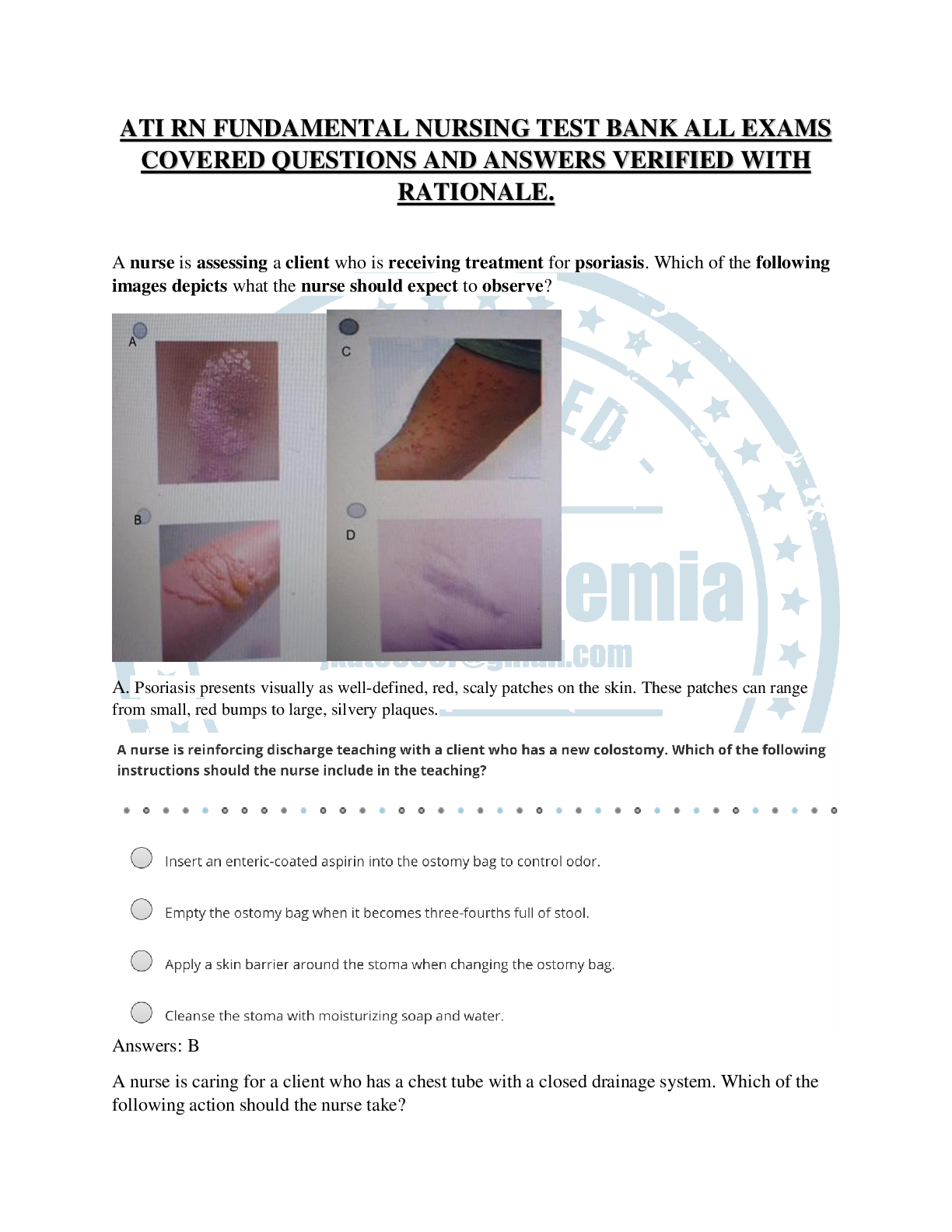
LETRS Unit 2 QUIZ A & Q graded A,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
LETRS Unit 2 QUIZ A & Q graded A Assessing phonological skills is almost never appropriate after a child has completed first grade. true false - Correct AnswerFalse Phonemic awareness is dif ... ficult to measure directly as an isolated skill. true false - Correct AnswerTrue What features separate the PAST from other phonological skills assessments? Select all that apply. a. It can be successfully administered to preschool-age children. b. Automaticity is a factor in determining a student's score. c. It is much briefer and more convenient to administer than other phonological awareness assessments. d. The assessor gives corrective feedback if the student responds incorrectly. - Correct Answerb. Automaticity is a factor in determining a student's score. d. The assessor gives corrective feedback if the student responds incorrectly. Which kinds of tasks are the primary focus of phonological skills assessment in grades K-1? a. counting and blending syllables b. identification of onset sounds, alliteration, and rhyme c. phoneme segmentation and blending d. phoneme deletion, substitution, and reversal - Correct Answerc. phoneme segmentation and blending Kelsey is in grade 2. Previously a strong reader, she has now fallen behind. She reads grade-level texts haltingly, struggling to recognize words with blends. Which phonological task would she likely struggle with? Select all that apply. a. "Say rainbow. Now say rainbow but don't say rain.'" b. "Say crate. Now say crate but don't say /k/." c. "Say sun. Now say sun but instead of /s/, say /f/." d. "Say bask. Now say bask but don't say /s/." - Correct Answerb. "Say crate. Now say crate but don't say /k/." d. "Say bask. Now say bask but don't say /s/." phonological processing system - Correct Answer-Front of brain -processes the sounds of speech phonological processing - Correct Answerability to discriminate and remember sounds within words -speech perception / production -phonological working memory -rapid automatic naming -phonological and phonemic awareness phonological awareness - Correct Answerin addition to phonemic awareness, includes the ability to identify, count, and manipulate the parts of words, including syllables, onsets and rimes, and phonemes. phoneme - Correct Answerin language, the smallest distinctive sound unit Phonemic Awareness - Correct AnswerThe ability to hear, identify,and manipulate the individual sounds, phonemes, in oral language. -do not involve print Phonology - Correct Answerthe study of speech sounds in language Phonetics - Correct Answerstudy of speech sounds coarticulation - Correct Answerwhen phonemes are spoken together to produce syllables or words phonological working memory - Correct AnswerIs a component of phonological processing that is important in reading comprehension, spelling, written expression, and retention. -the process of listening to language and extracting meaning rapid automatic naming - Correct Answerthe ability to quickly name a series of printed, repeating numbers, letters, objects, and/or colors Phonemic awareness instruction for young learners is most beneficial when linked with phonics instruction. true false - Correct AnswerTrue The inventory of phonemes used in Spanish is nearly identical to that used in English. true false - Correct AnswerFalse A third-grade teacher wants to determine whether any of her students are at risk for reading failure. She should use a screening measure that assesses which of the following? a. their ability to segment phonemes b. their ability to manipulate phonemes c. their ability to represent phonemes with letters (as shown in spelling samples) d. their ability to perform advanced phonemic awareness tasks - Correct Answerd. their ability to perform advanced phonemic awareness tasks How much phonological awareness training should be done with students for maximum effectiveness? a. at least 45 minutes a day b. once a week, for about 30 minutes c. a few minutes a day, several days per week d. about 30 minutes each day - Correct Answerc. a few minutes a day, several days per week Which of the following changes typically take place once a child has grasped the alphabetic principle? Select all that apply. a. Spelling becomes more phonetically accurate. b. The student can easily delete, substitute, or otherwise manipulate phonemes in words. c. Attempts to decode text focus more on blending sounds. d. Recognition improves for high-frequency words that are phonetically irregular. - Correct Answera. Spelling becomes more phonetically accurate. c. Attempts to decode text focus more on blending sounds. In many instances, two different consonant phonemes in English are formed the same way in the mouth, but one is voiced and the other is unvoiced. true false - Correct AnswerTrue Adults often miscount the number of phonemes in a word because they tend to recall how a word looks in print and count the letters, not the sounds. true false - Correct AnswerTrue Which of the following sounds is an affricate, meaning it combines features of fricatives and stops? /k/ /ng/ /ch/ /zh/ - Correct Answer/ch/ Which of the following pairs are consonant sounds that students frequently confuse? Select all that apply. a. /t/ and /d/ b. /f/ and /p/ c. /m/ and /n/ d. /z/ and /l/ - Correct Answera. /t/ and /d/ c. /m/ and /n/ Which of the following misspellings is phonetically accurate and does not indicate phonemic confusion? Select all that apply. a. writing "fan" for van b. writing "butn" for button c. writing "chow" for show d. writing "kitn" for kitten - Correct Answerb. writing "butn" for button d. writing "kitn" for kitten English vowels are easier for students to pronounce and write than consonants. true false - Correct AnswerFakse What makes r-controlled vowel sounds so confusing for students? The sounds make two mouth movements. The r takes over the preceding vowel sound. There is only one way to spell an r-controlled vowel. English does not allow this sound in the middle of words. - Correct AnswerThe r takes over the preceding vowel sound. Which of the following sounds is considered a front vowel? /ə/ /ā/ /ō/ /ŏ/ - Correct Answer/ā/ Which of the following vowels require that the mouth shift position during production of the sound? Select all