Astro 7N Exam 1
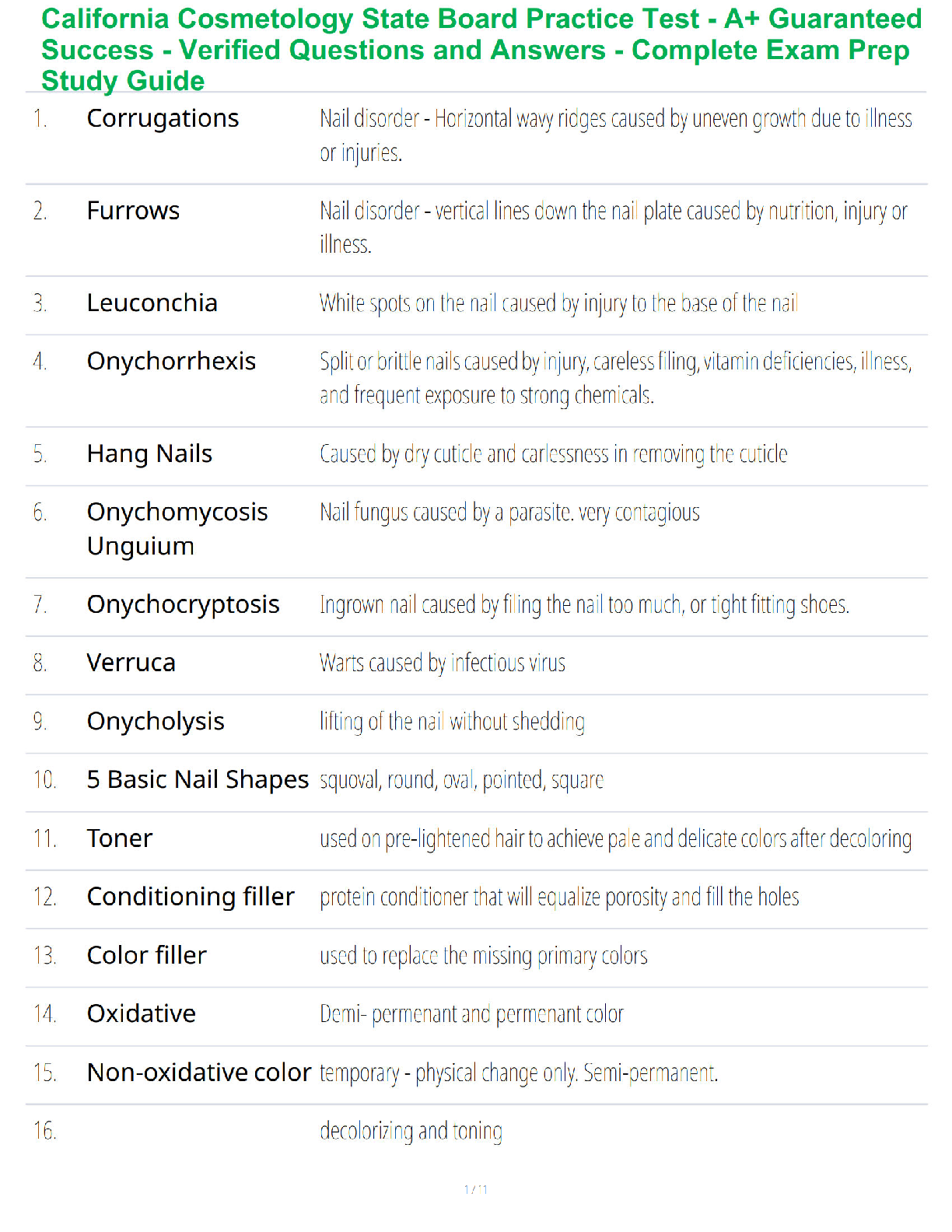
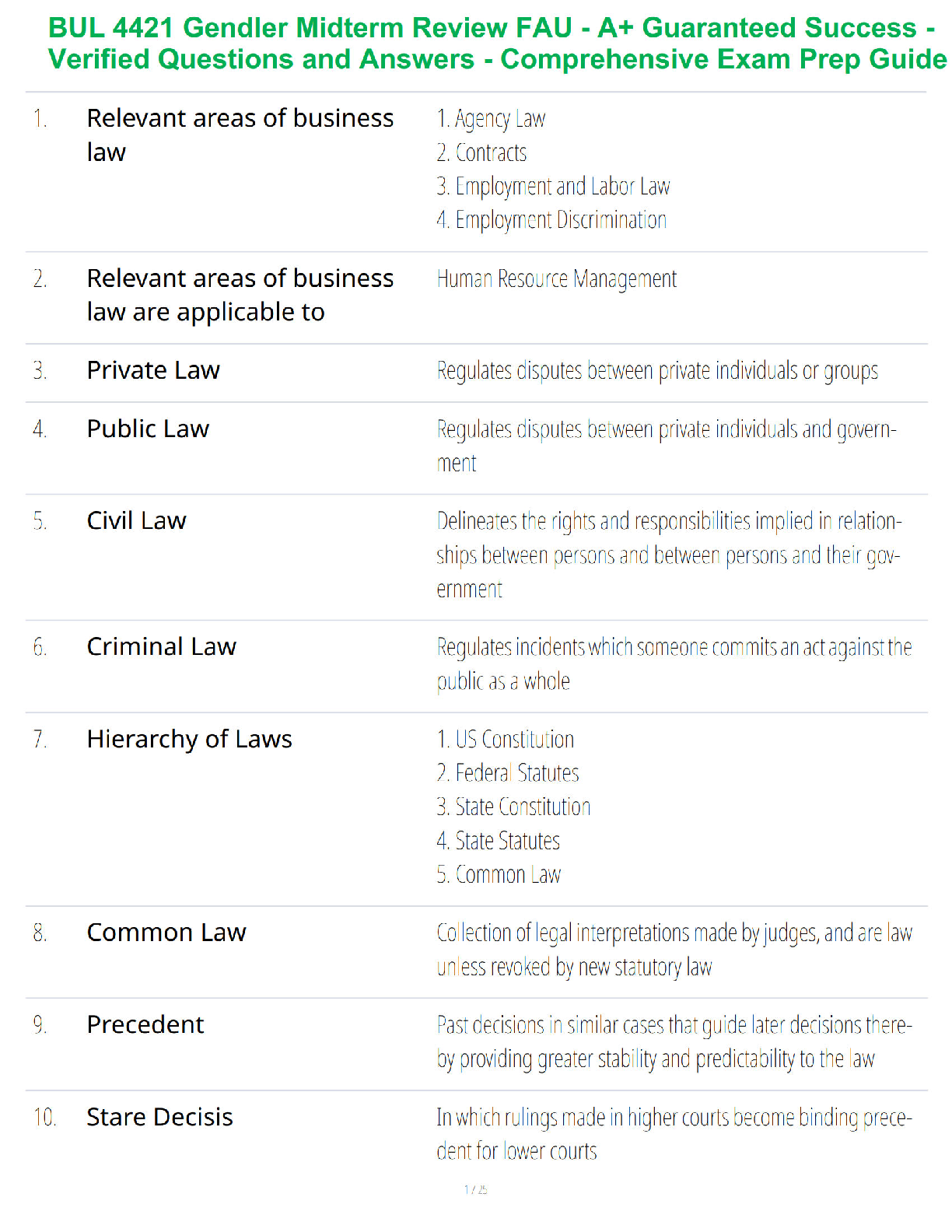
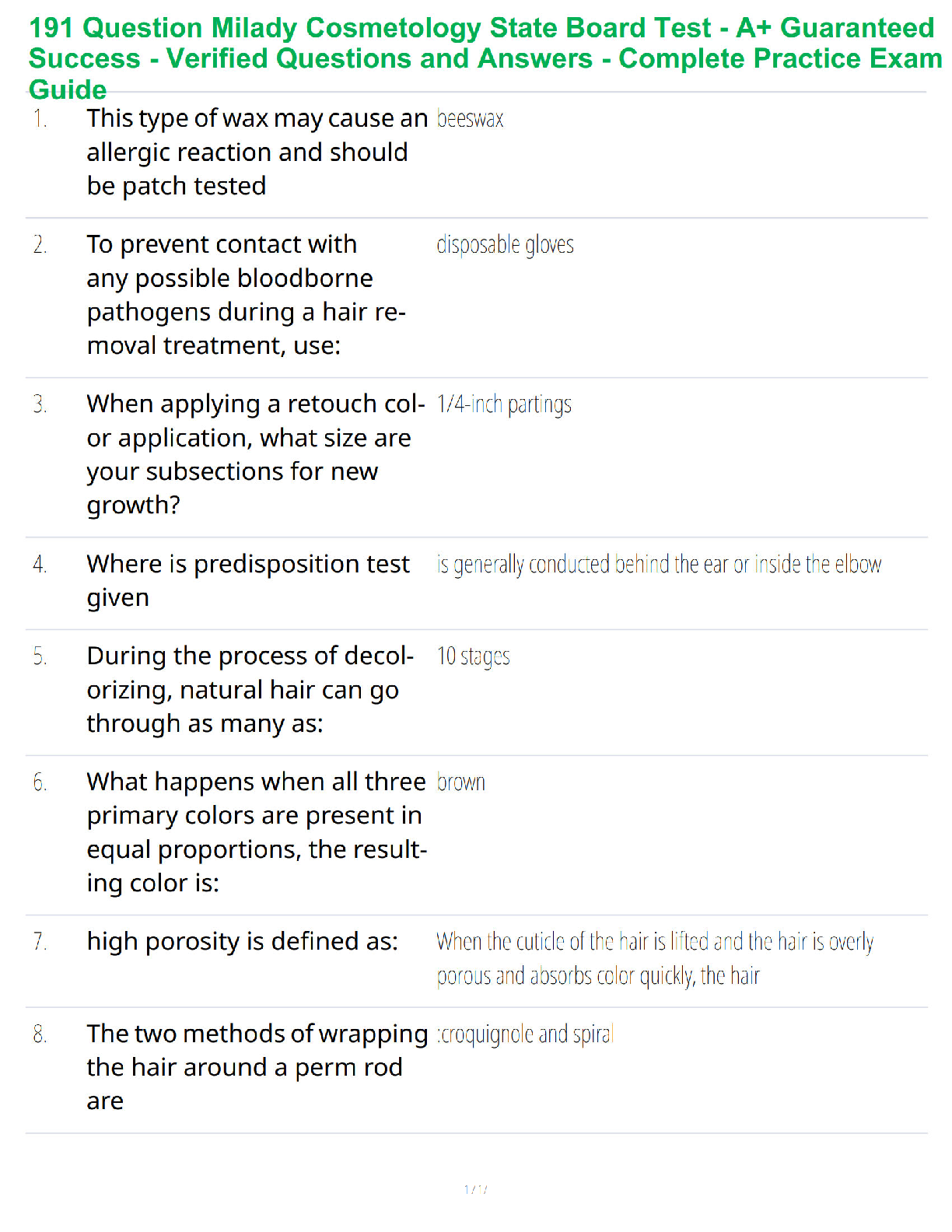
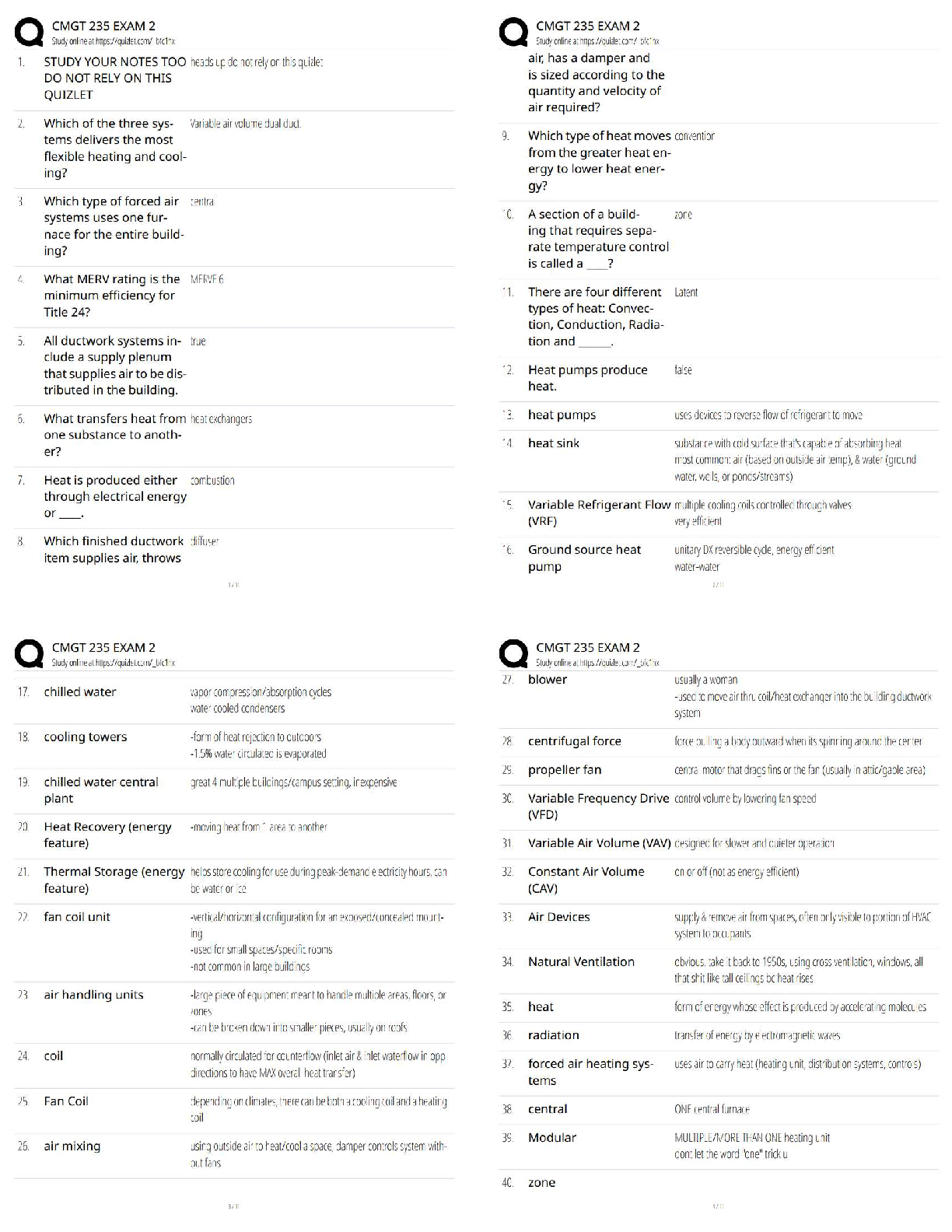
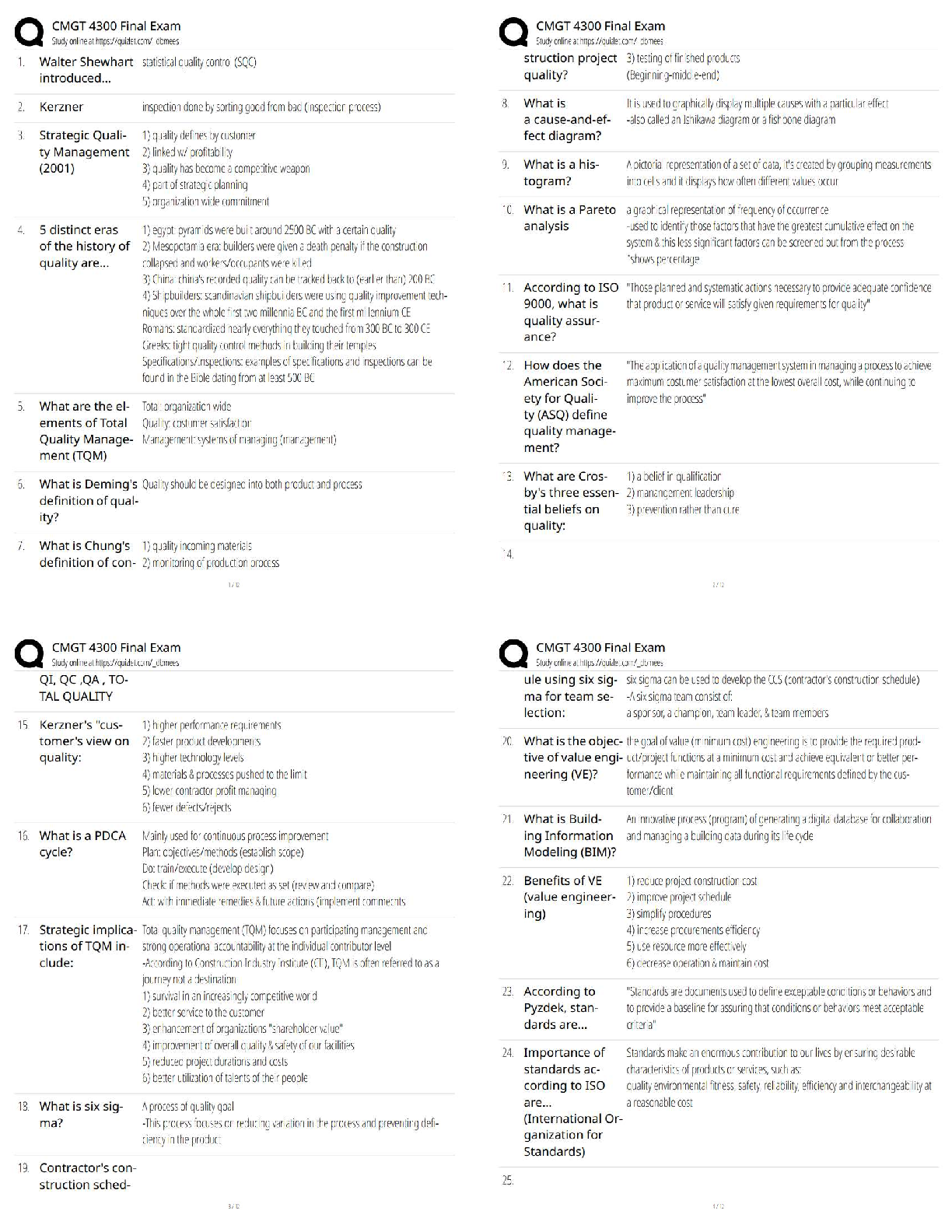
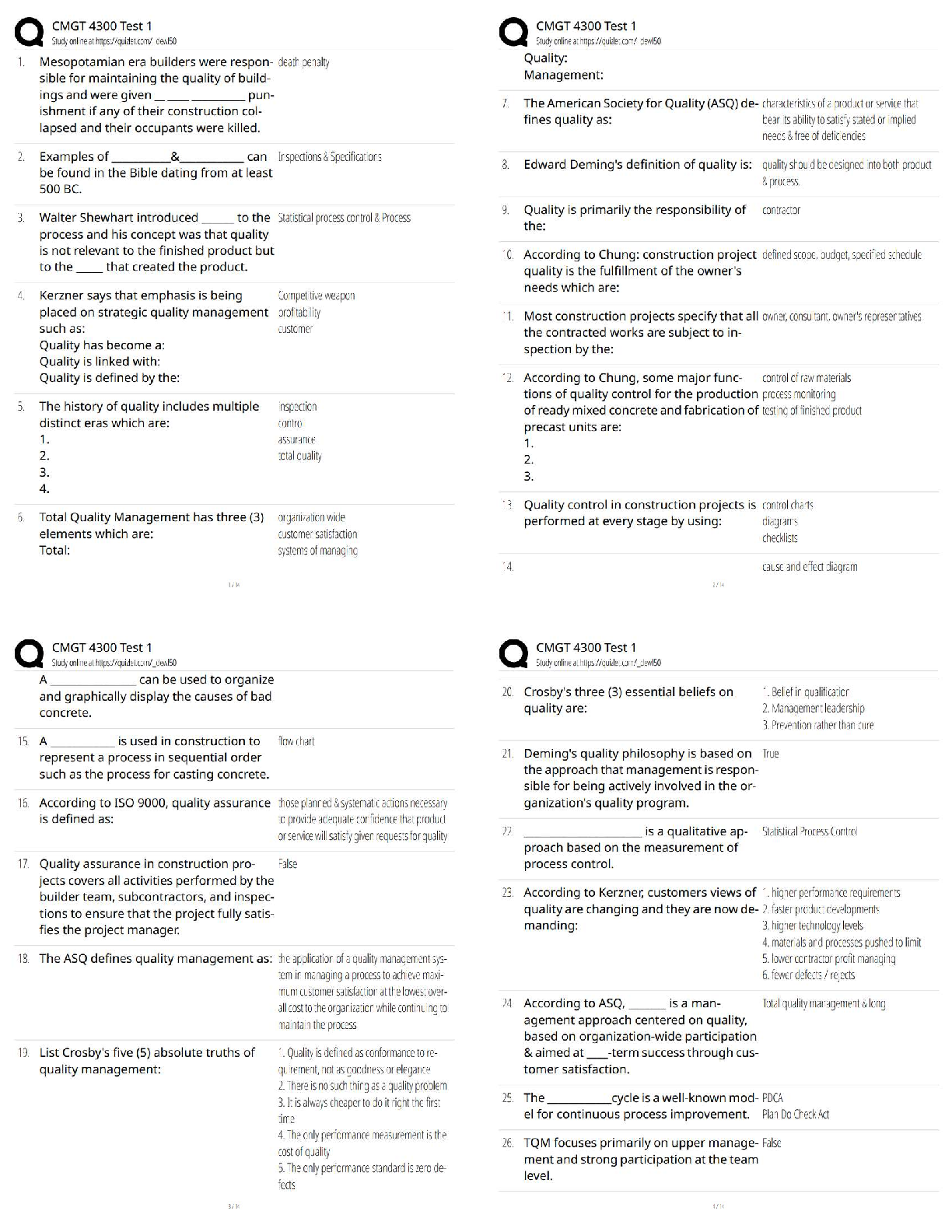
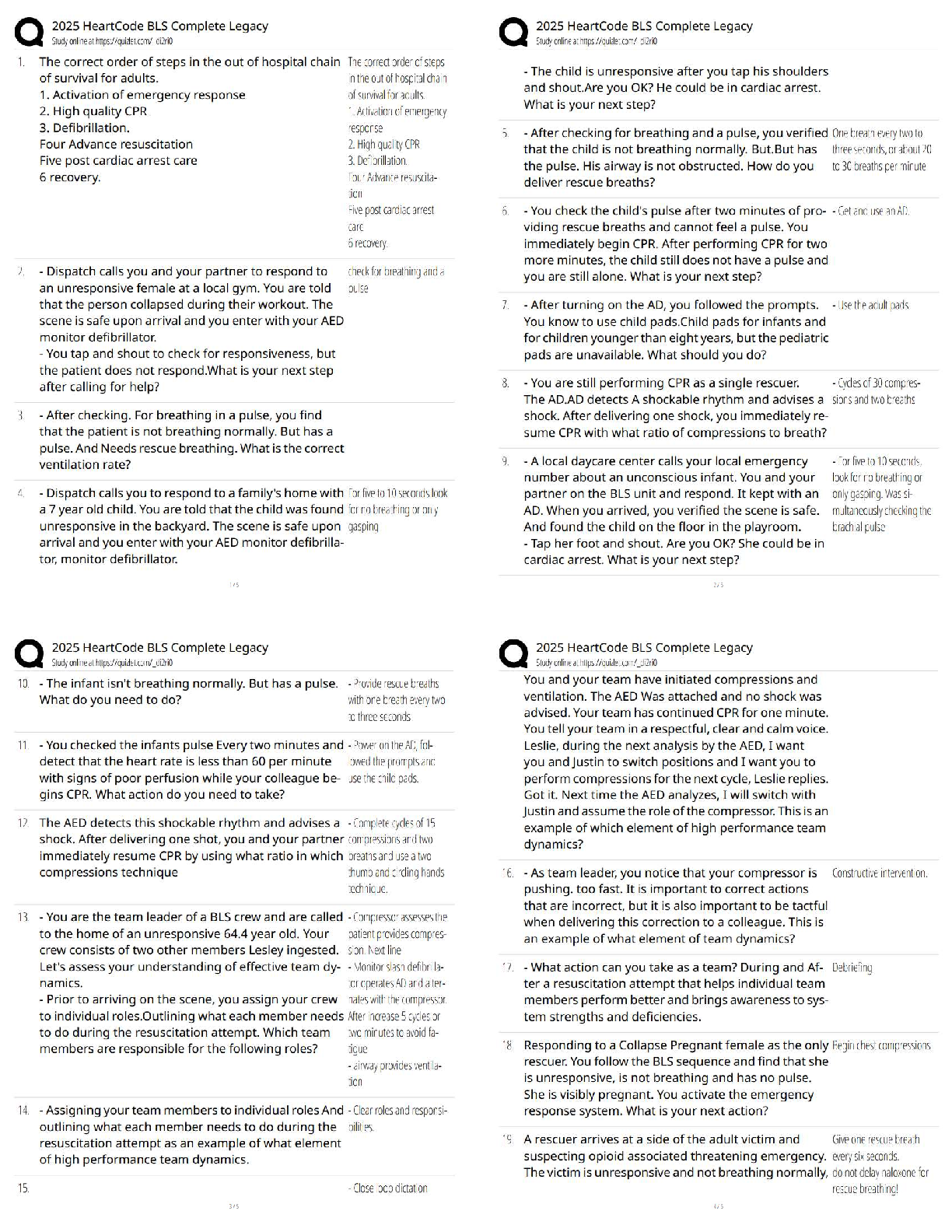
The force of gravity by the Sun keeps the planet in orbit around it, but how do the planets affect
