Social Sciences > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BCOR 1030 Final Exam Questions and Answers Rated A (All)
BCOR 1030 Final Exam Questions and Answers Rated A
Document Content and Description Below
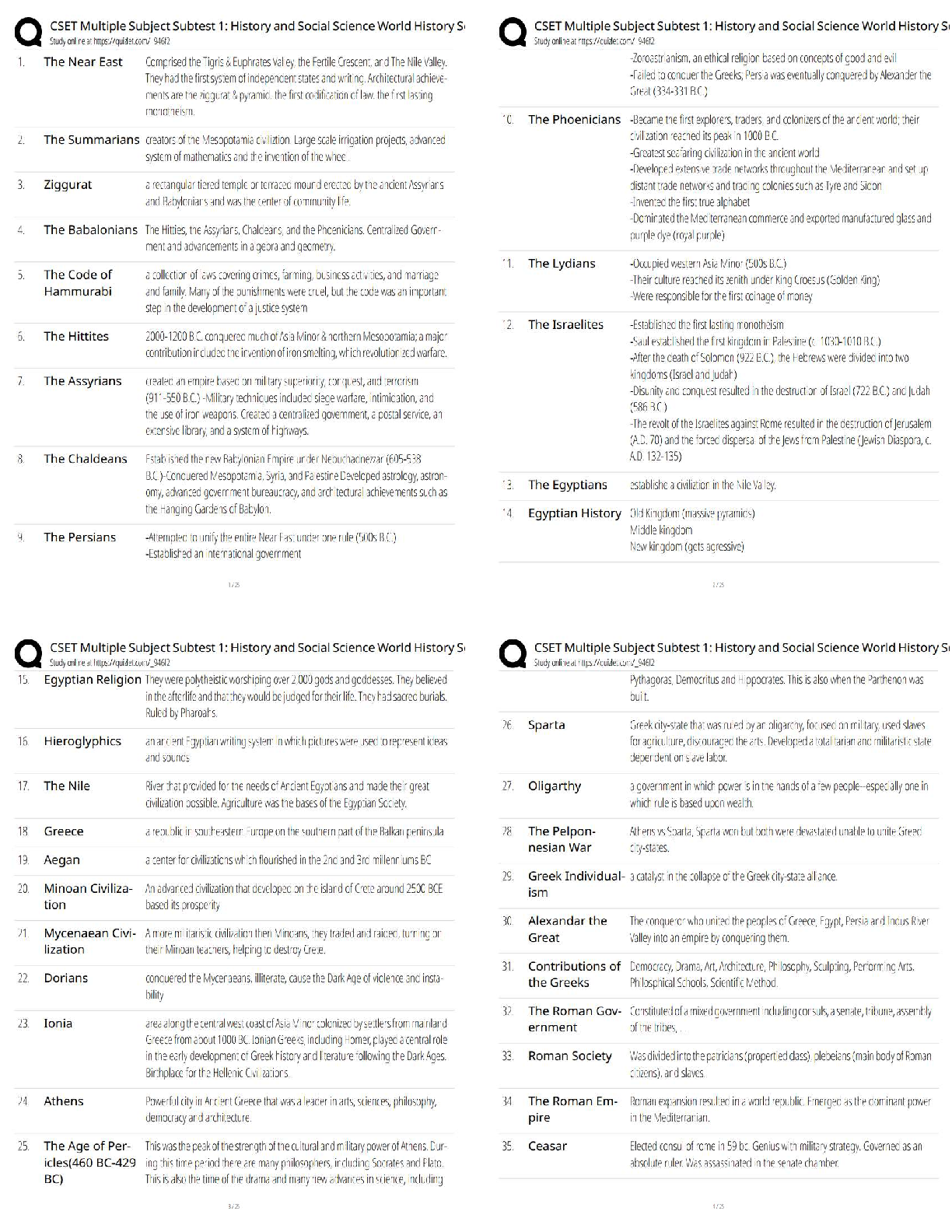
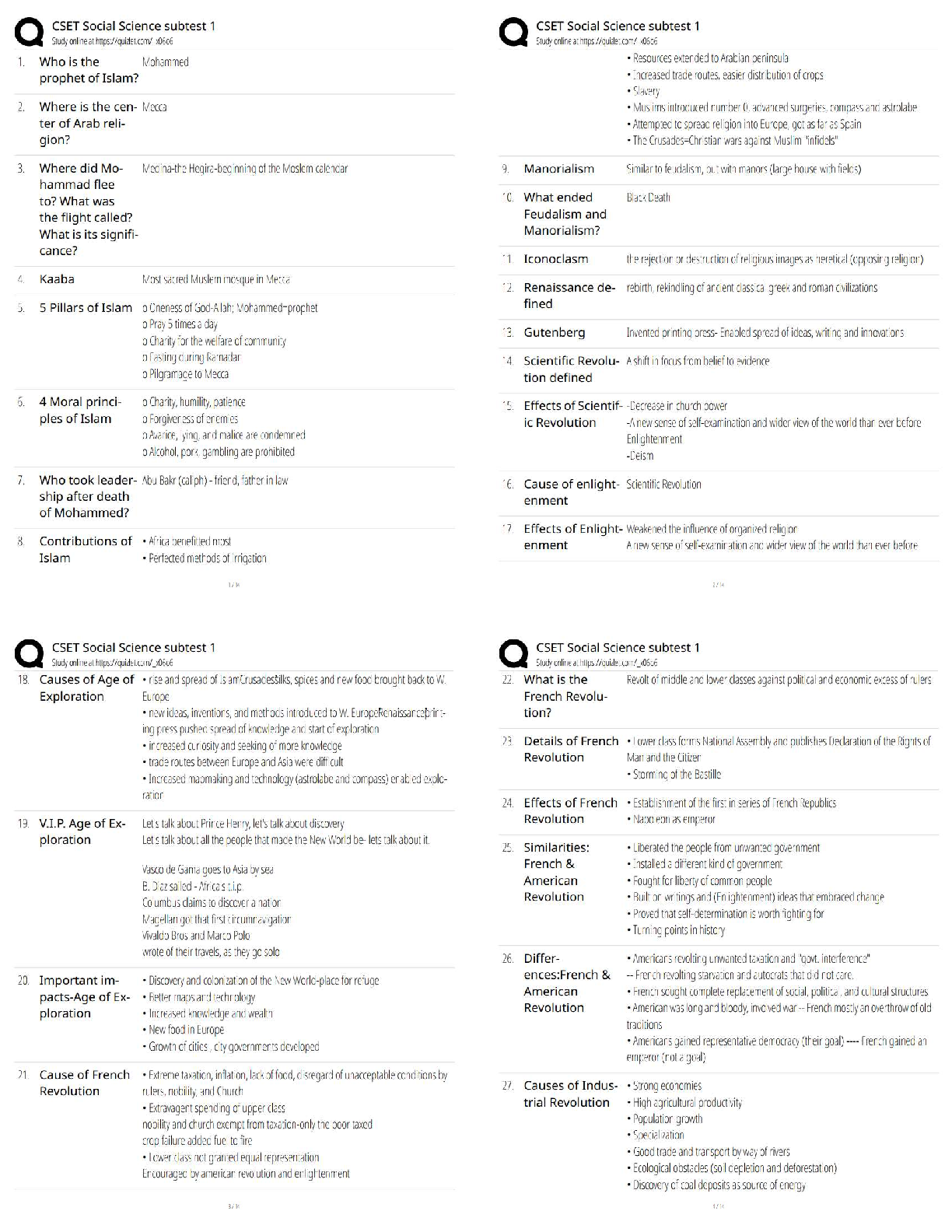
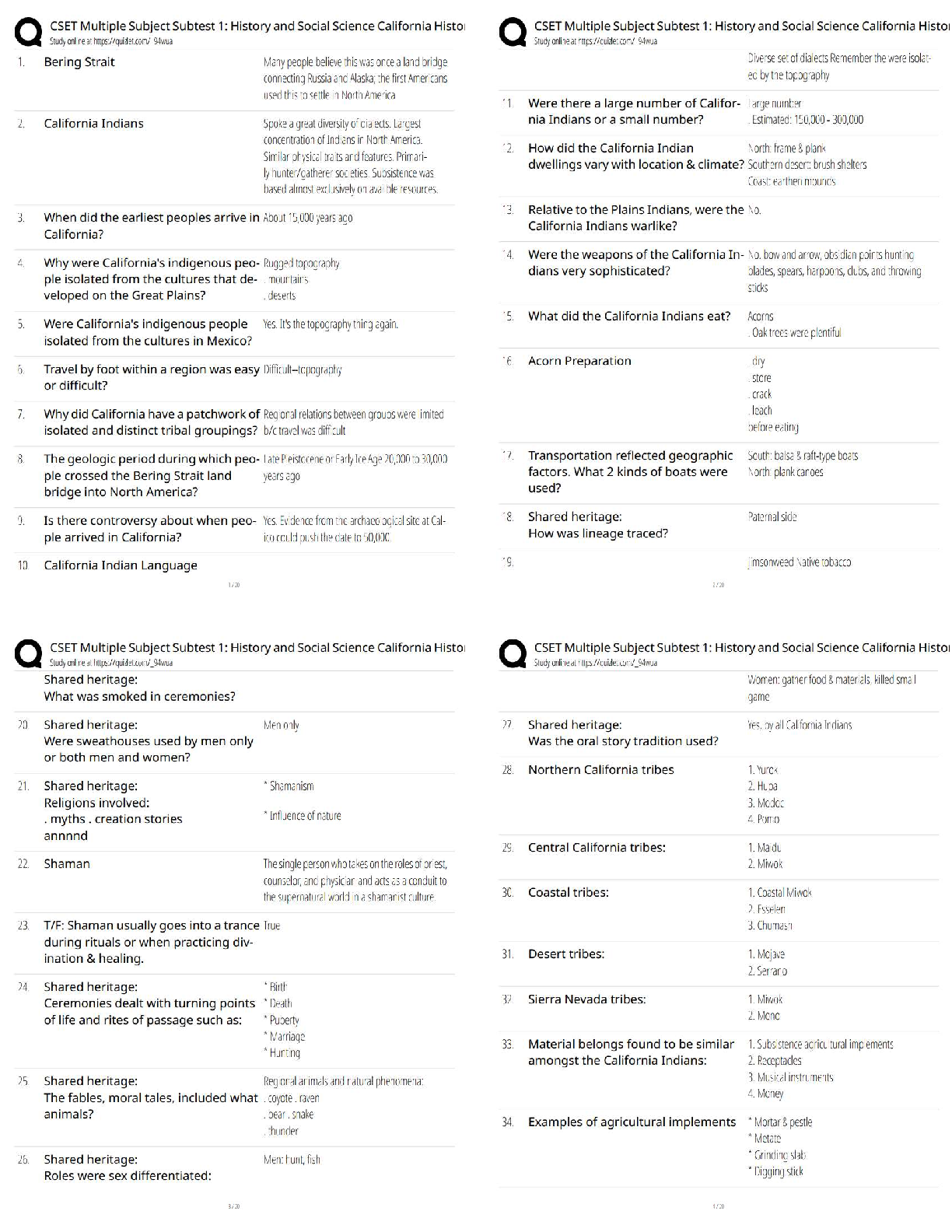
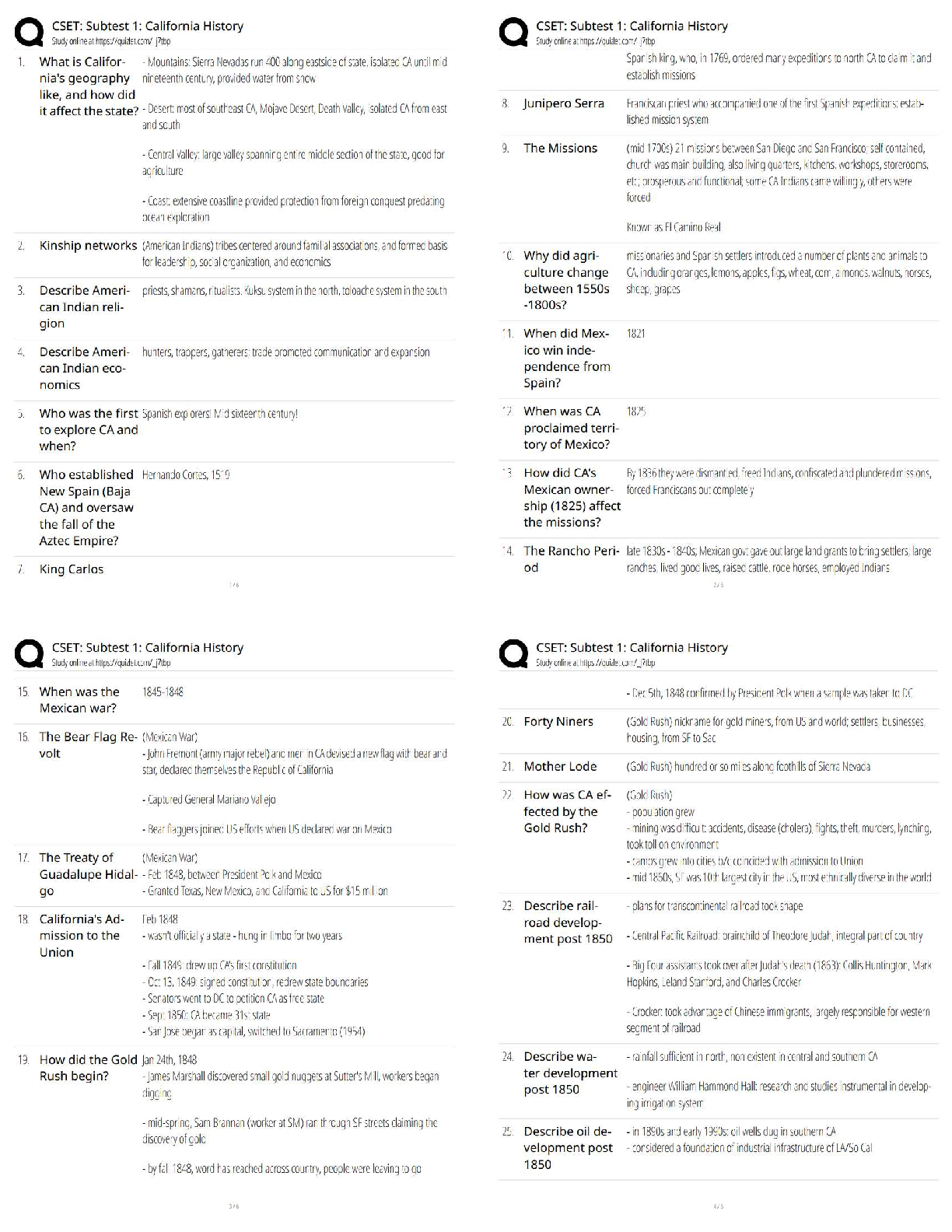
BCOR 1030 Final Exam Questions and Answers Rated A How does culture influence communication? it provides a framework that shapes the messages you send and receive everyday High context cultures g ... ather subtle information from facial expressions, vocal cues, and even silence in interpreting messages Low context cultures rely on language and meanings of words Individualistic cultures value their own interests more than the group Collectivist cultures value the group interests more than their own Decentralized power cultures value distribution of power to the people Centralized Power value a more concentrated or narrow distribution of power. The power is in one person or a select few. Low uncertainty avoidance people tolerate uncertainty and accept they can't predict the future High uncertainty avoidance people don't like uncertainty and structure their lives to provide predictability Short term orientation value fulfilling social obligations and saving face Long term orientation value commitment, thriftiness, and perserverance Masculine culture value more traditional roles for men and women Feminine culture value caring for the less fortunate and enhancing overall quality of life Sex biological characteristics present at birth (male/female) Gender cultural and psychological characteristics (man/woman) Rapport talk focused on developing relationships Report talk focused on sharing information Five components of emotional intelligence 1. self-awareness 2. self-regulation 3. motivation 4. empathy 5. social skills Blues thoughtful, loyal, opinionated, sincere, self-righteous Reds visionary, decisive, demanding, logical, insensitive Whites agreeable, generous, stubborn, kind, indecisive Yellows happy, impulsive, spontaneous, irresponsible, charismatic