that apply. /aw/ /er/ /oi/ /ou/ - Correct Answer/oi/ /ou/ Which of the following vowel sounds would be classified by a linguist as "tense" vowels? a. /ē/ and /yū/ b. /ă/ and /o˘o/ c. /ar/ and /er/ d. /ǝ/ and /ŏ/ - Correct Answera. /ē/ and /yū/ Even after first grade, skills such as phoneme segmentation and blending of single-syllable words without consonant blends are good predictors of reading ability. true false - Correct AnswerFalse Students' ability to acquire phonemic awareness is not dependent on which of the following factors? a. general language development and listening abilities b. word comprehension c. familiarity with vocabulary used in tasks d. the amount of practice received - Correct Answerb. word comprehension Which of these tasks could a student at the early phonological awareness level perform? Select all that apply. a. determining whether cat and kiss begin with the same sound b. segmenting and tapping the phonemes in the word slap c. clapping and counting the syllables in the word pencil d. saying the word marker, then deleting the last syllable and saying it again, mark - Correct Answera. determining whether cat and kiss begin with the same sound c. clapping and counting the syllables in the word pencil Which of these tasks could a student at the basic phonemic awareness level perform? Select all that apply. a. saying the word flame, then deleting the phoneme /l/ and saying the word without it b. saying the compound word rainbow, then deleting the first part and saying the new word c. determining which sound should be changed to make the word stream into scream d. segmenting and tapping the phonemes in the word beak - Correct Answerb. saying the compound word rainbow, then deleting the first part and saying the new word d. segmenting and tapping the phonemes in the word beak Which of these advanced phonemic awareness skills do children typically develop last? a. the ability to delete the final sound from a word b. the ability to substitute sounds within words of 5-6 phonemes c. the ability to reverse the first and final sounds in a word d. the ability to delete the initial sound from a word that begins with a blend - Correct Answerc. the ability to reverse the first and final sounds in a word How much phonological awareness training should be done with students for maximum effectiveness? - Correct Answera few minutes a day, several days per week The inventory of phonemes used in Spanish is nearly identical to that used in English. - Correct AnswerFalse Phonemic awareness instruction for young learners is most beneficial when linked with phonics instruction. - Correct AnswerTrue A third-grade teacher wants to determine whether any of her students are at risk for reading failure. She should use a screening measure that assesses which of the following? - Correct Answertheir ability to perform advanced phonemic awareness tasks Which of the following changes typically take place once a child has grasped the alphabetic principle? Select all that apply. - Correct Answera. Spelling becomes more phonetically accurate. c. Attempts to decode text focus more on blending sounds. Students in Ehri's pre-alphabetic phase need instruction in basic oral language skills before manipulating phonemes. true false - Correct AnswerTrue Sound chaining should begin with substituting the middle sounds and end sounds in a word, as these are most difficult. true false - Correct AnswerFalse Which of the following principles are important for teaching phonological skills in particular? Select all that apply. a. Focus students' attention on speech sounds before focusing on letters. b. Do a few brief activities once per week. c. Withhold feedback from students, so not to discourage them. d. Include all English phonemes in instruction. - Correct Answera. Focus students' attention on speech sounds before focusing on letters. d. Include all English phonemes in instruction. Which activities work with students at the early phonological awareness level? Select all that apply. a. having students identify rhyming words in texts you read aloud b. having students clap or tap to count the syllables in a word you say c. saying a word, then asking students to change the first or last phoneme and say the new word that results d. saying a two-syllable word, then asking students to delete one syllable and say the word that results - Correct Answera. having students identify rhyming words in texts you read aloud b. having students clap or tap to count the syllables in a word you say d. saying a two-syllable word, then asking students to delete one syllable and say the word that results A colleague is going to start beginning sound chaining activities with students at the basic phonemic awareness level, using colored blocks to represent sounds. What is the most important guideline to follow? a. Have students focus on adding or changing sounds before they practice deletion. b. Have students add, change, delete, or move only ONE sound at a time. c. Plan sound chains carefully so that they use only real words, never nonsense words. d. Avoid using any words that include consonant digraphs or vowel teams (e.g., chip, cheap). - Correct Answerb. Have students add, change, delete, or move only ONE sound at a time. Spanish has 22 phonemes represented by 27 symbols, compared to English's 44 phonemes and 26 symbols. true false - Correct AnswerTrue The variations common in African American English are predictable and governed by rules. true false - Correct AnswerTrue Which of the following occurs as a result of coarticulation? Select all that apply. a. allophonic variations, in which we pronounce individual phonemes differently from how would pronounce them in isolation b. dialect variations that include nonstandard usage and grammar as well as nonstandard pronunciation c. misspellings of words that are, in fact, phonetically logical d. increased controversy about how to pronounce specific phonemes correctly - Correct Answera. allophonic variations, in which we pronounce individual phonemes differently from how would pronounce them in isolation c. misspellings of words that are, in fact, phonetically logical Which of the following misspellings likely results from confusion about unaspirated or deaspirated stop consonants? a. spelling friend as "fred" b. spelling drop as "jrop" c. spelling batter as "badr" d. spelling