the sun? - ✔✔They exert an equally strong pull on the sun, causing it move slightly
Newton's First
...
Astro 7N Exam 1
The force of gravity by the Sun keeps the planet in orbit around it, but how do the planets affect
the sun? - ✔✔They exert an equally strong pull on the sun, causing it move slightly
Newton's First Law - ✔✔An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion
with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
ex: if the sun suddenly disappeared, the Earth would continue in the direction that it was
traveling in its orbit at that time
Newton's Second Law - ✔✔The acceleration of a body due to a force will be in the same
direction as the force, with magnitude directly proportional to its mass
Force = mass x acceleration
A smaller mas will move faster, if the same force is applied to it
Newton's Third Law - ✔✔For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
The Sun exerts force on planets, and they orbit it - he planets exert equal force on Sun, but it only
moves slightly because of its very large mass relative to the planets
Surface Gravity on a Planet - ✔✔the strength of gravity: g = m/r^2
where M is the mass of the planet and R is its radius. Note the radius is squared but the mass is
not.
More mass = more gravity.
- If the mass of a planet were twice that of another, but they had the same radius, the gravity felt
on the surface of the more-massive one would be twice as strong.
Larger separation = less gravity.
- If the radius of a planet were twice that of another, the gravity is 1 / (2) 2 = 1/4 as strong.
Putting the effects of mass and radius together, you should be able to figure out the surface
gravity of Mars, relative to the Earth.
- Mars has 1/10 the mass of the Earth and 1/2 the radius of Earth. So for Mars,
g = (1/10) / (1/2) 2 = (1/10) / (1/4) = 4/10
Mars has a surface gravity 4/10 that of Earth. You will need to be able to do this type of estimate
for the test, given the numbers for mass and radius.
