Exam 1: Dysrhythmias (NCLEX)
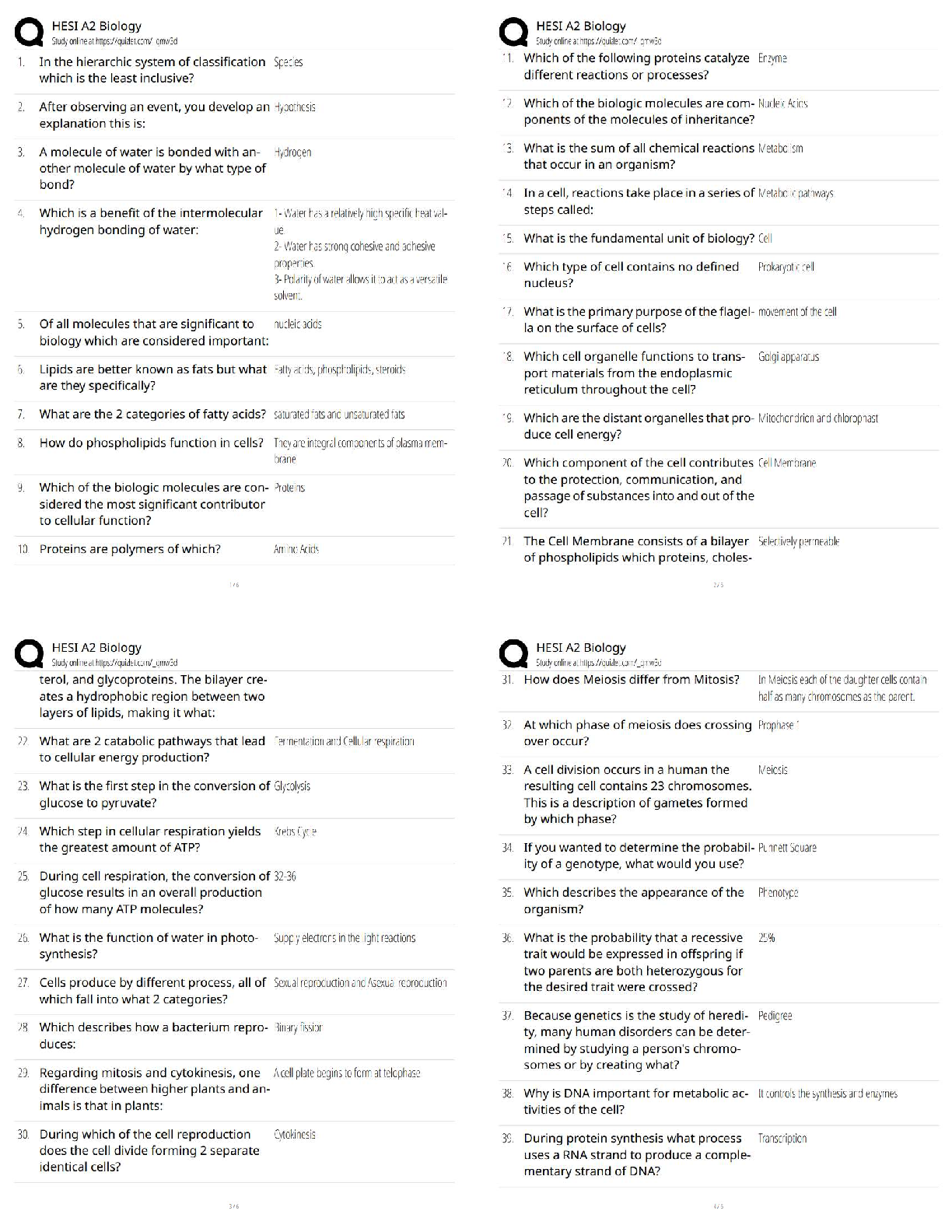
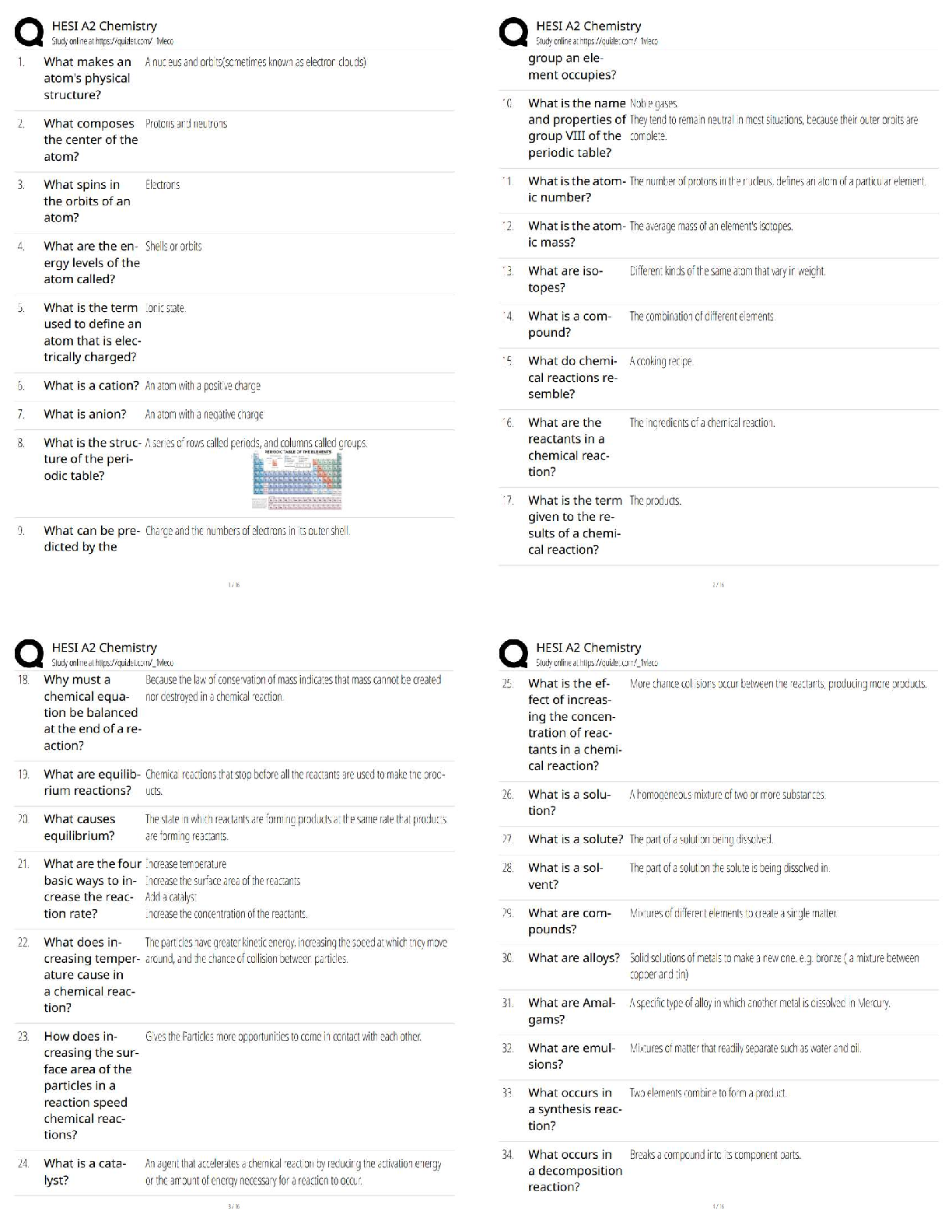
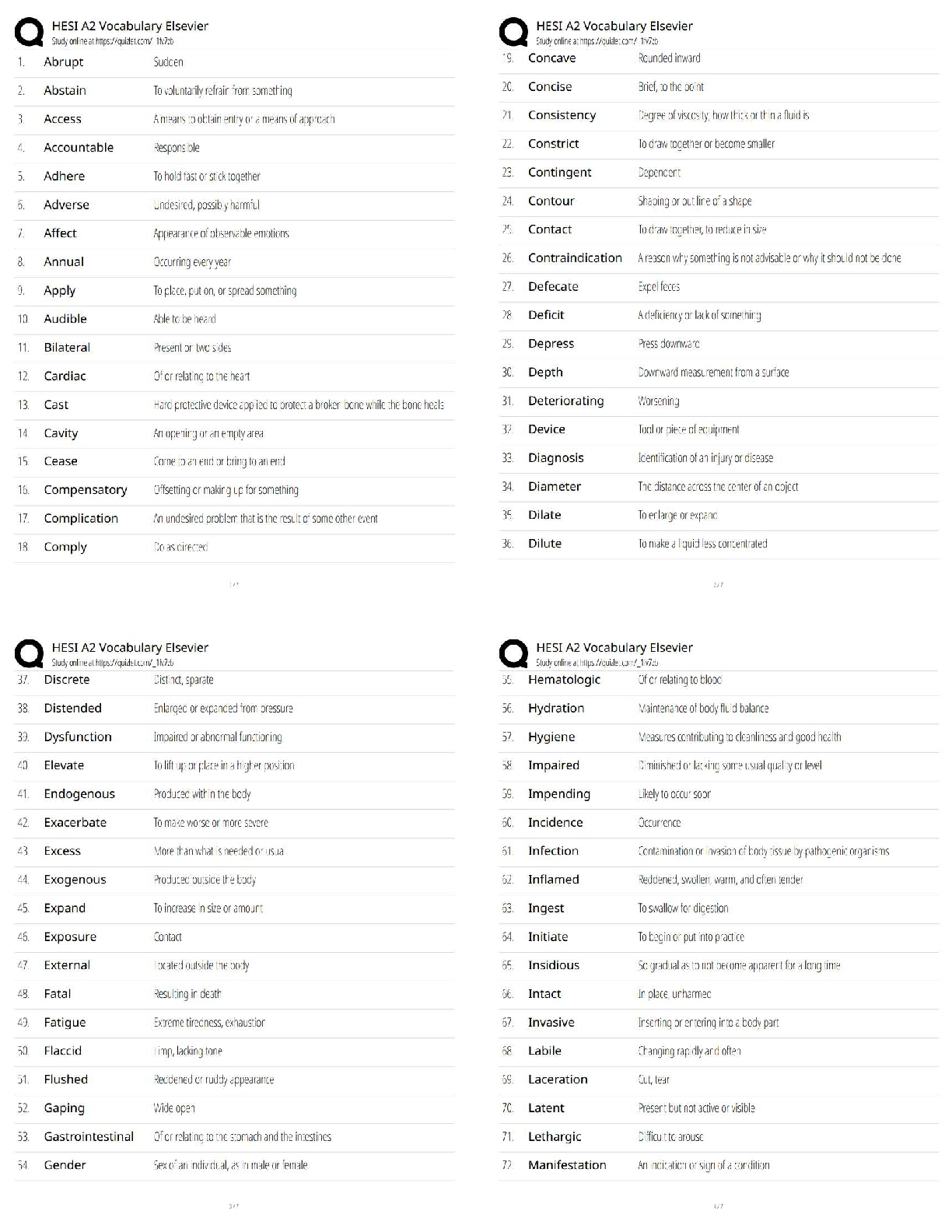
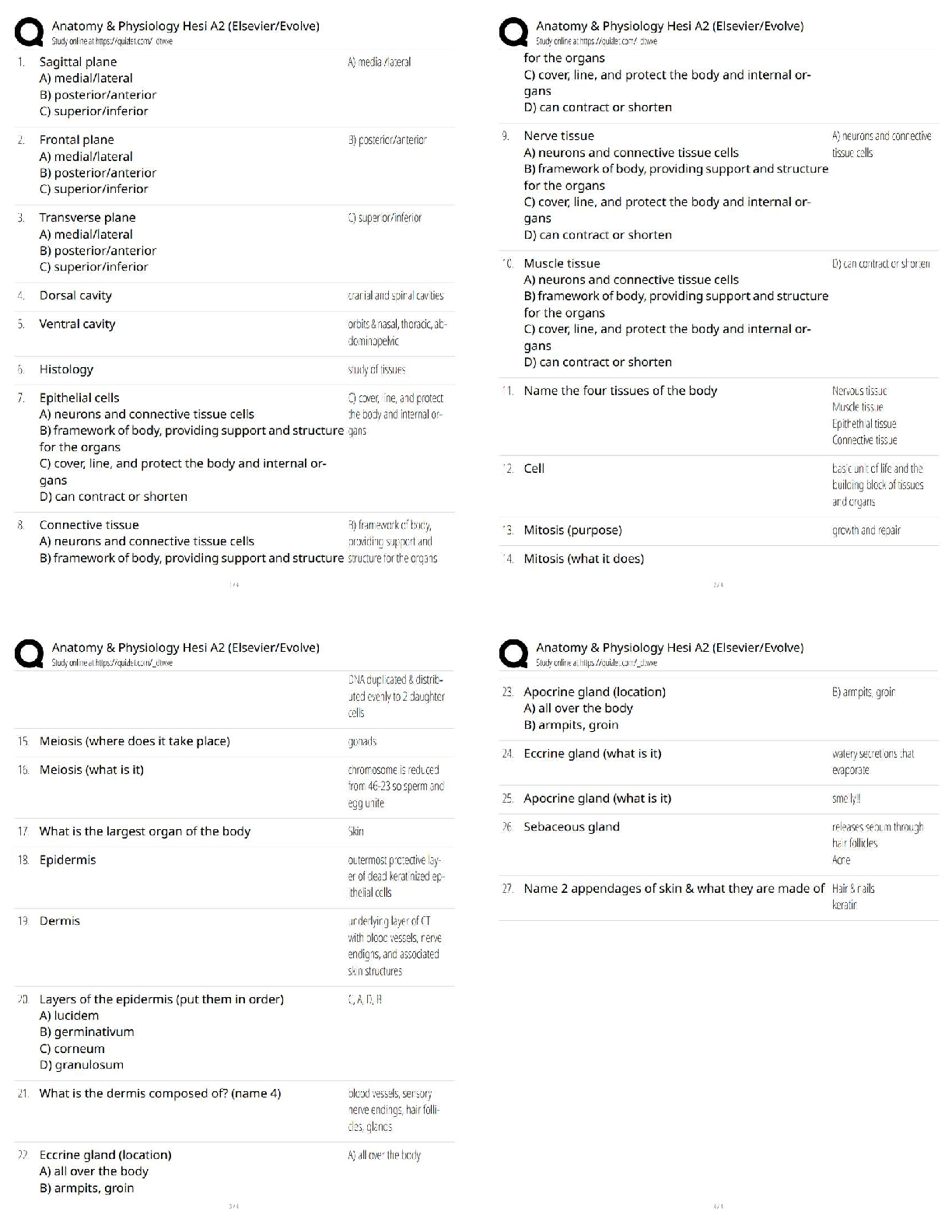
A client's electrocardiogram strip shows atrial and ventricular rates of 80 complexes per minute.
The PR interval is 0.14 second, and the QRS complex measures 0.08 second. The nurse
interp
...
Exam 1: Dysrhythmias (NCLEX)
A client's electrocardiogram strip shows atrial and ventricular rates of 80 complexes per minute.
The PR interval is 0.14 second, and the QRS complex measures 0.08 second. The nurse
