BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Biochemistry Questions and Answers Rated A (All)
Biochemistry Questions and Answers Rated A
Document Content and Description Below
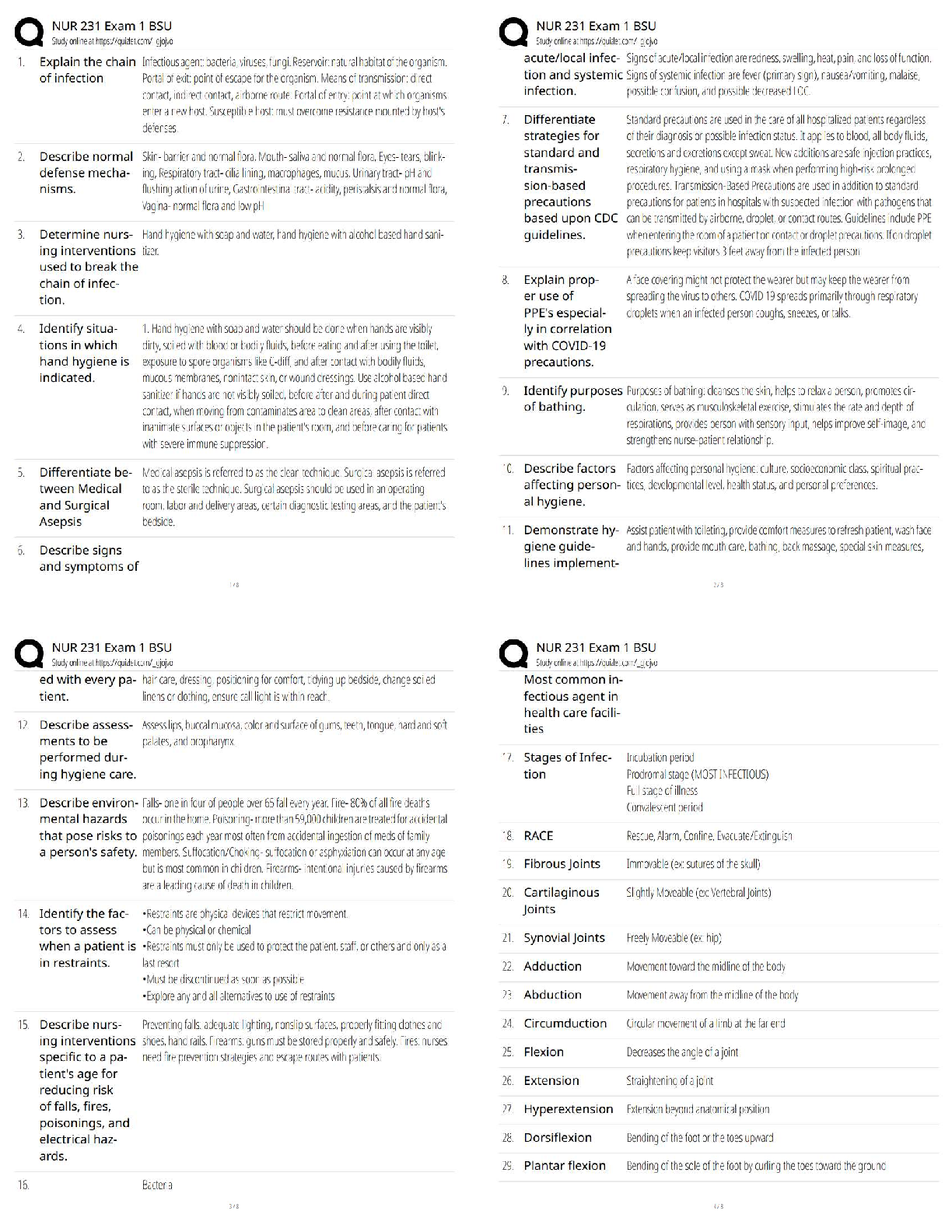
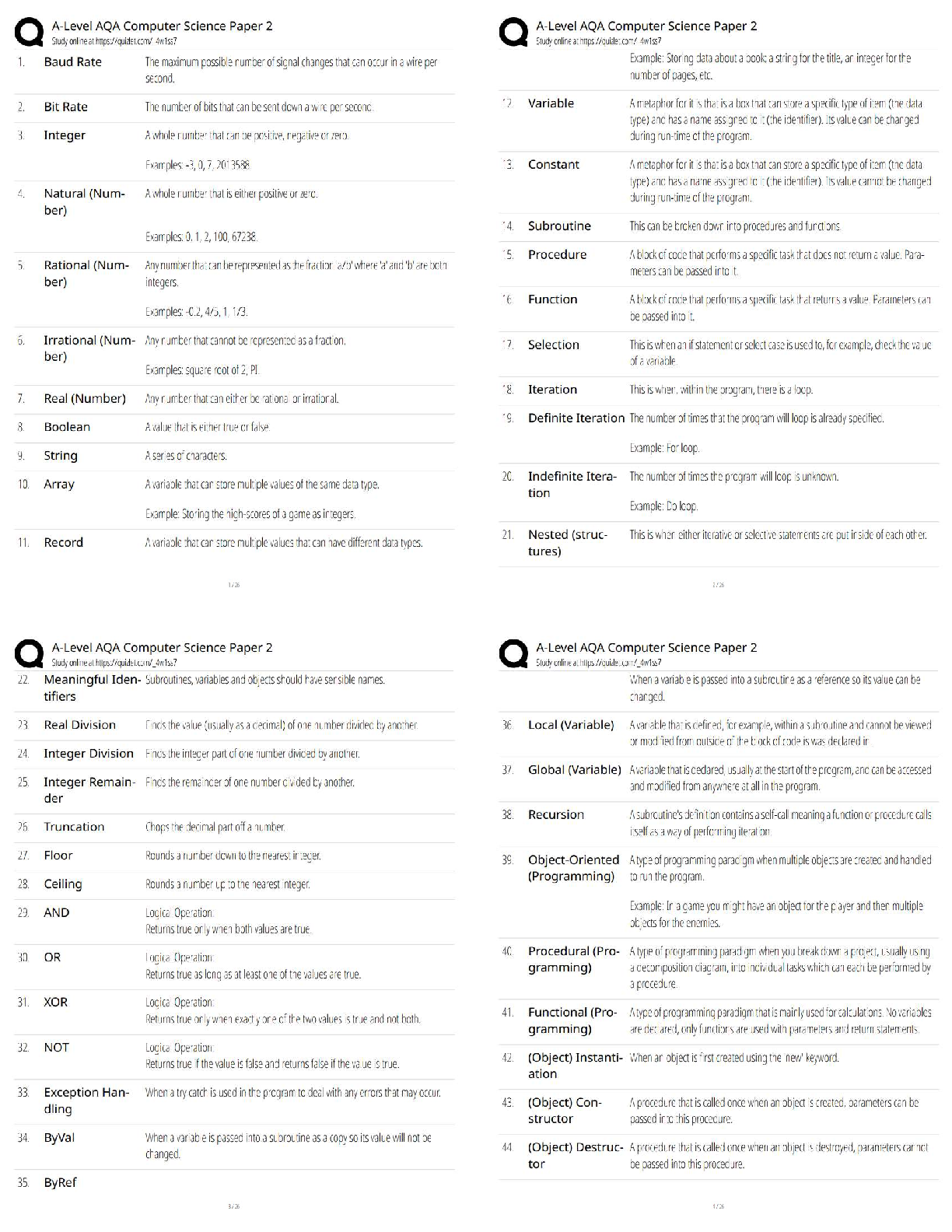
Biochemistry Questions and Answers Rated A Physical Property ✔✔Description of shape, mass, and volume Chemical Property ✔✔A property used to characterize materials in reactions that change ... their identity Element ✔✔Any of over 100 substances that can not be separated to become simpler, and singly or in combination make up all matter. Atom ✔✔Smallest particle of an element that has the characteristics of that element. Nucleus ✔✔The microscopic, positively charged central part of an atom made up of protons and neutrons, also orbited by electrons. Mixture ✔✔Combination of substances which individuals retain individual property. Solution ✔✔Mixture of one or more solutes evenly distributed in a solvent. Solute ✔✔The substance evenly distributed in the solvent to form a mixture. Solvent ✔✔Holds dissolved substance in a mixture; most of the time, it is water. pH ✔✔Measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. Acid ✔✔Describes a substance with a pH below 7. Base ✔✔Describes a substance with pH above 7. Polar Molecule ✔✔A molecule with a pair of equal and opposite charges. Hydrogen Bond ✔✔Chemical bonding in which two molecules link together by one or more hydrogen atoms. Cohesion ✔✔The attraction of similar molecules. Adhesion ✔✔The attraction of dissimilar molecules. Isomer ✔✔A compound with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Monomer ✔✔a simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers Polymer ✔✔A molecule composed of repeating structural units. Carbohydrates ✔✔An organic compound consisting only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; the food group consisting of sugars and starches. Monosaccharides ✔✔The simplest group of carbohydrates. Disaccharide ✔✔Any carbohydrates that have two monosaccharide molecules on complete hydrolysis. Polysaccharides ✔✔Any class of carbohydrates containing chains of disaccharide molecules. Lipid ✔✔Organic compound that can't dissolve in water; it is an essential structure component of living cells. Saturated Fat ✔✔Type of fat shown to increase the risk of heart disease; solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fat ✔✔A fat found most often in fish and vegetables; is considered relatively healthier than some other fats. Protein ✔✔Organic compounds made up of amino acids arranged in a linear chain. Amino Acid ✔✔A chemical building block of proteins. Peptide Bond ✔✔A covalent bond linking two amino acids together Enzyme ✔✔Proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions. Nucleic Acid ✔✔A substance composed of nucleotide chains that is a vital component of all living cells. (DNA + RNA) Nucleotide ✔✔The basic structural unit of DNA and RNA. DNA ✔✔The long, linear polymer of nucleotides found in the nucleus of a cell, formed from nucleotides and shaped like a double helix; associated with the transmission of genetic information. RNA ✔✔The long, linear polymer of nucleotides found in the cytoplasm of a cell; associated with the transmission