If I apply exactly the same amount of force to a pebble and a boulder, what will happen - ✔✔the
pebble will move faster
If the Earth were moved to half its current distance from the sun, how would the force of gravity
by the sun on the earth change? - ✔✔it would become 4 times weaker
Mass - ✔✔As the mass of the planet increases, the jump height does decreases by the same
factor
As the mass of the planet decreases, the jump height does increases by the same factor
According to Newton's Second law of motion, if the net force acting on the object increases
while the mass of the object remains constant, what happens to acceleration - ✔✔acceleration
increases
If the earth were moves to half its current distance from the Sun, how would the force of gravity
by the Sun on the Earth change - ✔✔it would become four times weaker
What did newton's law of universal gravitation tell us about how gravity works - ✔✔the force of
gravity from the sun will be stronger on object with more mass
If you were to sit on the ground, there would be a force due to gravity pulling you toward the
earth. which of the following is true according to newton's third law - ✔✔you are pushing the
earth away from yourself with the same force
what would happen to the earth sun's gravity somehow turned off instantaneously - ✔✔it would
continue to move in the line in the same direction it was moving when the gravity turned off
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation - ✔✔This law gives the force of gravity between any
two objects in the Universe. The force of gravity is proportional to (mass of object 1) × (mass of
object 2) divided by the distance between the two objects squared:
F M1 x M2 / d 2
Again, more mass = stronger gravity. If the objects were moved 2 times closer (or, to half of
their initial distance between), ...
F M1 x M2 / (1/2) 2 = M1 x M2 / (1/4) = 4 (M1 x M2)
... so, the gravitational attraction would become 4 times as great.
The Seasons, Day & Night - ✔✔Q: What causes day and night?
A: Rotation of the Earth on its axis.
Q: How does the Sun appear to move in the sky in the course of a day?
A: East to West, because of Earth's rotation. The stars and planets move in the same
way from our point of view, also, because of Earth's rotation.
Q: What happens to the Earth in one year?
A: It orbits the Sun, once (also referred to as one complete revolution about the Sun).
Q: Why do we have seasons?
A: The tilt of the Earth's axis of rotation, with respect to the plane of its orbit around
the Sun (and not because of changing distance from Sun).
The Earth's tilt is about 23 degrees.
Q: How is the Earth's axis tilted when we have summer in the Northern hemisphere?
A: With the North pole toward the Sun.
Q: What season is it in the Southern hemisphere when it is summer in the
Northern hemisphere?
A: Winter
The Seasons, Day & Night pt2 - ✔✔Winter begins on or about Dec. 21 = in the Northern
hemisphere, the nights are longer than days
Spring begins on or about March 21 = days and nights have equal length
Summer begins on or about June 21 = days longer than nights in the North
Fall begins on or about Sept. 21 = days and nights have equal length
Seasons would not happen if the Earth's axis were not tilted. The distance between the Earth and
the Sun does not change very much over the course of a year, so the temperature does not change
much for that reason. Without the tilt of Earth's axis there would be no seasons on Earth. Mars
has a similar tilt to its rotation axis as Earth does.
if earth rotated on it axis more slowly than it does now; - ✔✔days would be longer
if earth had its orbit changed so that all points along its orbit it were always the same distance
from the sun (circular orbit), how would this affect the seasons on earth? - ✔✔they would be the
same as they are now
a new planet orbits its star faster than the earth orbits the sun and it rotates more slowly than he
earth rotates. which is true - ✔✔the new planet has a shorter year than earth and a longer day
than earth
what time of year is it dark all (and night) at the south pole of earth? - ✔✔June
When the northern hemisphere is tilted TOWARDS the Sun the average daily temperature is
marked as____, suggested that the northern hemisphere is experiencing____ - ✔✔warm;summer
And, on the opposite site of the orbit, when the northern hemisphere is tilted the farther away
from the sun, the average daily temperature is marked as____, suggesting that the norther
hemisphere is experiencing___ - ✔✔cool;winter
in the southern hemisphere its___in late june, and__is in late december - ✔✔winter;summer
the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere is on or about____ and the shortest is,
again, six months later near___, when the earth is at the opposite point in its orbit around the sun
- ✔✔June 21 and December 21
These are called summer solstice and winter solstice
Two dates are on opposite sides of the earth's orbit near - ✔✔March 21 and September 21
these are called the Vernal Equinox and Autumnal equinox (equal night)
Moon Phases and Eclipses - ✔✔Q: What happens to the moon in 1 month?
A: It moves once around the Earth.
Q: What causes the phases of the Moon?
A: The Sun is lighting up different fractions of the part of the Moon we see from Earth.
Q: What is the order of the phases of the Moon? A: New - Waxing Crescent - First Quarter -
Waxing Gibbous - Full - - Waning Gibbous - Third Quarter - Waning Crescent - New (and
repeat...)
Q: When is the full moon visible?
A: Only at night. It transits (is highest in the sky, or overhead) at midnight; the full moon rises 6
hours earlier (at sunset), and sets 6 hours later (at sunrise).