Conflict styles avoider, accommodator, compromiser, competitor, collaborator Avoider an individual with a low concern for task and a low concern for people Accommodator an individual with a low concern for task and a high concern for people Competitor an individual with a high concern for task and a low concern for people Collaborator an individual with a high concern for task and a high concern for people Compromiser an individual with a moderate concern for task and a moderate concern for people PUGSS Model P = Describe the Problem U = Achieve Understanding G = Identify Goals S = Brainstorm Solutions S = Select the best Solution P describe the problem U achieve understanding G identify goals First S brainstorm solutions Second S select the best solution Strategies for managing conflict in the workplace PUGSS Upward communication communication that flows from subordinate to superior Horizontal communication communication between peers Downward communication communication that flows from superiors to subordinates DRGRAC Method DR - Desired Results G - Guidelines R - Resources A - Accountability C- Consequences Advantages of teamwork - Teams have more information available to them than individuals do. - Teams stimulate creativity. - Teamwork increases the likelihood that we'll remember what we discuss because we're actively involved in the discussion. - Team members are usually more satisfied with a decision if they are involved in the discussion. - Team members learn about themselves through feedback they receive from their fellow team members. Disadvantages of teamwork - One individual may dominate the discussion. - Team members may pressure others to conform. - Team members may rely too much on just a few people. - Teamwork takes more time than working individually. - Teams have difficulty rebuilding trust once trust has eroded. Characteristics of effective teams 1. Specify a Clear, Elevating Goal 2. Develop a Results-Driven Structure 3. Include competent team members 4. Unified commitment 5. A collaborative climate 6. Standards of excellence 7. External support and recognition 8. Principled leadership