skip as "sgip" - Correct Answerc. cattle, city, metal In which group of words does a tongue flap create significant differences between American and British pronunciations? a. space, stick, scab b. mend, won't, pink c. cattle, city, metal d. trip, stature, graduate - Correct Answerc. cattle, city, metal A student with general phonological awareness can learn to read fluently, even if the student has not yet developed awareness of speech sounds at the phoneme level. - Correct AnswerFalse If a student analyzes the sounds and syllables in a word, it is easier for the student to store the word in semantic memory. - Correct AnswerTrue Read the following list of classroom activities. Select the one that targets phonological awareness only, without attempting to address other language skills. - Correct Answerb. Ms. Chang says a word and has students repeat it, clap for each syllable, and count the syllables. Which of these skills should not be a direct focus of classroom instruction? (Select all that apply.) - Correct Answera. phonological working memory (PWM) c. rapid automatic naming (RAN) The term coarticulation means the ability to: - Correct Answerd. say the phonemes within a syllable so that all of the segments are seamlessly joined. Phonology - Correct Answerthe study of the sound system of a language Semantics - Correct Answerthe study of word and phrase meaning By five years old how many words should a child be speaking? - Correct Answer2,100-2,200 Semantics - Correct AnswerA major development in preschool vocabulary development is the ability to use decontextual talk Decontextual Talk - Correct Answeris speech that requires responses using information from the past or future; may include pretend, narrative, and explanatory talk Tier 1 - Correct AnswerEveryday words Tier 2 - Correct AnswerHigh-utility words Tier 3 - Correct AnswerSpecialized topic words Morphology - Correct Answerthe rule of word function How many morphemes in the word love - Correct Answer1 morpheme lovable - Correct Answer2 morphemes unlovable - Correct Answer3 morphemes syntax - Correct Answerthe rules of word order in grammatical form talk in short phrases - Correct Answer2 year-olds use three-to-six word sentences - Correct Answer3-year-olds combine several sentences about one topic - Correct Answer4-year-olds carry on a conversation with mostly correct grammar - Correct Answer5-year-olds Prosody - Correct Answerthe expression of speech (cooing and babbling)0:1 years - Correct Answerprelexic (whole oral words) 1-1.5 years - Correct Answerlexic (word combination) 1.5-2.5 years - Correct Answersystematic simplification (syllable combinations) 2.5-3.5 years - Correct Answerassembly (aware of word structure) 3-4 years - Correct Answermetaphonological parallel talk - Correct Answeran adult describes what the child is doing self-talk - Correct Answeran adult talks about what he or she is doing expansion - Correct Answeran adult adds more information to the sentence that the child expresses read-aloud scaffolding techniques - Correct Answer1.labeling and commenting 2. verbal dialogue about a picture or storyline 3. pauses (reader lets the child fill un words in stories) 4. sentence recasting (restating a sentence to help a child understand) 5. reading text with syntax simplification 6. tag questions ("thats a truck, isn't it?") 7.direct questions 8.story retelling hierarchy of questions - Correct Answer1.recall 2.application 3.analysis 4.synthesis 5.evaluation 1. Even after first grade, skills such as phoneme segmentation and blending of single-syllable words without consonant blends are good predictors of reading ability. - Correct AnswerFAlse Which of these advanced phonemic awareness skills do children typically develop last? - Correct Answerb. the ability to substitute sounds within words of 5-6 phonemes c. the ability to reverse the first and final sounds in a word Students' ability to acquire phonemic awareness is not dependent on which of the following factors? - Correct Answerword comprehension Which of these tasks could a student at the early phonological awareness level perform? Select all that apply. - Correct Answera. determining whether cat and kiss begin with the same sound c. clapping and counting the syllables in the word pencil Phonological processor - Correct AnswerWhich works with speech sounds Phonological awareness - Correct AnswerAwareness of all levels of the speech sound system is the foundation for reading and spelling. the ability to reflect on and manipulate the sound structure of spoken language Phonological awareness - Correct AnswerThe ability to identify think about and manipulate units of spoken language is the underpinning for processing reading language symbols. Like syllables, part of syllables called unsaid and rimes, and Phonemes is, the smallest segment of speech that combined to make new words. Four-Part processing model for Word Recognition Number 1: Phonological processor - Correct AnswerHelps you understand and produce oral language Four-Part processing model for Word Recognition Number 2: Orthographic processor - Correct AnswerHelps you connect words with your visual forms Four-Part processing model for Word Recognition Number 3: Meaning processor - Correct AnswerIs your internal dictionary of word definition Four-Part processing model for Word Recognition Number 4: Context processor - Correct AnswerHelps you use context to understand what a word means So the four processors from the Four-Part processing model work in isolation. True or False - Correct AnswerFalse they don't work in isolation they interact If you've heard a word spoken in your environment, you will recognize that word more rapidly when you see it in print. How? - Correct AnswerThis requires coordination between the phonological and orthographic processors. If you know what they were means and I have seen it in print, you can recognize or recall its pronunciation more automatically. How? - Correct AnswerIn this instance, the meaning processor, orthographic processor, and phonological processor work together. If you analyze the syllables in individual sounds in the word, the words meaning can be more easily stored in semantic memory. - Correct AnswerThis activate the phonological processor and meaning processor. If you can analyze and manipulated the specific sounds in spoken words, the corresponding