Q: When is the new moon visible?
A: The new moon is visible during the day. It transits at noon; it rises 6 hours earlier (at sunrise),
and sets 6 hours later (at sunset).
Q: How are the Sun, Earth, and Moon positioned when it is new Moon?
A: in a straight line: Sun — Moon — Earth
Q: How are the Sun, Earth, and Moon positioned when it is full Moon?
A: Sun — Earth — Moon
Q: What is a solar eclipse?
A: The Moon is blocking the Sun's light, or a location on the Earth's surface is passing under the
Moon's shadow.
Moon Phases and Eclipses pt2 - ✔✔The outer ring of Moons shows the orientation of the Sun-
illuminated half its surface; the inner ring of Moons shows how the Moon appears in our sky at
those times.
The Moon phase directly away from a point on the Earth's surface can be said to be "overhead"
at the time of day that corresponds to that
[Show More]



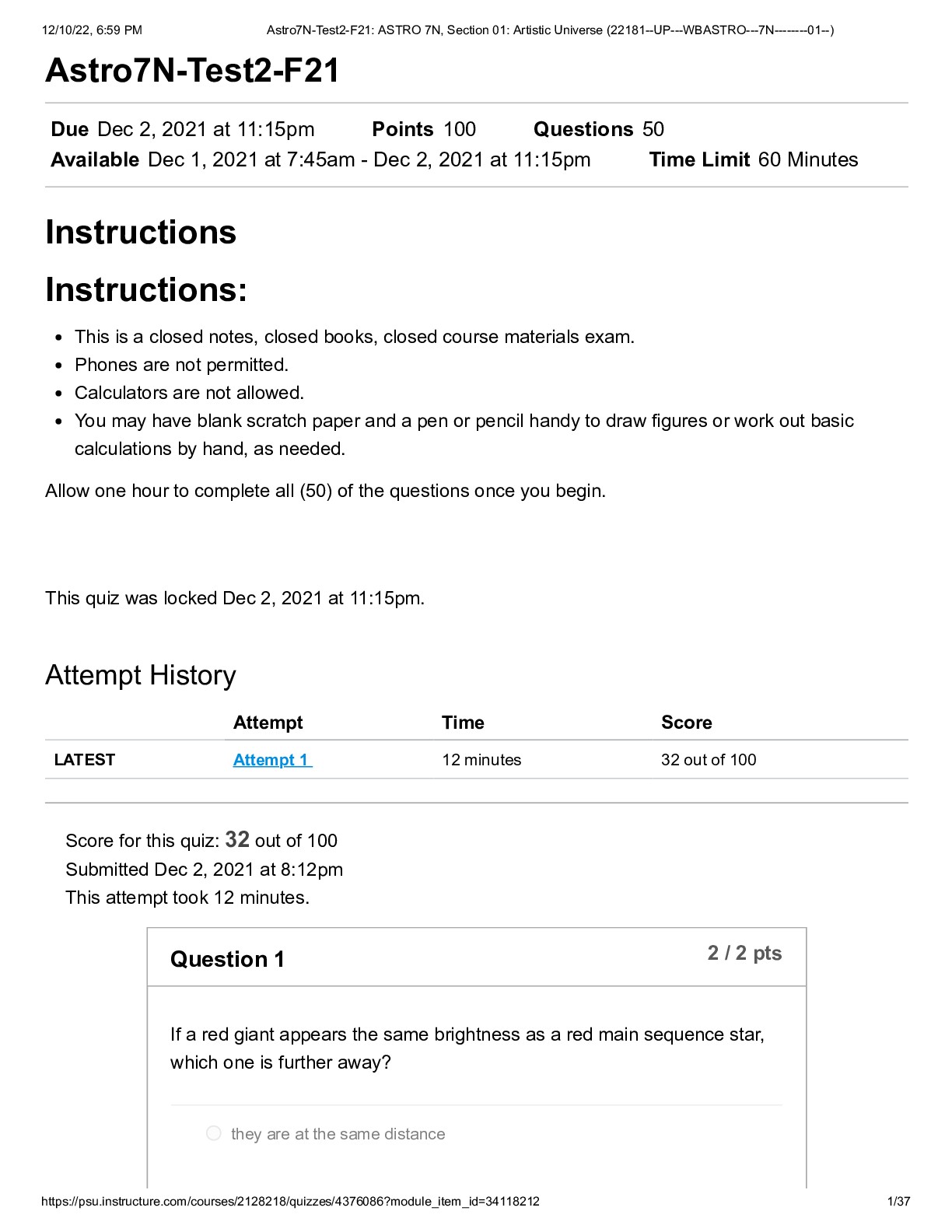








.png)