Virtual teams a team interacts via channels other than face-to-face communication. Differences between virtual teamwork and face to face teamwork 1. Anonymity 2. Physical Appearance 3. Distance 4. Time Norms standards that determine what behavior is appropriate and inappropriate in a group. Task roles behaviors that help a group achieve its goal and accomplish its work Role the consistent way someone communicates with others in a team, based on the person's own expectations and what others on the team expect of the person. Social roles behaviors that manage relationships and affect group climate; these roles help resolve conflict and enhance the flow of communication Individual roles behaviors that focus attention on an individual rather than the group All channel network a group in which everyone talks to everyone else Chain network people send messages through one person at a time rather than to all group members Wheel network one person in the team or organization receives more messages from other members; this pivotal communicator also is the prime source of information to other team or organization members Stages of team development forming, norming, storming, performing, adjorning A meeting should have 1. a structured conversation 2. people who interact to accomplish a specific task Group problem solving process 1. Identify the Problem 2. Analyze the Problem 3. Generate Possible Solutions 4. Select the Best Solution 5. Test and Implement Solution Groupthink a false sense of agreement How to minimize groupthink - Encourage independent, critical thought. - Assign someone to be a devil's advocate to challenge ideas. - Break into smaller teams to evaluate the pros and cons of proposed ideas Open types of interview questions more complex and require more elaboration Closed types of interview questions yes/no answer questions, very simple and straightforward Funnel sequence a questioning sequence that begins with broad, open questions and proceeds toward more closed questions Tunnel sequence a questioning sequence that uses a combination of open and closed questions to gather a large amount of information