of genetic information from DNA to the cytoplasm, controlling certain chemical processes in the cell. Chemical Equation ✔✔The means of writing out and describing chemical reactions. Reactant ✔✔A chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction. Product ✔✔The result of an act or process in a chemical reaction. Dehydration Synthesis ✔✔A chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule. Hydrolysis ✔✔A chemical reaction in which water reacts with a compound to produce other compounds. Substrate ✔✔The substance that is acted upon by an enzyme or ferment. Active Site ✔✔The part of the enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs Neutron ✔✔Makes up part of the nucleus; has no charge. Proton ✔✔Makes up part of the nucleus; has a positive charge. Electron ✔✔Orbits the nucleus; has a negative charge. Atomic Number ✔✔The number of protons in a nucleus Atomic Mass ✔✔The sum of the number of protons and neutrons inside the nucleus of the atom. Atomic Symbol ✔✔A standard chemical abbreviation of an element generally assigned in relation to its Latin name. Chemical Bond ✔✔Two or more atoms chemically bonded together. Molecular Formula ✔✔Uses atomic symbols to represent atoms bound together in a compound. Covalent Bond ✔✔A bond in which atoms share electrons. Ion ✔✔An electrically charged particle; protons and electrons. Ionic Bond ✔✔Attractive force between ions of opposite charge. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 20, 2023
Number of pages
7
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 20, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
81










.png)