printed words Will be easier to remember for reading and spelling. How? - Correct AnswerThis activate the final logical in orthographic processors. Phonological awareness - Correct Answerconscious awareness of all levels of speech sound system, including word boundaries, stress patterns, syllables, unset-rimes unit, and phonemes. Phonological processing - Correct AnswerMultiple functions of speech and language position in production, such as perceiving, interpreting, storing (remembering), recalling her retrieving, and generating the speech sound system of language. Phoneme - Correct AnswerIn any language, the smallest unit of sound used to build words. Phonemic awareness - Correct AnswerConscious awareness that words are made up of segment of our own speech that are represented with letters in an orthopedic orthography. Phonology - Correct AnswerThe rule system in the language by which phones can be sequenced, combined, and pronounce to make words. Phonetics - Correct AnswerThe study of sounds of human speech; articulatory phonetics refers to the way the sounds are physically produced in the human vocal track. Phon - Correct AnswerThe Greek root meaning vocal sound voice, sound Phonological processor - Correct AnswerAllows us to perceive, remember, interpret, and produce the speech sound system of our language——and learn the sounds of other languages. Phonological processor - Correct AnswerAnalyzes the sounds so we can learn to associate phonemes with their written representations, also known as graphemes. The ability to perceive, produce, and manipulate individual speech sound, or phonemes - Correct Answeris a necessary prerequisite for the ability to read words Does it matter if a phoneme is made in the front, middle, or back of the mouth? - Correct AnswerYes it does Grapheme - Correct AnswerWritten representation of a speech sound Providing direct, detailed phonemic awareness is only necessary for students who struggle with reading. True or false - Correct AnswerFalse all students need direct and detailed phonemic awareness Which of the following is necessary prerequisite to begin able to read words? a. Perceived individual speech sounds b. Produce individual speech sounds c. Manipulate individual speech sounds d. None of these - Correct Answera. Perceived b. Produce c. Manipulate individual speech sounds Is it necessary the students know how speech sounds look and feel were in produce as well as how they sound. True or false - Correct AnswerTrue Place of articulation - Correct AnswerWhere we make the sound—-in the front of The mouth, the back, or in between. Manner of articulation - Correct AnswerWhat we do with the lips, teeth, tongue, vocal cords, and airstream to produce sound. How many phonemes does English have? - Correct AnswerBetween 40 and 44 phonemes How many consonant phonemes are in English? - Correct Answer25 are constants phonemes Phonemes are altered due to: - Correct AnswerCoarticulation, Or the smooshing together of sounds in words Regional variations Or even having a cold RAN - Correct Answerrapid automatic naming RAN (Rapid automatic naming) - Correct AnswerIs the ability to name a series of printed letters, numbers, objects or colors. Rapid automatic naming can help us - Correct AnswerNo a little bit about how easily children will learn to read but it's predictive value is limited What can you do if you notice a child is bad at rapid automatic naming? - Correct AnswerPracticing phonological awareness skills and reading itself can sometimes improve RAN speed. Use instructional time to teach direct oral and written language How many syllables are in phonological? 4 5 6 - Correct Answer5 Consonant sounds before the vowel is the? - Correct AnswerOnsets Example: Plants Pl would be the onset because a is a vowel From the vowel and everything else that comes after it is the? - Correct AnswerRime Example: Plants Ants in the time because a is the vowel How many phonemes does the word shop have? - Correct Answer3 phonemes- 3 different sounds /sh/ /o/ /p/ How many phonies does the word cloud have? - Correct Answer4 phonemes- 4 sounds /k/ /l/ /ou/ /d/ Without chronological order and the students don't....? - Correct AnswerStudents don't know to read and spell Difficulty with phonological task it's often associated with..? - Correct AnswerDifficulty in reading and spelling Phonology - Correct AnswerServes as a foundation for all literacy Do all students need instruction at multiple levels of phonological and phonemic Awareness ? - Correct AnswerYes our students need this instruction Early Phonological awareness - Correct AnswerUsually develop by preschoolers by recognizing and playing with rhyming words as well as counting syllables Basic Phonemic awareness - Correct AnswerUsually for kindergarten and first grade they can segment words into sounds and blend them back together Advance phonemic awareness - Correct AnswerUsually for second grade and beyond they can use deletion, substitution and reversal but must be accurate and automatic Teachers can strengthen preschool a children's early Awareness by - Correct AnswerDrawing attention to rhyme and alliteration during read aloud's of stories and nursery rhymes Alphabetic principal - Correct AnswerIs the concept that a grapheme represents a phoneme. What happens when students understand the alphabetic principle? - Correct AnswerTheir spelling becomes more phonetic and their decoding improves. Phonics can refer to? - Correct Answer1. The system that tells us which graphemes spell which phonemes 2. The instruction or use of print patterns, syllable patterns, and meaningful word parts. Screening measures that's assess phonemic awareness? - Correct AnswerAre crucial for predicting which students will need extra help. Will a students native language have the exact same phonemes as English? - Correct AnswerNo they are not exact Alphabetic Principle - Correct AnswerThe concept that phonemes are represented by letters and graphemes. How many phonemes are in through 2 3 4 5 - Correct Answer3 phonemes- 3 sounds /th/ /r/ /u/ How many phonemes are in fox? 2 3 4 5 - Correct Answer4 phonemes- 4 different sounds /f/ /o/ /k/ /s/ because the letter x represents two sounds How many phonemes does the word stripe have? 2 3 4 5 - Correct Answer5 phonemes- 5 sounds /s/ /t/ /r/ /i/ /p/ Allophonic variations - Correct AnswerDistortions by