with the needs of his human
resources. What refers to the need of the employees for food, drinks, and
rest?
• A. Physiological need
• B. Security need
• C. Esteem need
• D. Self - actualization need
[Show More]

.png)



.png)