68WM6 Ph 2 Resp
Respiratory System
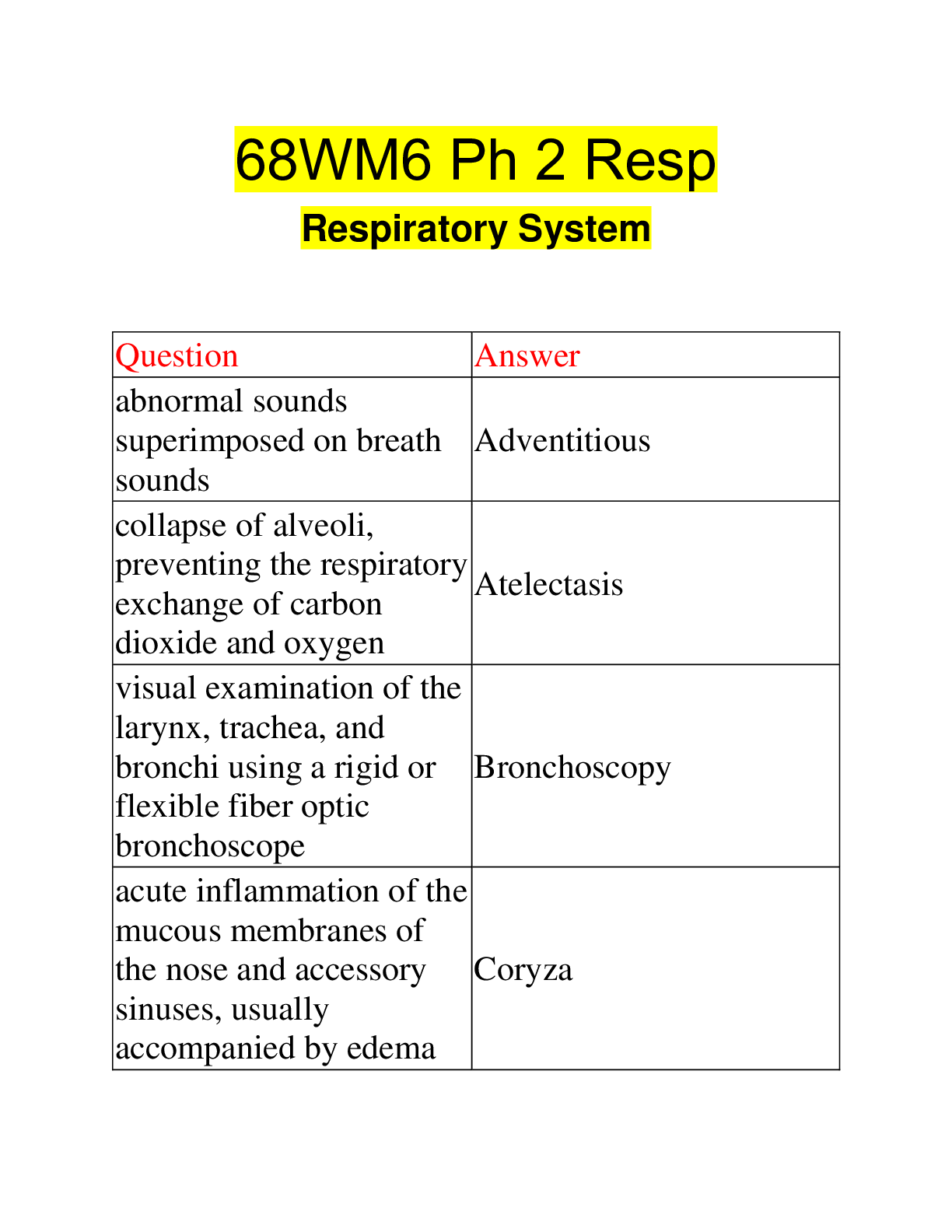
Question Answer
abnormal sounds
superimposed on breath
sounds
Adventitious
collapse of alveoli,
preventing the respiratory
exchange of carbon
dioxide and oxygen
Atelectasis
...
68WM6 Ph 2 Resp
Respiratory System
Question Answer
abnormal sounds
superimposed on breath
sounds
Adventitious
collapse of alveoli,
preventing the respiratory
exchange of carbon
dioxide and oxygen
Atelectasis
visual examination of the
larynx, trachea, and
bronchi using a rigid or
flexible fiber optic
bronchoscope
Bronchoscopy
acute inflammation of the
mucous membranes of
the nose and accessory
sinuses, usually
accompanied by edema
Coryza
of the mucus membranes
and nasal discharge
short, discrete,
interrupted crackling or
bubbling sounds; most
commonly heard upon
inspiration
Crackles
slightly bluish, gray, or
dark purple discoloration
of the skin resulting from
the presence of
abnormally reduced
amounts of oxygenated
hemoglobin in the blood
Cyanosis
shortness of breath or
difficulty in breathing;
may be caused by
disturbances in the lungs,
certain heart conditions,
and hemoglobin
deficiency
Dyspnea
obstruction of blood
vessel by a foreign Embolism
substance; blood clot, fat,
or air
accumulation of pus in a
body cavity, especially
the pleural space, as a
result of an infection
Empyema
hemorrhage of the nose;
nosebleed Epistaxis
an increase in the
severity of a disease or
disorder, marked by an
increase in signs and
symptoms
Exacerbation
caused by external
factors Extrinsic
greater than normal
amounts of carbon
dioxide in the blood
Hypercapnia
an abnormal condition of
the respiratory system
that occurs when the
volume of air inhaled is
not adequate for the
Hypoventilation
metabolic needs of the
body
an inadequate, reduced
tension of cellular
oxygen
Hypoxia
caused by internal factors Intrinsic
an abnormal condition in
which a person must sit
or stand in order to
breathe comfortable or
deeply
Orthopnea
low pitched, grating or
creaking lung sounds that
occur when inflamed
pleural surfaces rub
together during
respiration
Pleural Friction Rub
collection of air or gas in
the pleural cavity which
causes the lung to
collapse
Pneumothorax
musical, high pitched,
squeaking or whistle like
sound caused by rapid
Silibant Wheeze
movement of air through
narrowed bronchioles
low pitched, loud, coarse,
snoring sound Sonorous Wheeze
pertaining to respiratory
effort that is strenuous
and struggling; creates a
snoring sound
St
[Show More]