in a short amount of time Inverted funnel sequence a questioning sequence that begins with closed questions and proceeds to more open questions Relational messages messages that build rapport and are aimed at establishing relationships Task messages messages focused on the content of an interview Interview intro goals make a positive impression establish rapport clarify interview goals Interviewee's role listen actively provide thoughtful and clear responses ask appropriate questions Interview exit goals summarize the interview encourage friendly relations discuss the next step exchange thank yous Interviewer's role ask questions listen actively control breadth and depth of questions take notes ask questions monitor time As an interviewee, know when to send a thank you note following an interview within 24 hours Steps to Responding After a Presentation 1. Restate the Question 2. Acknowledge Emotions 3. Don't Make the Issue Personal 4. Get to the Heart of the Issue 5. When You Don't Know the Answer Admit it Be Brief Pie graph a circular graph that shows the distribution of data as a proportion of the total Bar graph a graph that uses bars for different lengths to represent statistical data Line graph a graph that shows trends over time and relationships among variables Walk in slide slide up when people enter the room (Ex: company branding) Title slide slide with title, name and company Navigation slide agenda slide Bullet slide used to cluster related ideas into a list Big word slide conveys one message/idea (literal big word) Quote slide projects expert quotes Data slide shows data when discussing research Diagram slide visually represents concepts Conceptual image slide for when showing is more powerful than telling Video slide provides a nice break from static slides Walkout slide leaves people with something useful as they walkout Strategies for presenting with visual aids 1. Make them easy to see 2. Make them simple 3. Develop a consistent visual theme 4. Communicate numerical data visually Strategies for effective slide design 1. Create slides people can get in 3 seconds 2. Limit text 3. Coordinate visual