the sounds before of after the sound we want to hear What are consonants phonemes? - Correct AnswerSpeech sounds produced by obstructing the flow of air out of the speaker's mouth. Phonemes is also called - Correct AnswerSpeech sounds Phonology - Correct AnswerThe study of speech sounds in language. An example of phonology is the study of different sounds and the way they come together to form speech and words Consonant Phonemes: Fricatives - Correct AnswerHissy sounds because we use our tongue, lips, and teeth in such a way to restrict airflow. Fricatives are: - Correct AnswerTeeth on lip: -Unvoiced; /f/ as in fish. -Voiced; /v/ as in Valentine Tongue between teeth: -Unvoiced; /th/ as in thumb -Voiced; /th ( with a little line on the bottom __) as in feather Tongue on Ridge behind teeth: -Unvoiced; /s/ as in son -Voiced; /z/ as in zebra Tongue pulled back on roof of mouth: -Unvoiced; /sh/ as in shoes -Voiced; /zh/ as in genre (gandra) Glottis: Unvoiced; /h/ as in hat Consonant phonemes - Correct AnswerAre speech sounds produced by obstructing the flow of air out of the speakers mouth. Fank you instead of thank you - Correct AnswerStudent confused the /th/ with /f/ because they have the same hissy sound and same position in mouth. Mat instead of Mad - Correct AnswerStudent confused /d/ with /t/ because they are similar in articulation ( in the way it's said in mouth) Chop instead of shop - Correct AnswerStudent confused /sh/ for /ch/ because both sounds have the same position of tongue, teeth, and lips. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Stops - Correct AnswerStops-made with one burst of air differ from continuants, such as the /s/ sound which can be held until you run out of breath. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Stops - Correct AnswerThe Stop sounds in English are /p/ as in pig, /b/ as in bat, /t/ as in tack /d/ as in dog, / k/as in cup, /g/ as in goat They can be difficult to say without adding an /uh/ sound at the end because they don't have a lot of airflow. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Stops - Correct AnswerUNVOICED: Lips together- /p/ as in pig, Tongue on Ridge behind teeth- /t/ as in tack, Back of Throat- / k/as in cup, VOICED: Lips together- /b/ as in bat, Tongue on Ridge behind teeth- /d/ as in dog, Back of Throat- /g/ as in goat Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Nasals - Correct AnswerNasals are produced by driving air through the nose. If you try to say those sounds and pinched your nose shut, you wouldn't be able to articulate them. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Nasals - Correct AnswerThe three nasal sounds are: /m/ as in man, /n/ as in nest, /ng/ as in sing No word in English begins with /ng/ it always comes after a vowel. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Nasals - Correct Answer/m/ as in man, Back of Throat /n/ as in nest, Lips together /ng/ as in sing Tongue on ridge behind teeth Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Fricatives - Correct AnswerFricatives are hissy sounds, because we use our tongue, lips, and teeth in such a way to construct the airflow. There is a lot of friction going on in fricatives. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Fricatives - Correct AnswerFricatives are: UNVOICED: Teeth on lip: /f/ as in fish, Tongue between teeth: /th/ as in thumb Tongue on ridge behind teeth: /s/ as in son Tongue pulled back on roof of mouth: /sh/ as in shoes Glottis: /h/ as in hat VOICED: Tongue pulled back on roof of mouth: /zh/ as in genre Tongue on ridge behind teeth: /z/ as in zebra Tongue between teeth: /th (with line on bottom)/ as in feather Teeth on lip: /v/ as in valentine Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Affricates - Correct AnswerThese can be considered chopped fricatives Because they combine features of stops with those of fricatives. Affricates are: /ch/ as in chin, /j/ as in jam, Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Affricates - Correct AnswerUNVOICED: Tongue pulled back on roof of mouth /ch/ as in chin VOICED: Tongue pulled back on roof of mouth /j/ as in jam Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Glides - Correct AnswerGlides are always followed by a vowel sound. We call them glides because the consonant sound glides right into the vowel sound. The three glide sounds are: /wh/ as in wheel (/wh/), /w/ as in window (/w/) /y/ as in yo-yo Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Glides - Correct AnswerNote that for /wh/ and /w/ some linguistics focus on the tongue retraction to the back of the throat. However the more obvious future is the rounding of the lips when articulating these sounds. Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Liquids - Correct AnswerThey impact the sounds that are around them in the word often, distorting the vowels that come before them. The two liquids are: /l/ as in leaf and /r/ as in rabbit Consonant Phonemes (sounds): Liquids - Correct Answer/l/ as in leaf: tongue on Ridge behind teeth /r/ as in rabbit: tongue pulled back on roof of mouth The student writes "bark" instead of brag - Correct AnswerA student who makes this error substitutes the unvoiced consonant /k/ for the voiced /g/. Both /k/ and /g/ have an identical place of articulation. They are both articulated at the back of the throat and they're both stop sounds. The students writes "smake" instead of snake - Correct AnswerThis confusion suggests that the student is confused about the position of the /n/ sound. In this example the student has substituted a sound articulated in the front of the mouth, /m/, with a sound articulated with the tongue in the middle of the mouth, /n/. The student writes "md" instead of "bed" - Correct AnswerThe error here is a little harder to understand. The student confused the nasal sound /m/ with the stop sound /b/ because both are articulated in the same place with the lips together. The student writes "md" instead of "bed" - Correct AnswerHowever the students need to distinguish the nasal /m/ from the stop /b/. Student writes "van" instead of fan - Correct AnswerThe student substituting voice fricative /v/ for unvoiced fricative /f/, Student writes "gad" instead of glad - Correct AnswerThis student likely does not quite here the /l/ in glad. Suppose a student writes "charp" instead of "sharp". What phonological error is