interprets this rhythm is:
A) Normal sinus rhythm
B) Sinus bradycardia
C) Sinus tachycardia
D) Sinus dysrhythmia - ✔✔A
A client has frequent bursts of ventricular tachycardia on the cardiac monitor. A nurse is most
concerned with this dysrhythmia because:
A) It is uncomfortable for the client, giving a sense of impending doom.
B) It produces a high cardiac output that quickly leads to cerebral and myocardial ischemia.
C) It is almost impossible to convert to a normal sinus rhythm.
D) It can develop into ventricular fibrillation at any time. - ✔✔D
Ventricular tachycardia is a life-threatening dysrhythmia that results from an irritable ectopic
focus that takes over as the pacemaker for the heart. The low cardiac output that results can lead
quickly to cerebral and myocardial ischemia. Client's frequently experience a feeling of
impending death. Ventricular tachycardia is treated with antidysrhythmic medications or
magnesium sulfate, cardioversion (client awake), or defibrillation (loss of consciousness),
Ventricular tachycardia can deteriorate into ventricular defibrillation at any time.
The nurse administers amiodarone (Cordarone) to a client with ventricular tachycardia. Which
monitoring by the nurse is necessary with this drug? Select all that apply.
a. Respiratory rate
b. QT interval
c. Heart rate and rhythm
d. Magnesium level
e. Urine output - ✔✔BCD
Amiodarone causes prolongation of the QT interval, which can precipitate dysrhythmia.
Antidysrhythmic medications cause changes in cardiac rhythm and rate; therefore monitoring of
heart rate and rhythm is needed.Electrolyte depletion, specifically potassium and magnesium,
may predispose to further dysrhythmia. Although it is always important to monitor vital signs
and urine output, these assessments are not specific to amiodarone
[Show More]