elements 4. Arrange slides with care Correspondence business letters sent to customers, coworkers, superiors, and subordinates Goodwill a positive perception of an author on the part of the audience Complaint letter a letter that expresses dissatisfaction with a product or service Memo a short, informal written communication within an organization Progress report a report that outlines for a customer or a client the status of a project Activity report a document that communicates progress on a project or achievements to others in an organization or on a team Sales proposal a document intended to persuade a possible client of his or her need for your product or service Legally binding documents documents that record an exchange of promises and are enforceable by law Formal report a highly detailed and comprehensive report on an ongoing project or a completed project, often coauthored by several writers Front matter the components of a report that come at the beginning and prepare the reader for the main information. Back matter the components of a report that traditionally come at the end, after the main body, and provide further detail and references Strategies for writing an email 1. Be concise 2. Use proper letter case 3. Use blind copy (BCC) and courtesy copy (CC) appropriately 4. Use the subject line 5. Use correct grammar and punctuation 6. Consider the appropriateness of your content 7. Don't use email as an excuse for not communicating through more appropriate channels of communication Pulitzer's ABC's of writing A - Accuracy B - Brevity C - Clarity Final challenge problem Identifying specific strategies to effectively convey Crowe's commitment to diversity and inclusion, one of the two components of their "just cause," or organizational purpose Final challenge goal Develop a compelling proposal that (1) demonstrates a basic understanding of organizational purpose beyond profit, (2) demonstrates a basic understanding of inclusivity in the workplace, and (3) presents at least two recommendations for how Crowe can successfully translate the higher purpose of an inclusive environment to its stakeholders—one