the likely cause? A. Confusing the two affricate sounds B. Substituting an affricate sound for a fricative sound C. Confusing two different unvoiced fricatives D. Substituting an unvoiced fricative for a voiced fricative - Correct AnswerB. Substituting an affricate sound for a fricative sound Because the /sh/ sound at the beginning of "sharp" is an unvoiced fricative, sometimes confused with the affricate sound /ch/. "This" begins with a voiced fricative, /th/, which can be confused with other voiced fricatives, such as /v/. "Mop" ends with an unvoiced stop, /p/, which can be confused with its voiced counterpart, /b/. Suppose a student writes "vis" instead of "this". What phonological error is the likely cause? A. Substituting a Nasal sound for a fricative sound B. Substituting a glide sound for a fricative sound C. Confusing two different voiced fricatives D. Substituting an unvoiced fricative for a voiced fricative - Correct AnswerC. Confusing two different voiced fricatives This begins with the voice fricative, /th/, which can be confused with other voiced fricatives, such as /v/. Suppose a student writes "mob" instead of "mop". What phonological error is the likely cause? A. Substituting a nasal sound for a stop B. Substituting a voice stop for an unvoiced stop C. Confusing two different voiced stops D. Misunderstanding where the sound is articulated in the mouth - Correct AnswerB. Substituting a voice stop for an unvoiced stop Mob ends with an unvoiced stop, /p/, which can be confused with its voiced counterpart, /b/. diphthong - Correct AnswerSingle vowel phonemes that glide in the middle. The mouth position shifts during the production of the phoneme. /oi/ in spoil /ou/ in couch /ī/ in light Schwa - Correct AnswerMeans empty in Hebrew. It is the vowel in an unaccented syllable such as the last syllable in wagon. Difference between long and short vowels - Correct AnswerLong (tense) and short (lax) are arbitrary. They have little to do with the time it takes to say a vowel. They are to do with the muscle tension in jaw. Long = beet, bait, boat, boot, beauty, bite. Short = bit, bet, bat, pot, but, bought, book. Vowels - Correct AnswerA set of 15 phonemes in English (not including r-controlled combinations or schwa). It is an open phoneme that is in every syllable. They can be classified by tongue position and height (e.g. front or low, mid or back, round) R-controlled vowels - Correct AnswerWhen a letter is followed by an /r/ it's sound usually changes. It may become totally unified as one phoneme or kept slightly separated. A student with general phonological awareness can learn to read fluently, even if the student has not yet developed awareness of speech sounds at the phoneme level. - Correct AnswerFalse If a student analyzes the sounds and syllables in a word, it is easier for the student to store the word in semantic memory. - Correct AnswerTrue Read the following list of classroom activities. Select the one that targets phonological awareness only, without attempting to address other language skills. - Correct AnswerMs. Chang says a word and has students repeat it, clap for each syllable, and count the syllables. The term coarticulation means the ability to: - Correct AnswerSay the phonemes within a syllable so that all of the segments are seamlessly joined. Even after first grade, skills such as phoneme segmentation and blending of single-syllable words without consonant blends are good predictors of reading ability. - Correct AnswerFalse Students' ability to acquire phonemic awareness is not dependent on which of the following factors? - Correct AnswerWord comprehension Which of these tasks could a student at the early phonological awareness level perform? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Determining whether cat and kiss begin with the same sound - Clapping and counting the syllables in the word pencil Which of these tasks could a student at the basic phonemic awareness level perform? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Saying the compound word rainbow, then deleting the first part and saying the new word - Segementing and tapping the phonemes in the word beak Which of these advanced phonemic awareness skills do children typically develop last? - Correct AnswerThe ability to reverse the first and final sounds in a word Phonemic awareness instruction for young learners is most beneficial when linked with phonics instruction. - Correct AnswerTrue Which of the following changes typically take place once a child has grasped the alphabetic principle? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Spelling becomes more phonetically accurate. - Attempts to decode text focus more on blending sounds. The inventory of phonemes used in Spanish is nearly identical to that used in English. - Correct AnswerFalse How much phonological awareness training should be done with students for maximum effectiveness? - Correct AnswerA few minutes a day, several days per week A third-grade teacher wants to determine whether any of her students are at risk for reading failure. She should use a screening measure that assesses which of the following? - Correct AnswerTheir ability to perform advanced phonemic awareness tasks In many instances, two different consonant phonemes in English are formed the same way in the mouth, but one is voiced and the other is unvoiced. - Correct AnswerTrue Adults often miscount the number of phonemes in a word because they tend to recall how a word looks in print and count the letters, not the sounds. - Correct AnswerTrue Which of the following sounds is an affricate, meaning it combines features of fricatives and stops? - Correct Answer/ch/ Which of the following pairs are consonant sounds that students frequently confuse? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- /t/ and /d/ - /m/ and /n/ Which of the following misspellings is phonetically accurate and does not indicate phonemic confusion? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Writing "butn" for button - Writing "kitn" for kitten English vowels are easier for students to pronounce and write than consonants. - Correct AnswerFalse What makes r-controlled vowel sounds so confusing for students? - Correct AnswerThe r takes over the preceding vowel sound. Which of the following sounds is considered a front vowel? - Correct Answer/ā/ Which of the following vowels require that the mouth shift position during production of the sound? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- /oi/ - /ou/ Which of the following vowel sounds would be classified by a linguist as "tense" vowels? - Correct Answer/ē/ and /yū/ Spanish has 22 phonemes represented by 27 symbols, compared to English's 44 phonemes and 26 symbols. - Correct AnswerTrue The variations common in African American English are predictable and governed by rules. - Correct AnswerTrue In which group of words does a tongue flap create significant differences between American and British pronunciations? - Correct AnswerCattle, city, metal Which of the following misspellings likely results from confusion about unaspirated or deaspirated stop consonants? - Correct AnswerSpelling skip as "sgip" Which of the following occurs as a result of coarticulation? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Allophonic variations, in which we pronounce individual phonemes differently from how would pronounce them in isolation - Misspellings of words that are, in fact, phonetically logical Students in Ehris prealphabetic phase need instruction in basic oral language skills before manipulating phonemes. - Correct AnswerTrue Sound chaining should begin with substituting the middle sounds and end sounds in a word, as these are most difficult. - Correct AnswerFalse A colleague is going to start beginning sound chaining activities with students at the basic phonemic awareness level, using colored blocks to represent sounds. What is the most important guideline to follow? - Correct AnswerHave students add, change, delete, or move only ONE sound at a time. Which activities work with students at the early phonological awareness level? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Having students identify rhyming words in texts you read aloud - Having students clap or tap to count the syllables in a word you say - Saying a two-syllable word, then asking students to delete one syllable and say the word that results Which of the following principles are important for teaching phonological skills in particular? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Focus students' attention on speech sounds before focusing on letters. - Include all English phonemes in instruction. Assessing phonological skills is almost never appropriate after a child has completed first grade. - Correct AnswerFalse Phonemic awareness is difficult to measure directly as an isolated skill. - Correct AnswerTrue Kelsey is in grade 2. Previously a strong reader, she has now fallen behind. She reads grade-level texts haltingly, struggling to recognize words with blends. Which phonological task would she likely struggle with? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- "Say crate. Now say crate but don't say /k/." - "Say bask. Now say bask but don't say /s/." Which kinds of tasks are the primary focus of phonological skills assessment in grades K1? - Correct AnswerPhoneme segmentation and blending What features separate the PAST from other phonological skills assessments? Select all that apply. - Correct Answer- Automaticity is a factor in determining a student's score. - The assessor gives corrective feedback if the student repsonds incorrectly. components of oral language - Correct Answer1) phonology 2) semantics 3)morphology 4)syntax 4) prosody what is phonology? - Correct Answersound system of a language put sounds together to create words what is semantics? - Correct Answerword meaning at 5 y/o how many words should a kid know? - Correct Answer2,100-2,200 words what is morphology? - Correct Answerword formation what is a morpheme? - Correct Answersmallest meaningful unit of language how many morphemes are in the word unlovable - Correct Answer3 what is syntax? - Correct Answerword order in a sentence grammar what is prosody? - Correct Answerexpression typical literacy development - Correct AnswerPrelogographic (before symbols): 0-2.5 years Logographic/Prealphabetic (whole written word): 2.5-4 years Early Alphabetic (simple letter-sounds correspondence): 4-5 years Later Alphabetic (phonetic spelling): 5-7 years Consolidated Alphabetic (fluent reader): 7+ years at what grade is learning to read crucial by? - Correct Answer3rd grade what are strategies to promote oral language - Correct Answer1) parallel talk~ narrate what child doing 2) self-talk~ adult narrate what doing 3) expansion~ adult add info to kids sentence read-aloud scaffolding techniques - Correct Answer- questions -story retelling -pause and let them fill in the word -verbal dialogue -label/commenting DOK levels of questions - Correct Answer1) recall 2) skills/concepts 3)strategic thinking 4)extended thinking speech development - Correct AnswerPrelexic (cooing and babbling): 0-1 years Lexic (whole oral words): 1-1.5 years Systematic Simplification (word combination): 1.5 - 2.5 years Assembly (syllable combinations): 2.5 - 3.5 years Metaphonological (aware of word structure): 3-4 years structural components of oral language - Correct Answerphonology semantics morphology syntax prosody phonology - Correct Answerstudy of the sound system of a language semantics - Correct Answerstudy of word and phrase meaning how many words should a child be speaking by 5 years old? - Correct Answer2100-2200 semantics - Correct Answermajor development in preschool vocabulary development is the ability to use decontextual talk decontextual talk - Correct Answerspeech that requires responses using information from the past or future three tiers of vocabulary words - Correct Answertier 1 tier 2 tier 3 tier 1 - Correct Answereveryday words tier 2 - Correct Answerhigh utility words tier 3 - Correct Answerspecialized topic words morphology - Correct Answerrules of the word formation morpheme - Correct Answersmallest meaningful unit of language syntax - Correct Answerrules of word in order in grammatical form prosody - Correct Answerexpression of speech prelexic language stage - Correct Answercooing and babbling lexic language stage - Correct Answerwhole oral words systematic simplification language stage - Correct Answerword combination assembly language stage - Correct Answersyllable combinations metaphonological language stage - Correct Answeraware of word structure parallel talk - Correct Answeradult describes what the child is doing self- talk - Correct Answeran adult talks about what he or she is doing expansion - Correct Answeran adult adds more info to the sentence that the child expresses Phonology - Correct Answerthe study of the sound system of a language Semantics - Correct Answerthe study of word and phrase meaning By five years old how many words should a child be speaking? - Correct Answer2,100-2,200 Semantics - Correct AnswerA major development in preschool vocabulary development is the ability to use decontextual talk Decontextual Talk - Correct Answeris speech that requires responses using information from the past or future; may include pretend, narrative, and explanatory talk Tier 1 - Correct AnswerEveryday words Tier 2 - Correct AnswerHigh-utility words Tier 3 - Correct AnswerSpecialized topic words Morphology - Correct Answerthe rule of word function How many morphemes in the word love - Correct Answer1 morpheme lovable - Correct Answer2 morphemes unlovable - Correct Answer3 morphemes syntax - Correct Answerthe rules of word order in grammatical form talk in short phrases - Correct Answer2 year-olds use three-to-six word sentences - Correct Answer3-year-olds combine several sentences about one topic - Correct Answer4-year-olds carry on a conversation with mostly correct grammar - Correct Answer5-year-olds Prosody - Correct Answerthe expression of speech (cooing and babbling)0:1 years - Correct Answerprelexic (whole oral words) 1-1.5 years - Correct Answerlexic (word combination) 1.5-2.5 years - Correct Answersystematic simplification (syllable combinations) 2.5-3.5 years - Correct Answerassembly (aware of word structure) 3-4 years - Correct Answermetaphonological parallel talk - Correct Answeran adult describes what the child is doing self-talk - Correct Answeran adult talks about what he or she is doing expansion - Correct Answeran adult adds more information to the sentence that the child expresses read-aloud scaffolding techniques - Correct Answer1.labeling and commenting 2. verbal dialogue about a picture or storyline 3. pauses (reader lets the child fill un words in stories) 4. sentence recasting (restating a sentence to help a child understand) 5. reading text with syntax simplification 6. tag questions ("thats a truck, isn't it?") 7.direct questions 8.story retelling hierarchy of questions - Correct Answer1.recall 2.application 3.analysis 4.synthesis 5.evaluation structural components of oral language - Correct Answerphonology semantics morphology syntax prosody phonology - Correct Answerstudy of the sound system of a language semantics - Correct Answerstudy of word and phrase meaning how many words should a child be speaking by 5 years old? - Correct Answer2100-2200 semantics - Correct Answermajor development in preschool vocabulary development is the ability to use decontextual talk decontextual talk - Correct Answerspeech that requires responses using information from the past or future three tiers of vocabulary words - Correct Answertier 1 tier 2 tier 3 tier 1 - Correct Answereveryday words tier 2 - Correct Answerhigh utility words tier 3 - Correct Answerspecialized topic words morphology - Correct Answerrules of the word formation morpheme - Correct Answersmallest meaningful unit of language syntax - Correct Answerrules of word in order in grammatical form prosody - Correct Answerexpression of speech prelexic language stage - Correct Answercooing and babbling lexic language stage - Correct Answerwhole oral words systematic simplification language stage - Correct Answerword combination assembly language stage - Correct Answersyllable combinations metaphonological language stage - Correct Answeraware of word structure parallel talk - Correct Answeradult describes what the child is doing self- talk - Correct Answeran adult talks about what he or she is doing expansion - Correct Answeran adult adds more info to the sentence that the child expresses Phonology - Correct Answerthe study of the sound system of a language Semantics - Correct Answerthe study of word and phrase meaning By five years old how many words should a child be speaking? - Correct Answer2,100-2,200 Semantics - Correct AnswerA major development in preschool vocabulary development is the ability to use decontextual talk Decontextual Talk - Correct Answeris speech that requires responses using information from the past or future; may include pretend, narrative, and explanatory talk Tier 1 - Correct AnswerEveryday words Tier 2 - Correct AnswerHigh-utility words Tier 3 - Correct AnswerSpecialized topic words Morphology - Correct Answerthe rule of word function How many morphemes in the word love - Correct Answer1 morpheme lovable - Correct Answer2 morphemes unlovable - Correct Answer3 morphemes syntax - Correct Answerthe rules of word order in grammatical form talk in short phrases - Correct Answer2 year-olds use three-to-six word sentences - Correct Answer3-year-olds combine several sentences about one topic - Correct Answer4-year-olds carry on a conversation with mostly correct grammar - Correct Answer5-year-olds Prosody - Correct Answerthe expression of speech (cooing and babbling)0:1 years - Correct Answerprelexic (whole oral words) 1-1.5 years - Correct Answerlexic (word combination) 1.5-2.5 years - Correct Answersystematic simplification (syllable combinations) 2.5-3.5 years - Correct Answerassembly (aware of word structure) 3-4 years - Correct Answermetaphonological parallel talk - Correct Answeran adult describes what the child is doing self-talk - Correct Answeran adult talks about what he or she is doing expansion - Correct Answeran adult adds more information to the sentence that the child expresses read-aloud scaffolding techniques - Correct Answer1.labeling and commenting 2. verbal dialogue about a picture or storyline 3. pauses (reader lets the child fill un words in stories) 4. sentence recasting (restating a sentence to help a child understand) 5. reading text with syntax simplification 6. tag questions ("thats a truck, isn't it?") 7.direct questions 8.story retelling hierarchy of questions - Correct Answer1.recall 2.application 3.analysis 4.synthesis 5.evaluation [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 31 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 12, 2023
Number of pages
31
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 12, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
55