on an institutional level, and one on an interpersonal level Disparate treatment is the denial of opportunity because of protected characteristics. For example, dissimilar compensation for the same work. Adverse impact an employment policy or practice that works against a group of people with same or similar protected characteristics. It is often unintentional, but unfairly targets a specific group. For example, adhering to promotion guidelines that state that eligibility for promotion is contingent upon minimal absence, thus inherently affecting those who take maternity leave, religious holiday leave, or medical leave). People resource networks business groups that educate employees about diversity and provide a forum for networking, support and recruiting efforts in order to promote inclusion within the firm. D&I north star Be you and crush it! Build, promote and sustain an inclusive work environment that inspires our people to be the best every day CAST where we allow students to conduct internships with us via our Crowe on Campus model. From a diversity perspective, we have this established at Florida A&M University (the HBCU we have partnered with for 3+ years). We have increased our pipeline of black students significantly through this program. Simon sinek's just cause a specific vision of a future state that does not exist yet; a future state so appealing that people are willing to make sacrifices to get there. Crowe LLC large US based accounting firm that is a part of a larger global Crowe network 5 standards to test a just cause 1. For something 2. Inclusive 3. Service oriented 4. Resilient 5. Idealistic [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)
.png)
BCOR BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS [MULTIPLE VERSIONS]
BCOR BUNDLED EXAMS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS [MULTIPLE VERSIONS]
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$20
16
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 01, 2023
Number of pages
17
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 01, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
219










.png)